Table of Contents
- Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches with 2 SFP 1G & 2 SFP+ 10G Fiber Ports
- Contents
- 1. Getting Started
- Switch Management Options and Default Management Mode
- Available Publications
- Web Browser Requirements and Supported Browsers
- User-Defined Fields
- Interface Naming Conventions
- Access the Switch
- Change the Management Mode of the Switch
- Register the Switch
- How to Configure Interface Settings
- Local Browser Interface Device View
- 2. Configure System Information
- View and Configure the Switch Management Settings
- View or Define System Information
- View the Switch CPU Status
- Configure the CPU Thresholds
- Configure the IPv4 Address for the Network Interface and Management VLAN
- Configure the IPv6 Address for the Network Interface
- View the IPv6 Network Neighbor
- Configure the Time Settings
- Configure Denial of Service Settings
- Configure DNS Settings
- Configure Green Ethernet Settings
- Manage the Bonjour Settings and View Bonjour Information
- Control the LEDs
- Use the Device View
- Configure Power over Ethernet
- Configure SNMP
- Configure Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Configure DHCP L2 Relay and DHCP Snooping
- Set Up PoE Timer Schedules
- View and Configure the Switch Management Settings
- 3. Configure Switching
- 4. Configuring Routing
- 5. Configure Quality of Service
- 6. Manage Device Security
- Management Security Settings
- Configure Management Access
- Configure Port Authentication
- Set Up Traffic Control
- Configure Access Control Lists
- Use the ACL Wizard to Create a Simple ACL
- Configure a Basic MAC ACL
- Configure MAC ACL Rules
- Configure MAC Bindings
- View or Delete MAC ACL Bindings in the MAC Binding Table
- Configure an IP ACL
- Configure Rules for a Basic IP ACL
- Configure Rules for an Extended IP ACL
- Configure an IPv6 ACL
- Configure Rules for an IPv6 ACL
- Configure IP ACL Interface Bindings
- View or Delete IP ACL Bindings in the IP ACL Binding Table
- Configure VLAN ACL Bindings
- 7. Perform Maintenance Tasks
- 8. Manage Power over Ethernet
- 9. Monitor the System
- A. Configuration Examples
- B. Hardware Specifications and Default Values
NETGEAR GC752XP User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for GC752XP by NETGEAR which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
August 2018
202-11864-03
Insight Managed 28-Port and
52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart
Cloud Switches with 2 SFP 1G &
2 SFP+ 10G Fiber Ports
Models GC728X, GC728XP
GC752X, GC752XP
User Manual
2
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Support
Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. You can visit https://www.netgear.com/support/ to register your product,
get help, access the latest downloads and user manuals, and join our community. We recommend that you use only official
NETGEAR support resources.
Conformity
For the current EU Declaration of Conformity, visit http://kb.netgear.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/11621.
Compliance
For regulatory compliance information, visit http://www.netgear.com/about/regulatory/.
See the regulatory compliance document before connecting the power supply.
Do not use this device outdoors. If you connect cables or devices that are outdoors to this device, see
http://kb.netgear.com/000057103 for safety and warranty information.
Trademarks
© NETGEAR, Inc., NETGEAR, and the NETGEAR Logo are trademarks of NETGEAR, Inc. Any non-NETGEAR trademarks are
used for reference purposes only.
Revision History
Publication Part
Number Publish Date Comments
202-11864-03 August 2018 Removed section on using the NETGEAR Switch Discovery Tool to access the
switch and made other minor changes or corrections
202-11864-02 July 2018 Various editorial updates.
202-11864-01 May 2018 First publication

3
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Contents
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Switch Management Options and Default Management Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Available Publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Web Browser Requirements and Supported Browsers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
User-Defined Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Interface Naming Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Access the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Access the Switch On-Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Access the Switch Off-Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Change the Management Mode of the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Change the Management Mode to Direct Connect
Web-browser Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Change the Management Mode Back to NETGEAR Insight
Mobile App and Insight Cloud Portal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Register the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
How to Configure Interface Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Local Browser Interface Device View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Chapter 2 Configure System Information
View and Configure the Switch Management Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
View or Define System Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
View the Switch CPU Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Configure the CPU Thresholds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Configure the IPv4 Address for the Network Interface and
Management VLAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configure the IPv6 Address for the Network Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
View the IPv6 Network Neighbor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Configure the Time Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Configure Denial of Service Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Configure DNS Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Configure Green Ethernet Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Manage the Bonjour Settings and View Bonjour Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Manage the Bonjour Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
View Bonjour Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Control the LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Use the Device View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Configure Power over Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Configure SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Configure the SNMPv1/v2 Community . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Configure SNMPv1/v2 Trap Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configure SNMPv1/v2 Trap Flags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
View the Supported MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Configure Authentication and Encryption for the SNMPv3 Admin Profile . 78
Configure Link Layer Discovery Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79

4
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure LLDP Global Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Configure LLDP Port Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
View the LLDP-MED Network Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Configure the LLDP-MED Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
LLDP-MED Neighbors Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
View Local LLDP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
View LLDP Neighbors Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Configure DHCP L2 Relay and DHCP Snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Configure a DHCP L2 Relay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Configure DHCP Snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Set Up PoE Timer Schedules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Chapter 3 Configure Switching
Configure Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Configure Link Aggregation Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Configure LAG Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Configure LAG Membership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Set the LACP System Priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Set the LACP Port Priority Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Configure VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Manage Basic VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Configure VLAN Trunking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Configure VLAN Membership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
View the VLAN Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Configure Port PVID Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Configure a MAC-Based VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Configure Protocol-Based VLAN Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Configure Protocol-Based VLAN Group Membership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Configure a Voice VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Configure Auto-VoIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Configure Protocol-Based Port Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Configure Auto-VoIP OUI-Based Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Configure OUI-Based Port Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Manage the OUI Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Display the Auto-VoIP Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Spanning Tree Protocol Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Configure STP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Configure CST Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Configure CST Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
View CST Port Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
View Rapid STP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Manage MST Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Configure MST Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
View STP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Configure Multicast. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
View or Clear the MFDB Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148

5
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View the MFDB Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Configure the Auto-Video Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Configure IGMP Snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Configure an IGMP Snooping Querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Configure MLD Snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
View, Search, and Configure the MAC Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
View and Search the MAC Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Set the Dynamic Address Aging Interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Add a Static MAC Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Remove a Static MAC Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Configure Layer 2 Loop Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Configure Global Layer 2 Loop Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Configure Layer 2 Loop Protection on a Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Chapter 4 Configuring Routing
How the Switch Handles Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Enable the Routing Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
View the IP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Configure IPv6 Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Configure the IPv6 Global Routing Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
View the IPv6 Route Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Configure IPv6 VLAN Interface Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Manage IPv6 Prefixes for Advertisement on an IPv6 VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
View IPv6 Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
View the IPv6 Neighbor Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Manage Static IPv6 Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
View the IPv6 Route Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Configure IPv6 Route Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Configure Routing VLANs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Configure VLAN Routing With the VLAN Routing Wizard. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Manually Manage Routing VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Configure Router Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Configure Routes and View Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
Delete Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
Configure ARP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
View Entries in the ARP Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
Create a Static ARP Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Configure the Global ARP Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Remove ARP Entries From the ARP Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Chapter 5 Configure Quality of Service
Manage Class of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Overview of CoS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Configure Global CoS Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Configure CoS Interface Settings for an Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
Configure CoS Queue Settings for an Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Map 802.1p Priorities to Queues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223

6
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Map DSCP Values to Queues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Manage Differentiated Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Overview of Defining DiffServ. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Configure DiffServ Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Configure the Global DiffServ Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Configure a DiffServ Class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Configure DiffServ IPv6 Class Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Configure a DiffServ Policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Configure the DiffServ Service Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
View DiffServ Service Statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
Chapter 6 Manage Device Security
Management Security Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Change the Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Reset the Password to the Default Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
RADIUS Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
Configure TACACS+ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
Configure Authentication Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
Configure Management Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
Configure HTTP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
HTTPS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
Manage Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
Download Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
Access Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Configure Access Rule Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
Configure Port Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
Configure Global 802.1X Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
Manage Port Authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
View the Port Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
View the Client Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
Set Up Traffic Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Manage MAC Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
View the MAC Filter Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
Configure Storm Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
Configure Port Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Configure Protected Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
Configure a Private VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
Configure Access Control Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295
Use the ACL Wizard to Create a Simple ACL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
Configure a Basic MAC ACL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
Configure MAC ACL Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
Configure MAC Bindings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 308
View or Delete MAC ACL Bindings in the MAC Binding Table . . . . . . . . . . . 310
Configure an IP ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
Configure Rules for a Basic IP ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
Configure Rules for an Extended IP ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
Configure an IPv6 ACL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 324

7
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Rules for an IPv6 ACL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
Configure IP ACL Interface Bindings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
View or Delete IP ACL Bindings in the IP ACL Binding Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
Configure VLAN ACL Bindings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
Chapter 7 Perform Maintenance Tasks
Reboot the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Reset the Switch to Its Factory Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Export a File From the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
Export a File to the TFTP Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
Use an HTTP Sessions to Export a File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
Export a File to a USB Storage Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using TFTP . . . . . 345
Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using HTTP . . . . 347
Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using
a USB Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
Manage Software Images . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
Copy an Image. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
Configure Dual Image Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
View the Dual Image Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 353
Perform Troubleshooting Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
Send an IPv4 Ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
Send an IPv6 Ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
Send an IPv4 Traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Send an IPv6 Traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
Enable Remote Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
Configure Memory Dump Settings and Perform a Full Memory Dump . . . 360
Chapter 8 Manage Power over Ethernet
PoE Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
Device Class Power Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
Power Allocation and Power Budget . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 365
Configure the Global PoE Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
Manage and View the PoE+ Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
Reset One or More PoE+ Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
Set Up PoE Timer Schedules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
Create a PoE Timer Schedule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
Specify the Settings for an Absolute PoE Timer Schedule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
Specify the Settings for a Recurring PoE Timer Schedule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
Change the Settings for a Recurring PoE Timer Schedule Entry . . . . . . . . . 375
Delete a PoE Timer Schedule Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 376
Delete a PoE Timer Schedule. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
Chapter 9 Monitor the System
Monitor the Switch and the Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379

8
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View or Clear the Switch Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379
View or Clear Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
View or Clear Detailed Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
View or Clear EAP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
Perform a Cable Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
Configure and View Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
Manage the Memory Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
Message Log Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 394
Manage the Flash Log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
Manage the Server Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 396
View or Clear the Trap Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400
View or Clear the Event Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 401
Configure Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 402
Appendix A Configuration Examples
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
VLAN Configuration Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
Access Control Lists (ACLs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
MAC ACL Sample Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
Standard IP ACL Sample Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 408
Differentiated Services (DiffServ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
Class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
DiffServ Traffic Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
Creating Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
DiffServ Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 412
802.1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 413
802.1X Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
MSTP Example Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 418
Appendix B Hardware Specifications and Default Values
Switch Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 421
Switch Features and Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422

9
1
1. Getting Started
This manual describes how you can configure and monitor the following NETGEAR Insight
managed switches by using the local browser–based management interface (which is not the
default management mode):
•Model GC728X. Insight Managed 28-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switch with 2
SFP 1G & 2 SFP+ 10G Fiber Ports
•Model GC728XP. Insight Managed 28-Port Gigabit Ethernet PoE+ Smart Cloud Switch
with 2 SFP 1G & 2 SFP+ 10G Fiber Ports
•Model GC752X. Insight Managed 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switch with 2
SFP 1G & 2 SFP+ 10G Fiber Ports
•Model GC752XP. Insight Managed 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet PoE+ Smart Cloud Switch
with 2 SFP 1G & 2 SFP+ 10G Fiber Ports
This chapter contains the following sections:
•Switch Management Options and Default Management Mode
•Available Publications
•Web Browser Requirements and Supported Browsers
•User-Defined Fields
•Interface Naming Conventions
•Access the Switch
•Change the Management Mode of the Switch
•Register the Switch
•How to Configure Interface Settings
•Local Browser Interface Device View
In this manual, we refer to all switch models as the switch. Unless noted otherwise, all
information applies to all switch models.
For more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit the support website at
netgear.com/support.
Firmware updates with new features and bug fixes are automatically made available through the
Insight app and, if selected, pushed straight from the cloud to the device. If you are not using the
Insight app to manage your device, you can manually download and install the latest firmware by
visiting downloadcenter.netgear.com. If the features or behavior of your product does not match
what is described in this manual, you might need to update your firmware.

Getting Started
10
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Switch Management Options and Default Management
Mode
If you prefer, you can use the switch as a plug-and-play device, so you do not need to set up
a custom configuration. Just connect power, connect to your network and to your other
devices, and you’re done.
The switch is designed for management by the NETGEAR Insight app on a smartphone or
tablet. Alternatively, you can manage the switch from the Insight Cloud portal that is available
from a web browser on your Windows-based computer, Mac, or tablet. By default, the local
browser interface is disabled and you cannot use it while the switch is managed by the
NETGEAR Insight app or Insight Cloud portal.
The switch provides management options that let you discover the switch on the network and
configure, monitor, and control the switch:
•NETGEAR Insight app. Using the NETGEAR Insight app, you can discover the switch
on the network and add the switch to the NETGEAR Insight app so that you can set up
the switch in the network and manage and monitor the switch remotely from your
smartphone.You can choose from four methods to add the switch to the NETGEAR
Insight app: You can scan your network for the switch, scan the QR code or the barcode
of the switch, or add the serial number of the switch. For more information, visit
netgear.com/insight and see the NETGEAR knowledge base articles at
netgear.com/support.
•Insight Cloud portal. Using the NETGEAR Insight Cloud portal, you can set up the
switch in the network, perform advanced remote setup, configuration, and management,
monitor the switch, analyze the switch and network usage, and, if necessary, troubleshoot
the switch and the network.
•Local browser interface. By default, the management mode of the switch is set to
NETGEAR Insight Mobile App and Insight Cloud Portal. With this setting you can manage
the switch using the Insight app or the Insight Cloud portal. For complex tasks such as
integrating with an existing network of devices that are not managed through Insight, and
for debugging purposes, you can change the management mode of the switch to Direct
Connect Web-browser Interface and access the local browser interface. In this mode, you
can change the settings of the specific device, but we recommend that you do not use
this mode to change settings that are Insight manageable because they would not be
synchronized with Insight or to the network location and other devices to which you
assigned the switch.
Note: Changes to Insight-manageable settings from the local browser
interface might also create conflicts with the rest of the
Insight-managed network to which the device is connected. While you
manage the switch with the local browser interface, you cannot use
the Insight app or Insight Cloud portal. To reenable management of

Getting Started
11
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
the device remotely or through the cloud, you can return the
management mode to NETGEAR Insight Mobile App and Insight
Cloud Portal at any time so that you can manage the switch with the
Insight app or Insight Cloud portal.
To use the local browser interface method, after you connect the switch to your network,
you must change the management method to Direct Connect Web-browser Interface
(see Change the Management Mode of the Switch on page 20).
Available Publications
The following guides are available at downloadcenter.netgear.com:
•Installation Guide
•Hardware Installation Guide
For information about the NETGEAR Insight app, visit netgear.com/insight and see the
NETGEAR knowledge base articles at netgear.com/support.
Web Browser Requirements and Supported Browsers
To access the switch by using a web browser, the browser must meet the following software
requirements:
•HTML version 4.0, or later
•HTTP version 1.1, or later
The following browsers were tested and support the local browser interface. Later browser
versions might function fine but were not tested. The following web browsers are supported:
•Microsoft Internet Explorer (IE) version 11
•Microsoft Edge
•Mozilla Firefox version 59.0.3
•Chrome version 66.0
•Safari on Mac OS 8.0 versions 10.1.2
Getting Started
12
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
User-Defined Fields
In the local browser interface, user-defined fields can contain 1 to 159 characters, unless
otherwise noted in the field label on the configuration page. All alphanumeric and special
characters can be used except for the following (unless specifically noted for that feature):
Interface Naming Conventions
The switch supports physical and logical interfaces. Interfaces are identified by their type and
the interface number. The physical ports include 24 Gigabit Ethernet ports for the GC728X
and GC728X models, and 48 Gigabit Ethernet ports for the GC752X and GC752XP models.
All of the models include two SFP 1G ports, and two SFP+ 10G ports. The ports are
numbered on the front panel. You configure the logical interfaces by using the software.
The following table describes the naming convention for all interfaces available on the switch.
Table 1. Disallowed characters in user-defined fields
Character Definition Character Definition
\ Backslash < Less than
/ Forward slash > Greater than
* Asterisk | Pipe
? Question mark
Table 2. Naming conventions for interfaces
Interface Description Example
Physical The physical ports include gigabit ports and are numbered
sequentially starting from 1 using the following format: gy.
g is for a 1G port and y is the port number.
The SFP+ 10G ports are prepended with an x.
g1, g2, g8
xg27
Link aggregation
group (LAG) LAG interfaces are logical interfaces that are used only for bridging
functions. l1, l2, l4
CPU management
interface This is the internal switch interface responsible for the switch base
MAC address. This interface is not configurable and is always listed in
the MAC Address Table.
CPU

Getting Started
13
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Access the Switch
When you use the local browser interface, for easiest access, we recommend that you cable
the switch to a network with a router or DHCP server that assigns IP addresses, power on the
switch, and then use a computer that is connected to the same network as the switch
(on-network, see Access the Switch On-Network on page 13).
It is also possible to configure the switch connected directly only to the computer that you are
using to configure it, and not connected to the network (off-network, see Access the Switch
Off-Network on page 19).
Access the Switch On-Network
The DHCP client on the switch is enabled by default, allowing a DHCP server on the network
(or router that functions as a DHCP server) to assign an IP address to the switch.
If the switch is connected to a network, you can use one of the following methods to
determine the IP address of the switch and access the switch:
•Use a Windows-based computer. See Access the Switch On-Network from a
Windows-Based Computer on page 13.
•Use a Mac. See Access the Switch On-Network from a Mac Using Bonjour on page 14.
•Use the NETGEAR Insight app. See Determine the Switch IP Address Using the
NETGEAR Insight App and Access the Switch On-Network on page 17.
•Access the DHCP server . See Determine the Switch IP Address From the DHCP Server
and Access the Switch On-Network on page 15.
•Use an IP scanner utility. See Determine the Switch IP Address Through an IP Scanner
and Access the Switch On-Network on page 18.
Access the Switch On-Network from a Windows-Based Computer
To use a Windows-based computer and web browser to access the switch that is
connected to a network:
1. Cable the switch to a network with a router or DHCP server that manages IP addresses.
2. Power on the switch.
The DHCP server assigns the switch an IP address.
3. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection.
4. Open Windows Explorer.
5. Click the Network link.
6. If prompted, enable the Network Discovery feature.
7. Under Network Infrastructure, locate the switch model number.
The model number can be GC728X, GC728XP, GC752X, or GC752XP.

Getting Started
14
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
8. Double-click GCmodel (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx) (where GCmodel is the model number of your
switch and xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx is the MAC address of the switch).
The login page of the local browser interface opens.
9. Enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
10. Click the Login button.
A notification displays.
11. Click the OK button to close the notification.
The System Information page displays. The IP address of the switch displays on the
System Information page.
12. Write down the IP address for future use.
13. Select the Direct Connect Web-browser Interface radio button.
14. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The System Information page closes, any current Insight-manageable device settings are
saved to the cloud server, and the login window displays again.
15. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays and the full local browser interface is now
available.
Access the Switch On-Network from a Mac Using Bonjour
If your Mac supports Bonjour, you can use the following procedure. If your Mac does not
support Bonjour, see Determine the Switch IP Address Using the NETGEAR Insight App and
Access the Switch On-Network on page 17.
To use a Mac and web browser to access the switch that is connected to a network:
1. Cable the switch to a network with a router or DHCP server that manages IP addresses.
2. Power on the switch.
The DHCP server assigns the switch an IP address.
3. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection.
4. Open the Safari browser.

Getting Started
15
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select Safari > Preferences.
The General page displays.
6. Click the Advanced tab.
The Advanced page displays.
7. Select the Include Bonjour in the Bookmarks Menu check box.
8. Close the Advanced page.
9. Select Bookmarks > Bonjour > GCmodel (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx) (where GCmodel is the
model number of your switch and xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx is the MAC address of the switch), or
Bookmarks > Bonjour > Webpages GCmodel (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx) depending on your
Mac OS version.
The login page of the local browser interface opens.
10. Enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
11. Click the Login button.
A notification displays.
12. Click the OK button to close the notification.
The System Information page displays. The IP address of the switch displays on the
System Information page.
13. Write down the IP address for future use.
14. Select the Direct Connect Web-browser Interface radio button.
15. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The System Information page closes, any current Insight-manageable device settings are
saved to the cloud server, and the login window displays again.
16. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays and the full local browser interface is now
available.
Determine the Switch IP Address From the DHCP Server and Access the
Switch On-Network
For information about how to access the DHCP server (or router that functions as a DHCP
server) in your network, see the documentation for your DHCP server (or router).

Getting Started
16
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To access the DHCP server and use a web browser to access the switch that is
connected to a network:
1. Cable the switch to a network with a router or DHCP server that manages IP addresses.
2. Power on the switch.
The DHCP server assigns the switch an IP address.
3. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection.
4. Access the DHCP server and view the IP address assigned to the switch.
5. Write down the IP address for future use.
6. Launch a web browser.
7. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
The login window opens.
8. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
9. Click the Login button.
A notification displays.
10. Click the OK button to close the notification.
The System Information page displays.
11. Select the Direct Connect Web-browser Interface radio button.
12. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The System Information page closes, any current Insight-manageable device settings are
saved to the cloud server, and the login window displays again.
13. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays and the full local browser interface is now
available.

Getting Started
17
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Determine the Switch IP Address Using the NETGEAR Insight App and Access
the Switch On-Network
To use the NETGEAR Insight app and a web browser to access the switch that is
connected to a network:
1. On your iOS or Android mobile device, go to the app store, search for NETGEAR
Insight, and download the app.
2. If the switch is directly connected to a WiFi router or access point, connect your mobile
device to the WiFi network of the router or access point.
3. Open the NETGEAR Insight app.
4. Select LOG IN to log in to your existing NETGEAR account or tap the CREATE NETGEAR
ACCOUNT button to create a new account.
5. After you log in to your account, name your network and specify a device admin password
that applies to all devices that you add to this network.
When you are done, tap the NEXT button.
6. You can now add the switch. Choose one of the following options:
•Tap Switch as the device type and follow the prompts to scan the network.
•Scan the QR code.
•Scan the serial number bar code.
•Type in the serial number.
Note: Screens might display and suggest that you connect the switch to
power and to an uplink. Since the switch is already connected to your
network, on these screens, tap the NEXT button.
7. If the switch is not yet connected to the same WiFi network as your mobile device, connect
it now to the same WiFi network, wait two minutes, and then tap the NEXT button.
The IP address of the switch displays in the device list.
8. Write down the IP address for future use.
9. Launch a web browser.
10. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
The login window opens.
11. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. Because you added the switch to a network on the
Insight app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser
interface, enter your Insight network password.
12. Click the Login button.
A notification displays.
13. Click the OK button to close the notification.

Getting Started
18
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
14. Select the Direct Connect Web-browser Interface radio button.
15. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The System Information page closes, any current Insight-manageable device settings are
saved to the cloud server, and the login window displays again.
16. When prompted, enter the password.
Because you added the switch to a network on the Insight app before and you did not yet
change the password through the local browser interface, enter your Insight network
password.
The System Information page displays and the full local browser interface is now
available.
Determine the Switch IP Address Through an IP Scanner and Access the
Switch On-Network
IP scanner utilities are available free of charge on the Internet.
To use an IP scanner utility and web browser to access the switch that is connected to
a network:
1. Cable the switch to a network with a router or DHCP server that manages IP addresses.
2. Power on the switch.
The DHCP server assigns the switch an IP address.
3. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection.
4. Using the IP scanner utility, scan your network for the IP address assigned to the switch.
5. Write down the IP address for future use.
6. Launch a web browser.
7. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
The login window opens.
8. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
9. Click the Login button.
A notification displays.
10. Click the OK button to close the notification.

Getting Started
19
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
11. Select the Direct Connect Web-browser Interface radio button.
12. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The System Information page closes, any current Insight-manageable device settings are
saved to the cloud server, and the login window displays again.
13. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays and the full local browser interface is now
available.
Access the Switch Off-Network
The default IP address of the switch is 192.168.0.239. The IP address of the computer that
you use to access the switch off-network must in the same subnet as the default IP address
of the switch.
To use your web browser to configure a switch that is not connected to a network:
1. Record your computer’s TCP/IP configuration settings, and then configure the computer
with a static IP address of 192.168.0.210 and 255.255.255.0 as the subnet mask.
Note: If you are unsure how to do this, visit netgear.com/search-support.aspx
and search for the following:
How to set a static IP address in Windows
or
Setting a static IP address on your network adapter in Mac OS
2. Plug the switch into a power outlet and then connect your computer to the switch using an
Ethernet cable.
You can connect the Ethernet cable to any Ethernet port on the switch.
3. Open a web browser, and enter http://192.168.0.239.
This is the default address of the switch.
4. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
5. Click the Login button.
A notification displays.

Getting Started
20
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Click the OK button to close the notification.
The System Information page displays.
7. Select the Direct Connect Web-browser Interface radio button.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The System Information page closes, any current Insight-manageable device settings are
saved to the cloud server, and the login window displays again.
9. When prompted, enter the password.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays and the full local browser interface is now
available.
10. After you complete the configuration of the switch, reconfigure the computer that you used
for this process to its original TCP/IP settings.
You can now connect your switch to your network using an Ethernet cable.
Change the Management Mode of the Switch
By default, the management mode on the switch is NETGEAR Insight Mobile App and Insight
Cloud Portal. With this setting you can manage the switch using the Insight app or the Insight
Cloud portal. The first time that you log in to the switch’s local browser interface, you must
change the management mode to Direct Connect Web-browser Interface (which is the same
as the local browser interface). You can also change the management mode back to
NETGEAR Insight Mobile App and Insight Cloud Portal, which also reenables supports for
the Insight Cloud portal.
Note the following about changing the management mode:
•Changing to Direct Connect Web-browser Interface. The NETGEAR Insight app
management mode becomes disabled and the current Insight-manageable device
settings are saved to the cloud server. Any changes that you make using the Direct
Connect Web-browser Interface management mode are not saved to the cloud server.
•Changing back to NETGEAR Insight Mobile App and Insight Cloud Portal. If you
added the switch to a network on the Insight app before, all Insight-manageable device
settings are returned to the last configuration saved on the cloud server, including the
switch password (that is, the password is reset to the Insight network password).

Getting Started
21
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Change the Management Mode to Direct Connect
Web-browser Interface
Note: If you already accessed the local browser interface (see Access the
Switch on page 13), you can skip this section.
To change the management mode of the switch to Direct Connect Web-browser
Interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the Password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select the Direct Connect Web-browser Interface radio button.
6. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved. The System Information page closes and the login window
displays again.
Any current Insight-manageable device settings are saved to the cloud server.
7. Enter the switch’s password in the Password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays and the full local browser interface is now
available.

Getting Started
22
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Change the Management Mode Back to NETGEAR Insight
Mobile App and Insight Cloud Portal
To change the management mode of the switch back to NETGEAR Insight Mobile App
and Insight Cloud Portal:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the Password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select the NETGEAR Insight Mobile App and Insight Cloud Portal radio button.
6. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved. The System Information page closes and the login page displays
again. (You can close the login page.)
The switch connects to the cloud server. If you added the switch to a network on the
Insight app before, all Insight-manageable device settings are returned to the last
configuration saved on the cloud server, including the switch password (that is, the
password is reset to the Insight network password)
Register the Switch
To qualify for product updates and product warranty, we encourage you to register your
product. The first time you log in to the switch, you are given the option of registering with
NETGEAR. Registration confirms that your email alerts work, lowers technical support
resolution time, and ensures that your shipping address accuracy. We would also like to
incorporate your feedback into future product development. We never sell or rent your email
address and you can opt out of communications at any time.
If you use the Insight app, after the app discovers the switch and you add it to a network
using the NETGEAR Insight app, the switch is automatically registered to your MyNETGEAR
account. This registration process is also referred to as claiming. For information about the
NETGEAR Insight app, see the NETGEAR knowledge base articles at netgear.com/support.

Getting Started
23
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
If you do not claim (register) the device and add it to an Insight network using the Insight app,
you can manually register the switch using the local browser interface as described in the
following procedure or you can visit the NETGEAR website for registration at
my.netgear.com.
To register the switch through the local browser interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
5. Select Help > Registration.
The Product Registration page displays.
6. Click the Register button.
A NETGEAR web page opens.
7. Follow the prompts online.
How to Configure Interface Settings
For some features you can apply the same settings simultaneously to any of the following:
•A single port
•Multiple ports
•All ports
•A single LAG
•Multiple LAGs
•All LAGs
•Multiple ports and LAGs
•All ports and LAGs
Many of the pages that allow you to configure or view interface settings include links to
display all ports, all LAGs, or all ports and LAGs on the page.
Getting Started
24
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
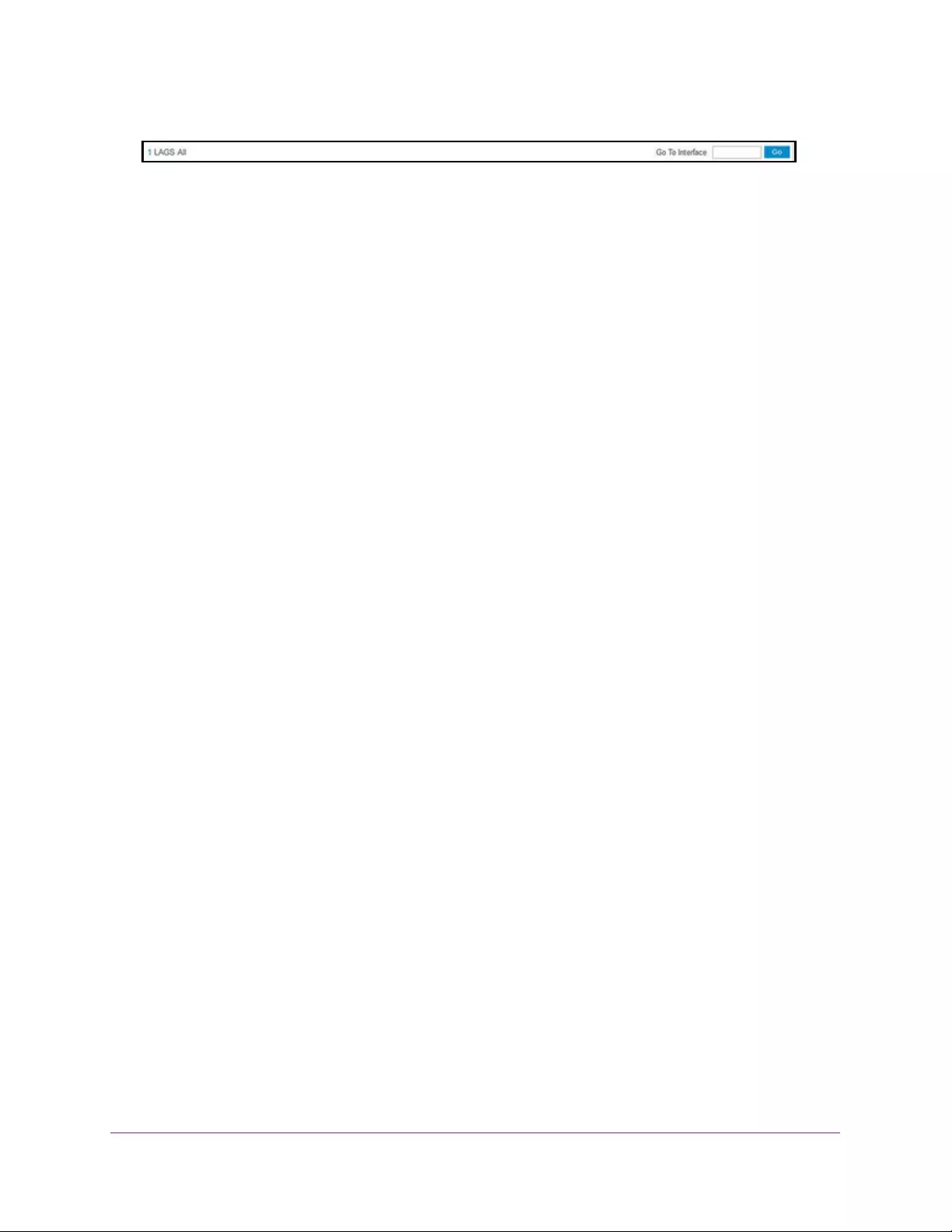
Use these links as follows:
•To display all ports, click the 1 link. The LAGs are not displayed.
•To display all LAGs, click the LAGS link. The ports are not displayed.
•To display all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
The procedures in this section describe how to select the ports and LAGs to configure. The
procedures assume that you are already logged in to the switch. If you do not know how to
log in to the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
To configure a single port or LAG:
1. Click the All link to display the all ports and LAGs.
2. Do one of the following:
a. In the Go To Interface field, type the port number and click the Go button.
For example, type g4 for a port or type l3 for a LAG. For more information, see
Interface Naming Conventions on page 12.
The check box for the interface is selected, the row for the selected interface is
highlighted, and the interface number displays in the heading row.
b. Select the check box for the port or LAG.
The row for the selected interface is highlighted, and the interface number displays in
the heading row.
3. Configure the desired settings.
4. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
To configure multiple ports and LAGs:
1. Click the All link to display all ports and LAGs.
2. Select the check box next to each port and LAG to configure.
The row for each selected interface is highlighted.
3. Configure the desired settings.
4. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
To configure all ports and LAGs:
1. Click the All link to display all ports and LAGs.
2. Select the check box in the heading row.
The check boxes for all ports and LAGs are selected and the rows for all ports and LAGs
are highlighted.

Getting Started
25
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. Configure the desired settings.
4. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Local Browser Interface Device View
The Device View page displays the ports on the switch. This graphic provides an alternate
way to navigate to configuration and monitoring options. The graphic also provides
information about device ports, current configuration and status, tables, and feature
components.
To use the Device View:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
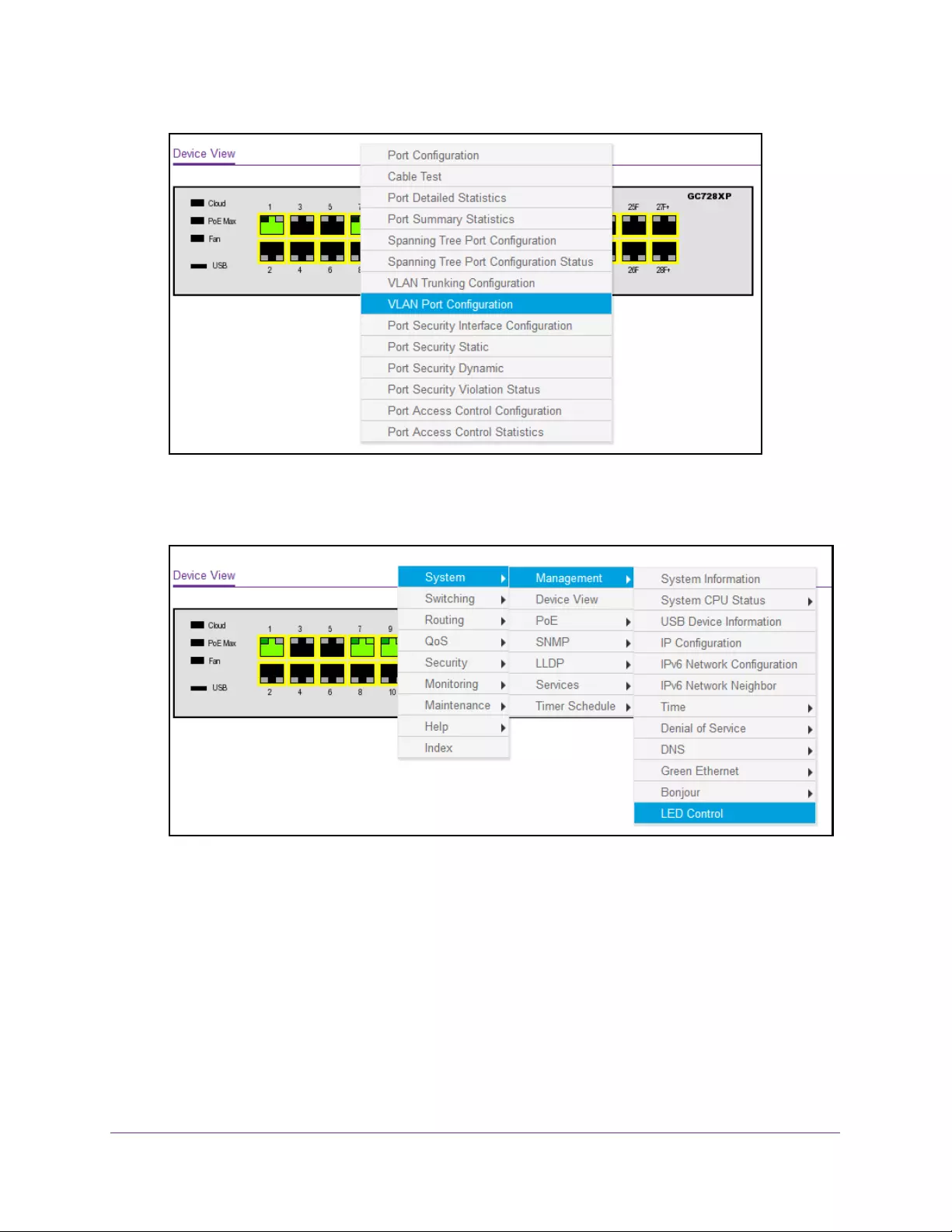
5. Select System > Device View.
The previous figure shows the Device View page for model GC728XP.
The port color indicates the port status:
•Green. The port is linking up.
•Red. An error occurred on the port or the port is administratively disabled.
•Black. No link is present.

Getting Started
26
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The left port LED indicates the connection, speed, and traffic status:
•Solid gray. The port is not connected. This is the default state.
•Solid green. The port is operating at its maximum speed.
•Blinking green. The port is transmitting or receiving traffic at its maximum speed
•Solid amber The port is operating at below its maximum speed.
•Blinking amber. The port is transmitting or receiving traffic below its maximum
speed.
The right port LED indicates the PoE status (this does not apply to models GC728X and
GC752X):
•Off. The port is not delivering PoE power.
•Solid green. The port is delivering PoE power.
•Solid amber. A PoE fault occurred.
The system LEDs indicate the following status:
•Cloud LED:
-Solid blue. The switch is connected to the cloud server and is set up to be
managed by the NETGEAR Insight app.
-Off. The switch is not connected to the cloud server or is set up to be managed by
the local browser interface.
•PoE Max LED (this does not apply to models GC728X and GC752X):
-Off. Sufficient (more than 7W of) PoE power is available.
-Solid amber. Less than 7W of PoE power is available.
-Blinking amber. At least once during the previous two minutes, less than 7W of
PoE power was available.
•Fan LED:
-Solid green. The fan is operating normally.
-Solid amber. A problem occurred with the fan.
6. To see a menu that displays statistics and configuration options, click a port.
Getting Started
27
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The previous figure shows the Device View page for model GC728XP.
7. To display the main menu that contains the same options as the navigation menu at the top
of the page, right-click the graphic without clicking a specific port.
The previous figure shows the Device View page for model GC728XP.

28
2
2. Configure System Information
This chapter covers the following topics:
•View and Configure the Switch Management Settings
•Manage the Bonjour Settings and View Bonjour Information
•Control the LEDs
•Use the Device View
•Configure Power over Ethernet
•Configure SNMP
•Configure Link Layer Discovery Protocol
•Configure DHCP L2 Relay and DHCP Snooping
•Set Up PoE Timer Schedules

Configure System Information
29
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View and Configure the Switch Management Settings
This section describes how to display the switch status and specify some basic switch
information, such as the management interface IP address, system clock settings, and DNS
information. The following sections describe how you can configure the switch management
settings:
•View or Define System Information on page 29
•View the Switch CPU Status on page 34
•Configure the IPv4 Address for the Network Interface and Management VLAN on
page 37
•Configure the IPv6 Address for the Network Interface on page 38
•View the IPv6 Network Neighbor on page 40
•Configure the Time Settings on page 41
•Configure Denial of Service Settings on page 55
•Configure DNS Settings on page 57
•Configure Green Ethernet Settings on page 61
View or Define System Information
When you log in, the System Information page displays. You can configure and view general
device information.
To view or define system information:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
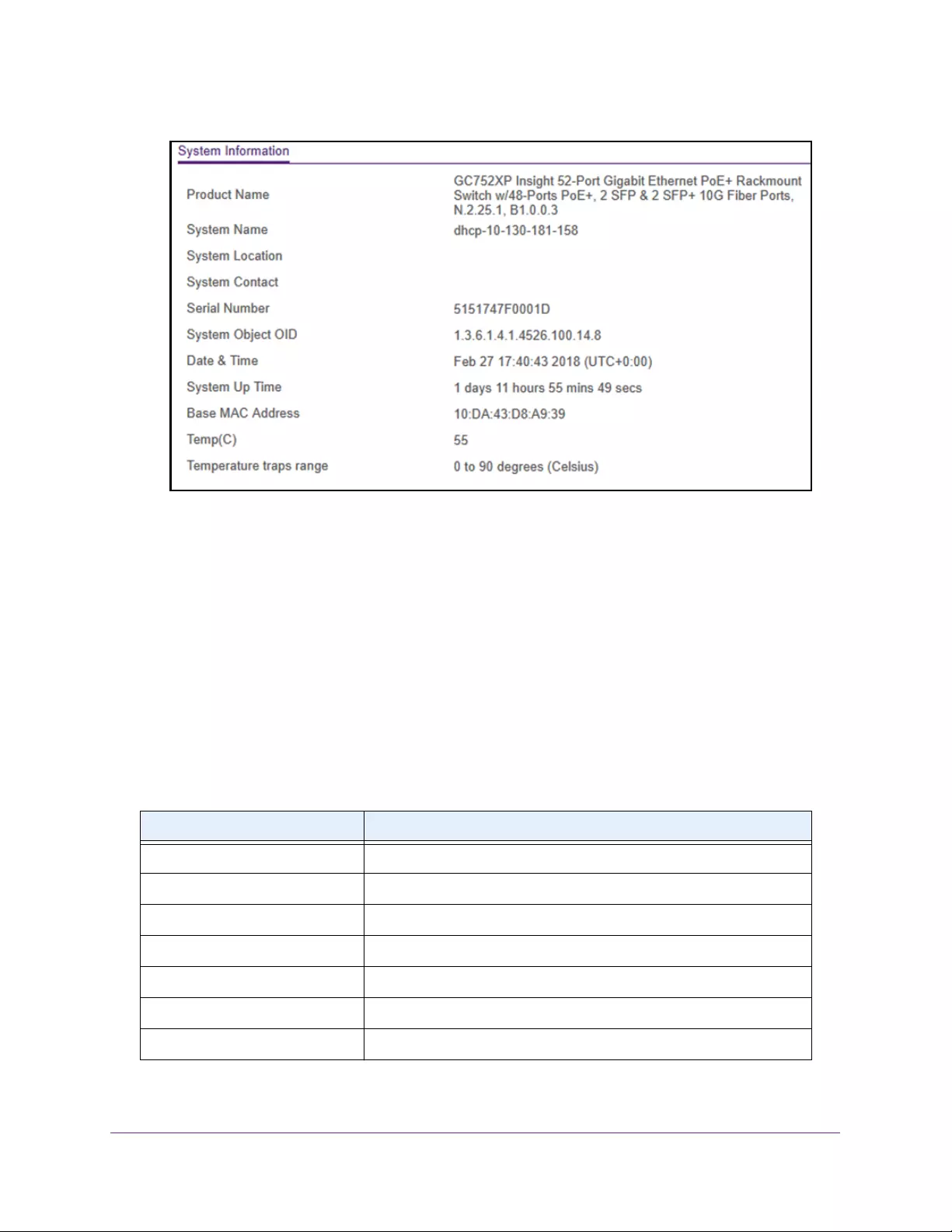
Configure System Information
30
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Define the following fields:
•System Name. Enter the name to identify this switch. You can use up to 255
alphanumeric characters.
•System Location. Enter the location of this switch. You can use up to 255
alphanumeric characters.
•System Contact. Enter the contact person for this switch. You can use up to 255
alphanumeric characters.
6. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the status information that the System Information page
displays.
Table 3. System Information
Field Description
Product Name The product name of this switch.
Serial Number The serial number of the switch.
Date & Time The current date and time.
System Up Time The time in days, hours, and minutes since the last switch reboot.
Base Mac Address Universally assigned hardware address of the switch.
Temp (C) The general temperature of the switch in degrees Centigrade.
Temperature traps range Identifies the minimum and maximum traps range.
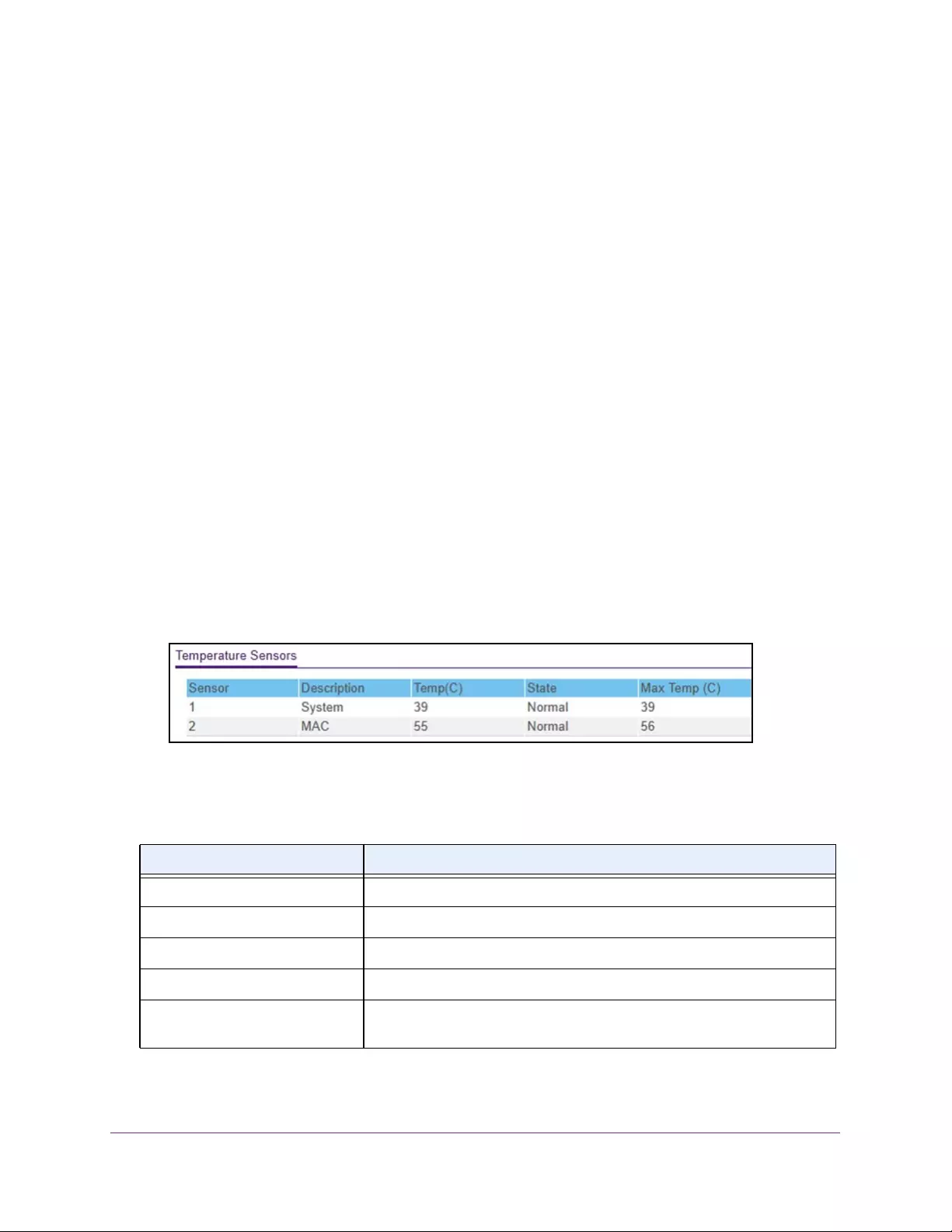
Configure System Information
31
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View the Temperature Sensor Information
You can view the current temperature of the temperature sensors. The temperature is instant
and can be updated with the latest information about the switch when you click the Refresh
button. The maximum temperature of the temperature sensors depends on the actual
hardware.
To view temperature information:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Scroll down to the Temperature Sensors section.
6. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable Temperature Sensors information.
Table 4. Temperature Sensors information
Field Description
Sensor The temperature sensor for the switch
Description The description of the temperature sensor.
Temp(C) The temperature of the switch in degrees Centigrade.
State The switch temperature state.
Max Temp (C) The maximum temperature value of CPU. If the switch exceeds this limit, it
shuts down.
Configure System Information
32
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View the Fan Status
You can view the status of the fans. These fans remove the heat generated by the power,
CPU, and other components, and allow the switch to function normally.
To view the fan status:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Scroll down to the Fans section.
The fan information displays.
6. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fan status information.
Table 5. Fan status
Field Description
FAN The fan index used to identify the fan for the switch. (The index is 1.)
Description The description of the temperature sensor.
Type Specifies whether the fan module is fixed or removable.
Speed The fan speed.
Duty level(%) The duty level of the fan.
State Specifies whether the fan is operational.
Configure System Information
33
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
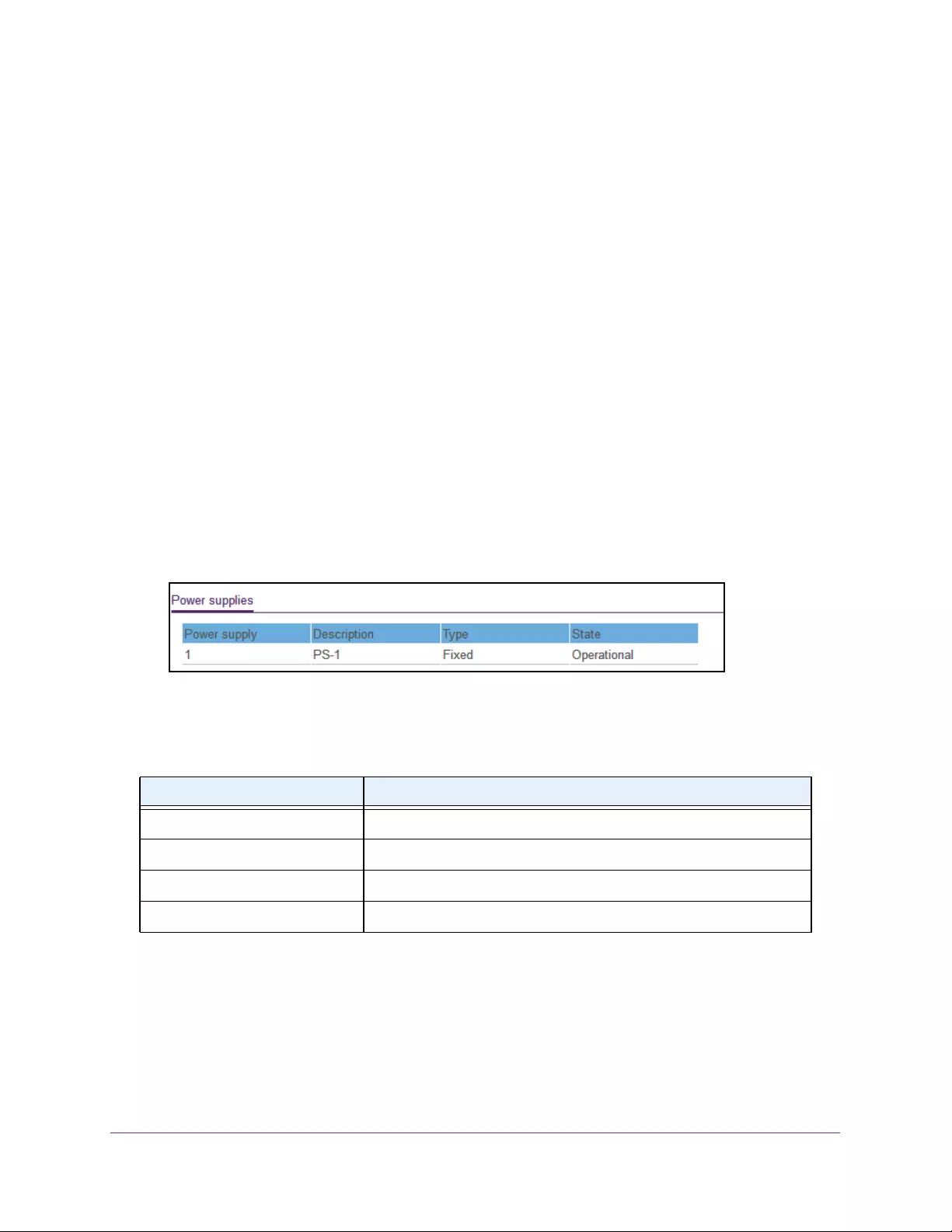
View the Power Supplies
You can view s the status of the power supplies.
To view the power supplies status:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Scroll down to the Power supplies section.
6. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable Power supplies information.
Table 6. Power supplies status
Field Description
Power supply The power supply index used for the switch.
Description The description of the power supply.
Type Specifies whether the power module is fixed or removable.
State Specifies the state of the power module.

Configure System Information
34
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View the Software Versions
You can view the software versions that are running on the switch.
To view the software versions:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Scroll down to the Versions section.
6. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed in the Versions
section of the System Information page.
View the Switch CPU Status
You can monitor the CPU, memory resources, and utilization patterns across various
intervals to assess the performance, load, and stability parameters of the switch.
To view the switch CPU status:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
Table 7. Versions information
Field Description
Model Name The model name of the switch.
Boot Version The version of the bootloader software of the switch.
Software Version The version number of the code currently running on the switch.
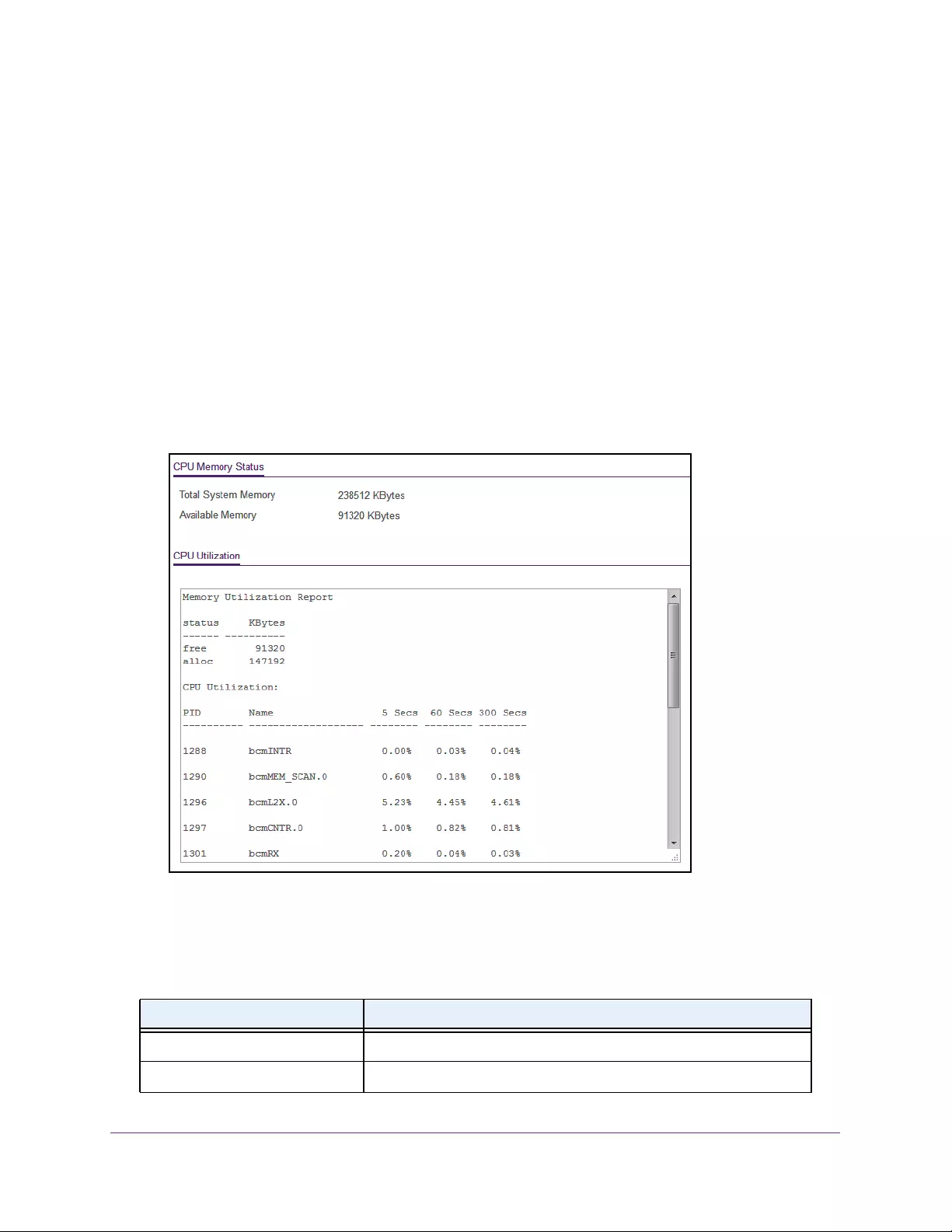
Configure System Information
35
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > System CPU Status > System CPU Status.
The CPU Utilization section shows the memory information, task-related information, and
percentage of CPU utilization per task.
The following table describes CPU Memory Status information.
Table 8. CPU Memory Status information
Field Description
Total System Memory The total memory of the switch in KBytes.
Available Memory The available memory space for the switch in KBytes.

Configure System Information
36
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure the CPU Thresholds
The CPU utilization threshold notification feature allows you to configure thresholds that,
when exceeded, trigger a notification. The notification occurs through SNMP trap and syslog
messages.
To configure the CPU thresholds:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > System CPU Status > CPU Threshold.
The CPU Threshold page displays.
6. Specify the thresholds:
•Rising Threshold. Notification is generated when the total CPU utilization exceeds
this threshold value over the configured time period. The range is 1 to 100.
•Rising Interval. This utilization monitoring time period can be configured from 5 to
86400 seconds in multiples of 5 seconds.
•Falling Threshold. Notification is triggered when the total CPU utilization falls below
this level for a configured period of time.
The falling utilization threshold must be equal to or less than the rising threshold
value. The falling utilization threshold notification is sent only if a rising threshold
notification was sent previously. Configuring the falling utilization threshold and time
period is optional. If the Falling CPU utilization parameters are not configured, the
parameters automatically get the same values as the Rising CPU utilization
parameters. The range is 1 to 100.
•Falling Interval. The utilization monitoring time period can be configured from 5
seconds to 86400 seconds in multiples of 5 seconds.
•Free Memory Threshold. The free memory threshold value for the CPU in KB.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure System Information
37
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure the IPv4 Address for the Network Interface and
Management VLAN
You can configure network information for the network interface, which is the logical interface
used for in-band connectivity with the switch through any of the switch’s ports. You also use
the IPv4 address of the network interface to connect to the switch through the local browser
interface. The configuration parameters that is associated with the switch’ s network interface
do not affect the configuration of the ports through which traffic is switched.
To configure the IPv4 address for the network interface and the management VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > IP Configuration.
The IP Configuration page displays.
6. Select a radio button to specify how the network information for the switch management
interface must be configured:
•Static IP Address. Specifies that the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
must be manually configured. Enter this information in the fields below this radio
button.
•Dynamic IP Address (BOOTP). Specifies that the switch must obtain the IP address
through a BootP server.
•Dynamic IP Address. Specifies that the switch must obtain the IP address through a
DHCP server. This is the default setting. By default, the DHCP client is enabled.
7. If you select the Static IP Address radio button, configure the following network information:
•IP Address. The IP address of the network interface. The default is 192.168.0.239.
Each part of the IP address must start with a number other than zero. For example, IP
addresses 001.100.192.6 and 192.001.10.3 are not valid.
•Subnet Mask. The IP subnet mask for the interface. The default value is
255.255.255.0.

Configure System Information
38
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Default Gateway. The default gateway for the IP interface. The default value is
192.168.0.254.
8. Specify the VLAN ID for the management VLAN.
The management VLAN is used to establish an IP connection to the switch from a
computer that is connected to a port in the same VLAN. If not specified, the active
management VLAN ID is 1 (default), which allows an IP connection to be established
through any port.
When the management VLAN is set to a different value, an IP connection can be made
only through a port that is part of the management VLAN. Also, the port VLAN ID (PVID)
of the port to be connected in that management VLAN must be the same as the
management VLAN ID.
Note: Make sure that the VLAN that you want to assign as the management
VLAN exists. Also make sure that the PVID of at least one port in the
VLAN is the same as the management VLAN ID. For information
about creating VLANs and configuring the PVID for a port, see
Configure VLANs on page 112.
The following requirements apply to the management VLAN:
•Only one management VLAN can be active at a time.
•When a new management VLAN is configured, connectivity through the existing
management VLAN is lost.
•The management station must be reconnected to the port in the new management
VLAN.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure the IPv6 Address for the Network Interface
You can configure the IPv6 address for the network interface, which is the logical interface
used for in-band connectivity with the switch through any of the switch’s front-panel ports.
You also use the IPv6 address of the network interface to connect to the switch through the
local browser interface. The configuration parameters that is associated with the switch’s
network interface do not affect the configuration of the ports through which traffic is switched.
To access the switch over an IPv6 network, you must initially configure the switch with IPv6
information (IPv6 prefix, prefix length, and default gateway). IPv6 can be configured using
any of the following options:
•IPv6 auto-configuration
•DHCPv6

Configure System Information
39
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
When in-band connectivity is established, you can change the IPv6 information through the
local browser interface.
To configure the IPv6 address for the network interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > IPv6 Network Configuration.
The IPv6 Network Global Configuration page displays.
6. Ensure that the Admin Mode Enable radio button is selected.
7. Determine how the switch acquires an IPv6 address:
•IPv6 Address Auto Configuration Mode. When this mode is enabled, the network
interface can acquire an IPv6 address through IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol
(NDP) and through the use of router advertisement messages. When this mode is
disabled, the network interface does not use the native IPv6 address
autoconfiguration feature to acquire an IPv6 address. Autoconfiguration can be
enabled only when DHCPv6 is not enabled on any of the management interfaces.
•DHCPv6. Next to Current Network Configuration Protocol, select the DHCPv6 radio
button to enable the DHCPv6 client on the interface. The switch attempts to acquire
network information from a DHCPv6 server. Selecting the None radio button disables
the DHCPv6 client on the network interface. When DHCPv6 is enabled, the DHCPv6
Client DUID field displays the client identifier used by the DHCPv6 client (if enabled)
when sending messages to the DHCPv6 server.
8. In the IPv6 Gateway field, specify the IPv6 address for the default gateway for the network
interface.
The gateway address is in IPv6 global or link-local address format.
9. To configure one or more static IPv6 addresses for the network interface, do the following:
a. In the IPv6 Prefix/Prefix Length field, specify the static IPv6 prefix and prefix to the
IPv6 network interface.
The address is in the global address format.
Configure System Information
40
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
b. In the EUI64 menu, select True to enable the Extended Universal Identifier (EUI)
flag for IPv6 address, or select False to omit the EUI flag.
c. Click the Add button.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
View the IPv6 Network Neighbor
You can view information about the IPv6 neighbors that the switch discovers through the
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP).
To view the IPv6 neighbor table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > IPv6 Network Neighbor.
The IPv6 Network Interface Neighbor Table page displays.
The following table describes the information the IPv6 Network Neighbor page displays about
each IPv6 neighbor that the switch discovered.
Table 9. IPv6 network interface neighbor table information
Field Description
IPv6 address The IPv6 address of a neighbor switch visible to the network interface.
MAC address The MAC address of a neighbor switch.
IsRtr • true (1). The neighbor machine is a router.
• false (2). The neighbor machine is not a router.

Configure System Information
41
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure the Time Settings
The switch supports the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP). As its name suggests, it is a
less complicated version of Network Time Protocol, which is a system for synchronizing the
clocks of networked computer systems, primarily when data transfer is handled through the
Internet. You can also set the system time manually.
Configure the Time Setting Manually
You can view and adjust date and time settings.
To manually configure the time setting:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > Time Configuration.
The Time Configuration page displays.
6. Select the Clock Source Local radio button.
7. In the Date field, specify the current date in months, days, and years (MM/DD/YYYY).
8. In the Time field, specify the current time in hours, minutes, and seconds (HH:MM:SS).
Neighbor State The state of the neighboring switch:
• reachable (1). The neighbor is reachable from the switch.
• stale (2). Information about the neighbor is scheduled for deletion.
• delay (3). No information was received from the neighbor during
the delay period.
• probe (4). The switch is attempting to probe the neighbor.
• unknown (5). Unknown status.
Last Updated The last time that the neighbor information was updated.
Table 9. IPv6 network interface neighbor table information (continued)
Field Description

Configure System Information
42
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Note: If you do not enter a date and time, the switch calculates the date and
time using the CPU’s clock cycle.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure the Time Settings With SNTP
To configure the time by using SNTP:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > Time Configuration.
The Time Configuration page displays.
6. Select the Clock Source SNTP radio button.
The page refreshes and displays the SNTP Global Configuration section and the SNTP
Global Status section.
The default is SNTP. The local clock can be set to SNTP only if the following two
conditions are met:
•The SNTP server is configured.
•The SNTP last attempt status is successful.
7. Next to Client Mode, select the mode of operation of the SNTP client:
•Disable. SNTP is not operational. No SNTP requests are sent from the client nor are
any incoming SNTP messages processed.
•Unicast. SNTP operates in a point-to-point fashion. A unicast client sends a request
to a designated server at its unicast address and expects a reply from which it can
determine the time and, optionally, the round-trip delay and local clock offset relative
to the server.

Configure System Information
43
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Broadcast. SNTP operates in the same manner as multicast mode but uses a local
broadcast address instead of a multicast address. The broadcast address provides a
single-subnet scope while a multicast address provides an Internet-wide scope.
The default value is Disable.
8. If the SNTP client mode is Unicast, use the SNTP Server Configuration page to add the IP
address or DNS name of one or more SNTP servers for the switch to poll.
For more information, see Configure an SNTP Server on page 47.
9. In the Port field, specify the local UDP port that the SNTP client receives server packets on.
The allowed range is 1025 to 65535 and 123. The default value is 123. When the default
value is configured, the actual client port value used in SNTP packets is assigned by the
operating system.
10. In the Unicast Poll Interval field, specify the number of seconds between unicast poll
requests expressed as a power of 2. to The allowed range is 6 to 10. The default value is 6.
11. In the Broadcast Poll Interval field, specify the number of seconds between broadcast poll
requests expressed as a power of 2.
Broadcasts received prior to the expiry of this interval are discarded. The allowed range is
6 to 10. The default value is 6.
12. In the Unicast Poll Timeout field, specify the number of seconds to wait for an SNTP
response to a unicast poll request.
The allowed range is 1 to 30. The default value is 5.
13. In the Unicast Poll Retry field, specify the number of times to retry a unicast poll request to
an SNTP server after the first time-out before the switch attempts to use the next configured
server.
The allowed range is 0 to 10. The default value is 1.
14. In the Time Zone Name field, specify a time zone.
You can also specify the number of hours and number of minutes that the time zone is
different from the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time zone can affect the
display of the current system time. The default value is UTC.
Note: When using SNTP/NTP time servers to update the switch’s clock, the
time data received from the server is based on the UTC, which is the
same as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). This might not be the time
zone in which the switch is located.
15. In the Offset Hours field, specify the number of hours that the time zone is different from
UTC.
See the description for Time Zone Name in Step 14 for more information. The allowed
range is –12 to 13. The default value is 0.
16. In the Offset Minutes field, specify the number of minutes that the time zone is different
from UTC.

Configure System Information
44
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
See the description for Time Zone Name in Step 14 for more information. The allowed
range is 0 to 59. The default value is 0.
17. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Modify the Global SNTP Settings
To modify the global SNTP settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > Time Configuration.
The Time Configuration page displays.
If the clock source is SNTP, the SNTP Global Configuration section displays below the
Time Configuration section.
6. Select a Client mode radio button to specify the mode of operation of the SNTP client:
•Disable. SNTP is not operational. No SNTP requests are sent from the client and no
received SNTP messages are processed.
•Unicast. SNTP operates in a point-to-point fashion. A unicast client sends a request
to a designated server at its unicast address and expects a reply from which it can
determine the time and, optionally, the round-trip delay and local clock offset relative
to the server.
•Broadcast. SNTP operates in the same manner as multicast mode but uses a local
broadcast address instead of a multicast address. The broadcast address provides a
single-subnet scope while a multicast address provides an Internet-wide scope.
The default value is Unicast.
7. In the Port field, specify the local UDP port that the SNTP client receives server packets on.

Configure System Information
45
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The allowed range is 1025 to 65535 and the value 123. The default value is 123. When
the default value is configured, the actual client port value used in SNTP packets is
assigned by the operating system.
8. In the Unicast Poll Interval field, specify the number of seconds between unicast poll
requests expressed as a power of 2.
The allowed range is 6 to 10. The default value is 6.
9. In the Broadcast Poll Interval field, specify the number of seconds between broadcast poll
requests expressed as a power of 2.
Broadcasts received prior to the expiry of this interval are discarded. The allowed range is
6 to 10. The default value is 6.
10. In the Unicast Poll Timeout field, specify the number of seconds to wait for an SNTP
response to a unicast poll request.
The allowed range is 1 to 30. The default value is 5.
11. In the Unicast Poll Retry field, specify the number of times to retry a unicast poll request to
an SNTP server after the first time-out before the switch attempts to use the next configured
server.
The allowed range is 0 to 10. The default value is 1.
12. In the Time Zone Name field, specify a time zone.
You can also specify the number of hours and number of minutes that the time zone is
different from the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time zone can affect the
display of the current system time. The default value is UTC.
Note: When using SNTP/NTP time servers to update the switch’s clock, the
time data received from the server is based on the UTC, which is the
same as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). This might not be the time
zone in which the switch is located.
13. In the Offset Hours field, specify the number of hours that the time zone is different from
UTC.
The allowed range is –12 to 13. The default value is 0.
14. In the Offset Minutes field, specify the number of minutes that the time zone is different
from UTC.
The allowed range is 0 to 59. The default value is 0.
15. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
16. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.

Configure System Information
46
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View SNTP Global Status
When you select the SNTP option as the clock source, the SNTP global status is displayed
below the SNTP Global Configuration section of the page. The SNTP Global Status table
displays information about the system’s SNTP client.
To view SNTP global status:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > Time Configuration.
The Time Configuration page displays.
If the clock source is SNTP, the SNTP Global Status section displays below the SNTP
Global Configuration section.
6. Click the Refresh button to update the page with the latest information about the switch.
The following table displays the nonconfigurable SNTP Global Status information.
Table 10. SNTP Global Status information
Field Description
Version The SNTP version that the client supports.
Supported mode The SNTP modes that the client supports. Multiple modes can be supported by
a client.
Last Update Time The local date and time (UTC) that the SNTP client last updated the system
clock.
Last Attempt Time The local date and time (UTC) of the last SNTP request or receipt of an
unsolicited message.
Configure System Information
47
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure an SNTP Server
SNTP assures accurate network device clock time synchronization up to the millisecond.
Time synchronization is performed by a network SNTP server. The switch operates only as
an SNTP client and cannot provide time services to other systems.
Time sources are established by strata. Strata define the accuracy of the reference clock.
The higher the stratum (where zero is the highest), the more accurate the clock. The device
receives time from Stratum 1 and above since it is itself a Stratum 2 device.
Last Attempt Status The status of the last SNTP request or unsolicited message for both unicast
and broadcast modes. If no message was received from a server, a status of
Other is displayed. These values are appropriate for all operational modes.
• Other. The status of the last request is unknown.
• Success. The SNTP operation was successful and the system time was
updated.
• Request Timed Out. After an SNTP request was sent to an SNTP server,
the response timer expired before a response from the server was
received.
• Bad Date Encoded. The time provided by the SNTP server is not valid.
• Version Not Supported. The SNTP version supported by the server is not
compatible with the version supported by the client.
• Server Unsynchronized. The SNTP server is not synchronized with its
peers. This is indicated by the leap indicator field in the SNTP message.
• Server Kiss Of Death. The SNTP server indicated that no further queries
were to be sent to this server. This is indicated by a stratum field equal to
0 in a message received from a server.
Server IP Address The IP address of the server for the last received valid packet. If no message
was received from any server, an empty string is shown.
Address Type The address type of the SNTP server address for the last received valid
packet.
Server Stratum The claimed stratum of the server for the last received valid packet.
Reference Clock ID The reference clock identifier of the server for the last received valid packet.
Server mode The mode of the server for the last received valid packet.
Unicast Server Max Entries The maximum number of unicast server entries that can be configured on this
client.
Unicast Server Current Entries The number of current valid unicast server entries configured for this client.
Broadcast Count The number of unsolicited broadcast SNTP messages that were received and
processed by the SNTP client since the last reboot.
Table 10. SNTP Global Status information (continued)
Field Description

Configure System Information
48
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following is an example of strata:
•Stratum 0. A real-time clock is used as the time source, for example, a GPS system.
•Stratum 1. A server that is directly linked to a Stratum 0 time source is used. Stratum 1
time servers provide primary network time standards.
•Stratum 2. The time source is distanced from the Stratum 1 server over a network path.
For example, a Stratum 2 server receives the time over a network link, through NTP, from
a Stratum 1 server.
Information received from SNTP servers is evaluated based on the time level and server
type.
SNTP time definitions are assessed and determined by the following time levels:
•T1. Time that the original request was sent by the client.
•T2. Time that the original request was received by the server.
•T3. Time that the server sent a reply.
•T4. Time that the client received the server's reply.
The device can poll unicast server types for the server time.
Polling for unicast information is used for polling a server for which the IP address is known.
SNTP servers that were configured on the device are the only ones that are polled for
synchronization information. T1 through T4 are used to determine server time. This is the
preferred method for synchronizing device time because it is the most secure method. If this
method is selected, SNTP information is accepted only from SNTP servers defined on the
device using the SNTP Server Configuration page.
The device retrieves synchronization information, either by actively requesting information or
at every poll interval.
You can view and modify information for adding and modifying Simple Network T ime Protocol
SNTP servers.
Add an SNTP Server
To add an SNTP server:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Configure System Information
49
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > SNTP Server Configuration.
The SNTP Server Configuration page displays.
6. From the Server Type menu, select the type of SNTP address to enter in the address field.
The address can be either an IP address (IPv4, IPv6) or a host name (DNS). The default
value is IPv4.
7. In the Address field, specify the IP address or the host name of the SNTP server.
This is a text string of up to 64 characters, containing the encoded unicast IP address or
host name of an SNTP server. Unicast SNTP requests are sent to this address. If this
address is a DNS host name, then that host name is resolved into an IP address each
time an SNTP request is sent to it.
8. If the UDP port on the SNTP server to which SNTP requests are sent is not the standard
port (123), specify the port number in the Port field.
The valid range is 1 to 65535. The default value is 123.
9. In Priority field, specify the priority order which to query the servers.
The SNTP client on the device continues sending SNTP requests to different servers until
a successful response is received, or all servers are exhausted. The priority indicates the
order in which to query the servers. The request is sent to an SNTP server with a priority
value of 1 first, then to a server with a priority value of 2, and so on. If any servers are
assigned the same priority, the SNTP client contacts the servers in the order that they
appear in the table. The valid range is 1 to 3. The default value is 1.
10. In the Version field, specify the NTP version running on the server.
The range is 1 to 4. The default value is 4.
11. Click the Add button.
The SNTP server entry is added.
12. Repeat the previous steps to add additional SNTP servers.
You can configure up to three SNTP servers.
The SNTP Server Status table displays status information about the SNTP servers
configured on your switch. The following table describes the SNTP Server Global Status
information.
Configure System Information
50
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Change the Settings for an Existing SNTP Server
To change the settings for an existing SNTP server:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
Table 11. SNTP Server Status information
Field Description
Address All the existing server addresses. If no server configuration exists, a message stating
that no SNTP server exists displays on the page.
Last Update Time The local date and time (UTC) that the response from the server was used to update the
system clock.
Last Attempt Time The local date and time (UTC) that the SNTP server was last queried.
Last Attempt Status The status of the last SNTP request or unsolicited message for both unicast and
broadcast modes. If no message was received from a server, a status of Other is
displayed. These values are appropriate for all operational modes:
• Other. The status of the last request is unknown, or no SNTP responses were
received.
• Success. The SNTP operation was successful and the system time was updated.
• Request Timed Out. After an SNTP request was sent to an SNTP server, the
response timer expired before a response from the server was received.
• Bad Date Encoded. The time provided by the SNTP server is not valid.
• Version Not Supported. The SNTP version supported by the server is not
compatible with the version supported by the client.
• Server Unsynchronized. The SNTP server is not synchronized with its peers. This
is indicated by the leap indicator field on the SNTP message.
• Server Kiss Of Death. The SNTP server indicated that no further queries were to
be sent to this server. This is indicated by a stratum field equal to 0 in a message
received from a server.
Requests The number of SNTP requests made to the server since the last reboot.
Failed Requests The number of failed SNTP requests made to the server since the last reboot.

Configure System Information
51
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > SNTP Server Configuration.
The SNTP Server Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the configured server.
7. Specify new values in the available fields.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Remove an SNTP Server
To remove an SNTP server:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > SNTP Server Configuration.
The SNTP Server Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the configured server to remove.
7. Click the Delete button.
The entry is removed, and the device is updated.
Configure Daylight Saving Time Settings
You can configure settings for summer time, which is also known as daylight saving time.
Used in some countries around the world, summer time is the practice of temporarily
advancing clocks during the summer months. Typically clocks are adjusted forward one or
more hours near the start of spring and are adjusted backward in autumn.
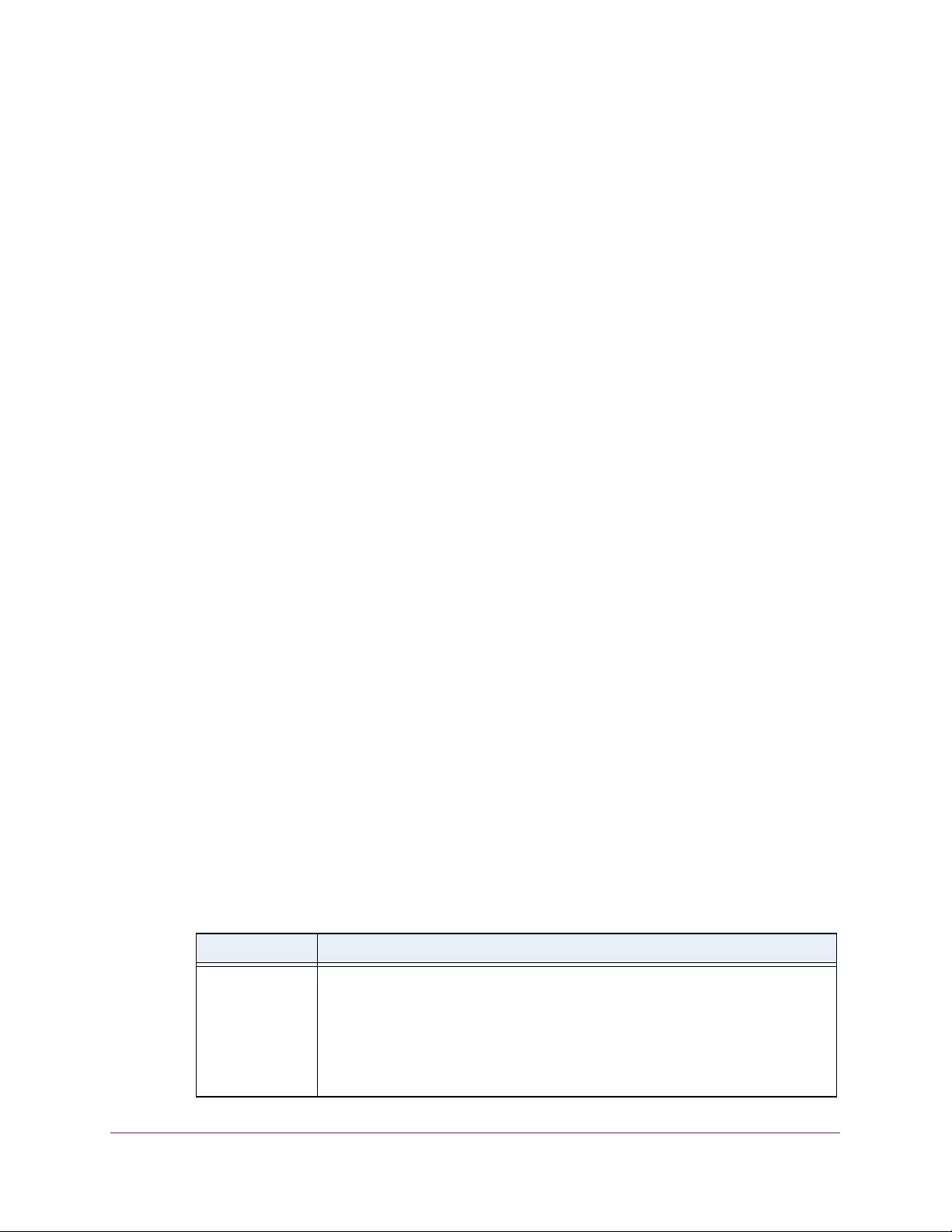
Configure System Information
52
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To configure the daylight saving time settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > DayLight Saving Configuration.
The DayLight Saving (DST) Configuration page displays.
6. Select a Daylight Saving (DST) radio button:
•Disable. Disable daylight saving time.
•Recurring. Daylight saving time occurs at the same time every year. The start and
end times and dates for the time shift must be manually configured.
•Recurring EU. The system clock uses the standard recurring summer time settings
used in countries in the European Union. When this option is selected, the rest of the
applicable fields on the page are automatically populated and cannot be edited.
•Recurring USA. The system clock uses the standard recurring daylight saving time
settings used in the United States. When this option is selected, the rest of the
applicable fields on the page are automatically populated and cannot be edited.
•Non Recurring. Daylight saving time settings are in effect only between the start date
and end date of the specified year. When this option is selected, the summer time
settings do not repeat on an annual basis.
7. Configure the settings for the selected daylight saving method by doing the following:
•If you select the DayLight Saving (DST) Recurring, Recurring EU, or Recurring
USA radio button, configure the settings that are shown in the following table.
Field Description
Begins At These fields are used to configure the start values of the date and time.
• Week. Configure the start week.
• Day. Configure the start day.
• Month. Configure the start month.
• Hours. Configure the start hour.
• Minutes. Configure the start minutes.

Configure System Information
53
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•If you select the DayLight Saving (DST) Non Recurring radio button, configure the
settings that are shown in the following table.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
View the DayLight Saving Time Status
The Daylight Saving (DST) Status section shows information about the summer time settings
and whether the time shift for summer time is currently in effect.
To view the daylight saving time status:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
Ends At These fields are used to configure the end values of date and time.
• Week. Configure the end week.
• Day. Configure the end day.
• Month. Configure the end month.
• Hours. Configure the end hour.
• Minutes. Configure the end minutes.
Offset Configure recurring offset in minutes. The valid range is 1–1440 minutes.
Zone Configure the time zone.
Field Description
Begins At These fields are used to configure the start values of the date and time.
• Month. Configure the start month.
• Date. Configure the start date.
• Year. Configure the start year.
• Hours. Configure the start hour.
• Minutes. Configure the start minutes.
Ends At These fields are used to configure the end values of date and time.
• Month. Configure the end month.
• Date. Configure the end date.
• Year. Configure the end year.
• Hours. Configure the end hour.
• Minutes. Configure the end minutes.
Offset Specify the number of minutes to shift the summer time from the standard time. The
valid range is 1–1440 minutes.
Zone Specify the acronym associated with the time zone when summer time is in effect.
This field is not validated against an official list of time zone acronyms.
Field Description
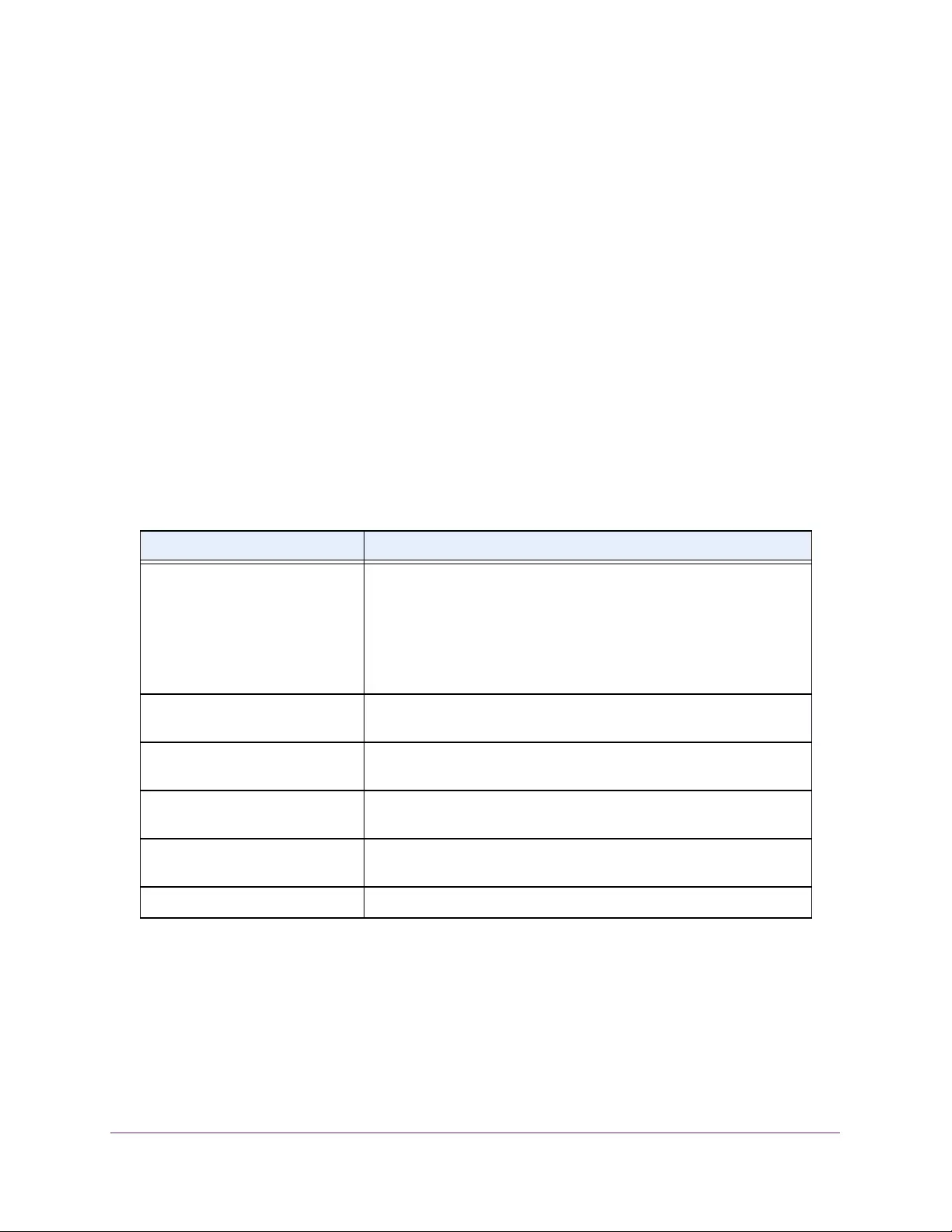
Configure System Information
54
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Time > DayLight Saving Configuration.
The DayLight Saving (DST) Configuration page displays.
6. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
The following table displays the nonconfigurable daylight saving status information.
Table 12. Daylight Saving (DST) Status information
Field Description
Daylight Saving (DST) The Daylight Saving value, which is one of the following:
• Disable
• Recurring
• Recurring EU
• Recurring USA
• Non Recurring
Begins At The start date of daylight saving time. This field is not displayed when
daylight saving time is disabled.
Ends At The end date of daylight saving time. This field is not displayed when
daylight saving time is disabled.
Offset (in Minutes) The offset value in minutes.This field is not displayed when daylight
saving time is disabled.
Zone The zone acronym. This field is not displayed when daylight saving
time is disabled.
Daylight Saving (DST) in Effect Indicates whether daylight saving time is in effect.

Configure System Information
55
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Denial of Service Settings
You can configure the Denial of Service (DoS) settings for the switch. The switch provides
support for classifying and blocking specific types of DoS attacks.
Configure Auto-DoS
You can automatically enable all the DoS features available on the switch, except for the L4
Port attack. For information about the types of DoS attacks the switch can monitor and block,
see Configure Denial of Service on page 56.
To enable the Auto-DoS feature:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Denial of Service > Auto-DoS Configuration.
The Auto-DoS Configuration page displays.
6. Select the Auto-DoS Mode Enable radio button.
When an attack is detected, a warning message is logged to the buffered log and is sent
to the syslog server. At the same time, the port is shut down and can be enabled only
manually by the admin user.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure System Information
56
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Denial of Service
The Denial of Service Configuration page allows you to select which types of DoS attacks the
switch monitors and blocks.
To configure individual DoS settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Denial of Service > Denial of Service Configuration.
The Denial of Service Configuration page displays.
6. Select the types of DoS attacks for the switch to monitor and block and configure any
associated values:
•Denial of Service Min TCP Header Size. Specify the minimum TCP header size
allowed. If DoS TCP Fragment is enabled, the switch drops packets with a TCP
header smaller than the configured value.
•Denial of Service ICMPv4. Enabling ICMPv4 DoS prevention causes the switch to
drop ICMPv4 packets with a type set to ECHO_REQ (ping) and a size greater than
the configured ICMPv4 packet size.
•Denial of Service Max ICMPv4 Packet Size. Specify the maximum ICMPv4 packet
size allowed. If ICMPv4 DoS prevention is enabled, the switch drops IPv4 ICMP ping
packets with a size greater than the configured value.
•Denial of Service ICMPv6. Enabling ICMPv6 DoS prevention causes the switch to
drop ICMPv6 packets with a type set to ECHO_REQ (ping) and a size greater than
the configured ICMPv6 packet size.
•Denial of Service Max ICMPv6 Packet Size. Specify the maximum IPv6 ICMP
packet size allowed. If ICMPv6 DoS prevention is enabled, the switch drops IPv6
ICMP ping packets with a size greater than the configured maximum ICMPv6 packet
size.
•Denial of Service First Fragment. Enabling First Fragment DoS prevention causes
the switch to check DoS options on first fragment IP packets when the switch receives
fragmented IP packets. Otherwise, the switch ignores the first fragment IP packages.

Configure System Information
57
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Denial of Service ICMP Fragment. Enabling ICMP Fragment DoS prevention
causes the switch to drop ICMP fragmented packets.
•Denial of Service SIP=DIP. Enabling SIP=DIP DoS prevention causes the switch to
drop packets with a source IP address equal to the destination IP address.
•Denial of Service SMAC=DMAC. Enabling SMAC=DMAC DoS prevention causes
the switch to drop packets with a source MAC address equal to the destination MAC
address.
•Denial of Service TCP FIN&URG&PSH. Enabling TCP FIN & URG & PSH DoS
prevention causes the switch to drop packets with TCP Flags FIN, URG, and PSH set
and TCP sequence number equal to 0.
•Denial of Service TCP Flag&Sequence. Enabling TCP Flag DoS prevention causes
the switch to drop packets with TCP control flags set to 0 and TCP sequence number
set to 0.
•Denial of Service TCP Fragment. Enabling TCP Fragment DoS prevention causes
the switch to drop packets with a TCP payload for which the IP payload length minus
the IP header size is less than the minimum allowed TCP header size.
•Denial of Service TCP Offset. Enabling TCP Offset DoS prevention causes the
switch to drop packets with a TCP header offset set to 1.
•Denial of Service TCP Port. Enabling TCP Port DoS prevention causes the switch to
drop packets for which the TCP source port is equal to the TCP destination port.
•Denial of Service TCP SYN. Enabling TCP SYN DoS prevention causes the switch
to drop packets with TCP flags SYN set.
•Denial of Service TCP SYN&FIN. Enabling TCP SYN & FIN DoS prevention causes
the switch to drop packets with TCP flags SYN and FIN set.
•Denial of Service UDP Port. Enabling UDP Port DoS prevention causes the switch
to drop packets for which the UDP source port is equal to the UDP destination port.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure DNS Settings
You can configure information about DNS servers that the network uses and how the switch
operates as a DNS client.
Configure Global DNS Settings
You can configure global DNS settings and DNS server information.
To configure the global DNS settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.

Configure System Information
58
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > DNS > DNS Configuration.
The DNS Configuration page displays.
6. Select the Disable or Enable radio button to specify whether to disable or enable the
administrative status of the DNS client.
•Enable. Allow the switch to send DNS queries to a DNS server to resolve a DNS
domain name. The DNS is enabled by default.
•Disable. Prevent the switch from sending DNS queries.
7. In the DNS Default Name field, enter the default DNS domain name to include in DNS
queries.
When the system is performing a lookup on an unqualified host name, this field is
provides the domain name (for example, if default domain name is netgear.com and the
user enters test, then test is changed to test.netgear .com to resolve the name). The name
must not be longer than 255 characters.
8. In the DNS Server field, specify the IPv4 address to which the switch sends DNS queries.
9. Click the Add button.
The server is added to the list. You can specify up to eight DNS servers. The Preference
field displays the server preference order. The preference is set in the order in which
preferences were entered.
10. To remove a DNS server from the list, select its check box and click the Delete button.
If you click the Delete button without selecting a DNS server, all the DNS servers are
deleted.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure System Information
59
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table displays DNS Server Configuration information.
Configure and View Host Name-to-IP Address Information
You can manually map host names to IP addresses or view dynamic host mappings.
Add a Static Entry to the Dynamic Host Mapping Table
To add a static entry to the local dynamic host mapping table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > DNS > Host Configuration.
The Host Configuration page displays.
6. In the Host Name (1 to 255 characters) field, specify the static host name to add.
Its length cannot exceed 255 characters and it is a required field.
7. In the IPv4/IPv6 Address field, enter the IP address to associate with the host name.
8. Click the Add button.
The entry displays in the list on the page.
Table 13. DNS Server Configuration information
Field Description
ID The identification of the DNS Server.
Preference Shows the preference of the DNS server. The preferences are
determined by the order in which they were entered.

Configure System Information
60
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Remove an Entry From the Dynamic Host Mapping Table
To remove an entry from the dynamic host mapping table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > DNS > Host Configuration.
The DNS Host Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the entry to remove.
7. Click the Delete button.
Change the Host Name or IP Address in an Entry of the Dynamic Host Mapping Table and
View All Entries
To change the host name or IP address in an entry of the dynamic host mapping table
and view all entries:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
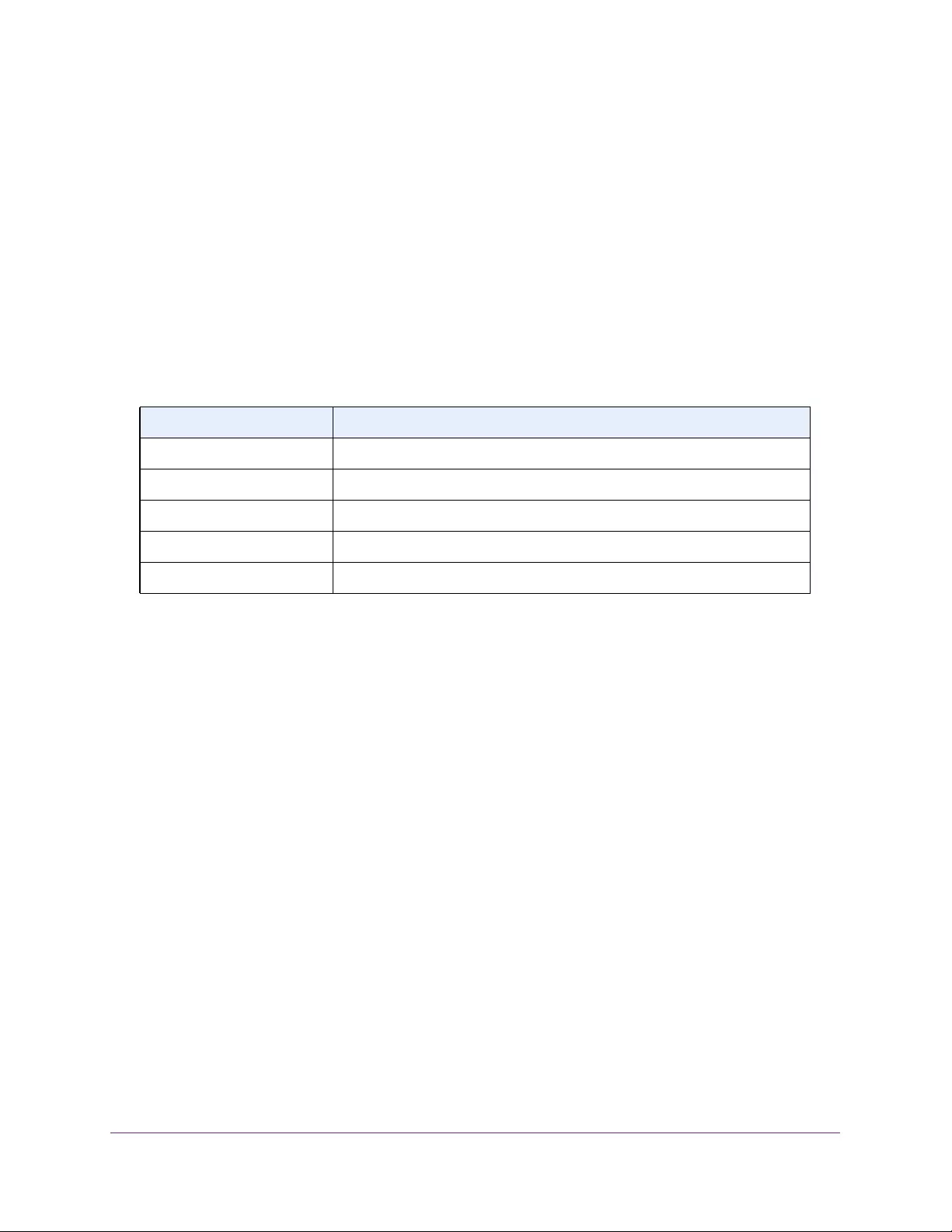
Configure System Information
61
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select System > Management > DNS > Host Configuration.
The DNS Host Configuration page display.
6. Select the check box next to the entry to update.
7. Enter the new information in the appropriate field.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
9. To clear all the dynamic host name entries from the list, click the Clear button.
The Dynamic Host Mapping table shows host name-to-IP address entries that the switch
learned. The following table describes the dynamic host fields.
Configure Green Ethernet Settings
You can configure the green Ethernet features to reduce power consumption.
To configure the Green Ethernet settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Green Ethernet > Green Ethernet Configuration.
Table 14. Dynamic Host Mapping information
Field Description
Host Lists the host name that you assign to the specified IP address.
Total Time since the dynamic entry was first added to the table.
Elapsed Time since the dynamic entry was last updated.
Type The type of the dynamic entry.
IPv4/IPv6 Address Lists the IP address that is associated with the host name.

Configure System Information
62
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The Green Ethernet Configuration page displays.
6. Select the Auto Power Down Mode Disable or Enable radio button.
By default, this mode is disabled. When a port link is down, the underlying physical layer
goes down for a short period and then checks for port link pulses again so that
autonegotiation remains possible. In this way, the switch saves power when no link
partner is present for the port.
7. Select the EEE Mode Disable or Enable radio button.
By default, this mode is disabled. Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) combines the MAC with
a family of physical layers that support operation in a low power mode. It is defined by the
IEEE 802.3az standard. Lower power mode enables both the send and receive sides of
the link to disable some functionality for power savings when lightly loaded. Transition to
low power mode does not change the link status. Frames in transit are not dropped or
corrupted in transition to and from low power mode. Transition time is transparent to
upper layer protocols and applications.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Green Ethernet Interface Settings
You can configure per-port Green Ethernet settings.
To configure the Green Ethernet interface settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Green Ethernet > Green Ethernet Interface
Configuration.
The Green Ethernet Interface Configuration page displays.

Configure System Information
63
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Do one of the following:
•In the Go To Interface field, enter the port using the respective naming convention
(for example, g1 or l1), and click the Go button.
The entry corresponding to the specified interface is selected.
For more information about naming conventions, see Interface Naming Conventions
on page 12.
•Select the port.
7. Select the Auto Power Down Mode Disable or Enable radio button.
By default, this mode is disabled. When a port link is down, the underlying physical layer
goes down for a short period and then checks for port link pulses again so that
autonegotiation remains possible. In this way, the switch saves power when no link
partner is present for the port.
8. Select the EEE Mode Disable or Enable radio button.
By default, this mode is disabled. Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) combines the MAC
with a family of physical layers that support operation in a low power mode. It is defined
by the IEEE 802.3az standard. Lower power mode enables both the send and receive
sides of the link to disable some functionality for power savings when lightly loaded.
Transition to low power mode does not change the link status. Frames in transit are not
dropped or corrupted in transition to and from low power mode. Transition time is
transparent to upper layer protocols and applications.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Green Ethernet Local and Remote Devices
You can view detailed per-port green Ethernet information and enable or disable green
Ethernet settings on a single port. Using the green Ethernet features allows for power
consumption savings.
To configure green Ethernet local and remote devices:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
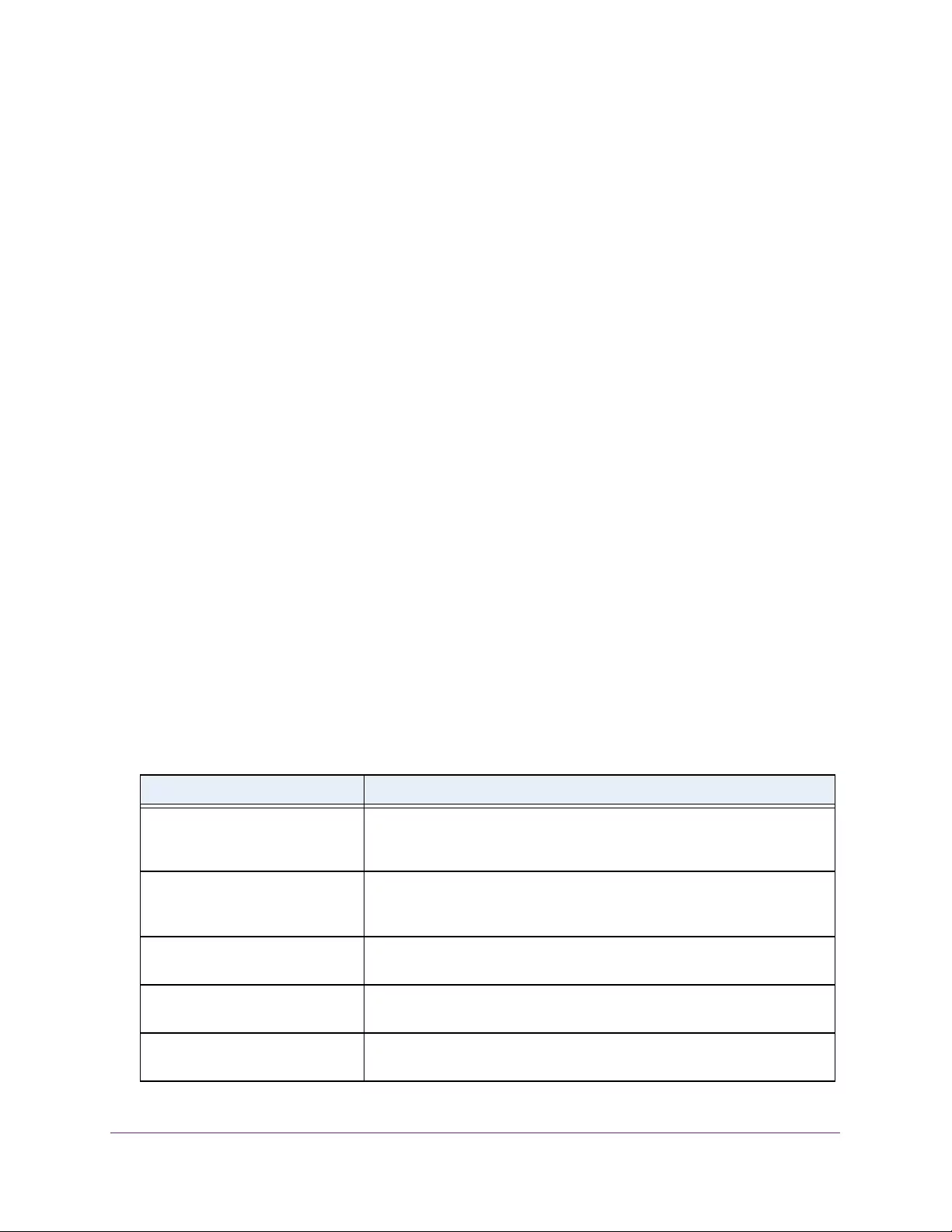
Configure System Information
64
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Green Ethernet > Green Ethernet Details.
The Green Ethernet Details page displays.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface.
7. From the EEE Admin mode menu, select Enable or Disable.
With the EEE mode enabled, the port transitions to low power mode during a link idle
condition. The default value is Disabled. If the EEE Admin Mode is not supported, N/A is
displayed.
8. In the EEE Transmit Idle Time field, enter the time after which switch transitions to the LPI
state.
The range is 600 to 4294967295. The default value is 600.
9. In the EEE Transmit Wake Time field, enter the time that the switch must wait before it
transitions to the active state after it receives a packet for transmission.
The range is 8 to 65535. The default value is 17.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
11. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
12. To clear the configuration, resetting all statistics for the selected interface to default values,
click the Clear button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields.
Table 15. Green Ethernet Local Device Information
Field Description
Cumulative Energy Saved on this
port due to Green mode(s) (Watts
* Hours)
Cumulative energy saved due to all green modes enabled on this port in
watts * hours.
Rx Low Power Idle Event Count This field is incremented each time MAC RX enters low-power idle (LPI)
state. Shows the total number of Rx LPI events since EEE counters were
last cleared.
Rx Low Power Idle Duration
(uSec) This field indicates duration of Rx LPI state in 10 us increments. Shows the
total duration of Rx LPI since the EEE counters were last cleared.
Tx Low Power Idle Event Count This field is incremented each time MAC TX enters LPI state. Shows the
total number of Tx LPI events since EEE counters were last cleared.
Tx Low Power Idle Duration
(uSec) This field indicates duration of Tx LPI state in 10 us increments. Shows the
total duration of Tx LPI since the EEE counters were last cleared.
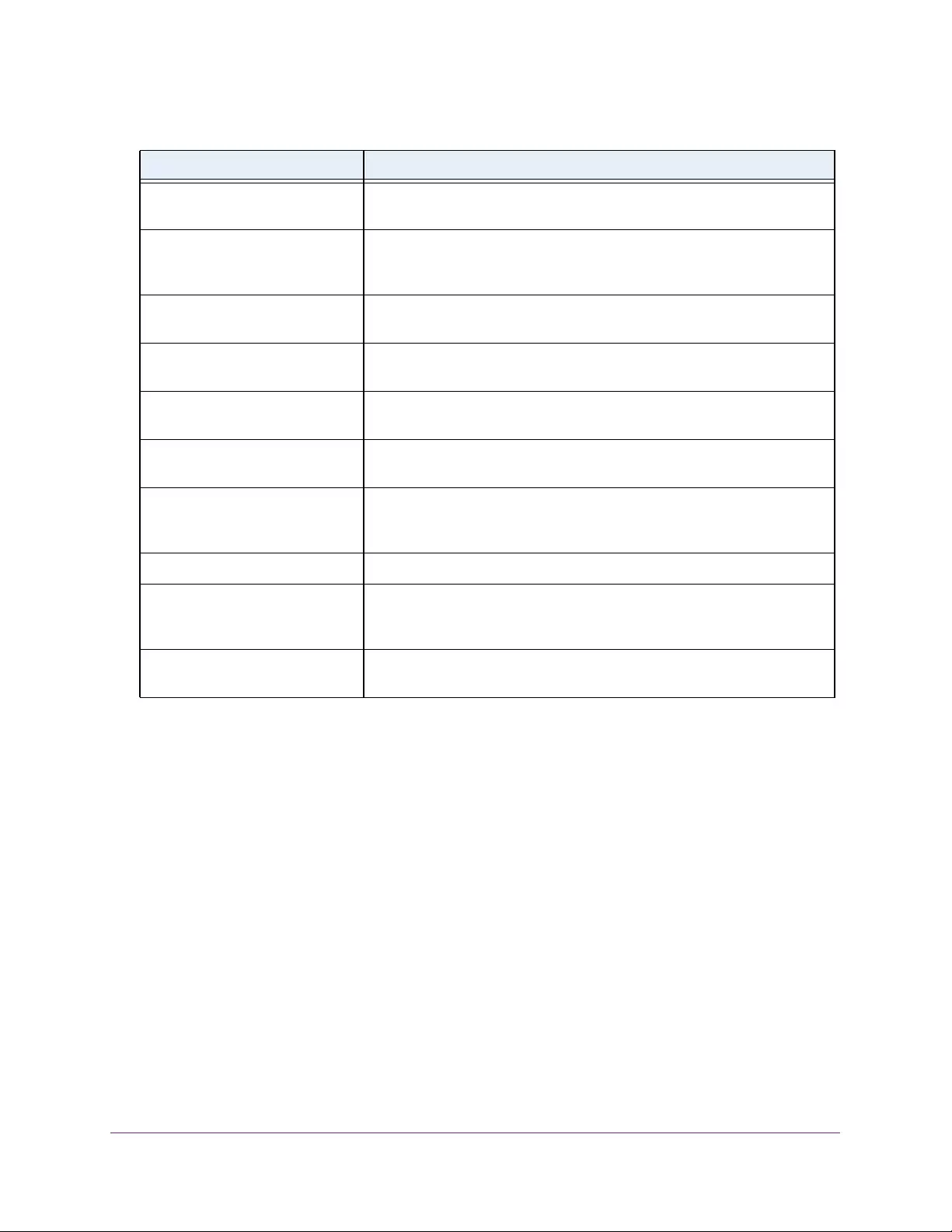
Configure System Information
65
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View Green Ethernet Remote Device Details
To view green Ethernet remote device information:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
Tw_sys_tx (uSec) Integer that indicates the value of Tw_sys that the local system can
support.
Tw_sys_tx Echo (uSec) Integer that indicates the remote system’s Transmit Tw_sys that was used
by the local system to compute the Tw_sys that it wants to request from the
remote system.
Tw_sys_rx (uSec) Integer that indicates the value of Tw_sys that the local system requests
from the remote system.
Tw_sys_rx Echo (uSec) Integer that indicates the remote system’s Receive Tw_sys that was used
by the local system to compute the Tw_sys that it can support.
Fallback Tw_sys (uSec) Integer that indicates the value of fallback Tw_sys that the local system
requests from the remote system.
Tx_dll_enabled Data Link Layer Enabled: Initialization status of the EEE transmit Data Link
Layer management function on the local system.
Tx_dll_ready Data Link Layer ready: This variable indicates that the tx system
initialization is complete and is ready to update/receive LLDPDU containing
EEE TLV.
Rx_dll_enabled Status of the EEE capability negotiation on the local system.
Rx_dll_ready Data Link Layer ready: This variable indicates that the rx system
initialization is complete and is ready to update/receive LLDPDU containing
EEE TLV.
Time Since Counters Last Cleared Time Since Counters Last Cleared (since the time of power-up, or after
EEE counters are cleared).
Table 15. Green Ethernet Local Device Information (continued)
Field Description
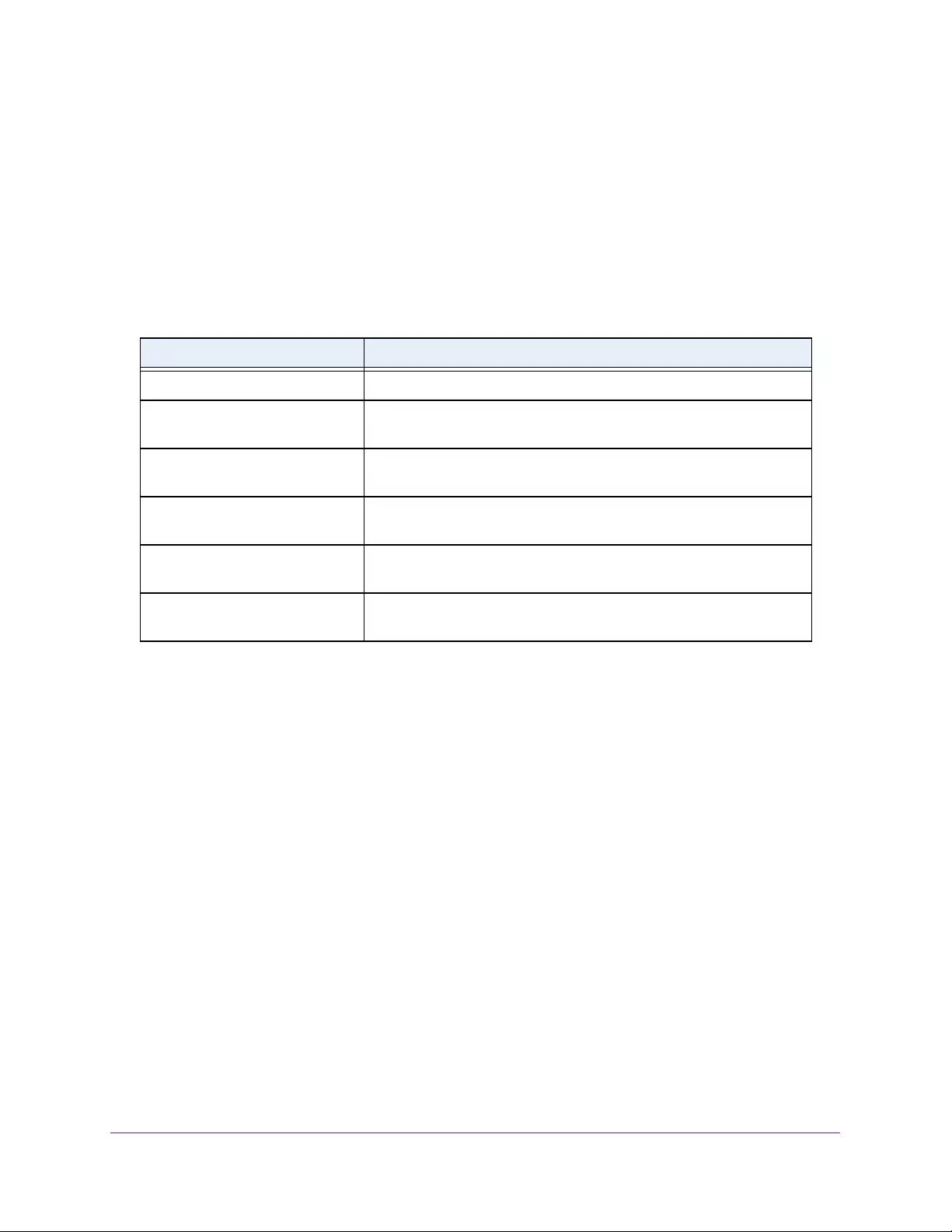
Configure System Information
66
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Green Ethernet >Green Ethernet Details.
The Green Ethernet Details page displays.
6. Scroll down to the Remote Device Information section.
7. Select the interface.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields.
View the Green Ethernet Statistics Summary
This page summarizes the green Ethernet settings currently in use.
To view the green Ethernet statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
Table 16. Green Ethernet Remote Device Information
Field Description
Remote ID The remote client identifier assigned to the remote system.
Remote Tw_sys_tx (uSec) Integer that indicates the value of Tw_sys that the remote system can
support.
Remote Tw_sys_tx Echo (uSec) Integer that indicates the value of Transmit Tw_sys echoed back by the
remote system.
Remote Tw_sys_rx (uSec) Integer that indicates the value of Tw_sys that the remote system
requests from the local system.
Remote Tw_sys_rx Echo (uSec) Integer that indicates the value of Receive Tw_sys echoed back by the
remote system.
Remote Fallback Tw_sys (uSec) Integer that indicates the value of fallback Tw_sys that the remote
system is advertising.
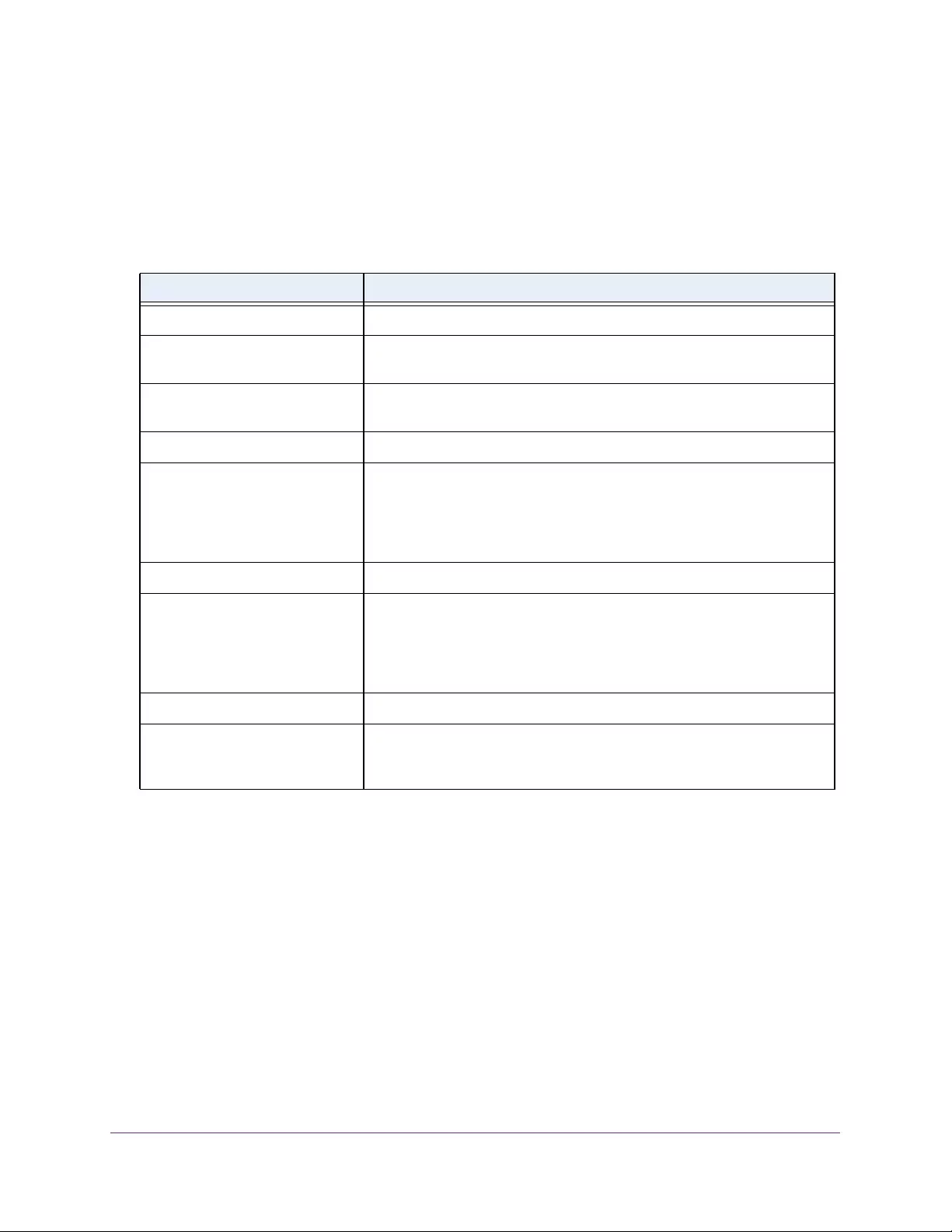
Configure System Information
67
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select System > Management > Green Ethernet > Green Ethernet Summary.
The Green Ethernet Statistics Summary page displays.
6. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields.
Configure the Green Ethernet EEE LPI History
You can configure and view the Green Ethernet low power idle (LPI) history.
To configure the port Green Ethernet EEE LPI history:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
Table 17. Green Ethernet Statistics Summary information
Field Description
Current Power Consumption (mW) Estimated power consumption by all ports of the switch in mWatts.
Percentage Power Saving (%) Estimated percentage of power saved on all ports of the switch if the green
modes are enabled.
Cumulative Energy Saving (W * H) Estimated cumulative energy saved on the switch in watts multiplied by
hours if all green modes are enabled.
Unit The unit ID.
Green Features supported on this
unit List of green features supported on the given unit, which could be one or
more of the following: Energy-Detect (Energy Detect), Short-Reach (Short
Reach), EEE (Energy Efficient Ethernet), LPI-History (EEE Low Power Idle
History), LLDP-Cap-Exchg (EEE LLDP Capability Exchange), Pwr-Usg-Est
(Power Usage Estimates).
Interface Interface for which data is displayed or configured.
Energy Detect Admin mode Enable or disable Energy Detect mode on the port. When this mode is
enabled, when the port link is down, the PHY automatically goes down for a
short period of time, then wakes up to check link pulses. This allows the
switch to perform autonegotiation and save power consumption when no
link partner is present.
Energy Detect Operational Status Current operational status of the Energy Detect mode.
EEE Admin mode Enable or disable Energy Efficient Ethernet mode on the port. With EEE
mode enabled, the port transitions to low power mode during link idle
conditions.
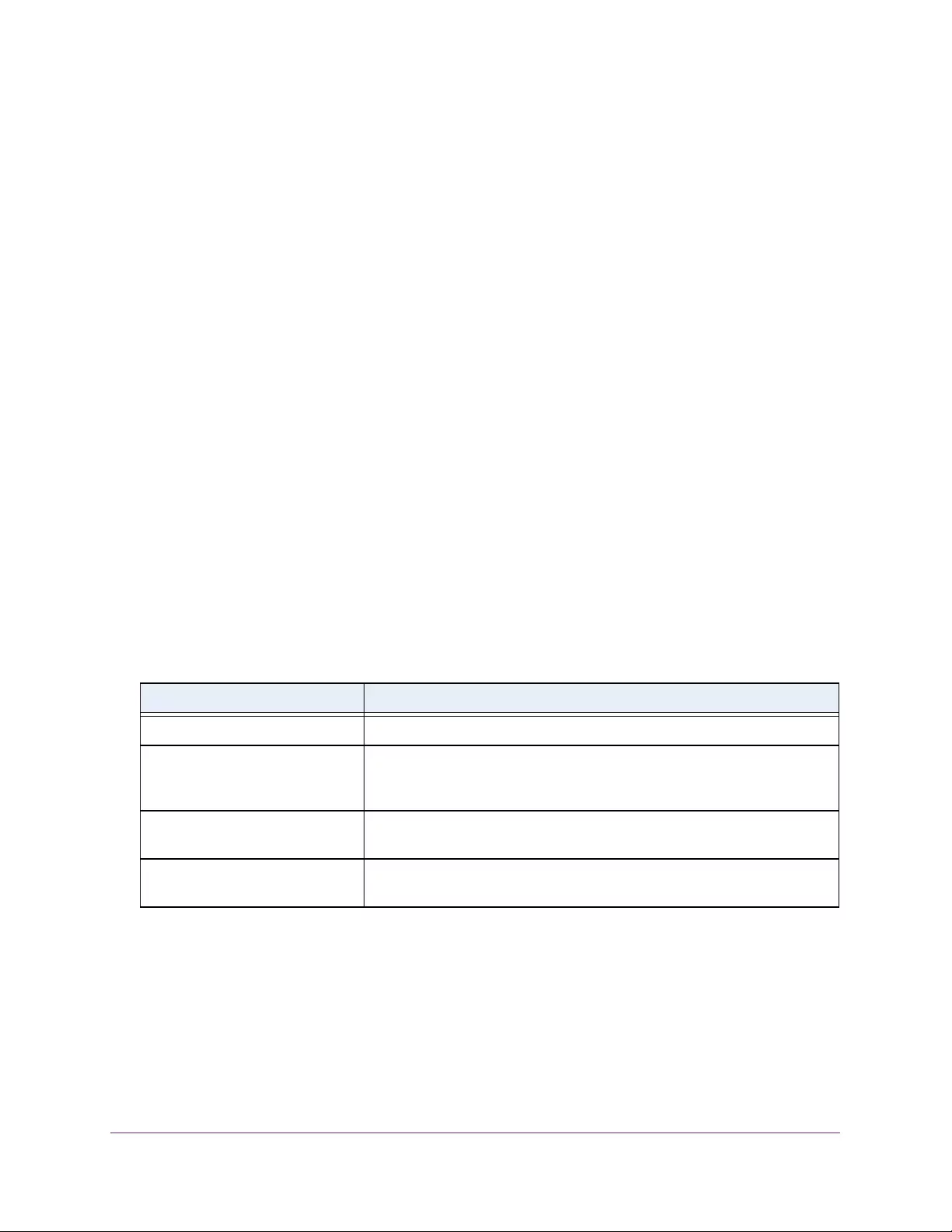
Configure System Information
68
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Green Ethernet > Green Ethernet LPI History.
The Green Ethernet LPI History page displays.
6. Select the interface.
7. In the Sampling Interval field, enter the interval at which EEE LPI data is collected.
This is a global setting and is applied to all interfaces. The range is 30 to 36000.The
default value is 3600.
8. In the Max Samples to keep field, enter the maximum number of samples to keep.
This is a global setting and is applied to all interfaces. The range is 1 to 168.The default
value is 168.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The Percentage LPI time field shows the time spent in LPI mode the since EEE counters
were last cleared.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields.
Manage the Bonjour Settings and View Bonjour
Information
A Mac OS device that supports Bonjour can discover the switch in the network so that you
can find the switch IP address and log in to the local browser interface of the switch. Bonjour
is enabled by default on the switch. You can disable Bonjour for security reasons.
Table 18. Interface Green Mode EEE LPI History information
Field Description
Sample No. Sample index.
Time Since The Sample Was
Recorded Each time the page is refreshed, it shows a different time as it reflects the
difference between current time and time at which the sample was
recorded.
Percentage Time spent in LPI
mode since last sample Percentage of time spent in LPI mode during the current measurement
interval.
Percentage Time spent in LPI
mode since last reset Percentage of time spent in LPI mode since EEE LPI statistics were reset.

Configure System Information
69
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Manage the Bonjour Settings
To manage the Bonjour settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Bonjour > Bonjour Configuration.
The Bonjour Global Configuration page displays.
6. Select one of the following radio buttons:
•Disable. Bonjour is disabled.
•Enable. Bonjour is enabled. This is the default setting.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
View Bonjour Information
To view Bonjour information:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Configure System Information
70
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > Bonjour > Bonjour Details.
The Bonjour Information page displays. The page also shows the Published Services
section.
The Bonjour Information section shows whether Bonjour is enabled on the switch.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields.
Control the LEDs
You can turn the system LEDs and port LEDs on the switch on and off. By default, a port LED
lights when you connect a powered-on device to the port. When the switch functions with its
LEDs off, we refer to it as Quiet mode.
To control the LEDs:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
Table 19. Published Services information
Field Description
Service Name The Bonjour service names in the switch.
Type The Bonjour service type names in the switch.
Domain The Bonjour service domain in the switch.
Port The Bonjour service port number.
TXT data The Bonjour service text.

Configure System Information
71
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Management > LED Control.
6. Select the System LEDs On or Off radio button.
By default, the On radio button is selected and the system LEDs are enabled. When you
select the Off radio button, the Cloud LED is disabled, and for models GC728XP and
GC752XP, the Max PoE LED is disabled.
7. Select the Port LEDs On or Off radio button.
By default, the On radio button is selected and the port LEDs are enabled. When you
select the Off radio button, the port LEDs are disabled.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Use the Device View
For information about the device view, see Local Browser Interface Device View on page 25.
Configure Power over Ethernet
For information about Power over Ethernet (PoE), see Chapter 8, Manage Power over
Ethernet.
Configure SNMP
You can configure SNMP settings for SNMPv1/v2 and SNMPv3. The switch supports the
configuration of SNMP groups and users that can manage traps that the SNMP agent
generates.
The switch uses both standard public MIBs for standard functionality and private MIBs that
support additional switch functionality. All private MIBs begin with a hyphen (-) prefix. The
main object for interface configuration is in -SWITCHING-MIB, which is a private MIB. Some
interface configurations also involve objects in the public MIB, IF-MIB.
The following sections describe how you can configure SNMP:
•Configure the SNMPv1/v2 Community on page 72
•Configure SNMPv1/v2 Trap Settings on page 74
•Configure SNMPv1/v2 Trap Flags on page 76
•View the Supported MIBs on page 78
•Configure Authentication and Encryption for the SNMPv3 Admin Profile on page 78

Configure System Information
72
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure the SNMPv1/v2 Community
Only the communities that you define can access to the switch using the SNMP V1 and
SNMP V2 protocols. Only those communities with read/write level access can be used to
change the configuration using SNMP.
Add an SNMP Community:
To add an SNMP community:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Community Configuration.
The Community Configuration page displays.
6. In the Management Station IP field, specify the IP address of the management station.
7. In the Management Station IP Mask field, specify the subnet mask to associate with the
management station IP address.
Together, the management station IP address and the management station IP mask
denote a range of IP addresses from which SNMP clients can use the community to
access this device. If either the management station IP address or management station
IP mask value is 0.0.0.0, access is allowed from any IP address. Otherwise, each client’s
address is ANDed with the mask, as is the management station IP address. If the values
are equal, access is allowed. For example, if the management station IP address is
192.168.1.0 and the management station IP mask is 255.255.255.0, any client whose
address is in the 192.168.1.0–192.168.1.255 range is allowed access.
To allow access from only one station, use that station’s IP address as the management
station IP address and use a management station IP mask value of 255.255.255.255.
8. In the Community String field, specify a community name.
9. From the Access Mode menu, select the access level for this community, which is either
Read/Write or Read Only.
10. From the Status menu, select to enable or disable the community.

Configure System Information
73
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
If you select Enable, the community name must be unique among all valid community
names or the set requests are rejected. If you select Disable, the community name
becomes invalid.
11. Click the Add button.
The selected community is added.
Modify an Existing SNMP Community
To modify an existing SNMP community:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Community Configuration.
The Community Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box for the community.
7. Update the desired fields.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete an SNMP Community
To delete an SNMP community:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.

Configure System Information
74
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Community Configuration.
The Community Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box for the community to remove.
7. Click the Delete button.
The community is removed.
Configure SNMPv1/v2 Trap Settings
You can configure settings for each SNMPv1 or SNMPv2 management host that must
receive notifications about traps generated by the device. The SNMP management host is
also known as the SNMP trap receiver.
Add an SNMP Trap Receiver
To add an SNMP trap receiver:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Trap Configuration .
The Trap Configuration page displays.
6. In the Recipients IP field, enter the IPv4 address in the x.x.x.x format to receive SNMP traps
from this device.

Configure System Information
75
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
7. From the Version menu, select the trap version to be used by the SNMP trap receiver:
•SNMPv1. The switch uses SNMPv1 to send traps to the receiver.
•SNMPv2. The switch uses SNMPv2 to send traps to the receiver.
8. In the Community String field, specify the name of the SNMP community that includes
the SNMP management host and the SNMP agent on the device.
This name can be up to 16 characters and is case-sensitive. The community name must
be unique.
9. From the Status menu, select Enable to enable the switch to send traps to the receiver or
Disable to prevent the switch from sending traps to the receiver.
10. Click the Add button.
The receiver configuration is added.
Modify Information for an Existing Trap SNMP Recipient
To modify information for an existing trap SNMP recipient:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Trap Configuration .
The Trap Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box for the recipient.
7. Update the fields as needed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure System Information
76
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Delete an SNMP Trap Recipient
To delete an SNMP trap recipient:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Trap Configuration .
The Trap Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box for the recipient.
7. Click the Delete button.
The trap recipient is removed.
Configure SNMPv1/v2 Trap Flags
You can enable or disable traps the switch can send to an SNMP manager. When the
condition identified by an active trap is encountered by the switch, a trap message is sent to
any enabled SNMP trap receivers, and a message is written to the trap log.
To configure the trap flags:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Configure System Information
77
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Trap Flags.
The Trap Flags page displays.
6. Configure the following options:
•Authentication. If this option is enabled, SNMP traps are sent when events involving
authentication occur. For example, when a user attempts to access the local browser
interface but fails to provide a valid user name and password, a trap is sent.
•Link Up/Down. If this option is enabled, SNMP traps are sent when the
administrative or operational state of a physical or logical link changes.
•Spanning T ree. If this option is enabled, SNMP traps are sent when various spanning
tree events occur.
•ACL. If this option is enabled, SNMP traps are sent when a packet matches a
configured ACL rule that includes ACL logging.
•PoE. (Models GC728XP and GC752XP only.) If this option is enabled, SNMP traps
are sent when the PoE status changes.
For all options, by default, the Enable radio is selected.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure System Information
78
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View the Supported MIBs
This page displays a list of all MIBs supported by the switch.
To view the supported MIBs:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Supported MIBs.
The Status page displays.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields.
Configure Authentication and Encryption for the SNMPv3
Admin Profile
Any user can connect to the switch using the SNMPv3 protocol, but for authentication and
encryption, the switch supports only one user (admin). Therefore, you can create or modify
only one profile.
To configure authentication and encryption settings for the SNMPv3 admin profile:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
Table 20. SNMP supported MIBs
Field Description
Name The RFC number, if applicable, and the name of the MIB.
Description The RFC title or MIB description.

Configure System Information
79
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > User Configuration.
The User Configuration page displays.
The SNMPv3 Access Mode field is a read-only field that shows the access privileges for
the user account. Access for the admin account is always Read/Write. Access for all
other accounts is Read Only.
6. To enable authentication, select an Authentication Protocol radio button.
You can select the MD5 radio button or the SHA radio button. With either of these
options, the user login password is used as SNMPv3 authentication password. For
information about how to configure the login password, see Change the Password on
page 250.
7. To enable encryption, do the following:
a. Select the Encryption Protocol DES radio button to encrypt SNMPv3 packets using
the DES encryption protocol.
b. In the Encryption key field, enter an encryption code of eight or more alphanumeric
characters.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Link Layer Discovery Protocol
The IEEE 802.1AB-defined standard, Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), allows stations
on an 802 LAN to advertise major capabilities and physical descriptions. This information is
viewed by a network manager to identify system topology and detect bad configurations on
the LAN.
The following sections describe how you can configure LLDP:
•Configure LLDP Global Settings on page 80
•Configure LLDP Port Settings on page 81
•View the LLDP-MED Network Policy on page 82
•Configure the LLDP-MED Port Settings on page 84
•LLDP-MED Neighbors Information on page 85

Configure System Information
80
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•View Local LLDP Information on page 87
•View LLDP Neighbors Information on page 89
LLDP is a one-way protocol without any request/response sequences. Information is
advertised by stations implementing the transmit function, and is received and processed by
stations implementing the receive function. The transmit and receive functions can be
enabled or disabled separately per port. By default, both transmit and receive are disabled on
all ports. The application is responsible for starting each transmit and receive state machine
appropriately, based on the configured status and operational state of the port.
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol-Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) is an
enhancement to LLDP with the following features:
•Autodiscovery of LAN policies (such as VLAN, Layer 2 priority, and DiffServ settings),
enabling plug and play networking.
•Device location discovery for creation of location databases.
•Extended and automated power management of Power over Ethernet endpoints.
•Inventory management, enabling network administrators to track their network devices
and determine their characteristics (manufacturer, software and hardware versions,
serial/asset number).
Configure LLDP Global Settings
You can specify the global LLDP and LLDP-MED parameters that are applied to the switch.
To configure global LLDP settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > LLDP > Basic > LLDP Configuration.
The LLDP Properties pager displays.

Configure System Information
81
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. To configure nondefault values for the following LLDP properties, specify the following
options:
•TLV Advertised Interval. The number of seconds between transmissions of LLDP
advertisements.
•Hold Multiplier. The transmit interval multiplier value, in which the transmit hold
multiplier multiplied by the transmit interval is the time to live (TTL) value that the
switch advertises to its neighbors.
•Reinitializing Delay. The number of seconds that the switch waits before attempting
to reinitialize LLDP on a port after the LLDP operating mode on the port changes.
•T ransmit Delay. The number of seconds that the switch waits between transmissions
of remote data change notifications to one or more SNMP trap receivers configured
on the switch.
7. To configure a nondefault value for LLDP-MED, enter a value in the Fast Start Duration
field.
This value sets the number of LLDP packets sent when the LLDP-MED fast start
mechanism is initialized, which occurs when a new endpoint device links with the
LLDP-MED network connectivity device.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure LLDP Port Settings
You can specify per-interface LLDP settings.
To configure the LLDP interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP Port Settings.
The LLDP Port Settings page displays.

Configure System Information
82
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
7. Use the following menus to configure the LLDP settings for the selected ports:
•Admin Status. Select the status for transmitting and receiving LLDP packets:
-Tx Only. Enable only transmitting LLDP PDUs on the selected ports.
-Rx Only. Enable only receiving LLDP PDUs on the selected ports.
-Tx and Rx. Enable both transmitting and receiving LLDP PDUs on the selected
ports.
-Disabled. Do not transmit or receive LLDP PDUs on the selected ports.
The default is Tx and Rx.
•Management IP Address. Choose whether to advertise the management IP address
from the interface. The possible field values are as follows:
-Stop Advertise. Do not advertise the management IP address from the interface.
-Auto Advertise. Advertise the current IP address of the device as the
management IP address.
The default is Auto Advertise.
•Notification. When notifications are enabled, LLDP interacts with the trap manager to
notify subscribers of remote data change statistics. The default is Disable.
•Optional TLV(s). Enable or disable the transmission of optional type-length value
(TLV) information from the interface. The default is Enable. The TLV information
includes the system name, system description, system capabilities, and port
description.
For information about how to configure the system name, see View and Configure the
Switch Management Settings on page 29. For information about how to configure the
port description, see Configure Port Settings on page 105.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
View the LLDP-MED Network Policy
This page displays information about the LLPD-MED network policy TLV transmitted in the
LLDP frames on the selected local interface.
Configure System Information
83
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To view LLDP-MED network policy information for an interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP-MED Network Policy.
The LLDP-MED Network Policy page displays.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface for which you want to view the information.
Note: The menu includes only the interfaces on which LLDP is enabled. If no
interfaces are enabled for LLDP, the Interface menu does not display.
The page refreshes and displays the data transmitted in the network policy TLVs for the
interface.
The following table describes the LLDP-MED network policy information that displays on the
page.
Table 21. LLDP-MED network policy information
Field Description
Network Policy Number The policy number.
Application The media application type associated with the policy, which can be one of the
following:
• Unknown
• Voice
• Guest Voice
• Guest Voice Signaling
• Softphone Voice
• Video Conferencing
• Streaming Video
• Video Signaling
A port can receive multiple application types. The application information is
displayed only if a network policy TLV was transmitted from the port.
Configure System Information
84
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure the LLDP-MED Port Settings
You can enable LLDP-MED mode on an interface and configure its properties.
To configure LLDP-MED settings for a port:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP-MED Port Settings.
The LLDP-MED Port Settings page displays.
6. From the Port menu, select the port to configure.
7. Use the following menus to enable or disable the following LLDP-MED settings for the
selected port:
•LLDP-MED Status. The administrative status of LLDP-MED on the interface. When
LLDP-MED is enabled, the transmit and receive function of LLDP is effectively
enabled on the interface.
•Notification. When notifications are enabled, the port sends a topology change
notification if a device is connected or removed.
•MED Capabilities. When MED capabilities are enabled, the port transmits the
capabilities type length values (TLVs) in the LLDP PDU frames.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID associated with the policy.
VLAN Type Indicates whether the VLAN associated with the policy is tagged or untagged.
User Priority The priority associated with the policy.
DSCP The DSCP associated with a particular policy type.
Table 21. LLDP-MED network policy information (continued)
Field Description

Configure System Information
85
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Network Policy. When the network policy is enabled, the port transmits the network
policy TLV in LLDP frames.
•Extended MDI-PSE. When the extended MDI-PSE is enabled, the port transmits the
extended PSE TLV in LLDP frames.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
LLDP-MED Neighbors Information
You can display the LLDP-MED neighbor or remote device information for an interface.
To view LLDP-MED Neighbor Information:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP-MED Neighbors Information.
The page that displays shows multiple sections with information about LLDP-MED
neighbors.
6. From the Interface menu, select an interface.
The menu includes only the interfaces for which LLDP is enabled.
7. To refresh the page, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the non-configurable LLDP-MED Neighbors Information that
displays for the selected interface.
Field Description
LLDP-MED Interface Selection
Remote ID Specifies the remote client identifier assigned to the remote system.
Capability Information
Configure System Information
86
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
This section of the page specifies the supported and enabled capabilities that are received in MED TLV on
this port.
Supported Capabilities Specifies supported capabilities that are received in MED TLV on this port.
Enabled Capabilities Specifies enabled capabilities that are received in MED TLV on this port.
Device Class Specifies device class as advertised by the device remotely connected to the
port.
Network Policies Information
This section of the page specifies if network policy TLV is received in the LLDP frames on this port.
Media Application Type Specifies the application type: unknown, voicesignaling, guestvoice,
guestvoicesignalling, softphonevoice, videoconferencing, streamingvideo, or
videosignaling.
Information for each application type includes the VLAN ID, priority, DSCP,
tagged bit status and unknown bit status. A port can receive information
about one or many of such application types. The application type is
displayed only if a network policy TLV is received on a port.
VLAN ID Specifies the VLAN ID associated with a particular policy type.
Priority Specifies the priority associated with a particular policy type.
DSCP Specifies the DSCP associated with a particular policy type.
Unknown Bit Status Specifies the unknown bit associated with a particular policy type.
Tagged Bit Status Specifies the tagged bit associated with a particular policy type.
Inventory Information
This section of the page specifies if inventory TLV is received in LLDP frames on this port.
Hardware Revision Specifies the hardware version of the remote device.
Firmware Revision Specifies the firmware version of the remote device.
Software Revision Specifies software version of the remote device.
Serial Number Specifies the serial number of the remote device.
Manufacturer Name Specifies the manufacturer’s name of the remote device.
Model Name Specifies the model name of the remote device.
Asset Id Specifies the asset ID of the remote device.
Location Information
This section of the page specifies if location TLV is received in LLDP frames on this port.
Sub Type Specifies the type of location information.
Location Information Specifies the location information as a string for a given type of location ID.
Field Description
Configure System Information
87
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View Local LLDP Information
You can view the data that each port advertises through LLDP.
To view local LLDP information:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
Extended PoE
This section of the page specifies if the remote device is a PoE device.
Device Type Specifies the remote device’s PoE device type connected to this port.
Extended PoE PSE
This section of the page specifies if extended PSE TLV is received in LLDP frame on this port.
Device Type Specifies the remote device’s PoE device type connected to this port.
Power Source Specifies the remote port’s PSE power source.
Power Priority Specifies the remote port’s PSE power priority.
Power Value Specifies the remote port’s PSE power value in tenths of watts.
Extended PoE PD
This section of the page specifies if extended PD TLV is received in LLDP frame on this port.
Device Type Specifies the remote device’s PoE device type connected to this port.
Power Source Specifies the remote port’s PD power source.
Power Priority Specifies the remote port's PD power priority.
Power Value Specifies the remote port's PD power requirement.
Field Description
Configure System Information
88
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select System > Advanced > LLDP > Local Information.
The page that displays shows the Device Information section and the Port Information
section.
The page includes only the interfaces on which LLDP is enabled.
The following table describes the LLDP device information and port summary information.
6. To view additional details about a port, click the name of the port in the Interface column of
the Port Information table.
The following table describes the detailed local information that displays for the selected
port.
Field Description
Device Information
Chassis ID Subtype The type of information used to identify the switch in the Chassis ID field.
Chassis ID The hardware platform identifier for the switch.
System Name The user-configured system name for the switch.
System Description The switch description, which includes information about the product model
and platform.
System Capabilities The primary functions that the switch supports.
Interface Information
Interface The interface associated with the LLDP data.
Port ID Subtype The type of information used to identify the interface in the Port ID field.
Port ID The port number.
Port Description The user-defined description of the port. For information about how to
configure the port description, see Configure Port Settings on page 105.
Advertisement The TLV advertisement status of the port.
Field Description
Managed Address
Address SubType The type of address the management interface uses, such as an IPv4
address.
Address The address used to manage the device.
Interface SubType The port subtype.
Interface Number The number that identifies the port.
Configure System Information
89
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View LLDP Neighbors Information
You can view the data that a specified interface received from other LLDP-enabled systems.
To view LLDP information received from a neighbor device:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
MAC/PHY Details
Auto Negotiation Supported Indicates whether the interface supports port speed autonegotiation. The
possible values are True and False.
Auto Negotiation Enabled The port speed autonegotiation support status. The possible values are True
(enabled) or False (disabled).
Auto Negotiation Advertised
Capabilities The port speed autonegotiation capabilities such as 1000BASE-T half-duplex
mode or 100BASE-TX full-duplex mode.
Operational MAU Type The Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) type. The MAU performs physical layer
functions, including digital data conversion from the Ethernet interface
collision detection and bit injection into the network.
MED Details
Capabilities Supported The MED capabilities enabled on the port.
Current Capabilities The TLVs advertised by the port.
Device Class Network Connectivity indicates that the device is a network connectivity
device.
Network Policies
Application Type The media application type associated with the policy.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID associated with the policy.
VLAN Type Specifies whether the VLAN associated with the policy is tagged or untagged.
User Priority The priority associated with the policy.
DSCP The DSCP associated with a particular policy type.
Field Description
Configure System Information
90
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Advanced > LLDP > Neighbor Information.
The Neighbor Information page displays.
If no information was received from a neighbor device, or if the link partner is not
LLDP-enabled, no information displays.
The following table describes the information that displays for all LLDP neighbors that
were discovered.
6. To view additional information about the remote device, click the link in the MSAP Entry
column.
A pop-up window displays information for the selected port.
The following table describes the information transmitted by the neighbor.
Field Description
MSAP Entry The Media Service Access Point (MSAP) entry number for the remote
device.
Local Port The interface on the local system that received LLDP information from a
remote system.
Chassis ID Subtype The type of data displayed in the Chassis ID field on the remote system.
Chassis ID The remote 802 LAN device’s chassis.
Port ID Subtype The type of data displayed in the remote system’s Port ID field.
Port ID The physical address of the port on the remote system from which the data
was sent.
System Name The system name associated with the remote device. If the field is blank, the
name might not be configured on the remote system.
Field Description
Port Details
Local Port The interface on the local system that received LLDP information from a
remote system.
MSAP Entry The Media Service Access Point (MSAP) entry number for the remote device.
Basic Details
Chassis ID Subtype The type of data displayed in the Chassis ID field on the remote system.
Chassis ID The remote 802 LAN device’s chassis.
Configure System Information
91
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Port ID Subtype The type of data displayed in the remote system’s Port ID field.
Port ID The physical address of the port on the remote system from which the data
was sent.
Port Description The user-defined description of the port.
System Name The system name associated with the remote device.
System Description The description of the selected port associated with the remote system.
System Capabilities The system capabilities of the remote system.
Managed Addresses
Address SubType The type of the management address.
Address The advertised management address of the remote system.
Interface SubType The port subtype.
Interface Number The port on the remote device that sent the information.
MAC/PHY Details
Auto-Negotiation Supported Specifies whether the remote device supports port-speed autonegotiation.
The possible values are True or False.
Auto-Negotiation Enabled The port speed autonegotiation support status. The possible values are True
and False.
Auto Negotiation Advertised
Capabilities The port speed autonegotiation capabilities.
Operational MAU Type The Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) type. The MAU performs physical layer
functions, including digital data conversion from the Ethernet interface
collision detection and bit injection into the network.
MED Details
Capabilities Supported The supported capabilities that were received in MED TLV from the device.
Current Capabilities The advertised capabilities that were received in MED TLV from the device.
Device Class The LLDP-MED endpoint device class. The possible device classes are as
follows:
• Endpoint Class 1 Indicates a generic endpoint class, offering basic LLDP
services.
• Endpoint Class 2 Indicates a media endpoint class, offering media
streaming capabilities as well as all Class 1 features.
• Endpoint Class 3 Indicates a communications device class, offering all
Class 1 and Class 2 features plus location, 911, Layer 2 switch support,
and device information management capabilities.
PoE Device Type The PoE device type advertised by the remote device.
PoE Power Source The PoE power type advertised by the remote device.
Field Description
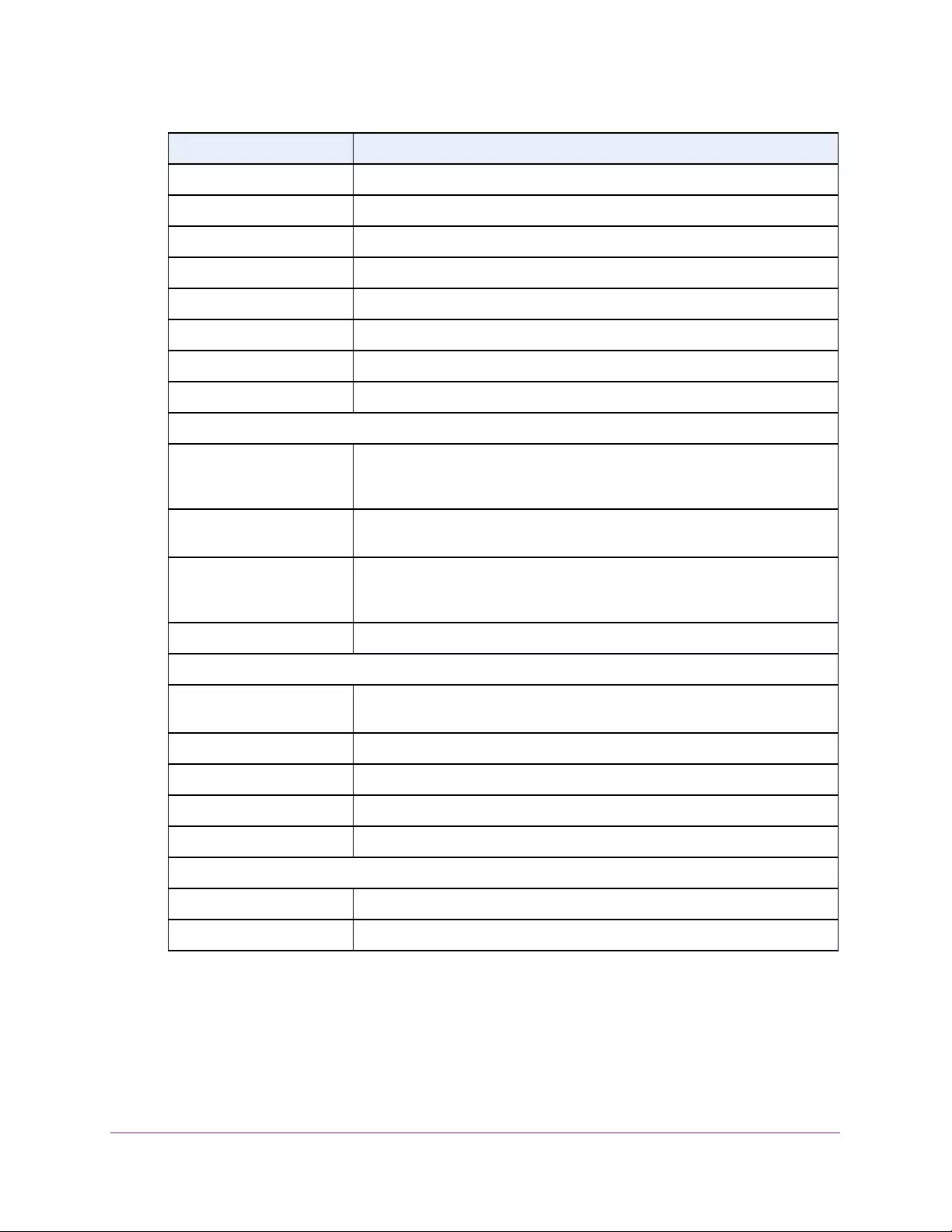
Configure System Information
92
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
PoE Power Priority The PoE power priority advertised by the remote device.
PoE Power Value The PoE power value advertised by the remote device.
Hardware Revision The hardware version advertised by the remote device.
Firmware Revision The firmware version advertised by the remote device.
Software Revision The software version advertised by the remote device.
Serial Number The serial number advertised by the remote device.
Model Name The model name advertised by the remote device.
Asset ID The asset ID advertised by the remote device.
Location Information
Civic The physical location, such as the street address, that the remote device
advertised in the location TLV, for example, 123 45th St. E. The field value
length range is 6–160 characters.
Coordinates The location map coordinates that the remote device advertised in the
location TLV, including latitude, longitude, and altitude.
ECS ELIN The Emergency Call Service (ECS) Emergency Location Identification
Number (ELIN) that the remote device advertised in the location TLV. The
field range is 10–25.
Unknown The unknown location information for the remote device.
Network Policies
Application Type The media application type associated with the policy advertised by the
remote device.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID associated with the policy.
VLAN T ype Specifies whether the VLAN associated with the policy is tagged or untagged.
User Priority The priority associated with the policy.
DSCP The DSCP associated with a particular policy type.
LLDP Unknown TLVs
Type The unknown TLV type field.
Value The unknown TLV value field.
Field Description

Configure System Information
93
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure DHCP L2 Relay and DHCP Snooping
The switch supports DHCP L2 Relay, DHCP snooping, and Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI).
DHCP snooping and DAI are Layer 2 security features that examine traffic to help prevent
accidental and malicious attacks on the switch or network.
The following sections describe how to configure DHCP L2 Relay, DHCP snooping, and
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI):
•Configure a DHCP L2 Relay on page 93
•Configure DHCP Snooping on page 97
Configure a DHCP L2 Relay
DHCP relay agents eliminate the need to connect to a DHCP server on each physical
network. Relay agents populate the giaddr field and also append the Relay Agent Information
option to the DHCP messages. DHCP servers use this option for IP addresses and other
parameter assignment policies. These DHCP relay agents are typically IP routing-aware
devices and are referred to as Layer 3 relay agents. In some network configurations, a need
might exist for Layer 2 devices to append the Relay Agent Information option as they are
closer to the end hosts.
These Layer 2 devices typically operate only as bridges for the network and might not include
an IPv4 address on the network. Lacking a valid IPv4 source address, they cannot relay
packets directly to a DHCP server located on another network. These Layer 2 devices
append the Relay Agent Information option and broadcast the DHCP message.
Enable the Global DHCP L2 Relay Settings
You can enable the global DHCP L2 relay settings for the switch.
To enable DHCP L2 relay global settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.

Configure System Information
94
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select System> Services > DHCP L2 Relay > DHCP L2 Relay Global Configuration.
The DHCP L2 Relay Global Configuration page displays.
6. Select the Admin Mode Enable radio button.
The default admin mode is disabled.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure the DHCP L2 Relay Settings for a VLAN
You can configure the DHCP L2 relay settings for a VLAN.
To configure the DHCP L2 relay settings for a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Services > DHCP L2 Relay > DHCP L2 Relay Global Configuration.
The DHCP L2 Relay Global Configuration page displays.
6. Select one or more VLANs, or select all VLANs by selecting the check box in the table
heading.
7. From the Admin Mode menu, select to enable or disable the DHCP L2 relay on the
selected VLAN or VLANs.
The default is Disable.
8. From the Circuit ID Mode menu, select to enable the interface number to be added as the
circuit ID in DHCP option 82 or to disable the interface number from being added as the
circuit ID in DHCP option 82.
The default is Disable.
9. In the Remote ID String field, enter a remote ID description of up to 32 characters.
10. Click the Apply button.

Configure System Information
95
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Your settings are saved.
Configure the DHCP L2 Relay Interface Settings
You can configure the DHCP L2 relay interface settings.
To configure the DHCP L2 relay interface settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Services > DHCP L2 Relay > DHCP L2 Relay Interface Configuration.
The DHCP L2 Relay Interface Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Admin Mode menu, select to enable or disable the DHCP L2 relay on the
selected interface.
The default is Disable.
9. From the 82 Option Trust Mode menu, select to enable or disable an interface to be trusted
for DHCP L2 Relay (Option-82) received.
The default is Disable.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure System Information
96
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View or Clear the DHCP L2 Relay Interface Statistics
You can view information about the DHCP L2 relay interfaces.
To view or clear the DHCP L2 relay interface statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Services > DHCP L2 Relay > DHCP L2 Relay Interface Statistics.
The DHCP L2 Relay Interface Statistics page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable data that is displayed.
Field Description
Interface The interface from which the DHCP message is received.
Untrusted Server
Messages With Opt82 The number of DHCP message with option82 received from an untrusted server.
Untrusted Client
Messages With Opt82 The number of DHCP message with option82 received from an untrusted client.
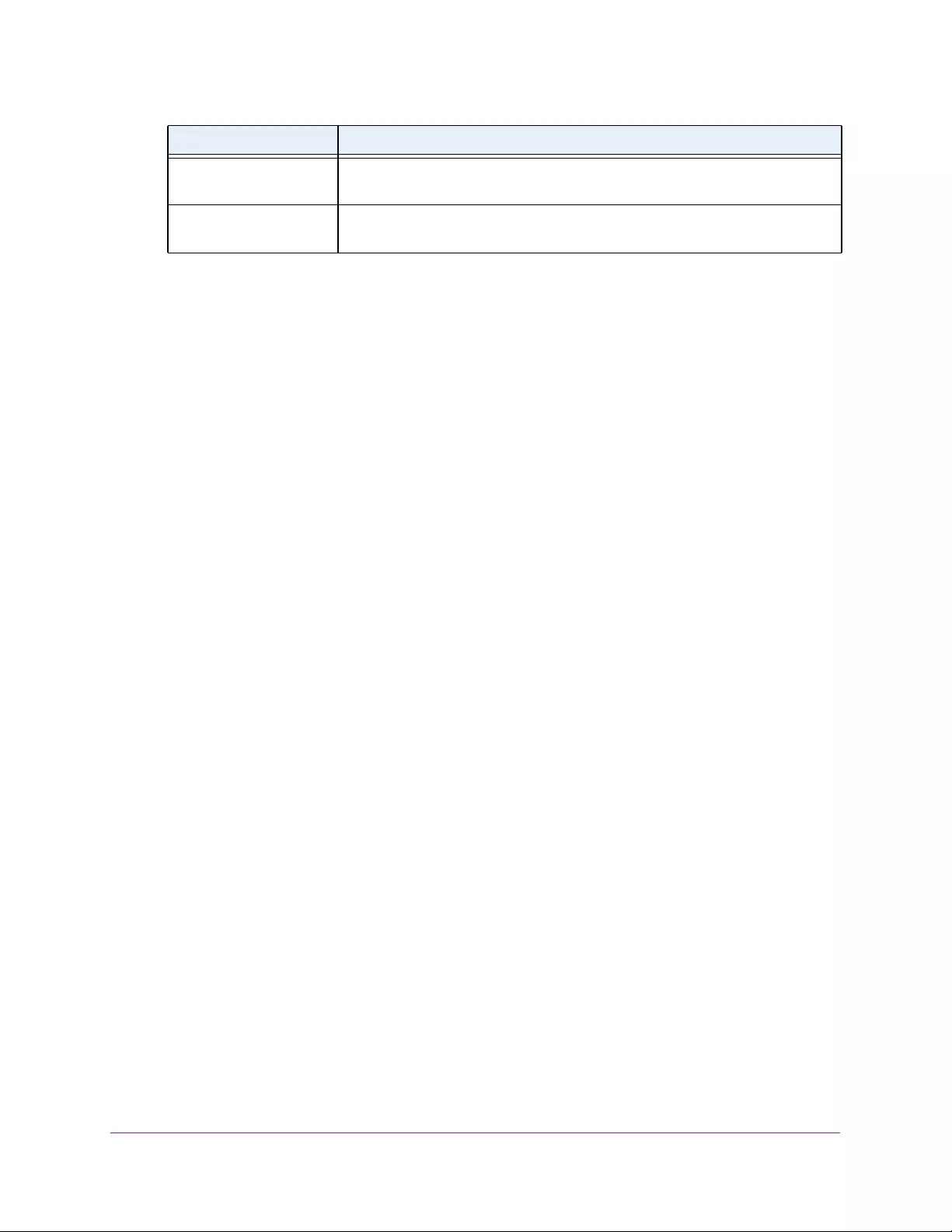
Configure System Information
97
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
8. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
9. To clear all interfaces statistics, click the Clear button.
Configure DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping is a useful feature that provides security by filtering untrusted DHCP
messages and by building and maintaining a DHCP snooping binding table. An untrusted
message is a message that is received from outside the network or firewall and that can
cause traffic attacks within your network. The DHCP snooping binding table contains the
MAC address, IP address, lease time, binding type, VLAN number, and interface information
that corresponds to the local untrusted interfaces of a switch. An untrusted interface is an
interface that is configured to receive messages from outside the network or firewall. A
trusted interface is an interface that is configured to receive only messages from within the
network.
DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and DHCP servers. It also
provides way to differentiate between untrusted interfaces connected to the end user and
trusted interfaces connected to the DHCP server or another switch.
Enable the Global DHCP Snooping Settings
You can view and configure the global settings for DHCP snooping.
To enable the global DHCP snooping settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
T rusted Server Messages
Without Opt82 The number of DHCP message without option82 received from a trusted server.
Trusted Client Messages
Without Opt82 The number of DHCP message without option82 received from a trusted client.
Field Description

Configure System Information
98
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select System> Services > DHCP Snooping > Global Configuration.
The DHCP Snooping Global Configuration page displays.
6. Select the DHCP Snooping Mode Enable radio button.
7. To enable the verification of the sender’s MAC address for DHCP snooping, select the MAC
Address Validation Enable radio button.
When MAC address validation is enabled, the device checks packets that are received on
an untrusted interface to verify that the MAC address and the DHCP client hardware
address match. If the addresses do not match, the device drops the packet.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Enable DHCP for All Interfaces in a VLAN
To enable DHCP snooping for all interfaces that are members of a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Services > DHCP Snooping > Global Configuration.
The DHCP Snooping Global Configuration page displays.
6. In the VLAN ID field, enter the VLAN on which DHCP snooping must be enabled.
7. From the DHCP Snooping Mode menu, select Enable.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure DHCP Snooping Interface Settings
You can view and configure each port as a trusted or untrusted port. Any DHCP responses
received on a trusted port are forwarded. If a port is configured as untrusted, any DHCP (or
BootP) responses received on that port are discarded.

Configure System Information
99
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To configure DHCP snooping interface settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Services > DHCP Snooping > Interface Configuration.
The DHCP Snooping Interface Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Trust Mode menu, select the desired trust mode:
•Disabled. The interface is considered to be untrusted and could potentially be used
to launch a network attack. DHCP server messages are checked against the bindings
database. On untrusted ports, DHCP snooping enforces the following security rules:
-DHCP packets from a DHCP server (DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK, DHCPNAK,
DHCPRELEASEQUERY) are dropped.
-DHCPRELEASE and DHCPDECLINE messages are dropped if the MAC address
is in the snooping database but the binding’s interface is other than the interface
where the message was received.
-DHCP packets are dropped when the source MAC address does not match the
client hardware address if MAC address validation is globally enabled.
•Enabled. The interface is considered to be trusted and forwards DHCP server
messages without validation.
9. From the Invalid Packets menu, select the packet logging mode.

Configure System Information
100
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
When enabled, the DHCP snooping feature generates a log message when an invalid
packet is received and dropped by the interface.
10. In the Rate Limit(pps) field, specify the rate limit value for DHCP snooping purposes.
If the incoming rate of DHCP packets per second exceeds the configured burst interval
per second, the port shuts down. If the rate limit value is N/A, then the burst interval is
also nonapplicable, and rate limiting is disabled.
11. In the Burst Interval(secs) field, specify the burst interval value for rate limiting purposes on
this interface.
If the rate limit is N/A, then the burst interval is also nonapplicable, and the field displays
N/A.
12. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Static DHCP Bindings
You can view , add, and remove static bindings in the DHCP snooping bindings database and
to view or clear the dynamic bindings in the bindings table.
To configure static DHCP bindings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Services > DHCP Snooping > Binding Configuration.
The Static Binding Configuration page displays.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface on which the DHCP client is authorized.
7. In the MAC Address field, specify the MAC address for the binding to be added.
This is the key to the binding database.
8. From the VLAN ID menu, select the ID of the VLAN the client is authorized to use.
9. In the IP Address field, specify the IP address of the client.
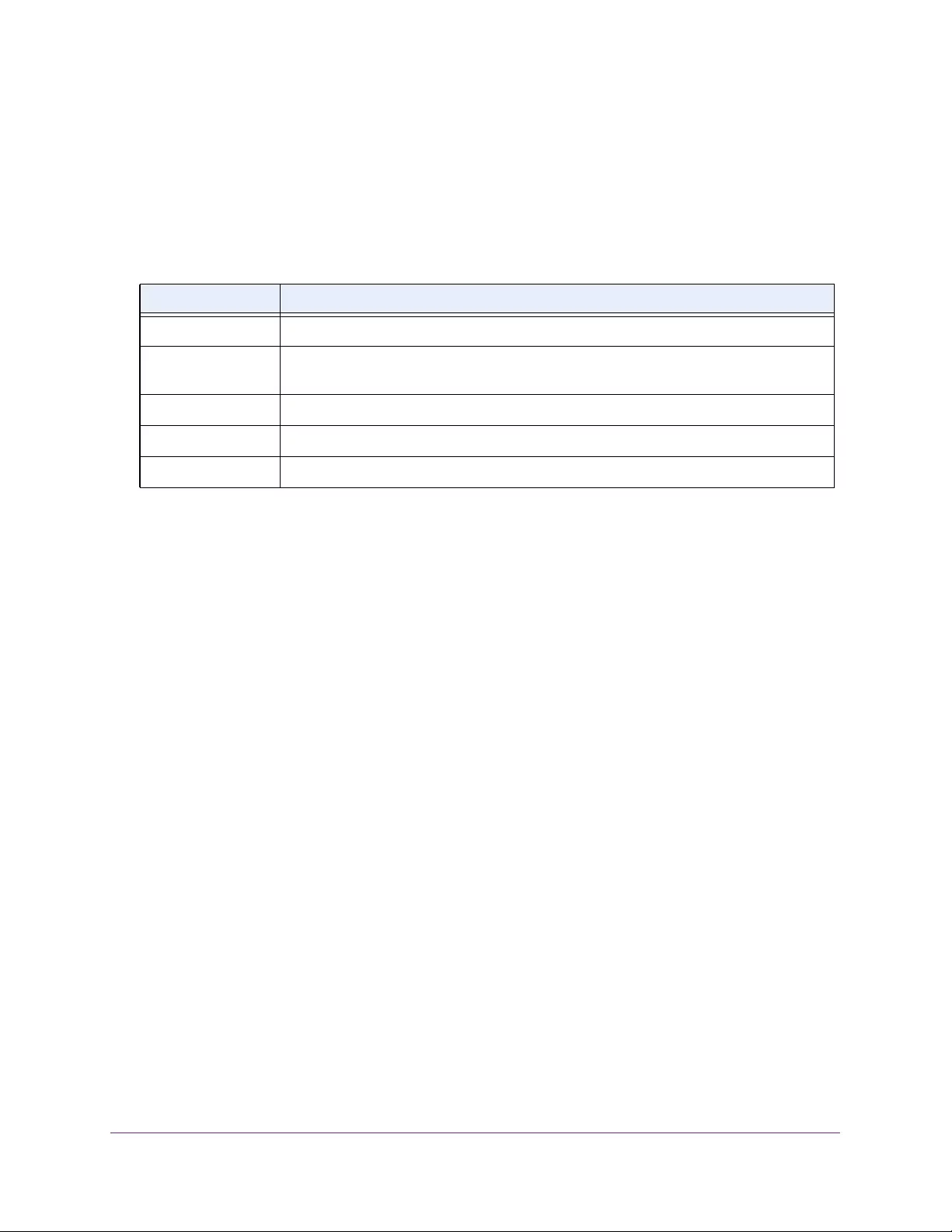
Configure System Information
101
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
10. Click the Add button.
The DHCP snooping binding entry is added to the database.
The Dynamic Binding Configuration table shows information about the DHCP bindings that
were dynamically (that is, automatically) learned on each interface on which DHCP snooping
is enabled. The following table describes the dynamic bindings information.
Configure the Persistent Location of the DHCP Snooping Bindings Database
You can configure the persistent location of the DHCP snooping bindings database. The
bindings database can be stored locally on the device or on a remote system somewhere
else in the network. The device must be able to reach the IP address of the remote system to
send bindings to a remote database.
To configure the persistent location of the DHCP snooping bindings database:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Services > DHCP Snooping > Persistent Configuration.
The DHCP Snooping Persistent Configuration page displays.
6. Specify where the DHCP snooping bindings database is located:
Table 22. DHCP Dynamic Configuration information
Field Description
Interface The interface on which the DHCP client message was received.
MAC Address The MAC address associated with the DHCP client that sent the message. This is the
key to the binding database.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID of the client interface.
IP Address The IP address assigned to the client by the DHCP server.
Lease Time The remaining IP address lease time for the client.

Configure System Information
102
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Local. The binding table is stored locally on the switch.
•Remote. The binding table is stored on a remote TFTP server.
If the database is stored on a remote server, specify the following information:
a. In the Remote IP Address field, enter the IP address of the TFTP server.
b. In the Remote File Name field, enter the file name of the DHCP snooping
bindings database in which the bindings are stored.
7. In the Write Delay field, specify the time to wait between writing bindings information to
persistent storage.
The delay allows the device to collect as many entries as possible (new and removed)
before writing them to the persistent file.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
View or Clear the DHCP Snooping Statistics
You can view and clear per-interface statistics about the DHCP messages filtered by the
DHCP snooping feature on untrusted interfaces.
To view or clear the DHCP snooping statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Services > DHCP Snooping > Statistics.
The DHCP Snooping Statistics page displays.
6. To refresh the information on the page, click the Refresh button.
7. To clear all interfaces statistics, click the Clear button.
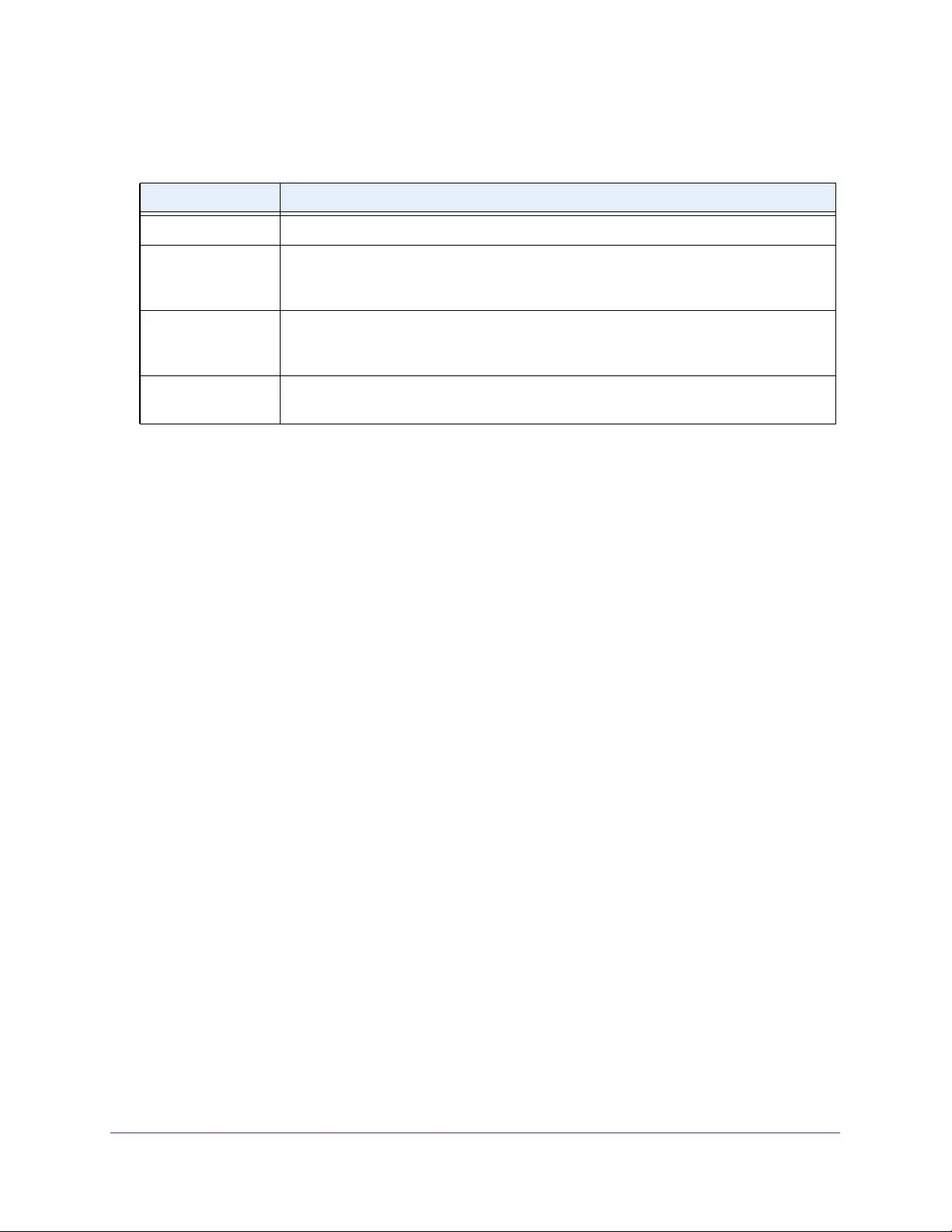
Configure System Information
103
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the DHCP snooping statistics.
Set Up PoE Timer Schedules
For information about PoE timer schedules, see Chapter 8, Manage Power over Ethernet.
Table 23. DHCP Snooping Statistics information
Field Description
Interface The interface associated with the rest of the data in the row.
MAC Verify Failures The number of DHCP messages that were dropped because the source MAC address
and client hardware address did not match. MAC address verification is performed only if
it is globally enabled.
Client Ifc Mismatch The number of packets that were dropped by DHCP snooping because the interface and
VLAN on which the packet was received do not match the client’s interface and VLAN
information stored in the binding database.
DHCP Server Msgs
Received The number of DHCP server messages ((DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK, DHCPNAK,
DHCPRELEASEQUERY) that were dropped on an untrusted port.

104
3
3. Configure Switching
This chapter covers the following topics:
•Configure Port Settings
•Configure Link Aggregation Groups
•Configure VLANs
•Configure a Voice VLAN
•Configure Auto-V oIP
•Configure Spanning Tree Protocol
•Configure Multicast
•View, Search, and Configure the MAC Address Table
•Configure Layer 2 Loop Protection

Configure Switching
105
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Port Settings
You can view, configure, and monitor the physical port information for the ports (that is, the
physical interfaces) on the switch.
To configure port settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Ports > Port Configuration.
The Port Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces (ports, LAGs, or both) by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. In the Description field, enter the description string to be attached to a port.
The string can be up to 64 characters in length.
9. From the Admin Mode menu, select Enable or Disable.
This sets the port control administrative mode. You must select Enable in order for the
port to participate in the network. The default is Enable.
10. From the Auto-negotiation menu, select Enable or Disable.
This specifies the autonegotiation mode for this port. The default is Enable.
Note: After you change the autonegotiation mode, the switch might be
inaccessible for a number of seconds while the new settings take effect.

Configure Switching
106
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
11. In the Speed field, specify the speed value for the selected port.
-Auto. All supported speeds. If you select Auto, the duplex mode and speed are
set by the autonegotiation process. The port’ s maximum capability (full duplex and
1000 Mbps) are advertised. Otherwise, your selection determines the port’s
duplex mode and transmission rate. The default setting is Auto.
-10. 10 Mbits/sec.
-100. 100 Mbits/sec.
-1000. 1000 Mbits/sec. This selection is available only if autonegotiation is
enabled.
The delimiter characters for setting different speed values are a comma (,), a period
(.) and a space ( ). For you to set the auto-negotiation speed, the autonegotiation
mode must be set to Enable. The default is Auto.
Note: After you change the speed settings, the switch might be inaccessible
for a number of seconds while the new settings take effect.
12. From the Duplex Mode menu, select the duplex mode for the selected port.
Possible values are as follows:
•Auto. Indicates that speed is set by the auto-negotiation process.
•Full. Indicates that the interface supports transmission between the devices in both
directions simultaneously.
•Half. Indicates that the interface supports transmission between the devices in only
one direction at a time.
The default is Auto.
Note: After you change the duplex mode, the switch might be inaccessible for
a number of seconds while the new settings take effect.
13. Use the Link Trap menu to specify whether or not to send a trap when link status changes.
The Link Trap menu is enabled by default. However, for LAG interfaces, the menu is
disabled.
14. In the Frame Size field, specify the maximum Ethernet frame size the interface supports or
is configured to use, including Ethernet header, CRC, and payload.
The range is 1500 to 9198. The default maximum frame size is 1500.
15. From the Flow Control menu, select the configuration for IEEE 802.3 flow control.
•Disable. If the port buffers become full, the switch does not send pause frames, and
data loss could occur. This is the default setting.
•Symmetric. If the port buffers become full, the switch sends pause frames to stop
traffic.
Flow control helps to prevent data loss when the port cannot keep up with the number
of frames being switched. When you enable flow control, the switch can send a pause
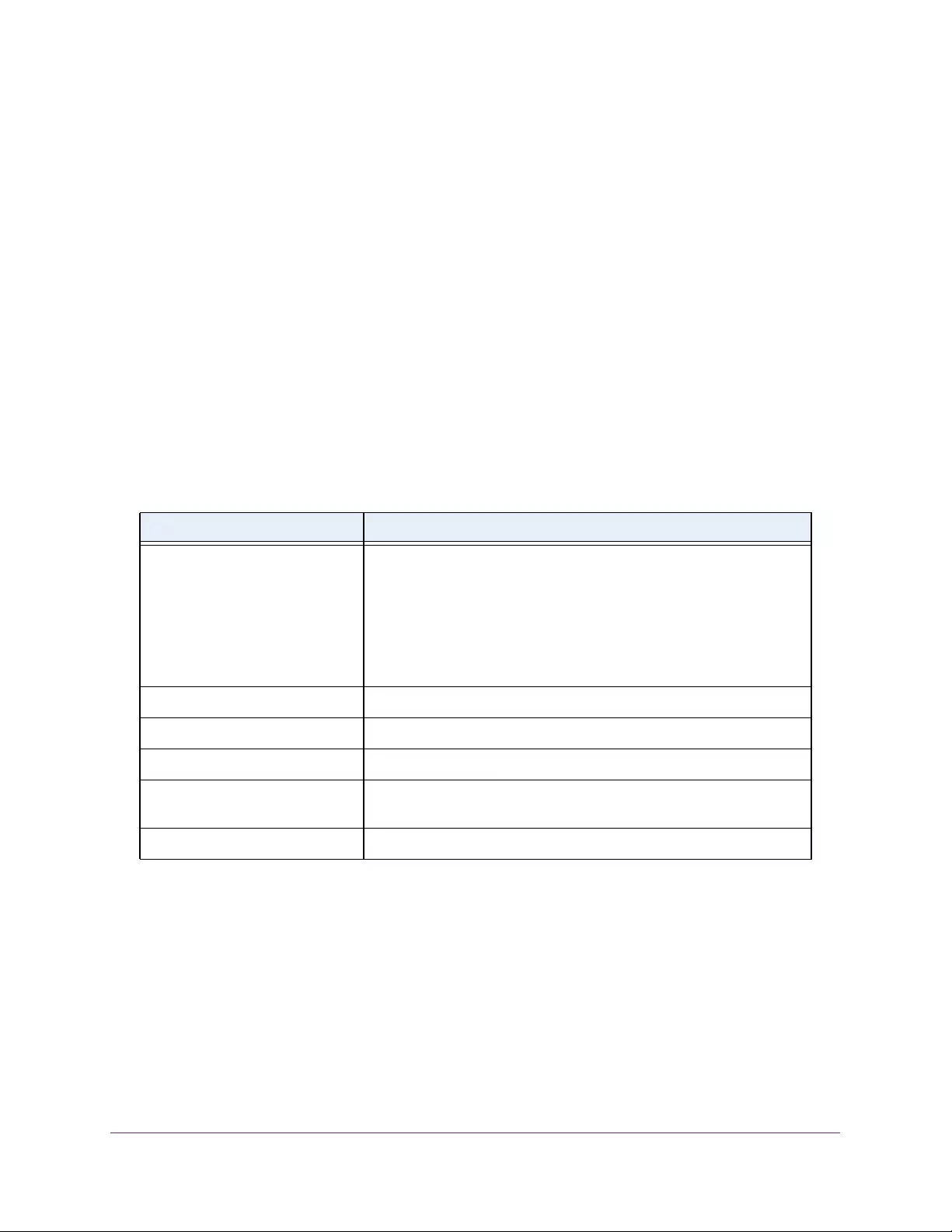
Configure Switching
107
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
frame to stop traffic on the port if the amount of memory used by the packets on the
port exceeds a preconfigured threshold and responds to pause requests from partner
devices. The paused port does not forward packets for the time that is specified in the
pause frame. When the pause frame time elapses, or the utilization returns to a
specified low threshold, the switch enables the port to again transmit frames. The
switch also honors incoming pause frames by temporarily halting transmission.
•Asymmetric. If the port buffers become full, the switch does not send pause frames,
and data loss could occur . However , the switch does honor incoming pause frames by
temporarily halting transmission.
Note: For LAG interfaces, flow control mode is displayed as a blank field
because flow control is not applicable.
16. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable data that is displayed.
Configure Link Aggregation Groups
Link aggregation groups (LAGs), which are also known as port channels, allow you to
combine multiple full-duplex Ethernet links into a single logical link. Network devices treat the
aggregation as if it were a single link, which increases fault tolerance and provides load
sharing. You assign the LAG VLAN membership after you create a LAG. The LAG by default
becomes a member of the default management VLAN (that is, VLAN 1).
Table 24. Port Configuration information
Field Description
Port Type For normal ports this field is blank. Otherwise, the possible values are
as follows:
• Mirrored. The port is a mirrored port on which all the traffic is
copied to the probe port.
• Probe. Use this port to monitor a mirrored port.
• Trunk Member. The port is a member of a link aggregation trunk.
Look at the LAG pages for more information.
Physical Status The port speed and duplex mode.
Link Status Indicates whether the link is up or down.
MAC Address The physical address of the specified interface.
PortList Bit Offset The bit offset value that corresponds to the port when the MIB object
type PortList is used to manage in SNMP.
ifIndex The ifIndex of the interface table entry associated with this port.

Configure Switching
108
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
A LAG interface can be either static or dynamic, but not both. All members of a LAG must
participate in the same protocols. A static port channel interface does not require a partner
system to be able to aggregate its member ports.
The switch supports static LAGs. When a port is added to a LAG as a static member, the port
neither transmits nor receives LACPDUs.
Configure LAG Settings
You can group one or more full-duplex Ethernet links to be aggregated together to form a link
aggregation group, which is also known as a port channel. The switch treats the LAG as if it
were a single link.
To configure LAG settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> LAG > Basic > LAG Configuration.
The LAG Configuration page displays.
6. In the LAG Name field, enter a name for the LAG.
You can enter any string of up to 15 alphanumeric characters. A valid name must be
specified for you to create the LAG.
7. In the Description field, enter the description string to be attached to a LAG.
The description can be up to 64 characters in length.
8. From the Admin Mode menu, select Enable or Disable.
When the LAG is disabled, no traffic flows and LACPDUs are dropped, but the links that
form the LAG are not released. The default is Enable.
9. From the Hash Mode menu, select the load-balancing mode for a port channel (LAG):
•1 Src MAC, VLAN, EType, incoming port. This mode uses the source MAC
address, VLAN, EtherType, and incoming port that are associated with the packet.
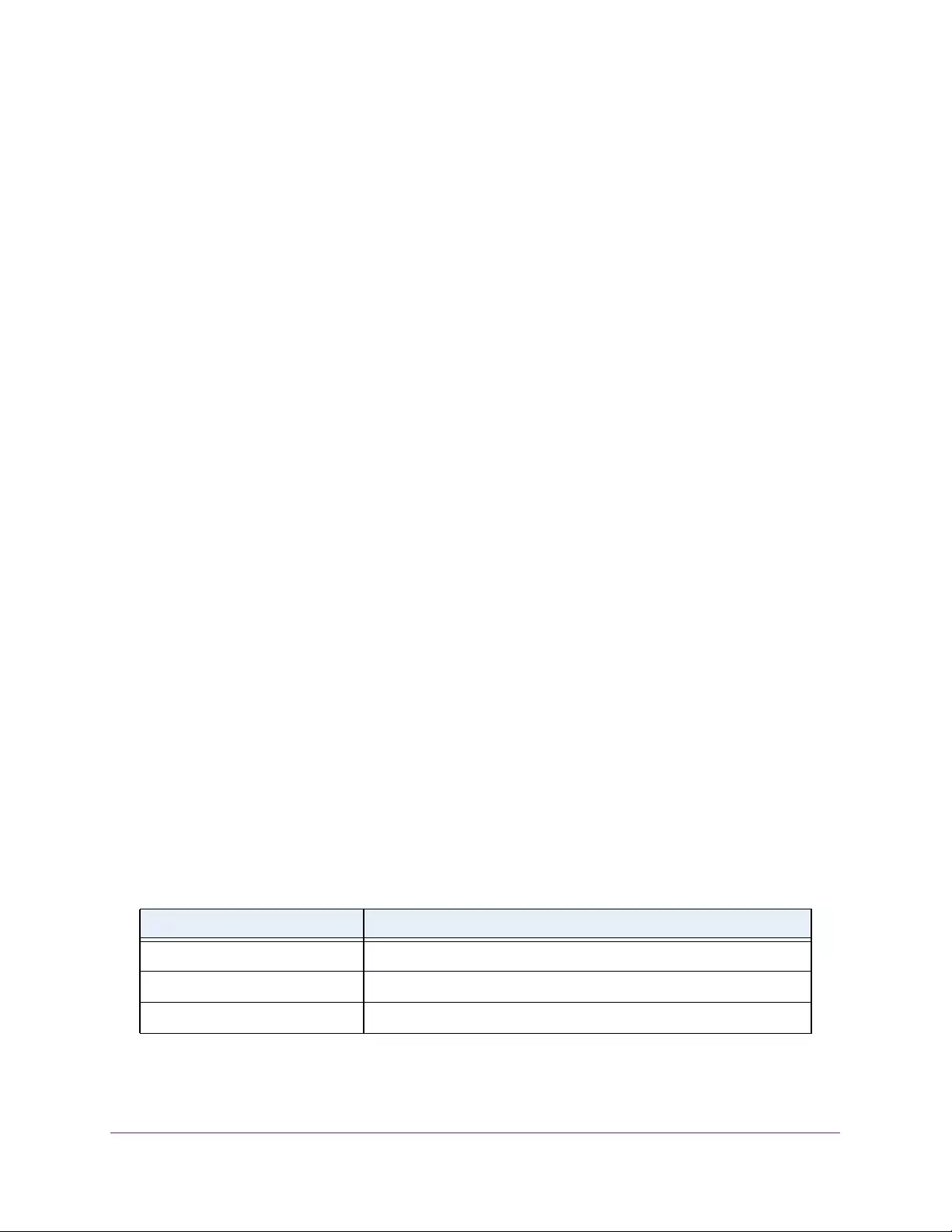
Configure Switching
109
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•2 Dest MAC, VLAN, EType, incoming port. This mode uses the destination MAC
address, VLAN, EtherType, and incoming port that are associated with the packet.
•3 Src/Dest MAC, VLAN, EType, incoming port. This mode uses the source and
destination MAC addresses, VLAN, EtherT ype, and incoming port that are associated
with the packet. This is the default mode.
•4 Src IP and Src TCP/UDP Port fields. This mode uses the source IP address and
source TCP or UDP port value that are associated with the packet.
•5 Dest IP and Dest TCP/UDP Port fields. This mode uses the destination IP address
and destination TCP or UDP port value that are associated with the packet.
•6 Src/Dest IP and TCP/UDP Port fields. This mode uses the source and destination
IP addresses and source and destination TCP or UDP port values that are associated
with the packet.
Note: The switch balances traffic on a port channel (LAG) by selecting one
of the links in the channel over which packets must be transmitted. The
switch selects the link by creating a binary pattern from selected fields
in a packet and associating that pattern with a particular link.
10. From the STP Mode menu, select the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) administrative mode
associated with the LAG. The possible values are as follows:
•Disable. Spanning tree is disabled for this LAG.
•Enable. Spanning tree is enabled for this LAG. Enable is the default.
11. From the Link Trap menu, select Enable or Disable to specify whether to send a trap when
the link status changes.
The default is Enable, which causes the trap to be sent.
12. From the LAG Type menu, select Static or LACP:
•Static. Disables Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on the selected LAG. The
LAG is configured manually. The default is Static.
•LACP. Disables LACP on the selected LA. The LAG is configured automatically.
13. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Table 25. LAG Configuration information
Field Description
LAG ID Identifier of the LAG.
Active Ports The ports that are actively participating in the LAG.
LAG State Indicates whether the link is up or down.

Configure Switching
110
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure LAG Membership
You can select two or more full-duplex Ethernet links to be aggregated together to form a link
aggregation group (LAG), which is also known as a port channel. The switch can treat the
port channel as a single link.
To configure LAG membership:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> LAG > Basic > LAG Membership.
The LAG Membership page displays.
6. From the LAG ID menu, select the LAG ID.
7. In the LAG Name field, enter the name to be assigned to the LAG.
You can enter any string of up to 15 alphanumeric characters. A valid name must be
specified for you to create the LAG.
8. In the Ports table, click each port that you want to include as a member of the selected
LAG.
A selected port is displayed by a check mark.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
10. To view the members of the LAG, click the Current members button.
A pop-up window opens and displays the list of current members.

Configure Switching
111
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Set the LACP System Priority
The LACP configuration page is used to set the LACP system priority.
To configure LACP:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> LAG > Advanced > LACP Configuration.
The LACP Configuration page displays.
6. In the LACP System Priority field, specify the device’s link aggregation priority relative to
the devices at the other ends of the links on which link aggregation is enabled.
A higher value indicates a lower priority. You can change the value of the parameter
globally by specifying a priority from 1 to 65535. The default value is 32768.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set the LACP Port Priority Settings
The LACP port configuration page is used to configure the LACP priority value for the selected
port and the administrative LACP time-out value.
To configure LACP port priority settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.

Configure Switching
112
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> LAG > Advanced > LACP Port Configuration.
The LACP Port Priority page displays.
6. Select one or more interfaces (ports only, no LAGs) by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the interface, or
type the interface number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
7. In the LACP Priority field, specify the LACP priority value for the selected interfaces.
This value specifies the device’s link aggregation priority relative to the devices at the
other ends of the links on which link aggregation is enabled. A higher value indicates a
lower priority. The range is 1 to 65535. The default value is 128.
8. In the Timeout field, configure the administrative LACP time-out value:
•Long. Specifies a long time-out value. This is the default setting.
•Short. Specifies a short time-out value.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure VLANs
Adding virtual LAN (VLAN) support to a Layer 2 switch offers some of the benefits of both
bridging and routing. Like a bridge, a VLAN switch forwards traffic based on the Layer 2
header, which is fast, and like a router, it partitions the network into logical segments, which
provides better administration, security, and management of multicast traffic.
By default, all ports on the switch are in the same broadcast domain. VLANs electronically
separate ports on the same switch into separate broadcast domains so that broadcast
packets are not sent to all the ports on a single switch. When you use a VLAN, users can be
grouped by logical function instead of physical location.
Each VLAN in a network is assigned an associated VLAN ID, which appears in the IEEE
802.1Q tag in the Layer 2 header of packets transmitted on a VLAN. An end station can omit
the tag, or the VLAN portion of the tag, in which case the first switch port to receive the packet

Configure Switching
113
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
can either reject it or insert a tag using its default VLAN ID. A given port can handle traffic for
more than one VLAN, but it can support only one default VLAN ID.
You can define VLAN groups stored in the VLAN membership table. The switch supports up
to 256 VLANs. VLAN 1 is created by default and is the default VLAN of which all ports are
members. VLAN 4089 is also created by default and is the Auto-Video VLAN. By default, the
Auto-Video VLAN does not include any members.
Manage Basic VLANs
You can add, change, and delete VLANs. For information about adding members to a VLAN,
see Configure VLAN Membership on page 117.
Add a VLAN
To add a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Basic > VLAN Configuration.
The VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. In the VLAN ID field, specify the VLAN identifier for the new VLAN.
The range of the VLAN ID can be from 1 to 4093.
7. In the VLAN Name field, specify a name for the VLAN.
The VLAN name can be up to 32 alphanumeric characters long, including blanks. The
default is blank. VLAN ID 1 always uses the name Default.
8. The VLAN Type field displays the type of the VLAN that you are configuring.
You cannot change the type of the default VLAN (VLAN ID = 1): it is always type Default.
When you create a VLAN using this page, its type is always Static.
9. Click the Add button.

Configure Switching
114
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The VLAN is added to the switch.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete a VLAN
To delete a VLAN from the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Basic > VLAN Configuration.
The VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. In the VLAN ID field, specify the VLAN identifier.
The range of the VLAN ID can be from 1 to 4093.
Note: You cannot delete VLANs 1 and VLAN 4089, which are created by
default.
7. Click the Delete button.
The VLAN is removed.
Reset a VLAN to Its Default Settings
To reset a VLAN to its default settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.

Configure Switching
115
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Basic > VLAN Configuration.
You can also select Switching> VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Configuration.
The VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. Select the Reset Configuration check box.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The default values are as follows:
•All ports are assigned to the default VLAN of 1.
•All ports are configured with a PVID of 1.
•All ports are configured to an Acceptable Frame Types value of Admit All Frames.
•All ports are configured with ingress filtering disabled.
•All ports are configured to transmit only untagged frames.
All VLANs, except for the default VLAN, are deleted.
Configure VLAN Trunking
You can configure switchport mode settings on interfaces. The switchport mode defines the
purpose of the port based on the type of device it connects to and constraints the VLAN
configuration of the port accordingly. Assigning the correct switchport mode simplifies VLAN
configuration and minimizes errors.
To configure VLAN trunking:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.

Configure Switching
116
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Trunking Configuration.
The Switchport Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Switchport Mode menu, select one of the following modes.
•Access. Access mode is suitable for ports connected to end stations or end users.
Access ports participate in only one VLAN. They accept both tagged and untagged
packets, but always transmit untagged packets.
•General. General mode enables a custom configuration of a port. You can configure
the general port VLAN attributes such as the membership, PVID, tagging, ingress
filter, and so on. For more information, see Configure Port Settings on page 105. By
default, all ports are initially configured in General mode.
•Trunk. Trunk mode is intended for ports that are connected to other switches. Trunk
ports can participate in multiple VLANs, and accept both tagged and untagged
packets.
9. From the Access VLAN ID menu, select the VLAN ID for the port, which is valid only when
the selection from the Switchport Mode menu Access.
By default, the access VLAN ID is 1.
10. From the Native VLAN ID menu, select the VLAN ID for the port, which is valid only when
the selection from the Switchport Mode menu Trunk.
By default, the native VLAN ID is 1.
11. In the Trunk Allowed VLANs field, enter the set of VLANs of which the port can be a
member if configured in Trunk mode.
By default, all possible VLANs in range from 1 to 4093 are listed, even if you did not yet
create any VLANs.
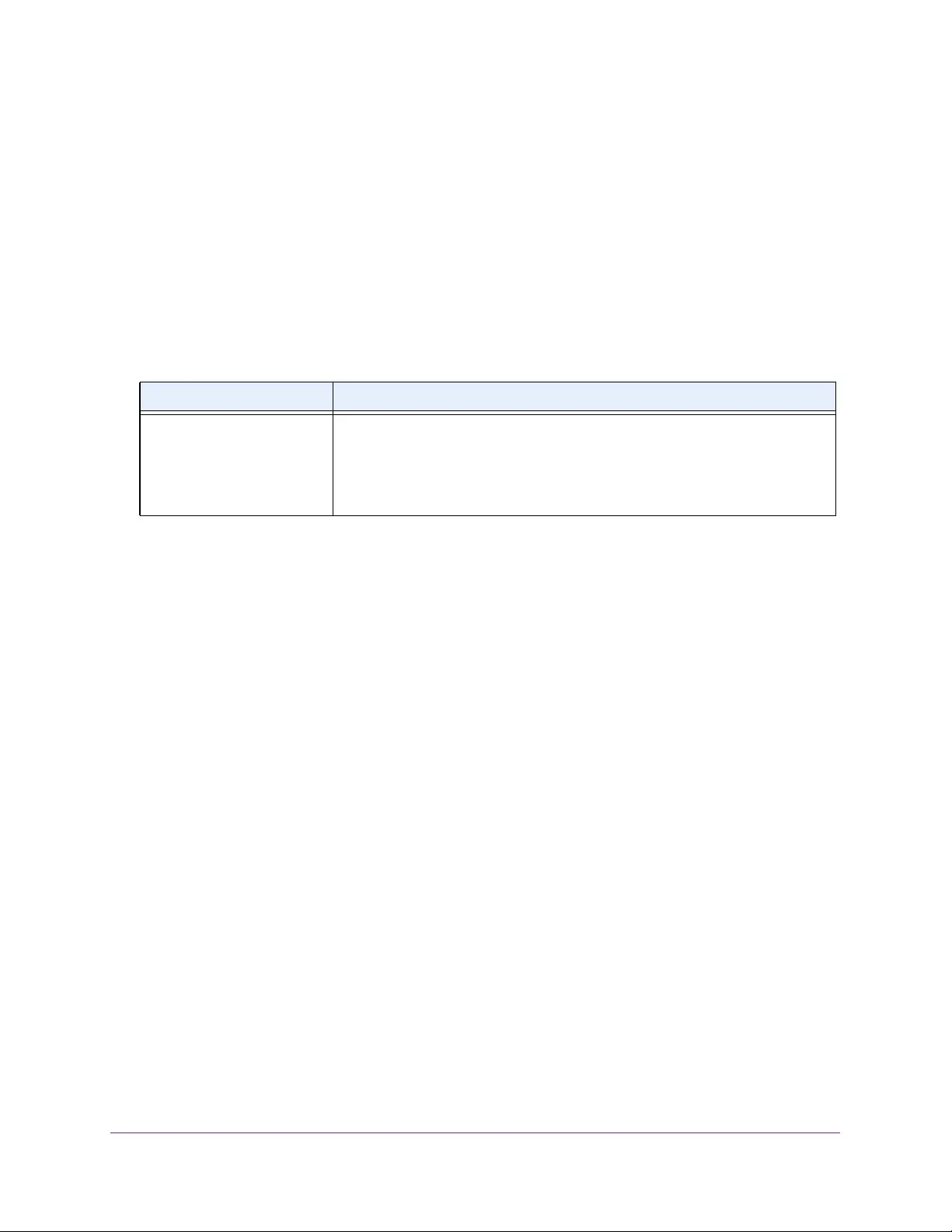
Configure Switching
117
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Note the following:
•Use a dash (–) to specify a range.
•Use a comma (,) to separate VLANs in a list. Spaces are not permitted.
•A zero value means that you want to clear the allowed VLANs.
•The All value means that you want to set all VLANs to the range (1 to 4093).
12. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table shows the nonconfigurable information on the page.
Configure VLAN Membership
To configure VLAN membership:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Membership.
Table 26. VLAN Trunking Configuration
Field Description
Native VLAN Tagging • Enable. If VLAN tagging is enabled and the trunk port receives untagged
frames, it forwards them to the native VLAN with no VLAN tag.
• Disable. If VLAN Tagging is disabled, and the port receives untagged
frames, it includes the native VLAN ID in the VLAN tag when forwarding. By
default, VLAN Tagging is disabled.
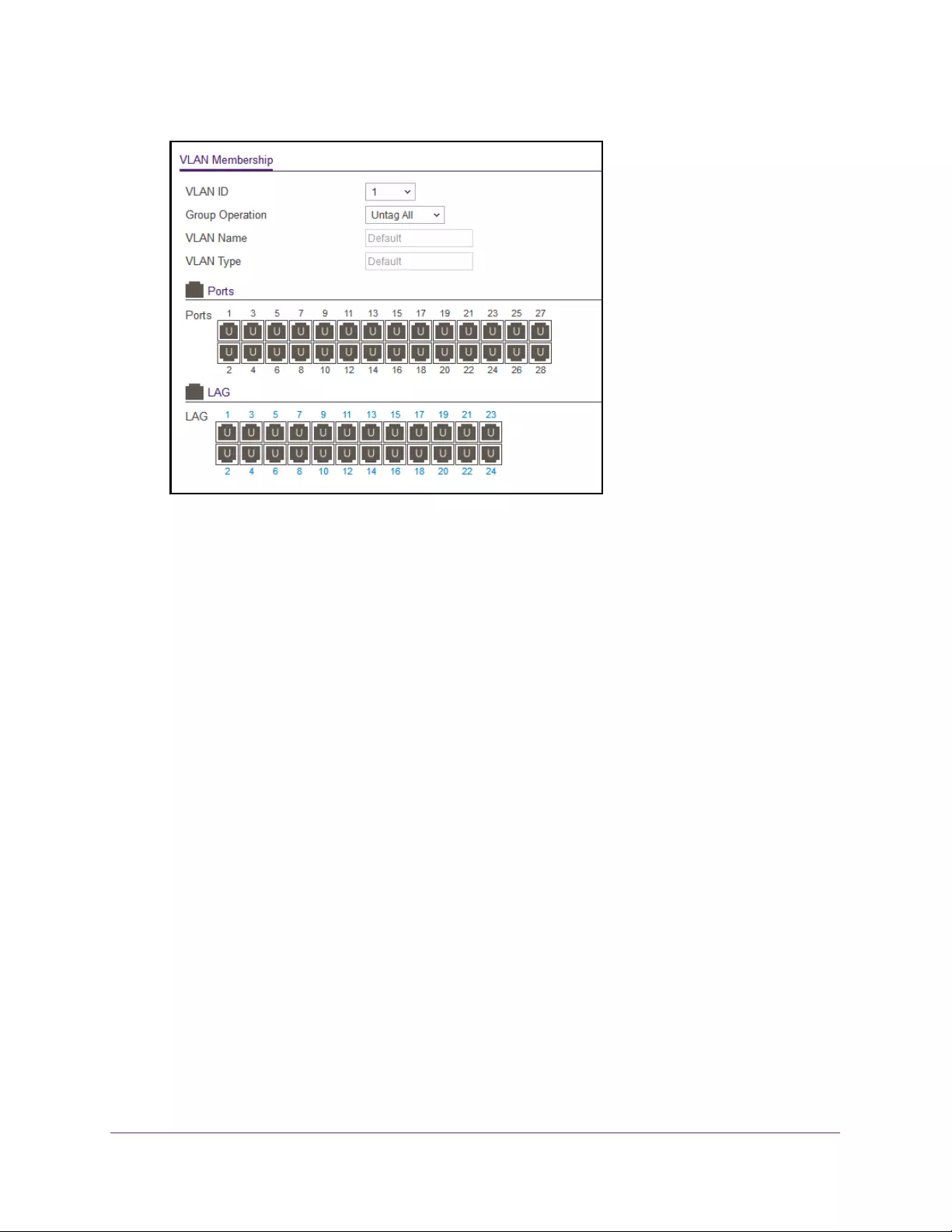
Configure Switching
118
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. In the VLAN ID menu, select the VLAN ID.
7. In the Group Operation menu, select one of the following options, which applies to all ports
in the VLAN:
•Untag All. For all ports that are members of the VLAN, tags are removed from all
egress packets.
•T ag All. For all ports that are members of the VLAN, all egress packets are tagged.
•Remove All. All ports are removed from the VLAN.
8. In the Ports table, click each port once, twice, or three times to configure one of the following
modes or reset the port to the default settings:
•T (T agged). Select the ports on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN are tagged.
The ports that are selected are included in the VLAN.
•U (Untagged). Select the ports on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN are
untagged. The ports that are selected are included in the VLAN.
By default, the selection is blank, which means that the port is excluded from the VLAN.
9. In the LAG table, click each LAG once, twice, or three times to configure one of the following
modes or reset the LAG to the default settings:
•T (Tagged). Select the LAGs on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN are
tagged. The LAGs that are selected are included in the VLAN.
•U (Untagged). Select the LAGs on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN are
untagged. The LAGs that are selected are included in the VLAN.
By default, the selection is blank, which means that the LAG is excluded from the VLAN.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Switching
119
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
View the VLAN Status
You can view the status of all currently configured VLANs.
To view the VLAN status:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Status.
The VLAN Status page displays.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Table 27. Advanced VLAN membership
Field Definition
VLAN Name The name for the VLAN that you selected. It can be up to 32
alphanumeric characters long, including blanks. VLAN ID 1 always
uses the name Default.
VLAN Type The type of the VLAN you selected:
• Default (VLAN ID = 1). Always present.
• Static. A VLAN that you configured.
Table 28. VLAN status
Field Definition
VLAN ID The VLAN identifier (VID) of the VLAN. The range of the VLAN ID is 1
to 4093.
VLAN Name The name of the VLAN. VLAN ID 1 is always named Default.
VLAN 4089 is always named Auto-Video.

Configure Switching
120
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Port PVID Settings
You can assign a port VLAN ID (PVID) to an interface. The following requirements apply to a
PVID:
•You must define a PVID for all ports.
•If no other value is specified, the default VLAN PVID is used.
•To change the port’s default PVID, you must first create a VLAN that includes the port as
a member (see Configure VLAN Membership on page 117).
To configure PVID settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Advanced > Port PVID Configuration.
The PVID Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces (ports, LAGs, or both) by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
VLAN Type The VLAN type:
• Default (VLAN ID = 1). Always present.
• Static. A VLAN that you added.
• Auto-Video. (VLAN ID = 4089). Always present.
Member Ports The ports that are included in the VLAN.
Table 28. VLAN status (continued)
Field Definition

Configure Switching
121
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. In the PVID field, specify the VLAN ID to assign to untagged or priority-tagged frames
received on this port.
The default is 1.
9. In the VLAN Member field, specify the VLAN ID or list of VLANs of a member port.
VLAN IDs range from 1 to 4093. The default is 1. Use a hyphen (-) to specify a range or a
comma (,) to separate VLAN IDs in a list. Spaces and zeros are not permitted.
10. In the VLAN Tag field, specify the VLAN ID or list of VLANs of a tagged port.
VLAN IDs range from 1 to 4093. Use a hyphen (-) to specify a range or a comma (,) to
separate VLAN IDs in a list. Spaces and zeros are not permitted. To reset the VLAN tag
configuration to the defaults, use the None keyword. Port tagging for the VLAN can be
set only if the port is a member of this VLAN.
11. From the Acceptable Frame menu, specify the types of frames that can be received on this
port:
•Admit All. Untagged frames or priority-tagged frames received on this port are
accepted and assigned the value of the port VLAN ID for this port. With either option,
VLAN-tagged frames are forwarded in accordance to the 802.1Q VLAN specification.
•VLAN only. Untagged frames or priority-tagged frames received on this port are
discarded.
•Admit Untagged Only. Untagged frames received on this port are accepted and
assigned the value of the port VLAN ID for this port. VLAN-tagged frames are
discarded.
12. From the Ingress Filtering menu, select one of the following options:
•Enable. The frame is discarded if this port is not a member of the VLAN with which
this frame is associated. In a tagged frame, the VLAN is identified by the VLAN ID in
the tag. In an untagged frame, the VLAN is the port VLAN ID specified for the port that
received this frame.
•Disable. All frames are forwarded in accordance with the 802.1Q VLAN bridge
specification. The default is Disable.
13. In the Port Priority field, specify the default 802.1p priority assigned to untagged packets
arriving at the port.
You can enter a number from 0 to 7.
14. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Switching
122
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields.
Configure a MAC-Based VLAN
The MAC-Based VLAN feature allows incoming untagged packets to be assigned to a VLAN
and thus classify traffic based on the source MAC address of the packet.
You define a MAC-to-VLAN mapping by configuring an entry in the MAC-to-VLAN table. An
entry is specified through a source MAC address and the desired VLAN ID. The
MAC-to-VLAN configurations are shared across all ports of the device (that is, a system-wide
table exists with MAC address–to–VLAN ID mappings).
When untagged or priority-tagged packets arrive at the switch and entries exist in the
MAC-to-VLAN table, the source MAC address of the packet is looked up. If an entry is found,
the corresponding VLAN ID is assigned to the packet. If the packet is already priority tagged
it maintains this value. Otherwise, the priority is set to zero. The assigned VLAN ID is verified
against the VLAN table. If the VLAN is valid, ingress processing on the packet continues.
Otherwise, the packet is dropped. This implies that the user is allowed to configure a MAC
address mapping to a VLAN that was not created on the system.
Add a MAC-Based VLAN
To add a MAC-based VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Table 29. Nonconfigurable fields on the PVID Configuration page
Field Description
Current Ingress Filtering Indicates whether ingress filtering is enabled for the interface.
Untagged VLANs The number of untagged VLANs for the interface.
Tagged VLANs The number of tagged VLANs for the interface.
Forbidden VLANs The number of forbidden VLANs for the interface.
Dynamic VLANs Indicates None because the switch does not support dynamic VLANs.

Configure Switching
123
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Advanced > MAC Based VLAN.
The MAC Based VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. In the MAC Address field, enter a valid MAC address to be bound to a VLAN ID.
This field is configurable only when a MAC-based VLAN is created.
7. In the VLAN ID field, specify a VLAN ID in the range of 1 to 4093.
8. Click the Add button.
The MAC address is added to the VLAN mapping table.
Delete a MAC Address From VLAN Mapping
To delete a MAC address from VLAN mapping:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Advanced > MAC Based VLAN.
The MAC Based VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. In the MAC Address field, enter a valid MAC address.
This field is configurable only when a MAC-based VLAN exists.
7. In the VLAN ID field, specify a VLAN ID in the range of 1 to 4093.
8. Click the Delete button.
The MAC address is removed from the VLAN mapping.

Configure Switching
124
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Protocol-Based VLAN Groups
You can use a protocol-based VLAN to define filtering criteria for untagged packets. By
default, if you do not configure any port-based (IEEE 802.1Q) or protocol-based VLANs,
untagged packets are assigned to VLAN 1. You can override this behavior by defining either
port-based VLANs or protocol-based VLANs, or both. Tagged packets are always handled
according to the IEEE 802.1Q standard and are not included in protocol-based VLANs.
If you assign a port to a protocol-based VLAN for a specific protocol, untagged frames
received on that port for that protocol are assigned the protocol-based VLAN ID. Untagged
frames received on the port for other protocols are assigned the port VLAN ID, either the
default PVID (1) or a PVID you specifically assigned to the port using the Port VLAN
Configuration page.
You define a protocol-based VLAN by creating a group. Each group forms a one-to-one
relationship with a VLAN ID, can include one to three protocol definitions, and can include
multiple ports. When you create a group, you specify a name and a group ID is assigned
automatically.
To configure a protocol-based VLAN group:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Advanced > Protocol Based VLAN Group Configuration.
The Protocol Based VLAN Group Configuration page displays.
6. In the Group ID field, type a number for the new group.
You can enter a number in the range from 1–128.
7. In the Group Name field, type a name for the new group.
You can enter up to 16 characters.
8. In the Protocol field, enter one or more protocols that must be associated with the group.
Configure Switching
125
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
You can enter keywords such as arp, ip, and ipx. Separate keywords with a comma. You
can also enter hexadecimal or decimal values in the range of 0x0600 (1536) to 0xFFFF
(65535).
9. In the VLAN ID field, enter the VLAN ID.
The ID can be any number in the range of 1 to 4093. All the ports in the group assign this
VLAN ID to untagged packets received for the protocols that you included in this group.
10. Click the Add button.
The protocol-based VLAN group is added to the switch.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Configure Protocol-Based VLAN Group Membership
To configure protocol-based VLAN group membership:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Advanced > Protocol Based VLAN Group Membership.
The protocol Based VLAN Group Membership page displays.
6. From the Group ID menu, select the protocol-based VLAN group ID.
The Group Name field shows the name that is associated with the group.
Table 30. Protocol Based VLAN Group Configuration information
Field Description
Ports Display all the member ports that belong to the group.

Configure Switching
126
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
7. In the Ports table and LAG table, click each port and LAG that you want to include in the
protocol-based VLAN group.
A protocol-based VLAN group can include both port and LAGs. A selected port or LAG is
displayed by a check mark.
8. Click the Apply button
Your settings are saved.
9. To view the members of the group, click the Current members button.
A pop-up window opens and displays the list of current members.
Configure a Voice VLAN
You can configure the parameters for a voice VLAN configuration.
To configure a voice VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> VLAN > Advanced > Voice VLAN Configuration.
The page that displays shows the Voice VLAN Global Admin section and Voice VLAN
Configuration section.
6. Select the Admin Mode Disable or Enable radio button.
This enables or disables the voice VLAN for the switch. The default is Disable.
7. Select the interface by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.

Configure Switching
127
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Interface Mode menu, select the voice VLAN mode for selected interfaces:
•Disable. This is the default value.
•None. Allow the IP phone to use its own configuration to send untagged voice traffic.
•VLAN ID. Configure the phone to send tagged voice traffic. With this selection, you
can enter a Dot1p value in the Value field.
•Dot1p. Configure voice VLAN 802.1p priority tagging for voice traffic. With this
selection, you must enter a dot1p value in the Value field.
•Untagged. Configure the phone to send untagged voice traffic.
9. In the Value field, enter the VLAN ID or dot1p value.
This field is enabled only when VLAN ID or dot1p is selected as the interface mode.
10. In the CoS Override Mode field, select Disable or Enable.
The default is Disable.
11. In the Authentication Mode field, select Enable or Disable.
The default is Enable. When the authentication mode is enabled, voice traffic is allowed
on an unauthorized voice VLAN port. When the authentication mode is disabled, devices
are authorized through dot1x.
Note: Authentication through dot1x is possible only if dot1x is enabled.
12. In the DSCP Value field, configure the Voice VLAN DSCP value for the port.
The valid range is 0 to 64. The default value is 0.
The Operational State field displays the operational status of the voice VLAN on the
interface.
13. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Auto-VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) enables telephone calls over a data network. Because
voice traffic is typically more time-sensitive than data traffic, the Auto-VoIP feature helps
provide a classification mechanism for voice packets so that they can be prioritized above
data packets in order to provide better Quality of Service (QoS). With the Auto-VoIP feature,
voice prioritization is provided based on call-control protocols (SIP, SCCP, H.323) or OUI bits.

Configure Switching
128
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Protocol-Based Port Settings
To prioritize time-sensitive voice traffic over data traffic, protocol-based Auto-VoIP checks for
packets carrying the following VoIP protocols:
•Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
•H.323
•Signalling Connection Control Part (SCCP)
VoIP frames that are received on ports that for which the Auto-VoIP feature is enabled are
marked with the specified CoS traffic class value.
To configure protocol-based port settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Auto-VoIP > Protocol-based > Port Settings.
The page displays the Protocol Based Global Settings section and the Protocol Based
Port Settings section.
6. From the Prioritization Type menu, select Traffic Class or Remark.
This specifies the type of prioritization.
7. From the Class Value menu, specify the CoS tag value to be reassigned for packets
received on the voice VLAN when Remark CoS is enabled.
8. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
9. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.

Configure Switching
129
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
10. From the Auto VoIP Mode menu, select Disable or Enable.
Auto-VoIP is disabled by default.
The Operational Status field displays the current operational status of each interface.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Auto-VoIP OUI-Based Properties
With Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI)–based Auto-VoIP, voice prioritization is
provided based on OUI bits.
To configure Auto-VoIP OUI-based properties:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Auto-VoIP > OUI-based > Properties.
The OUI-based Properties page displays.
6. In the Auto-VoIP VLAN ID field, enter the VoIP VLAN ID of the switch.
No default VLAN exists for Auto-VoIP, you must create a VLAN for Auto-VoIP.
7. From the OUI-based priority menu, select the OUI-based priority of the switch.
The default value is 7.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure Switching
130
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure OUI-Based Port Settings
The port settings page allows you to configure the OUI port settings.
To configure OUI-based port settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Auto-VoIP > OUI-based > Port Settings.
The OUI Port Settings page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Auto VoIP Mode menu, select Disable or Enable.
Auto-VoIP is disabled by default.
The Operational Status field displays the current operational status of each interface.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure Switching
131
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Manage the OUI Table
Device hardware manufacturers can include an OUI in a network adapter to help identify a
hardware device. The OUI is a unique 24-bit number assigned by the IEEE registration
authority. The switch comes preconfigured with the following OUIs that identify the IP phone
manufacturer:
•00:01:E3: SIEMENS
•00:03:6B: CISCO1
•00:12:43: CISCO2
•00:0F:E2: H3C
•00:60:B9: NITSUKO
•00:D0:1E: PINTEL
•00:E0:75: VERILINK
•00:E0:BB: 3COM
•00:04:0D: A VA Y A1
•00:1B:4F: A VA Y A2
•00:04:13: SNOM
You can select an existing OUI or add a new OUI and description to identify the IP phones on
the network.
Configure the OUI Table
To configure the OUI Table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Auto-VoIP > OUI-based > OUI Table.
The OUI Table page displays.

Configure Switching
132
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. In the Telephony OUI(s) field, specify the VoIP OUI prefix to be added in the format
AA:BB:CC.
Up to 128 OUIs can be configured.
7. In the Description field, enter the description for the OUI.
The maximum length of description is 32 characters. The following OUIs are present in
the configuration by default:
•00:01:E3 - SIEMENS
•00:03:6B - CISCO1
•00:12:43 - CISCO2
•00:0F:E2 - H3C
•00:60:B9 - NITSUKO
•00:D0:1E - PINTEL
•00:E0:75 - VERILINK
•00:E0:BB - 3COM
•00:04:0D - AVAYA1
•00:1B:4F - AVAYA2
•00:04:13 - SNOM
8. Click the Add button.
The telephony OUI entry is added.
Delete One or More OUI Prefixes From the OUI Table
To delete one or more OUI prefixes from the OUI table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Auto-VoIP > OUI-based > OUI Table.
The OUI Table page displays.
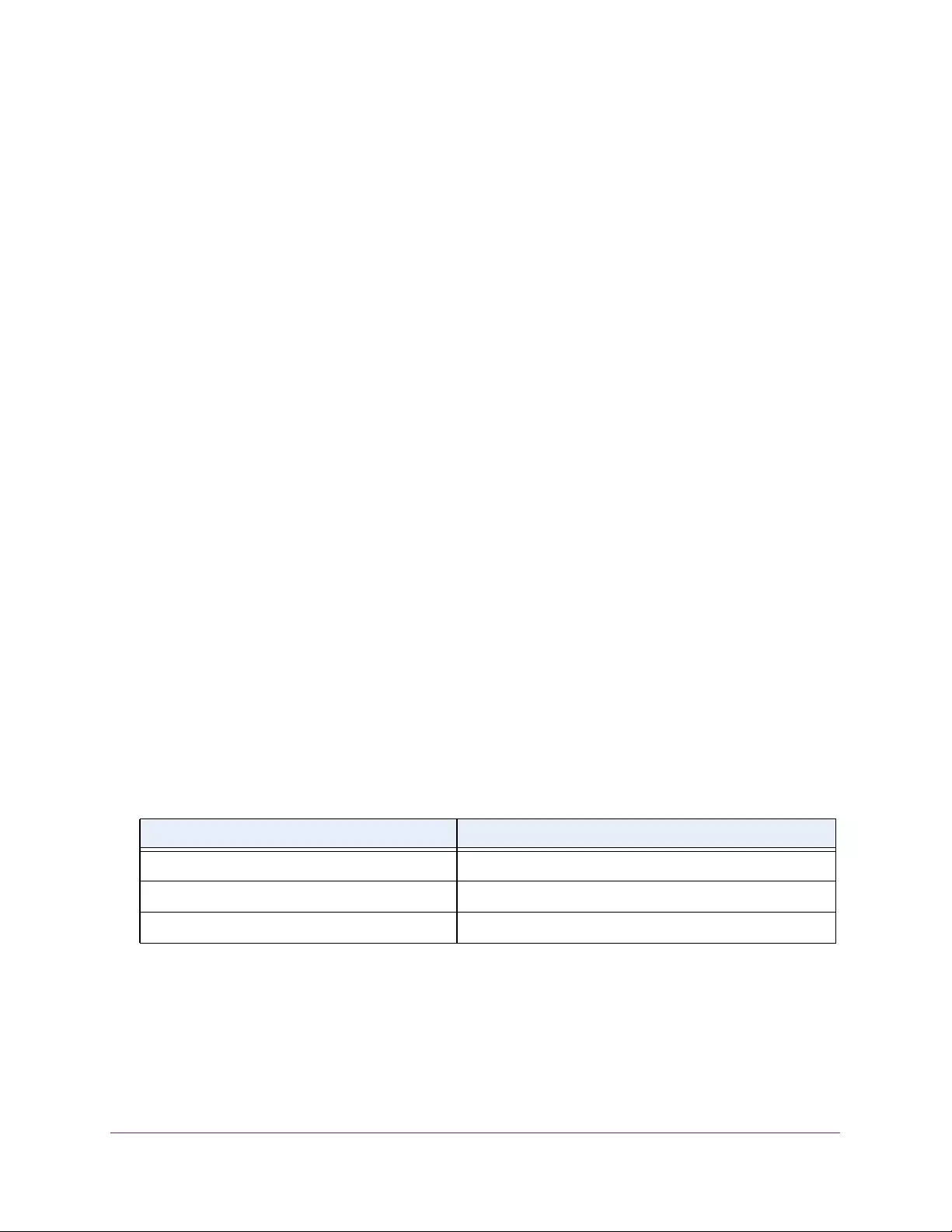
Configure Switching
133
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Select the check box next to each OUI prefix to be removed.
7. Click the Delete button.
The telephony OUI entries are removed.
Display the Auto-VoIP Status
You can display the Auto-VoIP status.
To view the Auto-VoIP status:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Auto-VoIP > Auto-VoIP Status.
The Auto-VoIP Status page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable Auto-VoIP status information.
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides a tree topology for any arrangement of bridges.
STP also provides one path between end stations on a network, eliminating loops. Spanning
tree versions supported include Common STP, Multiple STP, and Rapid STP.
Table 31. Auto-VoIP status
Field Description
Auto-VoIP VLAN ID The Auto-VoIP VLAN ID.
Maximum Number of Voice Channels Supported The maximum number of voice channels supported.
Number of Voice Channels Detected The number of VoIP channels prioritized successfully.

Configure Switching
134
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Spanning Tree Protocol Overview
Classic STP provides a single path between end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. For
information on configuring Common STP, see Configure CST Port Settings on page 137.
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) supports multiple instances of spanning tree to
efficiently channel VLAN traffic over different interfaces. Each instance of the spanning tree
behaves in the manner specified in IEEE 802.1w, Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP), with slight
modifications in the working but not the end effect (chief among the effects is the rapid
transitioning of the port to the forwarding state). The difference between the RSTP and the
traditional STP (IEEE 802.1D) is the ability to configure and recognize full-duplex connectivity
and ports that are connected to end stations, resulting in rapid transitioning of the port to the
forwarding state and the suppression of Topology Change Notification. These features are
represented by the parameters pointtopoint and edgeport. MSTP is compatible with both
RSTP and STP. It behaves in a way that is appropriate for STP and RSTP bridges. An MSTP
bridge can be configured to behave entirely as an RSTP bridge or an STP bridge.
Note: For two bridges to be in the same region, the force version must be
802.1s and their configuration names, digest keys, and revision levels
must match. For additional information about regions and their effect
on network topology, refer to the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
Configure STP Settings
The STP Configuration page contains fields for enabling STP on the switch.
To configure STP settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Basic > STP Configuration.
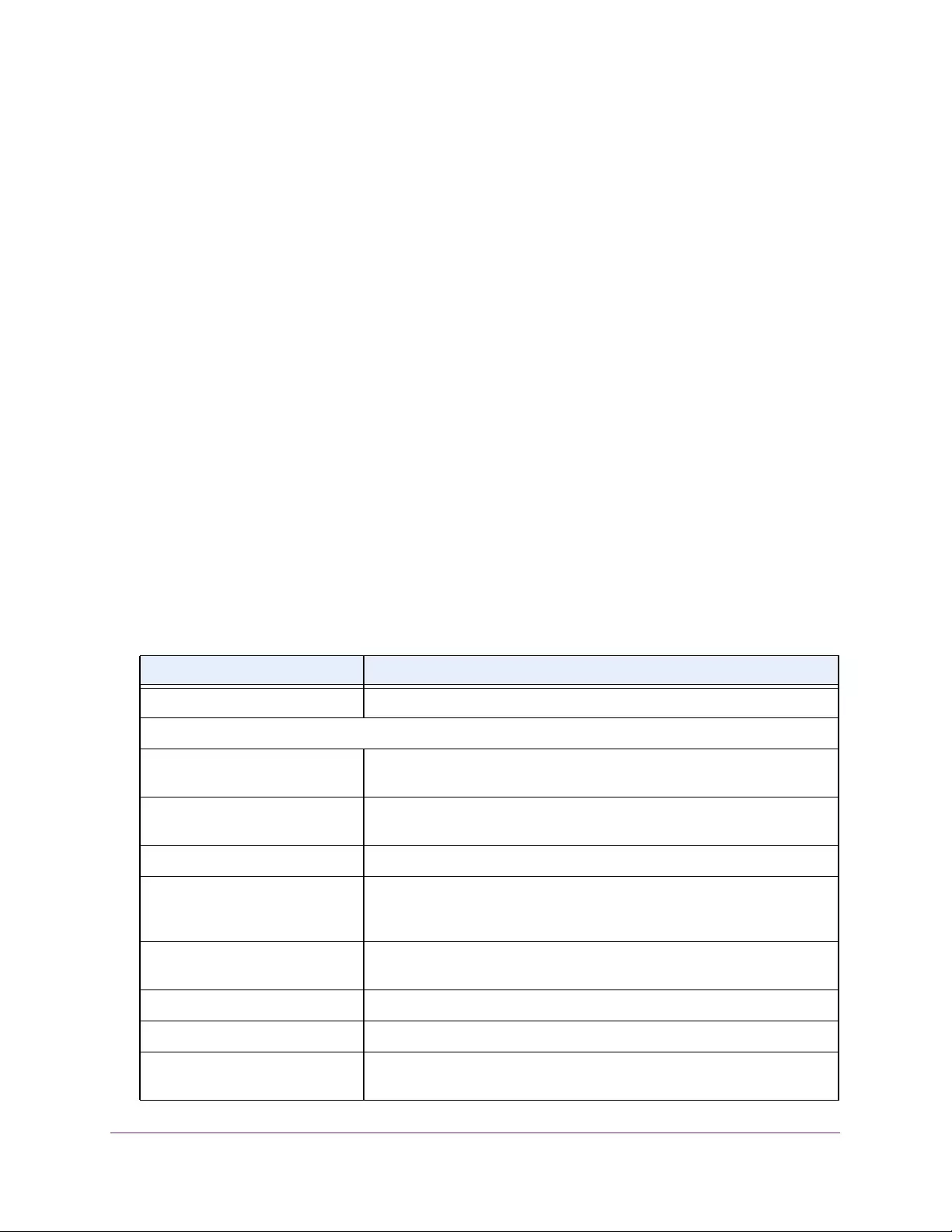
Configure Switching
135
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The Global Settings page displays.
6. Configure the following options:
•Spanning Tree State. Enable or disable the spanning tree operation on the switch.
•STP Operation Mode. Specify the STP version for the switch. The options are STP,
RSTP, and MSTP.
For more information, see Spanning Tree Protocol Overview on page 134.
•Configuration Name. Specify an identifier used to identify the configuration currently
being used.
The name can be up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
•Configuration Revision Level. Specify an identifier used to identify the configuration
currently being used.
The values allowed are between 0 and 65535. The default value is 0.
•Forward BPDU while STP Disabled. Enable or disable the BPDU Flood.
The BPDU flood option specifies whether spanning tree BPDUs are forwarded while
spanning tree is disabled on the switch.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable STP Status fields displayed on the page.
Table 32. STP configuration status
Field Description
Configuration Digest Key Identifier used to identify the configuration currently being used.
STP Status
Bridge Identifier The bridge identifier for the CST. It is made up using the bridge priority and
the base MAC address of the bridge.
Time Since Topology Change The time in day-hour-minute-second format since the topology of the CST
last changed.
Topology Change Count The number of times that the topology changed for the CST.
Topology Change The value of the topology change parameter for the switch indicating
whether a topology change is in progress on any port assigned to the CST.
Possible values are True and False.
Designated Root The bridge identifier of the root bridge. It is made up from the bridge priority
and the base MAC address of the bridge.
Root Path Cost Path cost to the designated root for the CST.
Root Port Port to access the designated root for the CST.
Max Age (secs) The maximum age timer controls the maximum length of time in seconds
that passes before a bridge port saves its configuration BPDU information.
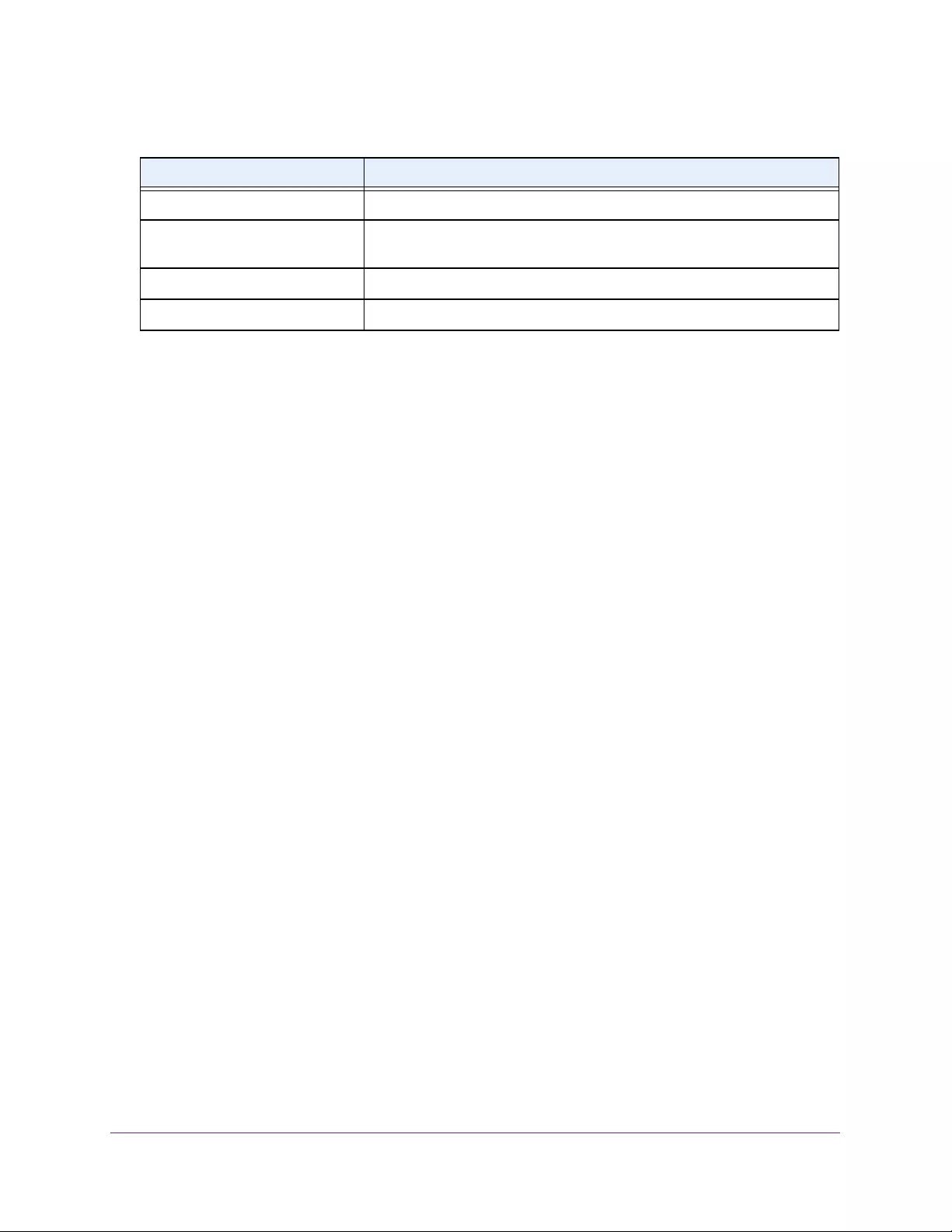
Configure Switching
136
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure CST Settings
You can configure a Common Spanning Tree (CST) and Internal Spanning Tree on the
switch.
To configure CST settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > CST Configuration.
The CST Configuration page displays.
6. Specify the CST options:
•Bridge Priority. When switches or bridges are running STP, each is assigned a
priority. After exchanging BPDUs, the switch with the lowest priority value becomes
the root bridge. Specify the bridge priority value for the Common and Internal
Spanning Tree (CST). The valid range is 0–61440. The bridge priority is a multiple of
4096. If you specify a priority that is not a multiple of 4096, the priority is automatically
set to the next lowest priority that is a multiple of 4096. For example, if you set the
priority to any value between 0 and 4095, the switch automatically sets the value to 0.
The default value is 32768.
Forward Delay (secs) The derived value of the Root Port Bridge Forward Delay parameter.
Hold Time (secs) Minimum time in seconds between the transmission of configuration
BPDUs.
CST Regional Root Priority and base MAC address of the CST regional root.
CST Path Cost Path cost to the CST tree regional root.
Table 32. STP configuration status (continued)
Field Description
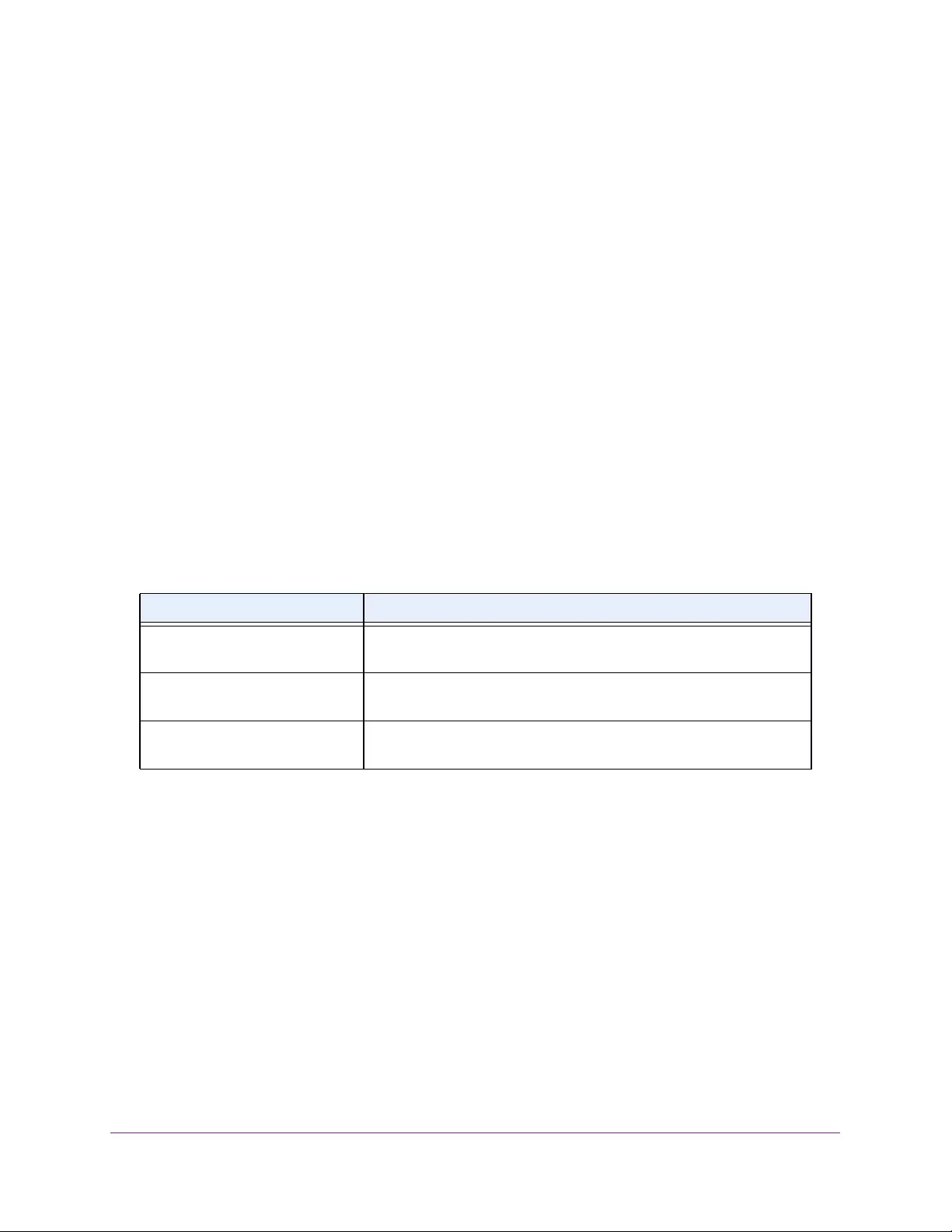
Configure Switching
137
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Bridge Max Age (secs). The bridge maximum age time for the Common and Internal
Spanning Tree (CST), which indicates the time in seconds a bridge must wait before
implementing a topological change. The valid range is 6–40, and the value must be
less than or equal to (2 * Bridge Forward Delay) – 1 and greater than or equal to 2 *
(Bridge Hello Time +1). The default value is 20.
•Bridge Hello Time (secs). The bridge hello time for the Common and Internal
Spanning Tree (CST), which indicates the time in seconds a root bridge must wait
between configuration messages. The value is fixed at 2 seconds. The value must be
less than or equal to (Bridge Max Age / 2) – 1. The default hello time value is 2.
•Bridge Forward Delay (secs). The bridge forward delay time, which indicates the
time in seconds a bridge must remains in a listening and learning state before
forwarding packets. The value must be greater or equal to (Bridge Max Age / 2) + 1.
The time range is from 4 seconds to 30 seconds. The default value is 15 seconds.
•Spanning Tree Maximum Hops. The maximum number of bridge hops the
information for a particular CST instance can travel before being discarded. The valid
range is 6–40. The default is 20 hops.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the MSTP Status information that is displayed.
Configure CST Port Settings
You can configure a common spanning tree (CST) and internal spanning tree on a specific
port on the switch.
A port can become diagnostically disabled if as error condition occurs such as severe BPDU
flooding with more than 15 BPDUs in a 3-second interval.
To configure CST port settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
Table 33. STP advanced CST configuration, MSTP status
Field Description
MST ID Table consisting of the MST instances (including the CST) and the
corresponding VLAN IDs associated with each of them.
VID ID Table consisting of the VLAN IDs and the corresponding FID
associated with each of them.
FID ID Table consisting of the FIDs and the corresponding VLAN IDs
associated with each of them.

Configure Switching
138
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > CST Port Configuration.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the STP Status menu, select the option to enable or disable the spanning tree
administrative mode associated with the port or port channel.
The possible values are Enable and Disable. The default value is Disable.
9. From the Fast Link menu, select whether the specified port is an edge port within the CST.
The possible values are Enable and Disable. The default value is Disable.
10. From the BPDU Forwarding menu, configure BPDU forwarding.
The possible values are Enable and Disable. The default value is Disable. When BPDU
forwarding is enabled, the switch forwards the BPDU traffic arriving on this port when
STP is disabled on this port.
11. From the Auto Edge menu, specify if the port is allowed to become an edge port if it does
not detect BPDUs for some duration.
The possible values are Enable and Disable. The default value is Enable.
12. In the Path Cost field, set the path cost to a new value for the specified port in the common
and internal spanning tree.
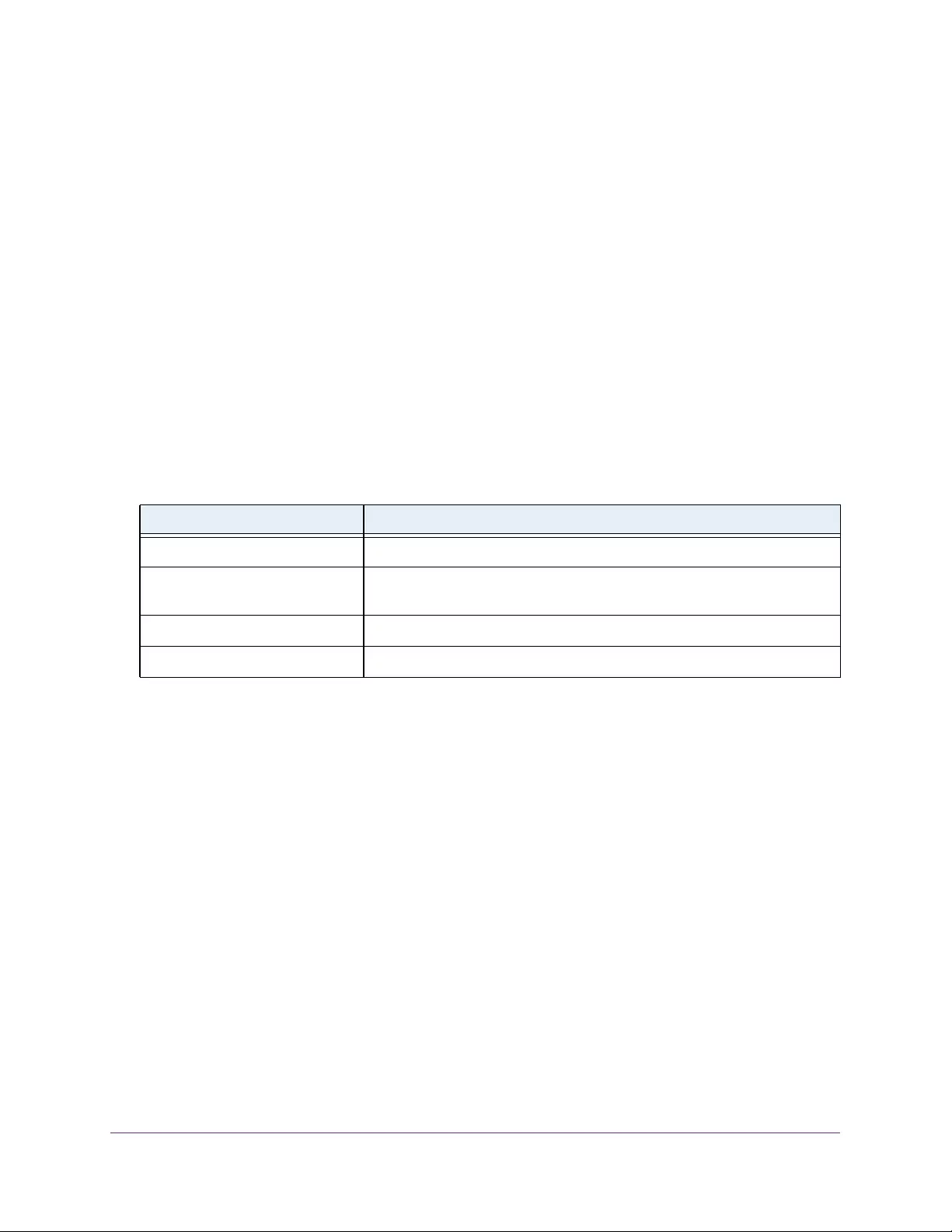
Configure Switching
139
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Specify a value in the range of 0 to 200000000. The default is 0. When the path cost is
set to 0, the value is updated with the external path cost from a received STP packet.
13. In the Priority field, specify the priority for a particular port within the CST.
The port priority is set in multiples of 16. For example if you attempt to set the priority to
any value between 0 and 15, it is set to 0. If you try to set it to any value between 16 and
(2*16 – 1), it is set to 16, and so on. The range is 0 to 240. The default value is 128.
14. In the External Port Path Cost field, set the external path cost to a new value for the
specified port in the spanning tree.
The value range is 0 to 200000000. The default is 0.
15. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
16. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
View CST Port Status
You can to display the common spanning tree (CST) and internal spanning tree for a specific
port on the switch.
To view the CST port status:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Table 34. CST port configuration
Field Description
Port State The forwarding state of the port. The default is Disabled.
Port ID The port identifier for the port within the CST. It is made up of the port priority
and the interface number of the port.
Port Path Cost The path cost for the port. The default is 0.
Hello Timer The value of the parameter for the CST. The default is 2 seconds.
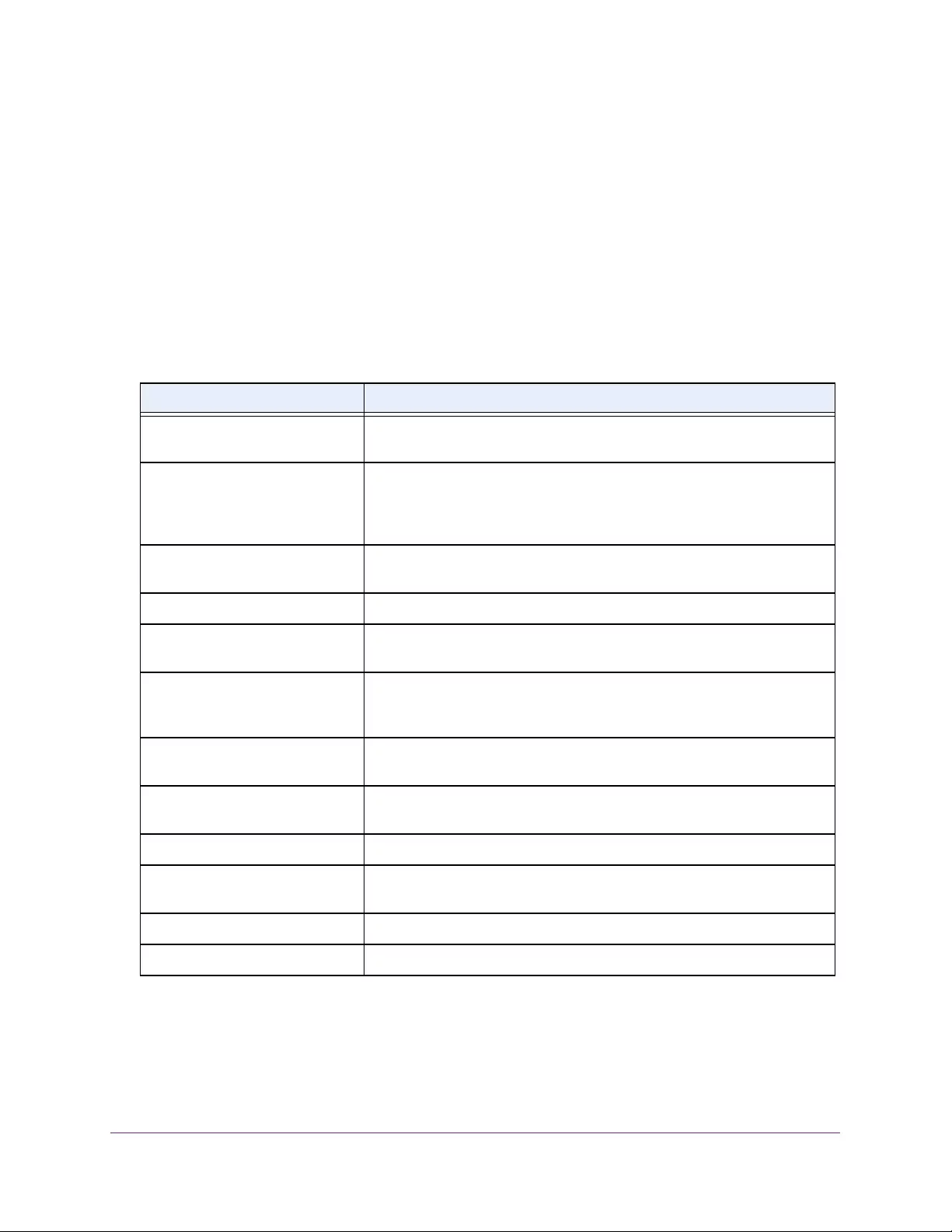
Configure Switching
140
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > CST Port Status.
The CST Port Status page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the CST Status information displayed on the page.
Table 35. CST port status
Field Description
Interface Identify the physical or port channel interfaces associated with VLANs
associated with the CST.
Port Role Each MST bridge port that is enabled is assigned a port role for each
spanning tree. The port role is one of the following values: Root Port,
Designated Port, Alternate Port, Backup Port, Master Port, or Disabled
Port.
Designated Root Root bridge for the CST. It is made up using the bridge priority and the base
MAC address of the bridge.
Designated Cost Path cost offered to the LAN by the designated port.
Designated Bridge Bridge identifier of the bridge with the designated port. It is made up using
the bridge priority and the base MAC address of the bridge.
Designated Port Port identifier on the designated bridge that offers the lowest cost to the
LAN. It is made up from the port priority and the interface number of the
port.
Topology Change Acknowledge Identifies whether the topology change acknowledgement flag is set for the
next BPDU to be transmitted for this port. It is either True or False.
Edge port Indicates whether the port is enabled as an edge port. It is either Enabled
or Disabled.
Point-to-point MAC Derived value of the point-to-point status.
CST Regional Root Bridge identifier of the CST regional root. It is made up using the bridge
priority and the base MAC address of the bridge.
CST Path Cost Path cost to the CST regional root.
Port Forwarding State The forwarding state of this port.
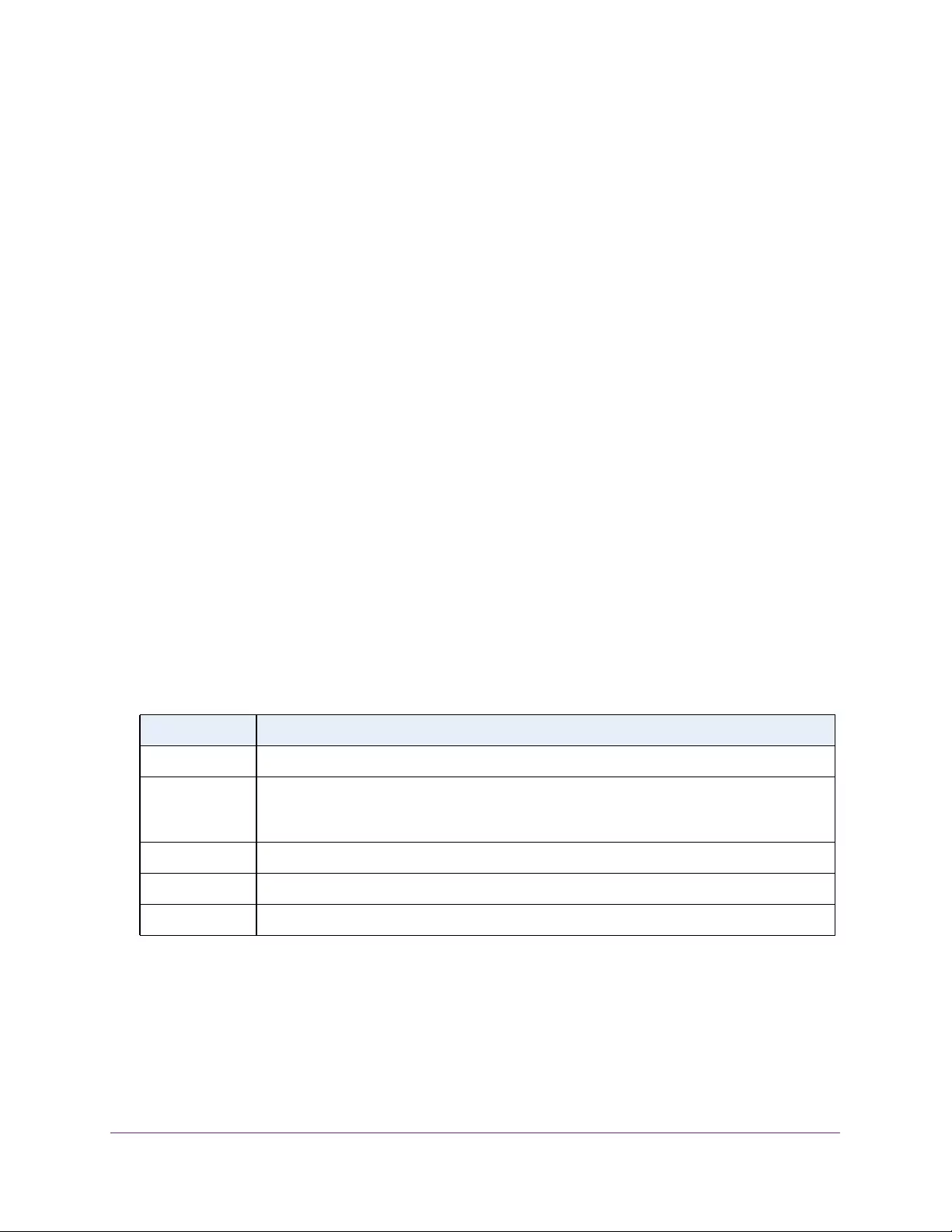
Configure Switching
141
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View Rapid STP Information
You can view information about the Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) port status.
To view information about RSTP:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > RSTP.
The Rapid STP page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the Rapid STP Status information displayed on the page.
Table 36. Rapid STP status information
Field Description
Interface The physical or port channel interfaces associated with VLANs associated with the CST.
Role Each MST bridge port that is enabled is assigned a port role for each spanning tree. The port
role is one of the following: Root Port, Designated Port, Alternate Port, Backup Port, Master
Port, or Disabled Port.
Mode Specifies the spanning tree operation mode. Different modes are STP, RSTP, and MSTP.
Fast Link Indicates whether the port is enabled as an edge port.
Status The forwarding state of this port.

Configure Switching
142
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Manage MST Settings
You can configure a multiple spanning tree (MST) on the switch.
Configure an MST Instance
To configure an MST instance:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > MST Configuration.
The MST Configuration page displays.
6. Configure the MST values:
•MST ID. Specify the ID of the MST to create. The valid values for this are 1 to 4094.
This is visible only when the select option of the MST ID select box is selected.
•Priority. The bridge priority value for the MST. When switches or bridges are running
STP, each is assigned a priority. After exchanging BPDUs, the switch with the lowest
priority value becomes the root bridge. The bridge priority is a multiple of 4096. If you
specify a priority that is not a multiple of 4096, the priority is automatically set to the
next lowest priority that is a multiple of 4096. For example, if you set the priority to any
value between 0 and 4095, the switch automatically sets the value to 0. The default
value is 32768. The valid range is 0–61440.
•Vlan Id. The menu includes all VLANs that are configured on the switch. You can
select VLANs that must be associated with the MST instance or clear VLANs that are
already associated with the MST instance.
7. Click the Add button.
The MST is added.
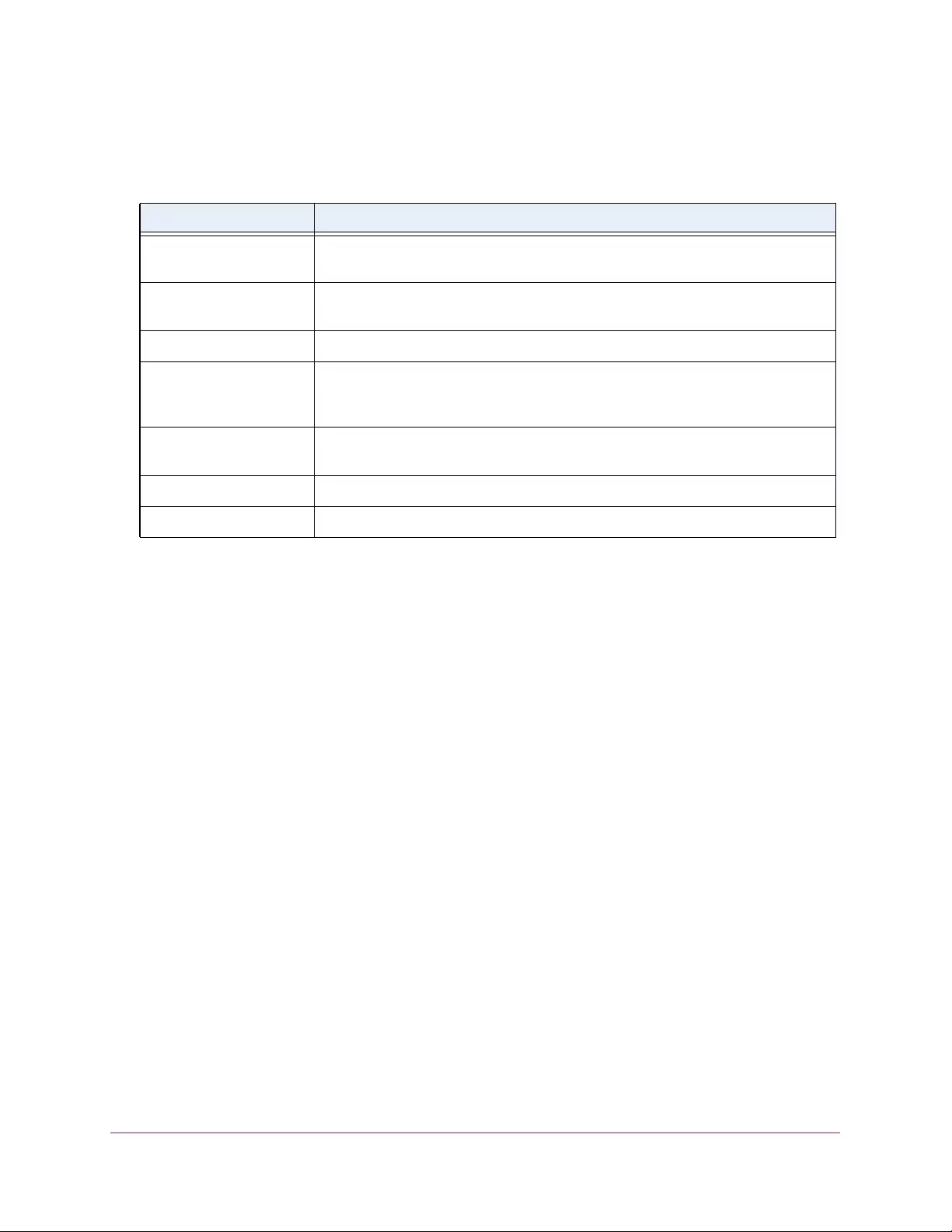
Configure Switching
143
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
For each configured instance, the information described in the following table displays on the
page.
Modify an MST Instance
To modify an MST instance:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > MST Configuration.
The MST Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the instance.
You can select multiple check boxes to apply the same setting to all selected ports.
7. Update the values.
Table 37. MST configuration
Field Description
Bridge Identifier The bridge identifier for the selected MST instance. It is made up using the bridge
priority and the base MAC address of the bridge.
Last TCN The time in day:hour:minute:second format since the topology of the selected MST
instance last changed.
Topology Change Count Number of times that the topology changed for the selected MST instance.
Topology Change The value of the topology change parameter for the switch indicating if a topology
change is in progress on any port assigned to the selected MST instance. It is
either True or False.
Designated Root The bridge identifier of the root bridge. It is made up from the bridge priority and the
base MAC address of the bridge
Root Path Cost Path cost to the designated root for this MST instance.
Root Port Port to access the designated root for this MST instance.

Configure Switching
144
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete an MST Instance
To delete an MST instance:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > MST Configuration.
The MST Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box for the instance.
7. Click the Delete button.
The MST instance is removed.
Configure MST Port Settings
You can configure and display the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) settings on a specific port
on the switch.
A port can become diagnostically disabled (D-Disable) when DOT1S experiences a severe
error condition. The most common cause is when the DOT1S software experiences BPDU
flooding. The flooding criteria is such that DOT1S receives more than 15 BPDUs in a
3-second interval. The other causes for DOT1S D-Disable are extremely rare.
To configure MST port settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
Configure Switching
145
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > MST Port Configuration.
The Status section and MST Port Configuration section display.
Note: If no MST instances are configured on the switch, the page displays a
“No MSTs Available” message.
6. From the Select MST menu, select the MST for which you want to configure the port
settings.
7. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
8. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
9. Configure the MST values for the selected interfaces:
•Port Priority. The priority for a particular port within the selected MST instance. The
port priority is set in multiples of 16. If you specify a value that is not a multiple of 16,
the priority is set to the priority is automatically set to the next lowest priority that is a
multiple of 16. For example, if you set a value between 0 and 15, the priority is set to
0. If you specify a number between 16 and 31, the priority is set to 16. Specify a value
in the range of 0–240. By default, the value is 128.
•Port Path Cost. Set the path cost to a new value for the specified port in the selected
MST instance. Specify a value in the range of 0–200000000. By default, the value
is 0.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
11. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
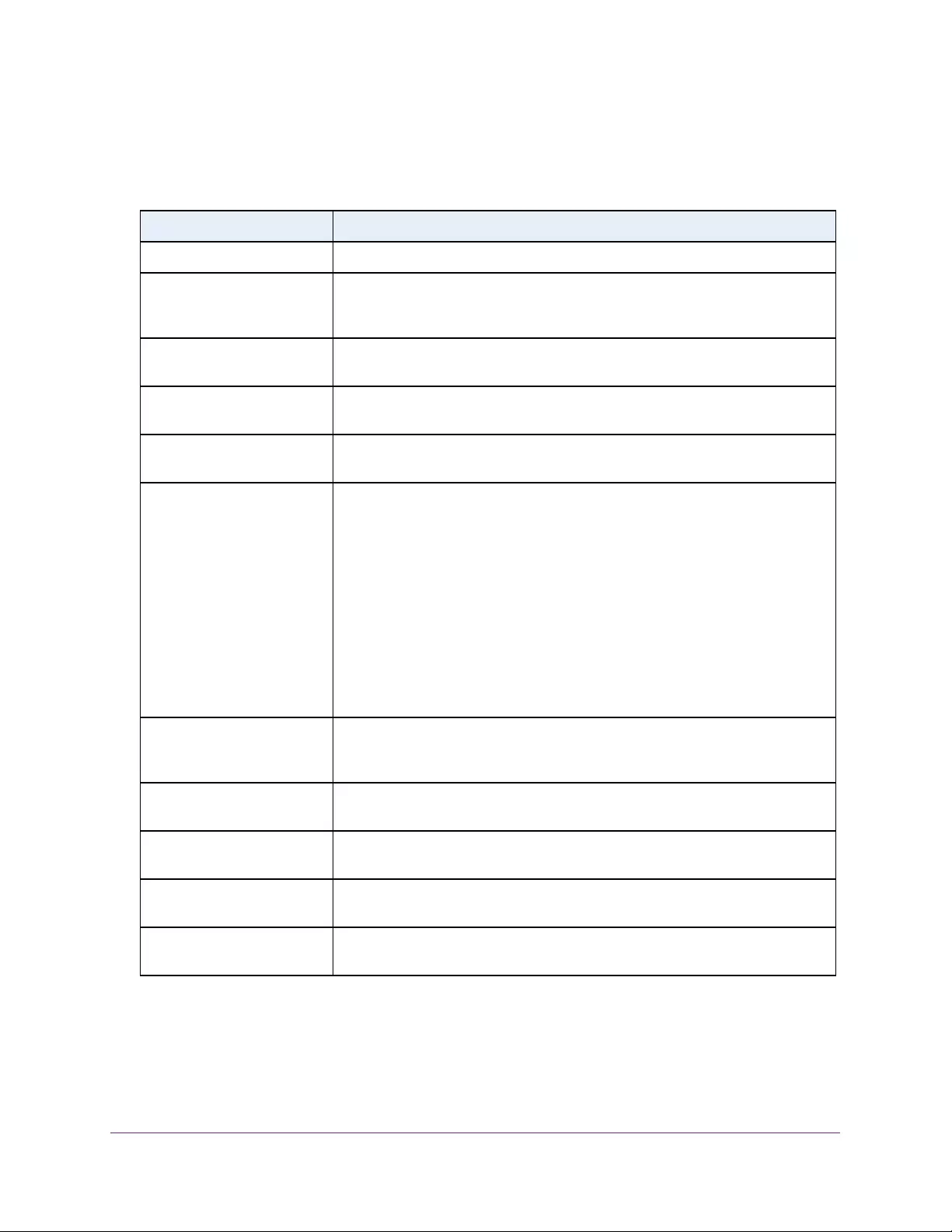
Configure Switching
146
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the read-only MST port configuration information displayed on
the Spanning Tree CST Configuration page.
Table 38. MST port status information
Field Description
Operational Port Path Cost The operational path cost for the port in the MST instance.
Auto-calculated Port Path
Cost Indicates whether the path cost is automatically calculated (Enabled) or not
(Disabled). If the configured value for the port path cost is zero, the path cost is
calculated based on the link speed of the port.
Port ID The port identifier for the specified port within the selected MST instance. It is
made up from the port priority and the interface number of the port.
Port Up Time Since Counters
Last Cleared The time since the counters were last cleared, displayed in days, hours,
minutes, and seconds.
Port Mode The Spanning T ree Protocol administrative mode that is associated with the port
or port channel. The possible values are Enable and Disable.
Port Forwarding State Indicates the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines
what forwarding action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are as follows:
• Disabled. STP is currently disabled on the port. The port forwards traffic
while learning MAC addresses.
• Blocking. The port is currently blocked and cannot be used to forward
traffic or learn MAC addresses.
• Listening. The port is currently in the listening mode. The port cannot
forward traffic nor can it learn MAC addresses.
• Learning. The port is currently in the learning mode. The port cannot
forward traffic. However, it can learn new MAC addresses.
• Forwarding. The port is currently in the forwarding mode. The port can
forward traffic and learn new MAC addresses
Port Role Each MST bridge port that is enabled is assigned a port role for each spanning
tree. The port role is one of the following: Root Port, Designated Port, Alternate
Port, Backup Port, Master Port, or Disabled Port.
Designated Root The root bridge for the selected MST instance. It is made up using the bridge
priority and the base MAC address of the bridge.
Designated Cost The cost of the port participating in the STP topology. Ports with a lower cost are
less likely to be blocked if STP detects loops.
Designated Bridge The bridge identifier of the bridge with the designated port. It is made up using
the bridge priority and the base MAC address of the bridge.
Designated Port The port identifier on the designated bridge that offers the lowest cost to the
LAN. It is made up from the port priority and the interface number of the port.
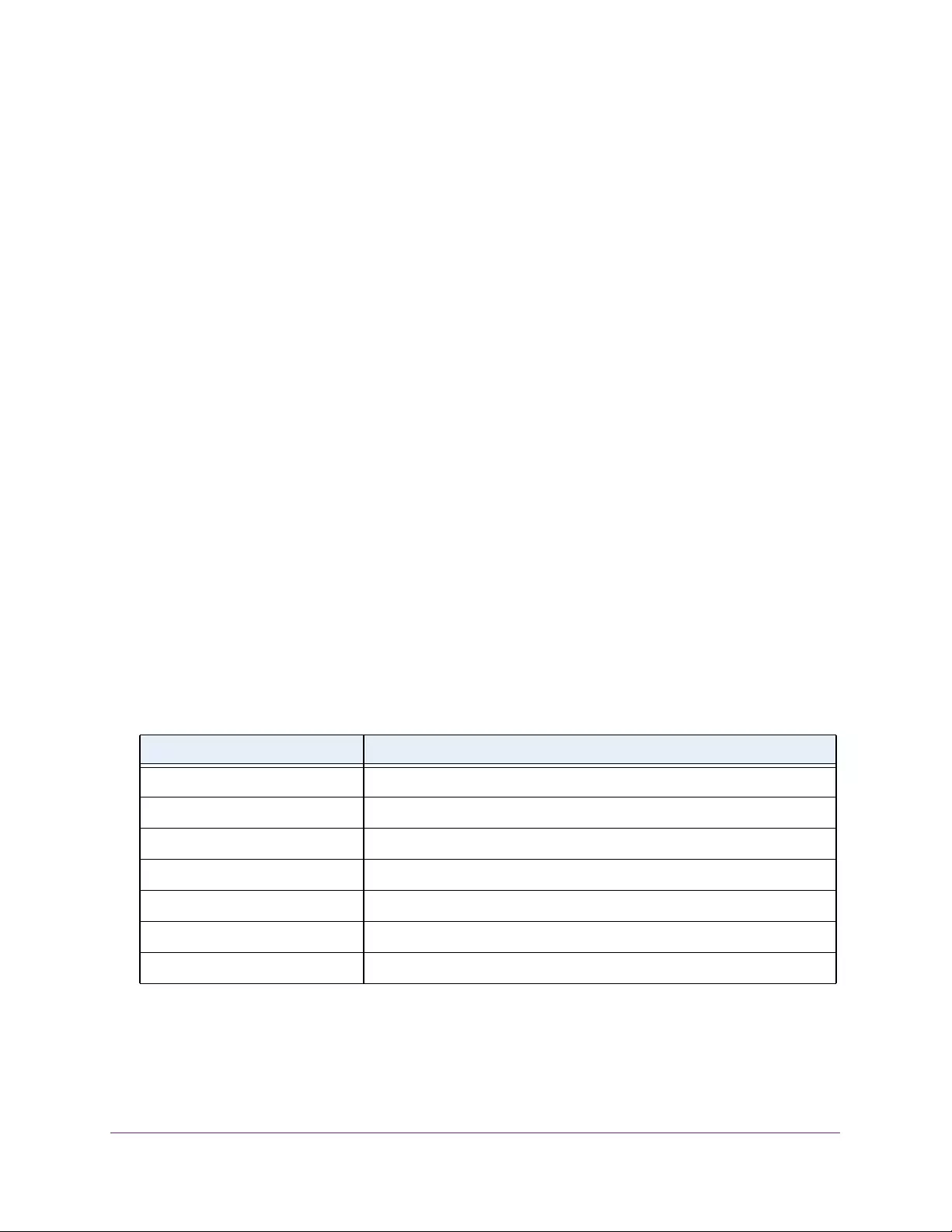
Configure Switching
147
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View STP Statistics
You can view information about the number and type of bridge protocol data units (BPDUs)
transmitted and received on each port.
To view Spanning Tree statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > STP > Advanced > STP Statistics.
The STP Statistics page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the information available about the STP Statistics page.
Table 39. STP Statistics
Field Description
Interface The physical or port channel interfaces of the switch.
STP BPDUs Received The number of STP BPDUs received at the port.
STP BPDUs Transmitted The number of STP BPDUs transmitted from the port.
RSTP BPDUs Received The number of RSTP BPDUs received at the port.
RSTP BPDUs Transmitted The number of RSTP BPDUs transmitted from the port.
MSTP BPDUs Received The number of MSTP BPDUs received at the port.
MSTP BPDUs Transmitted The number of MSTP BPDUs transmitted from the port.

Configure Switching
148
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Multicast
Multicast IP traffic is traf fic that is destined to a host group. Host groups for IPv4 multicast are
identified by class D addresses, which range from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. Host groups
for IPv6 multicast are identified by the prefix ff00::/8.
View or Clear the MFDB Table
The Multicast Forwarding Database holds the port membership information for all active
multicast address entries. The key for an entry consists of a VLAN ID and MAC address pair.
Entries can contain data for more than one protocol.
To view or clear the MFDB Table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Multicast > MFDB > MFDB Table.
The MFDB Table page displays.
6. In the Search by MAC Address field, enter a MAC address.
Enter six two-digit hexadecimal numbers separated by colons, for example
00:01:23:43:45:67.
7. Click the Go button.
If the address exists, the entry is displayed. An exact match is required.
8. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
9. To clear the information, click the Clear button.
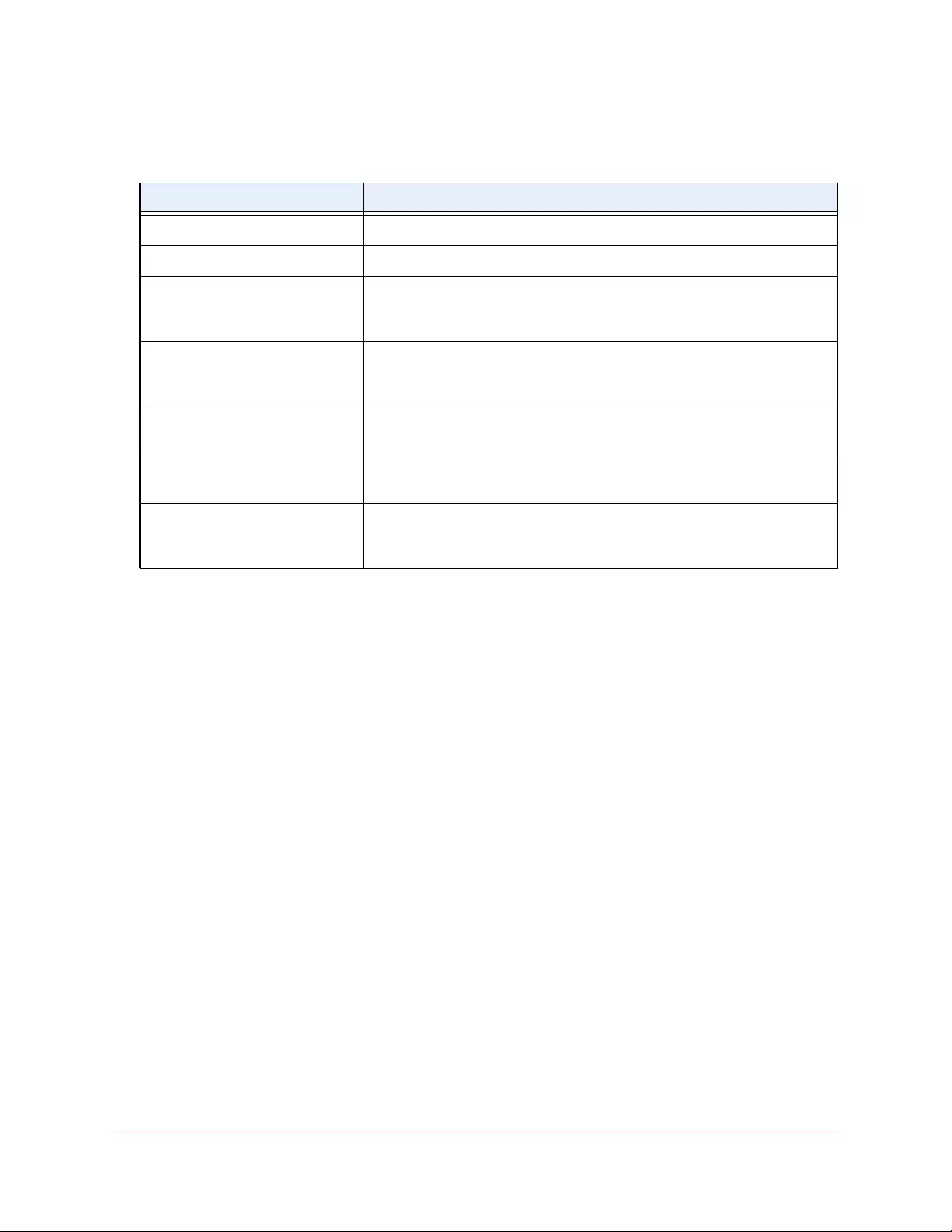
Configure Switching
149
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the information in the MFDB table.
View the MFDB Statistics
To view the MFDB statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Multicast > MFDB > MFDB Statistics.
The MFDB Statistics page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
Table 40. MFDB table information
Field Description
MAC Address The multicast MAC address for which you requested data.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID to which the multicast MAC address is related.
Component The component that is responsible for this entry in the Multicast Forwarding
Database. Possible values are IGMP snooping, GMRP, Static Filtering and
MLD snooping.
T ype The type of the entry. Static entries are those that are configured by the end
user. Dynamic entries are added to the table as a result of a learning
process or protocol.
Description The text description of this multicast table entry. Possible values are
Management Configured, Network Configured, and Network Assisted.
Interfaces The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:) and filtering
(Flt:) for the selected address.
Forwarding Interfaces The list of forwarding interfaces. This list is derived from combining all
forwarding interfaces and removing the interfaces that are listed as static
filtering interfaces.
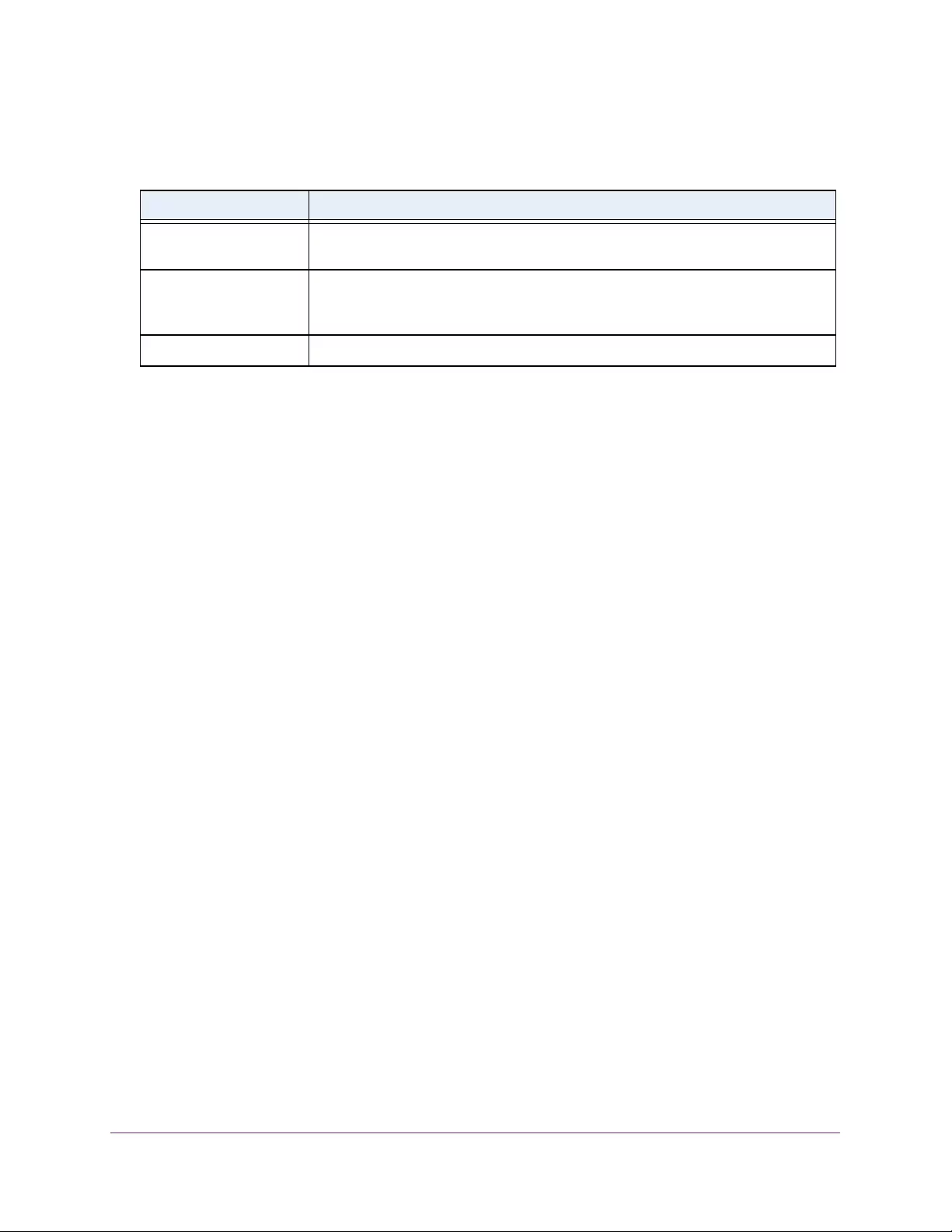
Configure Switching
150
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the MFDB Statistics fields.
Configure the Auto-Video Settings
You can configure the auto-video settings for multicast traffic.
To the configure auto-video settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > Auto-Video.
The Auto-Video Configuration page displays.
6. Select one of the following radio buttons:
•Select the Disable radio button to globally disable the Auto-Video mode for the
switch.
•Select the Enable radio button to globally enable the Auto-Video mode for the switch.
The Auto-Video VLAN field shows the ID for the Auto-Video VLAN. By default, the VLAN
ID is 4089.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Table 41. MFDB Statistics information
Field Description
Max MFDB Table Entries The maximum number of entries that the Multicast Forwarding Database table can
hold.
Most MFDB Entries Since
Last Reset The largest number of entries that were present in the Multicast Forwarding
Database table since last reset. This value is also known as the MFDB high-water
mark.
Current Entries The current number of entries in the Multicast Forwarding Database table.

Configure Switching
151
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure IGMP Snooping
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping is a feature that allows a switch to
forward multicast traffic intelligently. Multicast IP traffic is traffic that is destined to a host
group. Host groups are identified by class D IP addresses, which range from 224.0.0.0 to
239.255.255.255. Based on the IGMP query and report messages, the switch forwards traffic
only to the ports that request the multicast traffic. This prevents the switch from broadcasting
the traffic to all ports and possibly affecting network performance.
IGMP Snooping Overview
A traditional Ethernet network can be separated into different network segments to prevent
placing too many devices onto the same shared media. Bridges and switches connect these
segments. When a packet with a broadcast or multicast destination address is received, the
switch forwards a copy to each of the remaining network segments in accordance with the
IEEE MAC Bridge standard. Eventually, the packet is made accessible to all nodes
connected to the network.
This approach works well for broadcast packets that are intended to be seen or processed by
all connected nodes. In the case of multicast packets, however, this approach could lead to
less efficient use of network bandwidth, particularly when the packet is intended for only a
small number of nodes. Packets are flooded into network segments where no node is
receptive to the packet. While nodes rarely incur any processing overhead to filter packets
addressed to unrequested group addresses, they cannot transmit new packets onto the
shared media for the period of time that the multicast packet is flooded. The problem of
wasting bandwidth is even worse when the LAN segment is not shared, for example in
full-duplex links.
Allowing switches to snoop IGMP packets is a creative effort to solve this problem. The
switch uses the information in the IGMP packets as they are being forwarded throughout the
network to determine which segments receive packets directed to the group address.
In addition to building and maintaining lists of multicast group memberships, the IGMP
snooping switch also maintains a list of multicast routers. Multicast packets are forwarded on
ports to which multicast routers are connected. With IGMP snooping, only one querier can be
active in the network. All other routers in the network are suppressed and are not detectable
by the switch. If a query is not received on an interface within a specified period, the interface
is removed from the list of interfaces to which multicast routers are attached. However, by
default, the multicast router expiration time is zero, that is, the multicast router does not
expire.
A statically configured router that is connected to an interface or VLAN on the switch is
automatically added to the list with learned multicast routers. The interface must be active or
must be both active and a member of the VLAN.

Configure Switching
152
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure IGMP Snooping Globally
You can configure the parameters for IGMP snooping, which is used to build forwarding lists
for multicast traffic.
To configure IGMP snooping globally:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Configuration.
The IGMP Snooping Configuration page displays.
6. Select the IGMP Snooping Status Enable or Disable radio button.
This specifies whether IGMP snooping is enabled for the switch. The default is Enable.
7. Select the Validate IGMP IP header Enable or Disable radio button.
When IGMP IP header validation is enabled, any IGMP IP header must include the
Router Alert, ToS, and TTL information. Otherwise, the IGMP packet is discarded. The
default value is Enable.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
9. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table displays information about the global IGMP snooping status and statistics
on the page.
Table 42. IGMP Snooping Configuration information
Field Description
Multicast Control Frame Count The number of multicast control frames that are processed by the CPU.
Interfaces Enabled for IGMP
Snooping The interfaces that are enabled for IGMP snooping.
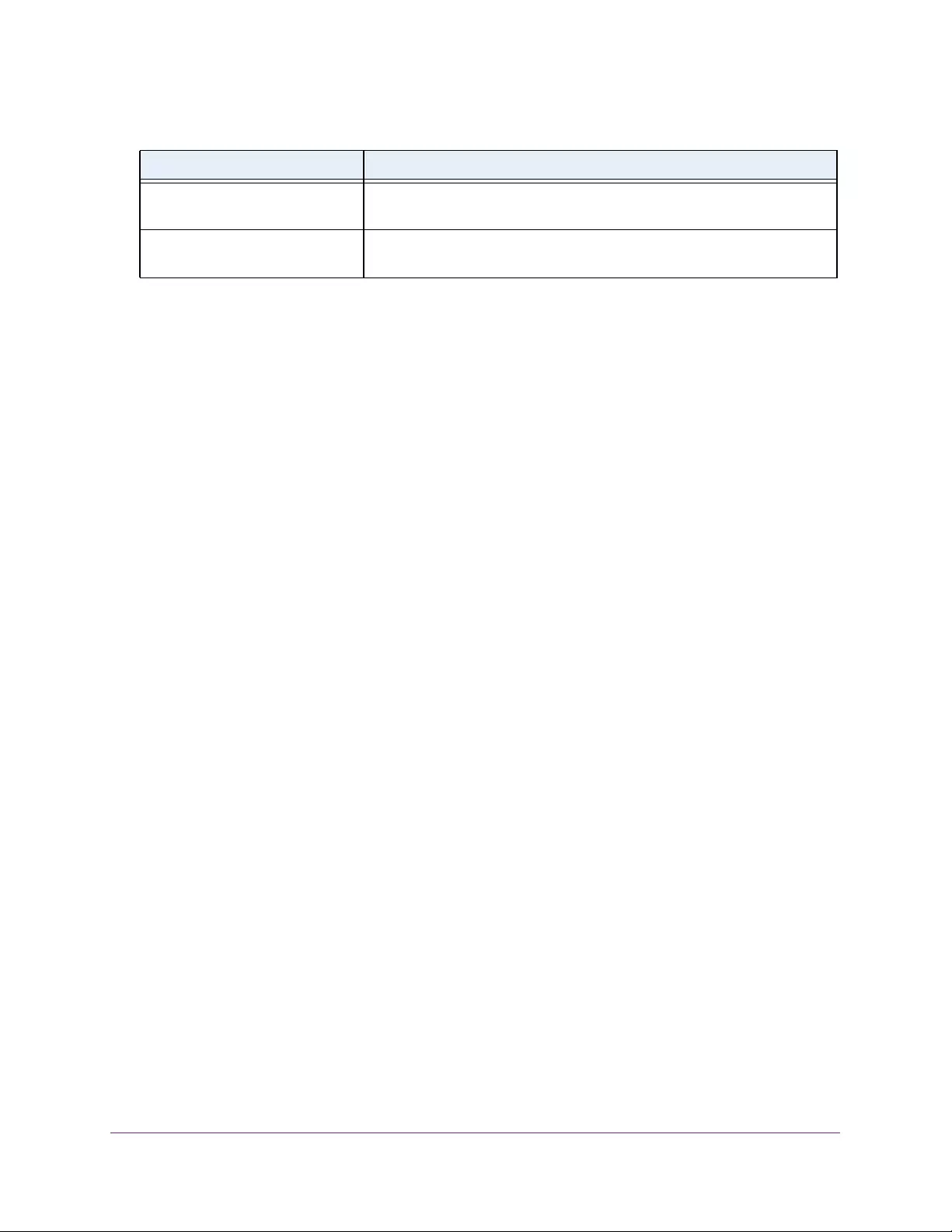
Configure Switching
153
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure IGMP Snooping for Interfaces
To configure IGMP snooping for interfaces:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Interface
Configuration.
The IGMP Snooping Interface Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Admin Mode menu, select Disable or Enable.
This specifies the interface mode for the selected interface for IGMP snooping for the
switch. The default is Disable.
9. In the Host Timeout field, specify the time that the switch must wait for a report for a
particular group on a particular interface before it deletes that interface from the group.
VLAN IDs Enabled For IGMP
Snooping The IDs of the VLANs that are enabled for IGMP snooping.
VLAN IDs Enabled For IGMP
Snooping Querier The IDs of the VLANs that are enabled for IGMP snooping querier.
Table 42. IGMP Snooping Configuration information (continued)
Field Description

Configure Switching
154
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Enter a value between 1 and 3600 seconds. The default is 260 seconds.
10. In the Max Response Time field, specify the time that the switch must wait after sending a
query on an interface because it did not receive a report for a particular group on that
interface.
Enter a value greater or equal to 1 and less than the group membership interval in
seconds. The default is 10 seconds. The configured value must be less than the group
membership interval.
11. In the MRouter Timeout field, specify the time that the switch must wait to receive a query
on an interface before removing it from the list of interfaces with multicast routers attached.
Enter a value between 0 and 3600 seconds. The default is 0 seconds. A value of zero
indicates an infinite time-out, that is, no expiration.
12. From the Fast Leave Mode menu, select whether fast leave mode is enabled.
The option are Enable and Disable. The default is Disable.
13. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
View the IGMP Snooping Table
You can view all of the entries in the Multicast Forwarding Database that were created for
IGMP snooping.
To view the entries in the IGMP snooping table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Table.
The IGMP Snooping Table page displays.
6. In the Search By MAC Address field, specify the MAC address whose MFDB table entry
you want to view.
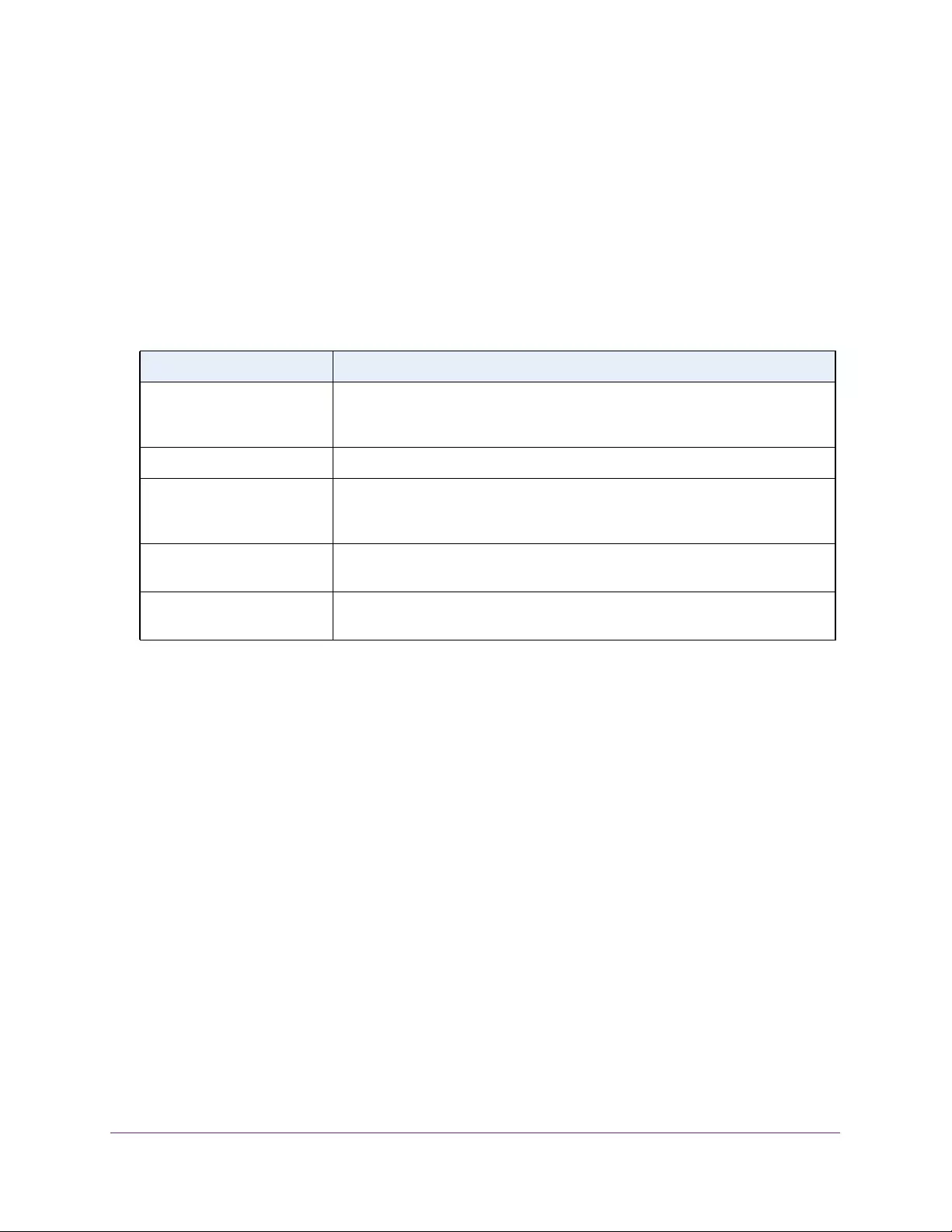
Configure Switching
155
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Enter six two-digit hexadecimal numbers separated by colons, for example
00:01:23:43:45:67.
7. Click the Go button.
If the address exists, the entry is displayed. An exact match is required.
8. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
9. To clear the information, click the Clear button.
The following table describes the information in the IGMP snooping table.
Configure IGMP Snooping for VLANs
To configure IGMP snooping settings for VLANs:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration.
Table 43. IGMP Snooping Table information
Field Description
MAC Address The multicast MAC address for which the switch holds forwarding and/or filtering
information. The format is six two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated
by colons, for example, 01:00:5e:45:67:89.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID for which the switch holds forwarding and filtering information.
Type The type of the entry. Static entries are those that are configured by the end
user. Dynamic entries are added to the table as a result of a learning process or
protocol.
Description The text description of this multicast table entry. Possible values are
Management Configured, Network Configured, and Network Assisted.
Interface The interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd) and filtering (Flt) for the
associated address.

Configure Switching
156
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. To enable IGMP snooping on a VLAN, in the VLAN ID field, enter the VLAN ID.
7. Configure the IGMP snooping values:
•Admin Mode. Enable or disable IGMP snooping for the specified VLAN ID. The
default is Disable.
•Fast Leave Mode. Enable or disable the IGMP snooping fast leave mode for the
specified VLAN ID. The default is Disable.
•Host Timeout. Set the value for group membership interval of IGMP snooping for the
specified VLAN ID. The valid range is Maximum Response Time + 1 to 3600 seconds.
•Maximum Response Time. Set the value for the maximum response time of IGMP
snooping for the specified VLAN ID. The valid range is 1 to Group Membership
Interval –1. This value must be greater than group membership interval value.
•MRouter Timeout. Set the value for multicast router expiry time of IGMP snooping for
the specified VLAN ID. The valid range is 0 to 3600 seconds.
•Report Suppression Mode. Enable or disable IGMP snooping report suppression
mode for the specified VLAN ID. IGMP snooping report suppression allows the
suppression of the IGMP reports sent by the multicast hosts by building a Layer 3
membership table. The results is that only the most essential reports are sent to the
IGMP routers so that the routers can continue to receive the multicast traffic.The
default is Disable.
•Querier Mode. Enable or disable the IGMP querier mode. If proxy querier mode is
disabled, then an IGMP proxy query with source IP 0.0.0.0 is not sent in response to
an IGMP leave packet. The default is Disable.
•Query Interval. Set the IGMP query interval for the specified VLAN ID. The valid
range is 1 to 1800 seconds. The default is 60 seconds.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Modify IGMP Snooping Settings for a VLAN
To modify IGMP snooping settings for a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Configure Switching
157
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration.
The IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the VLAN ID.
7. Update the values.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Disable IGMP Snooping on a VLAN
To disable IGMP snooping on a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration.
The IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the VLAN ID.
7. Click the Delete button.
Snooping is disabled on the VLAN and the VLAN is removed from the table.
Configure Multicast Router Interfaces for IGMP Snooping
You can configure an interface as the designated interface to which a multicast router is
attached. All IGMP packets snooped by the switch are forwarded to the multicast router
reachable from this interface. Configuring a multicast router interface is usually not required
because the switch automatically detects the multicast router and forwards IGMP packets

Configure Switching
158
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
accordingly. It is required only if you want to make sure that the multicast router always
receives IGMP packets from the switch in a complex network.
To configure multicast router interfaces:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping > Multicast Router Configuration.
The Multicast Router Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. In the Multicast Router field, select Enable or Disable.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure a Multicast Router VLAN for IGMP Snooping
You can configure an interface to forward snooped IGMP packets only from a specific VLAN
to the multicast router that is attached to the interface. This configuration is usually not
required because the switch automatically detects a multicast router and forwards the IGMP
packets accordingly. However , in a complex network, it might be required if you want to make
sure that the multicast router always receives IGMP packets from the switch.

Configure Switching
159
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To configure a multicast router VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping > Multicast Router VLAN
Configuration.
The Multicast Router VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface.
7. In the VLAN ID field, enter the VLAN ID.
8. From the Multicast Router menu, select Enable or Disable.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure an IGMP Snooping Querier
An IGMP snooping querier is a device that queries devices on the network for multicast
membership.
IGMP Snooping Querier Overview
IGMP snooping requires that one central switch or router periodically query all end-devices
on the network to announce their multicast memberships. This central device is the IGMP
querier. The IGMP query responses, known as IGMP reports, keep the switch updated with
the current multicast group membership on a port-by-port basis. If the switch does not
receive updated membership information in a timely fashion, it stops forwarding multicasts to
the port where the end device is located.
You can configure and display information about IGMP snooping queriers on the network
and, separately, on VLANs.

Configure Switching
160
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure the Global IGMP Snooping Querier Settings
You can configure the global settings for an IGMP snooping querier.
To configure the global IGMP snooping querier settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping Querier > Querier Configuration.
The Querier Configuration page displays.
6. Configure the following settings:
•Querier Admin Mode. Enable or disable IGMP snooping for the switch. The default is
Enable.
•Snooping Querier Address. Enter the snooping querier IP address to be used as
the source address in periodic IGMP queries. This address is used when no address
is configured on the VLAN on which a query is being sent.
•IGMP Version. Specify the IGMP protocol version used in periodic IGMP queries.
The range is 1 to 2. The default value is 2.
•Query Interval(secs). Specify the time interval in seconds between periodic queries
sent by the snooping querier. The query interval must be a value in the range of 1 and
1800. The default value is 60.
•Querier Expiry Interval(secs). Specify the time interval in seconds after which the
last querier information is removed. The querier expiry Interval must be a value in the
range of 60 and 300. The default value is 125.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
8. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The page lists the VLAN IDs for the VLANs on which the IGMP snooping querier feature
is enabled.

Configure Switching
161
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure an IGMP Snooping Querier for a VLAN
You can configure an IGMP snooping querier for use with a VLAN on the network.
To configure an IGMP querier snooping for a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping Querier > Querier VLAN Configuration.
The Querier VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. From the VLAN ID menu, select New Entry.
7. Configure the following settings:
•VLAN ID. The VLAN ID for which the IGMP snooping querier is to be enabled.
•Querier Election Participate Mode. Enable or disable querier this mode:
-Disable. Upon seeing another querier of the same version in the VLAN, the
snooping querier moves to the non-querier state.
-Enable. The snooping querier participates in querier election, in which the lowest
IP address operates as the querier in that VLAN. The other querier moves to
non-querier state.
•Snooping Querier VLAN Address. Specify the snooping querier IP address to be
used as the source address in periodic IGMP queries sent on the specified VLAN.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure Switching
162
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Remove an IGMP Snooping Querier From a VLAN
You can remove an IGMP snooping querier from a VLAN.
To remove an IGMP snooping querier from a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping Querier > Querier VLAN Configuration.
The Querier VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. From the VLAN ID menu, select the VLAN ID.
7. Click the Delete button.
Your settings are saved. The IGMP snooping querier is no longer supported on the VLAN.
The VLAN itself is not deleted.
Display the IGMP Snooping Querier Status for VLANs
To display the IGMP snooping querier status for VLANs:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
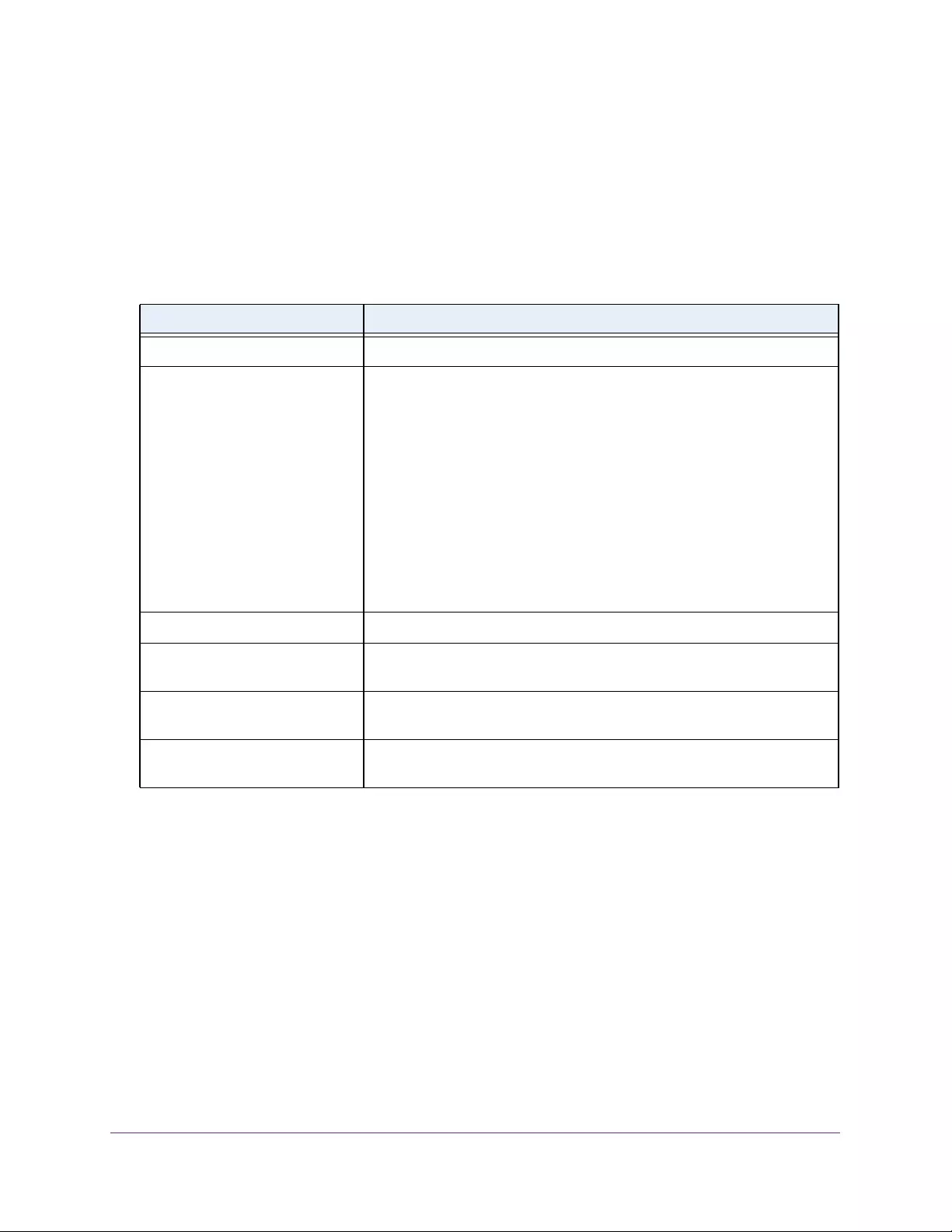
Configure Switching
163
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > IGMP Snooping Querier > Querier VLAN Status.
The Querier VLAN Status page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Configure MLD Snooping
In IPv4, Layer 2 switches can use IGMP snooping to limit the flooding of multicast traffic by
dynamically configuring Layer 2 interfaces so that multicast traffic is forwarded to only those
interfaces associated with IP multicast address. In IPv6, MLD snooping performs a similar
function. With MLD snooping, IPv6 multicast data is selectively forwarded to a list of ports
that want to receive the data, instead of being flooded to all ports in a VLAN. This list is
constructed by snooping IPv6 multicast control packets.
MLD Snooping Overview
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) is a protocol used by IPv6 multicast routers to discover
the presence of multicast listeners (nodes that must receive IPv6 multicast packets) on its
directly attached links and to discover which multicast packets are of interest to neighboring
Table 44. Querier VLAN Status information
Field Description
VLAN ID The VLAN ID on which IGMP snooping querier is enabled.
Operational State The operational state of the IGMP snooping querier on a VLAN. It can be in
any of the following states:
• Querier. The snooping switch is the querier in the VLAN. The snooping
switch sends out periodic queries with a time interval equal to the
configured querier query interval. If the snooping switch finds a better
querier in the VLAN, it moves to non-querier mode.
• Non-Querier. The snooping switch is in non-querier mode in the VLAN.
If the querier expiry interval timer expires, the snooping switch moves
into querier mode.
• Disabled. The snooping querier is not operational on the VLAN. The
snooping querier moves to disabled mode when IGMP snooping is not
operational on the VLAN or when the querier address is not configured
or the network management address is also not configured.
Operational Version The operational IGMP protocol version of the querier.
Last Querier Address The IP address of the last querier from which a query was snooped on the
VLAN.
Last Querier Version The IGMP protocol version of the last querier from which a query was
snooped on the VLAN.
Operational Max Response Time The maximum response time to be used in the queries that are sent by the
snooping querier.

Configure Switching
164
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
nodes. MLD is derived from IGMP; MLD version 1 (MLDv1) is equivalent to IGMPv2 and MLD
version 2 (MLDv2) is equivalent to IGMPv3. MLD is a subprotocol of Internet Control
Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6), and MLD messages are a subset of ICMPv6
messages, identified in IPv6 packets by a preceding Next Header value of 58.
The switch can snoop on both MLDv1 and MLDv2 protocol packets and bridge IPv6 multicast
data based on destination IPv6 Multicast MAC Addresses. The switch can be configured to
perform MLD snooping and IGMP snooping simultaneously.
In addition to building and maintaining lists of multicast group memberships, the MLD
snooping switch also maintains a list of multicast routers. Multicast packets are forwarded on
ports to which multicast routers are connected. With MLD snooping, only one querier can be
active in the network. All other routers in the network are suppressed and are not detectable
by the switch. If a query is not received on an interface within a specified period, the interface
is removed from the list of interfaces to which multicast routers are attached. However, by
default, the multicast router expiration time is zero, that is, the multicast router does not
expire.
A statically configured router that is connected to an interface or VLAN on the switch is
automatically added to the list with learned multicast routers. The interface must be active or
must be both active and a member of the VLAN.
Enable MLD Snooping
You can enable MLD snooping.
To enable MLD snooping:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > Configuration.
The MLD Snooping Configuration page displays.
6. Select the MLD Snooping Admin Mode Enable radio button.
By default, the Enable radio button is selected.

Configure Switching
165
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
8. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable MLD Snooping Configuration fields.
Configure an MLD Snooping Interface
To configure an MLD snooping interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > Interface Configuration.
The MLD Snooping Interface Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
Table 45. MLD Snooping Configuration information
Field Definition
Multicast Control Frame Count The number of multicast control frames that were processed by the CPU.
Interfaces Enabled for MLD
Snooping The interfaces on which MLD snooping is administratively enabled. MLD
snooping must be enabled globally and on an interface for the interface to
be able to snoop MLD packets to determine which segments must receive
multicast packets directed to the group address.
VLAN IDs Enabled For MLD
Snooping The VLANs on which MLD snooping is administratively enabled.

Configure Switching
166
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Admin Mode menu, select to enable or disable the interface mode for the
selected interface for MLD snooping for the switch.
The default is Disable.
9. In the Membership Interval field, specify the time that the switch must wait for a report for a
particular group on a particular interface before it deletes that interface from the group.
The valid range is from 2 to 3600 seconds. The configured value must be greater than the
maximum response time. The default is 260 seconds.
10. In the Max Response T ime in seconds field, specify the time that the switch must wait after
sending a query on an interface because it did not receive a report for a particular group on
that interface.
Enter a value greater than or equal to 1 and less than the group membership interval in
seconds. The default is 10 seconds. The configured value must be less than the group
membership interval.
11. In the Expiration Time field, specify the time that the switch must wait to receive a query on
an interface before removing the interface from the list of interfaces with multicast routers
attached.
Enter a value between 0 and 3600 seconds. The default is 0 seconds. A value of zero
indicates an infinite time-out, that is, no expiration.
12. From the Fast Leave menu, select to enable or disable Fast Leave on the interface.
If Fast Leave is enabled, the interface can be immediately removed from the Layer 2
forwarding table when the switch receives an MLD leave message for a multicast group
without first sending MAC-based general queries. The default is Disable.
13. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure MLD Snooping for VLANs
To configure MLD snooping for a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Configure Switching
167
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > MLD VLAN Configuration.
The MLD VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. In the VLAN ID field, specify the VLAN IDs for which MLD snooping must be enabled.
7. From the Fast Leave menu, select to enable or disable the MLD snooping Fast Leave
mode for the specified VLAN ID.
8. In the Membership Interval field, set the value for the group membership interval of MLD
snooping for the specified VLAN ID.
The valid range is Maximum Response Time + 1 to 3600.
9. In the Maximum Response Time field, set the value for the maximum response time of
MLD snooping for the specified VLAN ID.
The valid range is 1 to Group Membership Interval –1. This value must be less than the
group membership interval value.
10. In the Multicast Router Expiry Time field, set the value for the multicast router expiry time
of MLD snooping for the specified VLAN ID.
The valid range is 0 to 3600.
11. Click the Add button.
MLD snooping is enabled on the specified VLAN.
Remove MLD Snooping From a VLAN
You can remove MLD snooping from a VLAN.
To remove MLD snooping from a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.

Configure Switching
168
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > MLD VLAN Configuration.
The MLD VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box for the VLAN ID.
7. Click the Delete button.
Your settings are saved. MLD snooping is no longer supported on the VLAN. The VLAN
itself is not deleted.
Configure a Multicast Router Interface for MLD Snooping
To configure a multicast router interface for MLD snooping:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > Multicast Router Configuration.
The Multicast Router Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Multicast Router menu, select to enable or disable the multicast router for the
selected interfaces.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure Switching
169
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure a Multicast Router VLAN for MLD Snooping
To configure a multicast router VLAN for MLD snooping:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > Multicast Router VLAN Configuration.
The Multicast Router VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface for which you want the multicast router to be
enabled.
7. In the VLAN ID field, specify the VLAN ID.
8. From the Multicast Router menu, select to enable or disable the multicast router for the
VLAN.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure an MLD Snooping Querier
You can configure the settings for an MLD snooping querier.
To configure an MLD snooping querier:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Configure Switching
170
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > Querier Configuration.
The MLD Snooping Querier Configuration page displays.
6. Configure the following settings:
•Querier Admin Mode. Enable or disable MLD snooping for the switch. The default is
Disable.
•Querier Address. Enter an IP address. This specifies the snooping querier address
to be used as the source address in periodic MLD queries. This address is used when
no address is configured on the VLAN on which a query is being sent. The supported
IPv6 formats are x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x and x::x.
•MLD Version. The MLD protocol used in periodic MLD queries is version 1. This
value is not configurable.
•Query Interval (secs). Specify the interval in seconds between periodic queries sent
by the snooping querier. The query interval must be a value in the range of 1 to 1800.
The default value is 60.
•Querier Expiry Interval (secs). Specify the interval in seconds after which the last
querier information is removed. The querier expiry interval must be a value in the
range of 60 to 300. The default value is 60.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The page displays the IDs of the VLANS for which the MLD snooping querier is enabled.
Configure an MLD Snooping Querier for a VLAN
You can configure an MLD snooping querier for use with a VLAN on the network.
To configure an MLD snooping querier for a VLAN
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Configure Switching
171
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > Querier VLAN Configuration.
The MLD Snooping Querier VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. In the VLAN ID field, specify the VLAN ID on which the MLD snooping querier must be
enabled and for which a VLAN exists in the VLAN database.
7. From the Querier Election Participate Mode menu, select to enable or disable the querier
participation election mode for MLD snooping.
When this mode is disabled, on detecting another querier of same version in the VLAN,
the snooping querier moves to a non-querier state. When this mode is enabled, the
snooping querier participates in querier election where the lowest IP address wins the
querier election and operates as the querier in that VLAN. The other querier moves to
non-querier state.
8. In the Querier VLAN Address field, specify the snooping querier address to be used as the
source address in periodic MLD queries sent on the specified VLAN.
9. Click the Add button.
Your settings are saved and the MLD snooping querier is added on the VLAN.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Table 46. MLD Snooping Querier VLAN Configuration information
Field Description
Operational State The operational state of the MLD snooping querier on a VLAN. It can be in any of the
following states:
• Querier. Snooping switch is the querier in the VLAN. The snooping switch sends
out periodic queries with a time interval equal to the configured querier query
interval. If the snooping switch sees a better querier in the VLAN, it moves to
non-querier mode.
• Non-Querier. Snooping switch is in non-querier mode in the VLAN. If the querier
expiry interval timer is expired, the snooping switch moves into querier mode.
• Disabled. Snooping querier is not operational on the VLAN. The snooping querier
moves to disabled mode when MLD snooping is not operational on the VLAN or
when the querier address is not configured or the network management address is
also not configured.
Operational Version The operational MLD protocol version of the querier.
Last Querier Address The IP address of the last querier from which a query was snooped on the VLAN.
Last Querier Version The MLD protocol version of the last querier from which a query was snooped on the
VLAN.
Operational Max
Response T ime The maximum response time to be used in the queries that are sent by the snooping
querier.

Configure Switching
172
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Remove an MLD Snooping Querier From a VLAN
You can remove an MLD snooping querier from a VLAN.
To remove an MLD snooping querier from a VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching> Multicast > MLD Snooping > Querier VLAN Configuration.
The MLD Snooping Querier VLAN Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box for the VLAN ID.
7. Click the Delete button.
Your settings are saved. The MLD snooping querier is no longer supported on the VLAN.
The VLAN itself is not deleted.
View, Search, and Configure the MAC Address Table
You can view or configure the MAC address table. This table contains information about
unicast entries for which the switch holds forwarding or filtering information. The transparent
bridging function uses the forwarding database entries to determine how to forward an
incoming frame.
View and Search the MAC Address Table
You can use the search function for the MAC address table to display information about the
entries in the table.
To view and search the MAC address table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.

Configure Switching
173
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Address Table > Basic > Address Table.
The MAC Address Table page displays.
6. Use the Search menu and field to search for a MAC address, VLAN ID, or interface number
and display the information:
•Search by MAC Address. From the Search menu, select MAC Address, and enter
the 6-byte hexadecimal MAC address in two-digit groups separated by colons, for
example, 01:23:45:67:89:AB. Then click the Go button.
If the address exists, that entry is displayed as the first entry followed by the
remaining (higher) MAC addresses. An exact match is required.
•Search by VLAN ID. From the Search menu, select VLAN ID, and enter the VLAN ID,
for example, 100. Then click the Go button.
•Search by Interface. From the Search menu, select Interface, and enter the
interface ID using the respective interface naming convention (for example, g1 or l1).
Then click the Go button.
7. To refresh the information on the page, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Table 47. MAC Address Table information
Field Description
Total MAC Address The number of total MAC addresses learned or configured.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID associated with the MAC address.
MAC Address The unicast MAC address for which the switch holds forwarding, filtering information, or
both. The format is a 6-byte MAC address that is separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB.

Configure Switching
174
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Set the Dynamic Address Aging Interval
You can set the address aging interval for the specified forwarding database.
To set the address aging interval:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Address Table > Advanced > Dynamic Address.
The Dynamic Address page displays.
6. In the Address Aging T imeout (seconds) field, specify the time-out period in seconds for
aging out dynamically learned forwarding information.
The value can be any number between 10 and 1000000 seconds. The default is 300.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Interface The interface on which the address was learned.
Status The status of this entry, which can be one of the following:
• Static. The instance was added by the system or a user and cannot be relearned.
• Learned. The instance was learned, and is being used.
• Management. The value of the corresponding instance for the system MAC
address is also the value of an existing instance for dot1dStaticAddress.
Table 47. MAC Address Table information (continued)
Field Description

Configure Switching
175
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Add a Static MAC Address
You can manually add MAC addresses to the MAC address table. Such MAC addresses are
static MAC addresses.
To add a static MAC address:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Address Table > Advanced > Static MAC Address.
The page displays the Port List section and the Static MAC ADdress Table section.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface.
7. In the Static MAC Address field, enter the MAC address.
8. From the VLAN ID menu, select the VLAN ID that must be associated with the MAC
address.
9. Click the Add button.
The static MAC address is added to the MAC address table.
Remove a Static MAC Address
You can manually remove static MAC addresses from the MAC address table.
To add a static MAC address:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.

Configure Switching
176
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > Address Table > Advanced > Static MAC Address.
The page displays the Port List section and the Static MAC ADdress Table section.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface.
7. Select the check box for the static MAC address.
You can select multiple MAC addresses.
8. Click the Delete button.
The static MAC address is removed from the MAC address table.
Configure Layer 2 Loop Protection
Loops inside a network are costly because they consume resources and reduce the
performance of the network. Detecting loops manually can be cumbersome.
The switch can automatically identify loops in the network. You can enable loop protection
per port or globally.
If loop protection is enabled, the switch sends predefined PDU packets to a Layer 2 multicast
destination address (09:00:09:09:13:A6) on all ports for which the feature is enabled. You can
selectively disable PDU packet transmission for loop protection on specific ports even while
port loop protection is enabled. If the switch receives a packet with the previously mentioned
multicast destination address, the source MAC address in the packet is compared with the
MAC address of the switch. If the MAC address does not match, the packet is forwarded to all
ports that are members of the same VLAN, just like any other multicast packet. The packet is
not forwarded to the port from which it was received.
If the source MAC address matches the MAC address of the switch, the switch can perform
one of the following actions, depending on how you configure the action:
•The port is shut down.
•A log message is generated. (If a syslog server is configured, the log message can be
sent to the syslog server.)
•The port is shut down and a log message is generated.
If loop protection is disabled, the multicast packet is silently dropped.
Loop protection is not intended for ports that serve as uplinks between spanning tree–aware
switches. It is intended for unmanaged switches that drop spanning tree BPDUs. Loop
protection detects physical and logical loops between Ethernet ports on a device. You must

Configure Switching
177
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
enable loop protection globally before you can enable and configure it at the interface level.
Loop protection is supported on physical interfaces and static LAG interfaces, but not on
dynamic LAG interfaces.
Configure Global Layer 2 Loop Protection
To configure global Layer 2 loop protection:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > L2 Loop Protection > L2 Loop Protection Configuration.
6. To enable or disable loop protection, select the Admin Mode Enable or Disable radio
button.
The default is Enable.
7. From the Transmit Interval menu, select the time in seconds between transmission of loop
packets.
The default transmit interval is 5 seconds.
8. From the Max PDU Receive menu, select the maximum number of packets to be received
before an action is taken.
The default is 1.
9. In the Disable Timer field, enter the time in seconds after which a port is disabled when a
loop is detected.
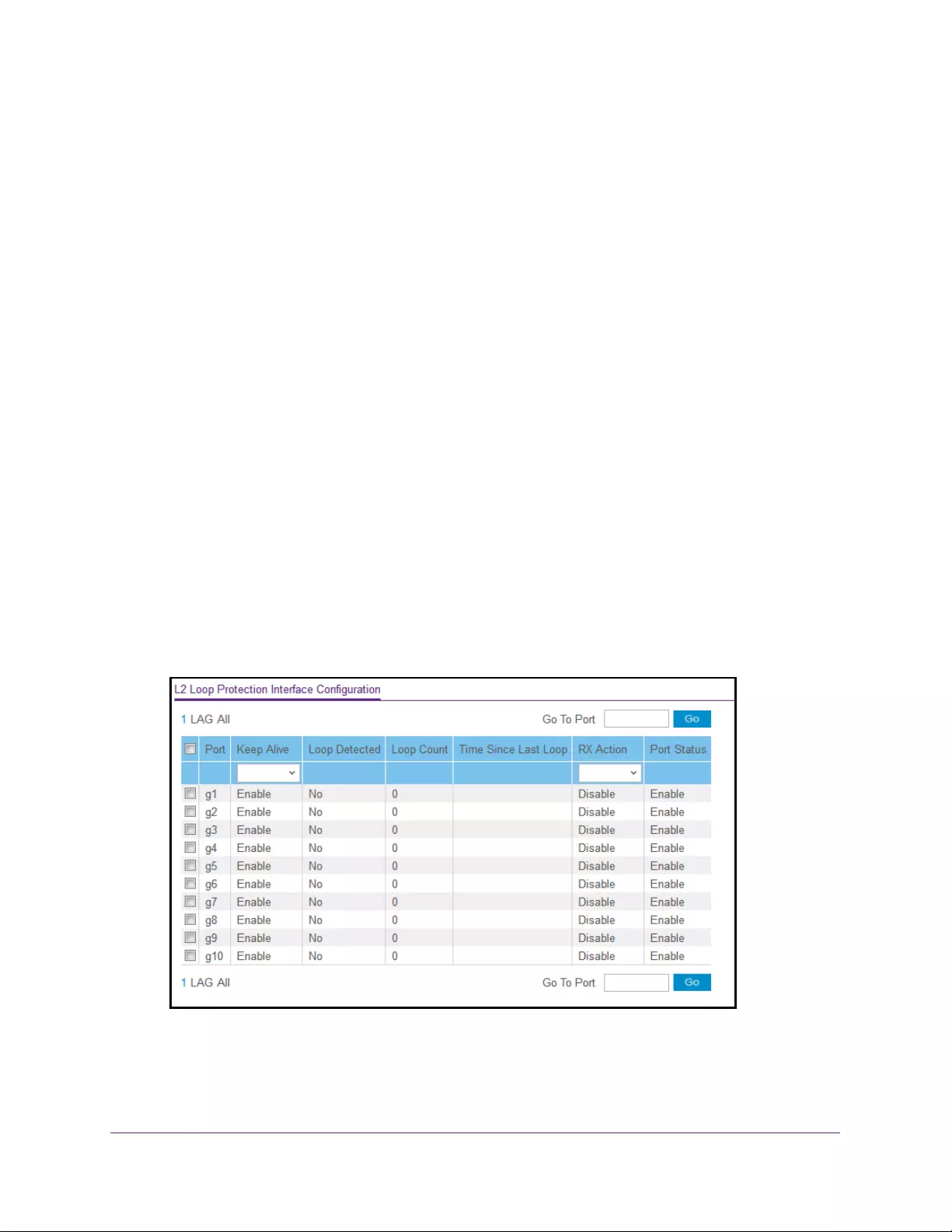
Configure Switching
178
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The range is from 0 to 604800 seconds. The default is 0 seconds.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Layer 2 Loop Protection on a Port
To configure Layer 2 loop protection on a port:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Switching > L2 Loop Protection > L2 Loop Protection Configuration.
6. Use one of the following methods to narrow down the ports that are displayed:
•To display all the physical ports, click the 1 link.
•To display all LAGs only, click the LAG link.
Configure Switching
179
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•To display all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
•In the Go To Port field, type the port number, for example g18, and click the Go
button.
7. In the Port field, select the port for which data is to be displayed or configured.
8. From the Keep Alive menu, select Enable or Disable to specify whether keep-alives are
enabled on an interface.
The default is Disable.
9. From the RX Action menu, select the action that occurs when the switch detects a loop on
an interface:
•Log. The switch logs a message.
•Disable. The switch disables the interface. This is the default action.
•Both. The switch both logs a message and disables the interface.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
11. To show the latest information on the page, click the Refresh button.
12. To clear all the statistics in the table, click the Clear button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Table 48. L2 Loop Protection Interface Information
Field Description
Loop Detected Shows whether a loop is detected on the interface. If the interface is
disabled and then reenabled, the status changes back to No.
Loop Count The number of packets that were received after the loop was detected.
Time Since Last Loop The time that elapsed since the loop was detected.
Port Status The status of the interface (Enabled, Disabled, or D-Disabled, which stands
for diagnostically disabled).

Configure Switching
180
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches

Configuring Routing
182
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
How the Switch Handles Routing
For each incoming packet, the switch uses the destination MAC address to determine if the
address matches a configured routing interface. If it does, the switch searches the host table
for a matching destination IP address:
•The host table contains a matching IP address.The packet is routed to the host.
•The host table does not contain a matching IP address. The switch searches for the
longest prefix match on the destination IP address:
-A match occurs. The packet is routed to the next hop.
-No match occurs but a default route exists. The packet is routed to the next hop
that is specified in the default route.
-No match occurs and no default route exists. The packet is dropped.
The routing table can include entries that were manually added. The host table can include
entries that were manually added or dynamically added through ARP.
Enable the Routing Mode
By default, the routing mode is disabled on the switch. You can enable the routing mode to let
the switch route traffic through its interfaces.
You can also enable routing for a VLAN interface (see Configure Routing VLANs on
page 204) and use the VLAN routing wizard to create a VLAN routing interface (see
Configure VLAN Routing With the VLAN Routing Wizard on page 204).
To enable routing on the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > IP > IP Configuration.
The IP Configuration page displays.

Configuring Routing
183
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Select the Routing Mode Enable radio button.
7. Click the Apply button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
View the IP Statistics
The IP Statistics page displays the IP statistics conform RFC 1213.
To display the IP statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > IP > Statistics.
The IP Statistics page displays.
Table 49. IP Configuration information
Field Description
Default Time to Live The default value that is inserted into the Time-To-Live field of the IP header of
datagrams originated by the switch, if a TTL value is not supplied by the transport
layer protocol. The default value is 64.
Maximum Next Hops The maximum number of hops supported by the switch. The default value is 1.
Configuring Routing
184
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Table 50. IP routing statistics information
Field Description
IpInReceives The total number of input datagrams received from interfaces, including those
received in error.
IpInHdrErrors The number of input datagrams discarded because of errors in IP headers,
including bad checksums, version number mismatch, other format errors,
time-to-live exceeded, errors discovered in processing their IP options, and so
on.
IpInAddrErrors The number of input datagrams discarded because the IP address in the IP
header’s destination field was not a valid address to be received at this entity.
This count includes invalid addresses (for example, 0.0.0.0) and addresses of
unsupported classes (for example, Class E). For entities that are not IP
gateways and therefore do not forward datagrams, this counter includes
datagrams discarded because the destination address was not a local address.
IpForwDatagrams The number of input datagrams for which this entity was not the final IP
destination, which caused the switch to attempt to forward them to the final
destination. In entities that do not act as IP gateways, this counter includes only
those packets that were source-routed via this entity, and the source-route
option processing was successful.
IpInUnknownProtos The number of locally addressed datagrams received successfully but discarded
because of an unknown or unsupported protocol.
IpInDiscards The number of input IP datagrams for which no problems were encountered to
prevent their continued processing, but which were discarded (for example, for
lack of buffer space). This counter does not include any datagrams discarded
while awaiting reassembly.
IpInDelivers The total number of input datagrams successfully delivered to IP user-protocols
(including ICMP).
IpOutRequests The total number of IP datagrams that local IP user-protocols (including ICMP)
supplied to IP in requests for transmission. This counter does not include any
datagrams counted in ipForwDatagrams.
IpOutDiscards The number of output IP datagrams for which no problem was encountered to
prevent their transmission to their destination, but which were discarded (for
example, for lack of buffer space). This counter includes datagrams counted in
ipForwDatagrams if any such packets met this discretionary discard criterion.
IpOutNoRoutes The number of IP datagrams discarded because no route could be found to
transmit them to their destination. This counter includes any packets counted in
ipForwDatagrams that meet this no-route criterion. This includes any datagrams
that a host cannot route because all of its default gateways are down.
IpReasmTimeout The maximum number of seconds that received fragments are held while they
are awaiting reassembly at this entity.
IpReasmReqds The number of IP fragments received that needed to be reassembled at this
entity.
IpReasmOKs The number of IP datagrams successfully reassembled.
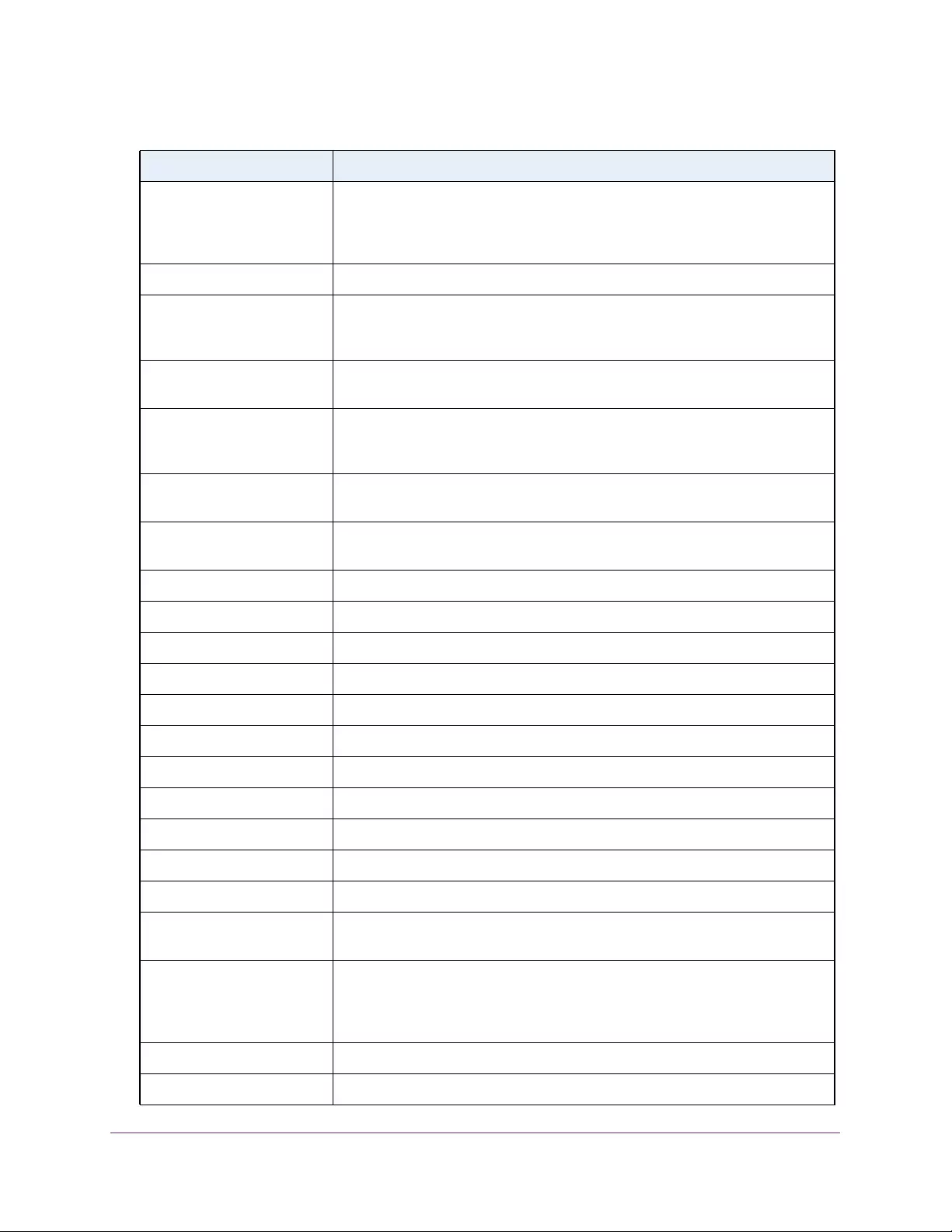
Configuring Routing
185
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
IpReasmFails The number of failures detected by the IP reassembly algorithm (for example,
because of timing out, errors, and so on). This is not necessarily a count of
discarded IP fragments because some algorithms can lose track of the number
of fragments by combining them as they are received.
IpFragOKs The number of IP datagrams that were successfully fragmented at this entity.
IpFragFails The number of IP datagrams that were discarded because they needed to be
fragmented at this entity but could not be, for example, because their Don’t
Fragment flag was set.
IpFragCreates The number of IP datagram fragments that were generated as a result of
fragmentation at this entity.
IpRoutingDiscards The number of routing entries that were discarded even though they were valid.
One possible reason for discarding such an entry could be to free buffer space
for other routing entries.
IcmpInMsgs The total number of ICMP messages that the entity received. This counter
includes all those counted by icmpInErrors.
IcmpInErrors The number of ICMP messages that the entity received but that included
ICMP-specific errors (bad ICMP checksums, bad length, and so on).
IcmpInDestUnreachs The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages received.
IcmpInTimeExcds The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages received.
IcmpInParmProbs The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages received.
IcmpInSrcQuenchs The number of ICMP Source Quench messages received.
IcmpInRedirects The number of ICMP Redirect messages received.
IcmpInEchos The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages received.
IcmpInEchoReps The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages received.
IcmpInTimestamps The number of ICMP Timestamp (request) messages received.
IcmpInTimestampReps The number of ICMP Timestamp Reply messages received.
IcmpInAddrMasks The number of ICMP Address Mask Request messages received.
IcmpInAddrMaskReps The number of ICMP Address Mask Reply messages received.
IcmpOutMsgs The total number of ICMP messages that this entity attempted to send. This
counter includes all those counted by icmpOutErrors.
IcmpOutErrors The number of ICMP messages that this entity did not send because of
problems discovered within ICMP, such as a lack of buffers. This value does not
include errors discovered outside the ICMP layer, such as the inability of IP to
route the resulting datagram.
IcmpOutDestUnreachs The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages sent.
IcmpOutTimeExcds The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages sent.
Table 50. IP routing statistics information (continued)
Field Description
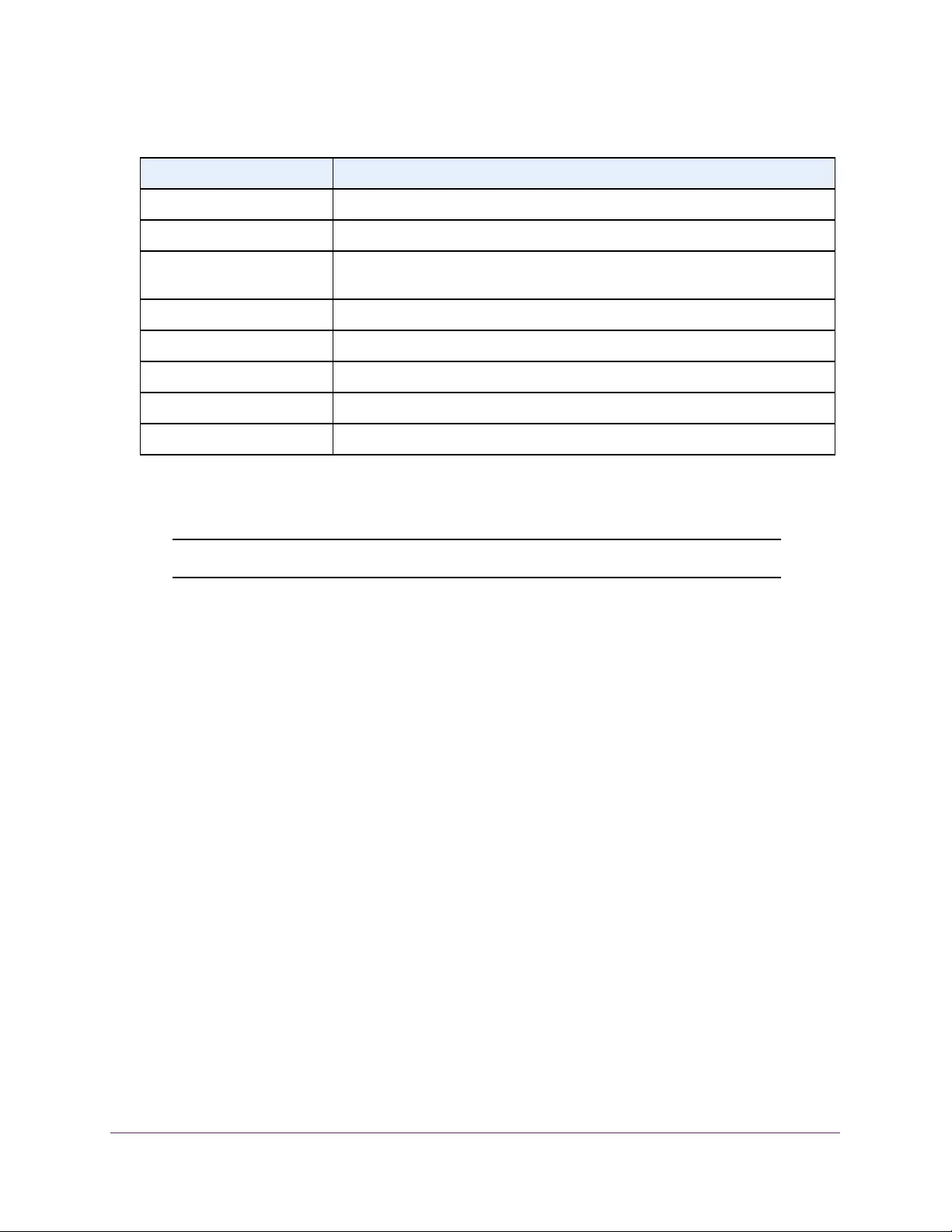
Configuring Routing
186
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure IPv6 Routing
Note: IPv6 is supported on VLAN interfaces only, not on physical ports.
Configure the IPv6 Global Routing Settings
You can configure IPv6 the global routing settings for the switch (as opposed to the IPv6
settings for an interface).
To configure the IPv6 global routing settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Basic > Global Configuration.
IcmpOutParmProbs The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages sent.
IcmpOutSrcQuenchs The number of ICMP Source Quench messages sent.
IcmpOutRedirects The number of ICMP Redirect messages sent. Because hosts do not send
redirects, this counter is always zero for a host.
IcmpOutEchos The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages sent.
IcmpOutEchoReps The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages sent.
IcmpOutTimestamps The number of ICMP Timestamp (request) messages.
IcmpOutTimestampReps The number of ICMP Timestamp Reply messages sent.
IcmpOutAddrMasks The number of ICMP Address Mask Request messages sent.
Table 50. IP routing statistics information (continued)
Field Description

Configuring Routing
187
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The IPv6 Global Configuration page displays.
6. To globally enable IPv6 unicast routing, select the IPv6 Unicast Routing Enable radio button.
By default, IPv6 unicast routing is disabled and the Disable radio button is selected.
7. In the Hop Limit field, enter the number for the unicast hop count that is used in IPv6
packets that originate in the switch.
The value is also included in router advertisements. The valid values for hops are 1
through 255. The default is 64.
8. In the ICMPv6 Rate Limit Error Interval field, enter the number of ICMP error packets that
are allowed per burst interval.
This value controls the ICMPv6 error packets. The default rate limit is 100 packets per
second, meaning that the burst interval is 1000 mseconds. To disable ICMP rate limiting,
enter 0. The valid rate interval must be in the range from 0 to 2147483647 mseconds.
9. In the ICMPv6 Rate Limit Burst Size field, enter the number of ICMP error packets that are
allowed per burst interval.
This value controls the ICMP error packets. The default burst size is 100 packets. The
valid burst size is 1 to 200. (Do not enter 0.)
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
View the IPv6 Route Table
To view the IPv6 Route Table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Basic > Route Table.
The IPv6 Routing Table page displays.
6. From the Routes Displayed menu, select one of the following options:
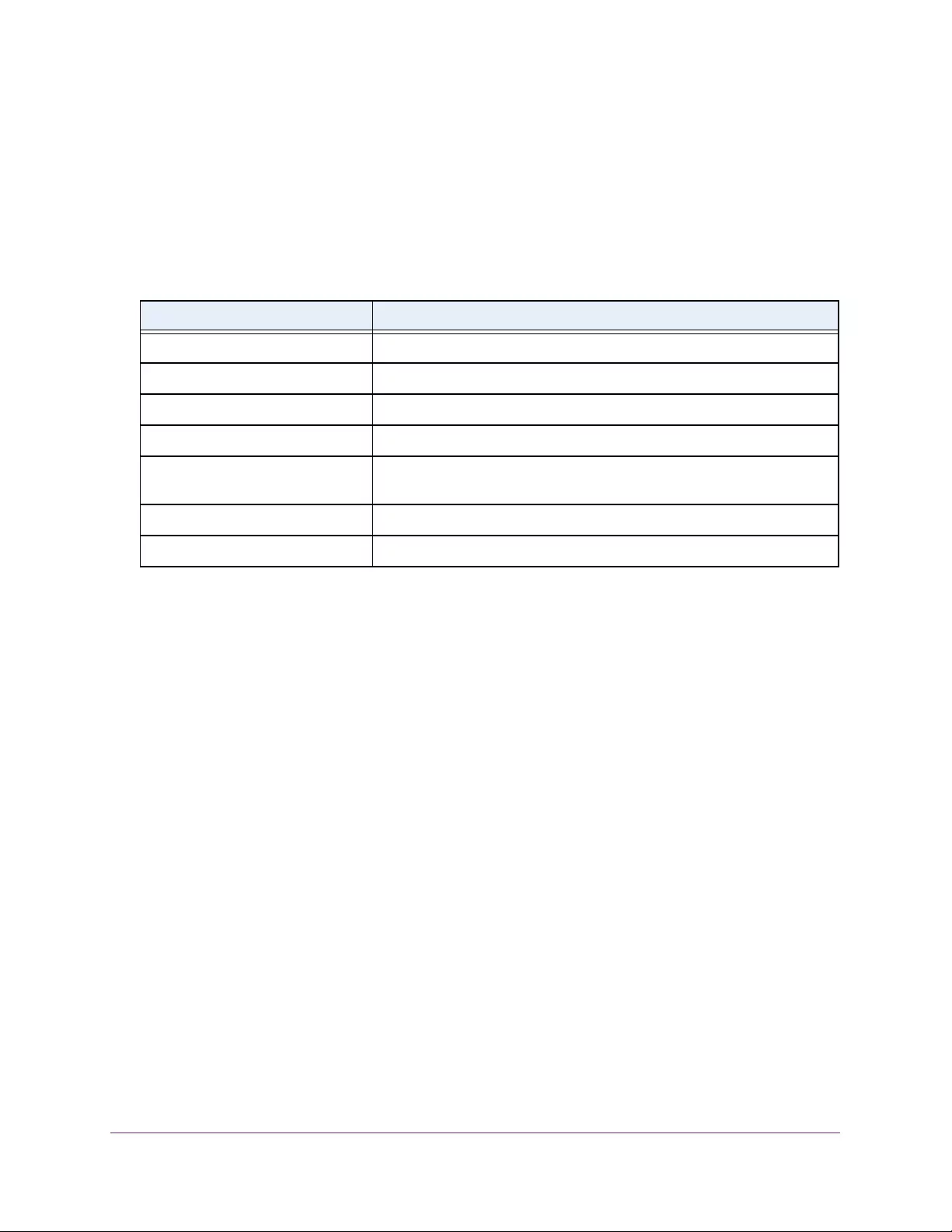
Configuring Routing
188
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•All Routes. Show all active IPv6 routes.
•Best Routes Only. Show only the best active routes.
•Configured Routes Only. Show only the manually configured routes.
7. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Update button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Configure IPv6 VLAN Interface Settings
For you to be able to configure IPv6 VLAN interface setting, IPv6 must be configured for the
network interface, IPv6 global routing must be enabled, and a routing VLAN must exist. For
more information, see the following sections:
•Configure the IPv6 Address for the Network Interface on page 38
•Configure the IPv6 Global Routing Settings on page 186
•Configure Routing VLANs on page 204.
IPv6 is supported on VLAN interfaces only, not on physical ports.
Configure IPv6 VLAN interface settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Table 51. IPv6 Route Table information
Field Description
Number of Routes The total number of active routes in the route table.
IPv6 Prefix The network prefix for the active route.
Prefix Length The prefix length for the active route.
Protocol The type of protocol for the active route.
Next Hop Interface The interface over which the route is active. For a reject route, the next
hop would be a Null0 interface.
Next Hop IP Address The next hop IPv6 address for the active route.
Preference The route preference of the configured route.

Configuring Routing
189
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > VLAN Configuration.
The IPv6 Global Configuration page displays.
6. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
7. From the IPv6 Mode menu, select Enable or Disable.
When IPv6 mode is enabled, the interface is capable of IPv6 operation without a global
address. In this case, an EUI-64-based link-local address is used. The default value is
Disable.
8. From the DHCPv6 Client Mode menu, select to enable or disable the DHCPv6 client mode
on an interface.
Only one interface can function as a client. The default value is Disable.
9. From the Stateless Address AutoConfig Mode menu, select to enable or disable the
stateless address autoconfiguration mode on an interface.
The default value is Disable.
10. From the Admin Mode menu, select to enable or disable the IPv6 mode.
The default is Disable. When the IPv6 mode is enabled, the interface is capable of IPv6
operation without a global address. In this case, an EUI-64-based link-local address is
used.
11. In the MTU field, specify the maximum transmit unit (MTU) for an interface.
If the value is 0, then this interface is not enabled for routing. It is not valid to set this value
to 0 if routing is enabled. The MTU range 1280 to 9198. The default is 1800.
12. In the Duplicate Address Detection Transmits field, specify the number of duplicate
address detection (DAD) transmits on an interface.
The DAD transmits value must be in the range 0 to 600. The default is 1.
13. In the Life Time Interval field, specify the router advertisement life time interval that is sent
from the interface.
This value must be greater than or equal to the maximum advertisement interval.
0 means do not use the VLAN interface as the default routing interface. The range of
router life time is 0 to 9000. The default is 1800.

Configuring Routing
190
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
14. In the Adv NS Interval field, specify the retransmission time of router advertisements that
are sent from the interface.
A value of 0 means the interval is not specified. The range of the neighbor solicit interval
is 1000 to 4294967295. The default is 0.
15. In the Adv Reachable Interval field, specify the router advertisement time.
This is the time allocated to consider the neighbors reachable after ND confirmation. The
range of reachable time is 0 to 3600000. The default is 0.
16. Use the Adv Interval field to specify the maximum time allowed between sending router
advertisements from the interface.
The range of the maximum advertisement interval is 4 to 1800. The default value is 600.
17. From the Adv Managed Config Flag menu, specify the setting for the router advertisement
managed address configuration flag.
When the selection is Enable, end nodes use DHCPv6. When the selection is Disable,
end nodes autoconfigure addresses. The default value is Disable.
18. From the Adv Other Config Flag menu, select to enable or disable the router
advertisement other stateful configuration flag.
The default value is Disable.
19. From the Router Preference menu, specify the router preference advertisement on an
interface.
The default value is Medium.
20. From the Adv Suppress Flag menu, select to enable or disable the router advertisement
suppression on an interface.
The default value is Disable.
21. From the Destination Unreachables menu, select to enable or disable the mode for
sending ICMPv6 destination unreachable messages on this interface.
If this mode is disabled, the interface does not send ICMPv6 destination unreachable
messages. The default value is Enable.
22. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Table 52. IPv6 VLAN Configuration information
Field Description
Routing Mode Displays the routing mode of an interface. The default is Disable.
Operational Mode Specifies the operational state of an interface. The default value is
Disable.
Link State Indicates whether the link is up or down.

Configuring Routing
191
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Manage IPv6 Prefixes for Advertisement on an IPv6 VLAN
When you add an IPv6 prefix for advertisement on an IPv6 VLAN, the prefix is advertised on
all interfaces that are members of the VLAN. You can change and remove existing IPv6
prefixes.
Add an IPv6 Prefix for Advertisement on an IPv6 VLAN
To add an IPv6 prefix for advertisement on an IPv6 VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Prefix Configuration.
The IPv6 Interface Selection page displays. The page also shows the IPv6 Interface
Configuration table.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface to be configured.
When the selection is changed, the page refreshes, causing all fields to be updated for
the newly selected interface.
7. In the Ipv6 Prefix field, specify the IPv6 prefix for an interface.
8. In the Prefix Length field, specify the IPv6 prefix length for an interface.
9. From the EUI64 menu, select Enable or Disable to indicate whether the specified 64-bit
unicast prefix is enabled.
10. In the Valid Life Time field, specify the router advertisement per prefix time.
This is the time allowed to consider the prefix valid for the purpose of on-link
determination. The valid life time is 0 to 4294967295.
11. In the Preferred Life Time field, specify the router advertisement per prefix time.
An autoconfigured address generated from this prefix is preferred. The preferred life time
must be in the range 0 to 4294967295.

Configuring Routing
192
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
12. From the Onlink Flag menu, select Enable or Disable to specify whether the selected
prefix can be used for on-link determination.
The default is Enable.
13. From the Autonomous Flag menu, select Enable or Disable to specify whether the
selected prefix can be used for autonomous address configuration.
The default value is Enable.
The Current State field displays the state of the IPV6 address. The state is TENT if routing
is disabled or DAD fails. The state is Active if the interface is active and DAD is
successful.
14. Click the Add button.
The IPv6 address prefix is added to the interface.
Change the Settings for an IPv6 Prefix for Advertisement on
an IPv6 VLAN
You can change the settings for a prefix for advertisement on an IPv6 VLAN.
To change the settings for an IPv6 prefix for advertisement on an IPv6 VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Prefix Configuration.
The IPv6 Interface Selection page displays. The page also shows the IPv6 Interface
Configuration table.
6. From the Interface menu, select the VLAN.
7. Select the check box for the IPv6 prefix.
The settings display in the fields in the table heading.
8. Change the settings as needed.

Configuring Routing
193
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Remove an IPv6 Prefix From an IPv6 VLAN
You can remove one or more IPv6 prefixes from an IPv6 VLAN. You cannot remove the
default IPv6 prefix.
To remove one or more IPv6 prefixes from an IPv6 VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Prefix Configuration.
The IPv6 Interface Selection page displays. The page also shows the IPv6 Interface
Configuration table.
6. From the Interface menu, select the VLAN.
7. Select the check boxes for the IPv6 prefixes.
8. Click the Delete button.
The IPv6 prefixes are removed from the IPv6 VLAN.
View IPv6 Statistics
To display the IPv6 statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
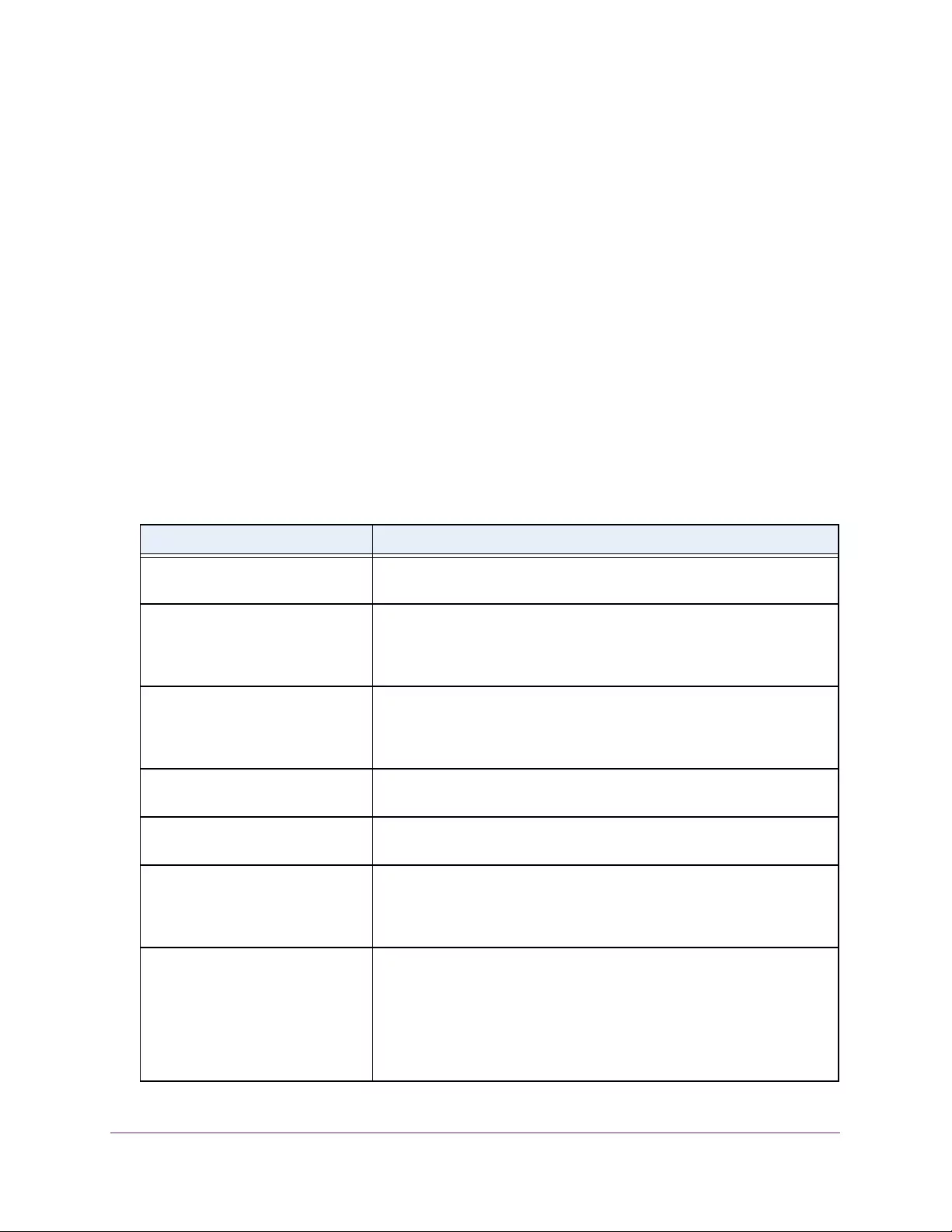
Configuring Routing
194
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Statistics.
The IPv6 Statistics page displays.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface.
When the selection is changed, the page refreshes, causing all fields to be updated for
the newly selected interface.
7. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Update button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Table 53. IPv6 Statistics information
Field Description
Total Datagrams Received The total number of input datagrams received by the interface, including
those received in error.
Received Datagrams Locally
Delivered The total number of datagrams successfully delivered to IPv6
user-protocols (including ICMP). This counter is incremented at the
interface to which these datagrams were addressed, which might not be
the input interface for some of the datagrams.
Received Datagrams Discarded
Due To Header Errors The number of input datagrams discarded due to errors in their IPv6
headers, including version number mismatch, other format errors, hop
count exceeded, errors discovered in processing their IPv6 options, and
so on.
Received Datagrams Discarded
Due To MTU The number of input datagrams that could not be forwarded because their
size exceeded the link MTU of outgoing interface.
Received Datagrams Discarded
Due To No Route The number of input datagrams discarded because no route could be
found to transmit them to their destination.
Received Datagrams With Unknown
Protocol The number of locally addressed datagrams received successfully but
discarded because of an unknown or unsupported protocol. This counter
is incremented at the interface to which these datagrams were addressed,
which might not be the input interface for some of the datagrams.
Received Datagrams Discarded
Due To Invalid Address The number of input datagrams discarded because the IPv6 address in
their IPv6 header's destination field was not a valid address to be received
at this entity. This count includes invalid addresses (for example, ::0) and
unsupported addresses (such as addresses with unallocated prefixes).
For entities that are not IPv6 routers and therefore do not forward
datagrams, this counter includes datagrams discarded because the
destination address was not a local address.
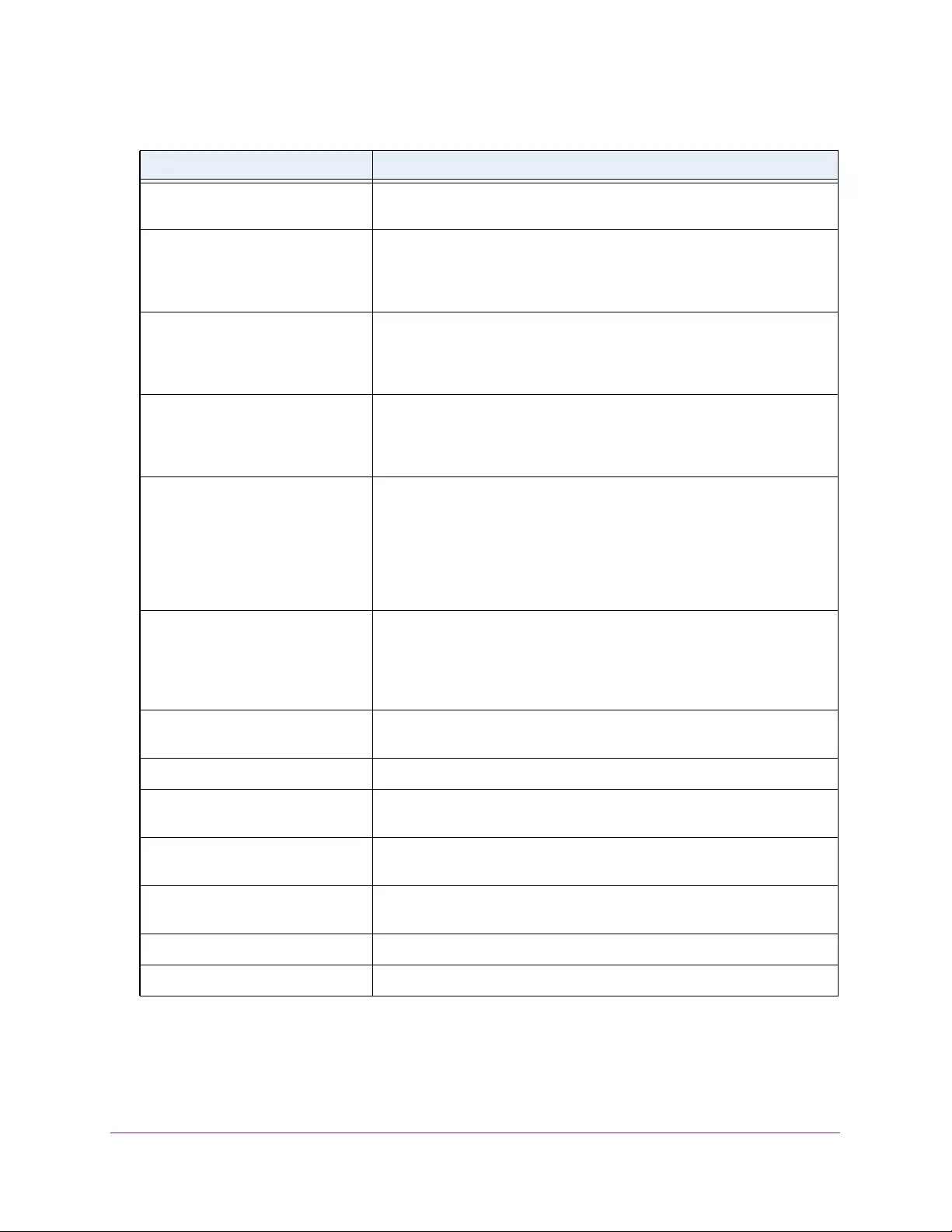
Configuring Routing
195
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Received Datagrams Discarded
Due To T runcated Data The number of input datagrams discarded because datagram frame did
not carry enough data.
Received Datagrams Discarded
Other The number of input IPv6 datagrams for which no problems were
encountered to prevent their continued processing, but that were
discarded for reasons such as lack of buffer space. This counter does not
include any datagrams discarded while awaiting reassembly.
Received Datagrams Reassembly
Required The number of IPv6 fragments received that needed to be reassembled at
this interface. This counter is incremented at the interface to which these
fragments were addressed, which might not be the input interface for
some of the fragments.
Datagrams Successfully
Reassembled The number of IPv6 datagrams successfully reassembled. This counter is
incremented at the interface to which these datagrams were addressed,
which might not be necessarily the input interface for some of the
fragments.
Datagrams Failed To Reassemble The number of failures detected by the IPv6 reassembly algorithm (for
whatever reason: timed out, errors, and so on). This is not necessarily a
count of discarded IPv6 fragments since some algorithms (notably the
algorithm in RFC 815) can lose track of the number of fragments by
combining them as they are received. This counter is incremented at the
interface to which these fragments were addressed, which might not be
the input interface for some of the fragments.
Datagrams Forwarded The number of output datagrams that this entity received and forwarded to
their final destinations. In entities that do not act as IPv6 routers, this
counter includes only those packets that were source-routed through this
entity, and the source-route processing was successful. For a successfully
forwarded datagram the counter of the outgoing interface is incremented.
Datagrams Locally T ransmitted The number of datagrams that this entity successfully transmitted from this
output interface.
Datagrams Transmit Failed The number of datagrams that this entity failed to transmit successfully.
Datagrams Successfully
Fragmented The number of IPv6 datagrams that were fragmented at this output
interface.
Datagrams Failed To Fragment The number of output datagrams that could not be fragmented at this
interface.
Datagrams Fragments Created The number of output datagram fragments that were generated as a result
of fragmentation at this output interface.
Multicast Datagrams Received The number of multicast packets received by the interface.
Multicast Datagrams Transmitted The number of multicast packets transmitted by the interface.
Table 53. IPv6 Statistics information (continued)
Field Description
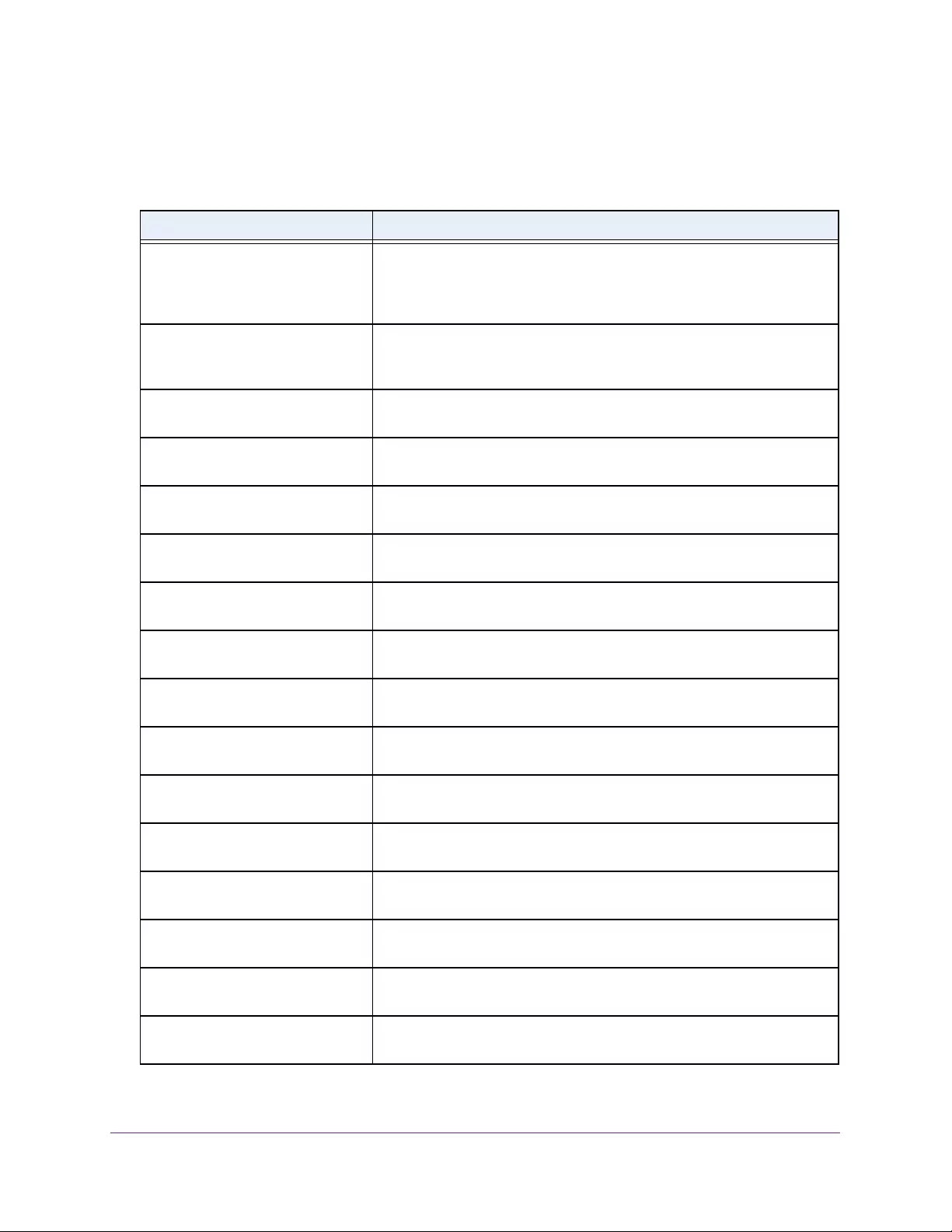
Configuring Routing
196
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the nonconfigurable ICMPv6 information displayed on the
page.
Table 54. ICMPv6 Statistics information
Field Description
Total ICMPv6 Messages Received The total number of ICMP messages received by the interface, which
includes all those counted by IPv6IfIcmpInErrors. This interface is the
interface to which the ICMP messages were addressed, which might not
be the input interface for the messages.
ICMPv6 Messages With Errors
Received The number of ICMP messages that the interface received but determined
as having ICMP-specific errors (bad ICMP checksums, bad length, and so
on).
ICMPv6 Destination Unreachable
Messages Received The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages received by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Messages Prohibited
Administratively Received The number of ICMP destination unreachable/communication
administratively prohibited messages received by the interface.
ICMPv6 Time Exceeded Messages
Received The number of ICMP T ime Exceeded messages received by the interface.
ICMPv6 Parameter Problem
Messages Received The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages received by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Packet Too Big Messages
Received The number of ICMP Packet Too Big messages received by the interface.
ICMPv6 Echo Request Messages
Received The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages received by the interface.
ICMPv6 Echo Reply Messages
Received The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages received by the interface.
ICMPv6 Router Solicit Messages
Received The number of ICMP Router Solicit messages received by the interface.
ICMPv6 Router Advertisement
Messages Received The number of ICMP Router Advertisement messages received by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicit Messages
Received The number of ICMP Neighbor Solicit messages received by the interface.
ICMPv6 Neighbor Advertisement
Messages Received The number of ICMP Neighbor Advertisement messages received by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Redirect Messages
Received The number of ICMPv6 Redirect messaged received by the interface.
ICMPv6 Group Membership Query
Messages Received The number of ICMPv6 Group Membership Query messages received by
the interface.
ICMPv6 Group Membership
Response Messages Received The number of ICMPv6 Group Membership Response messages received
by the interface.
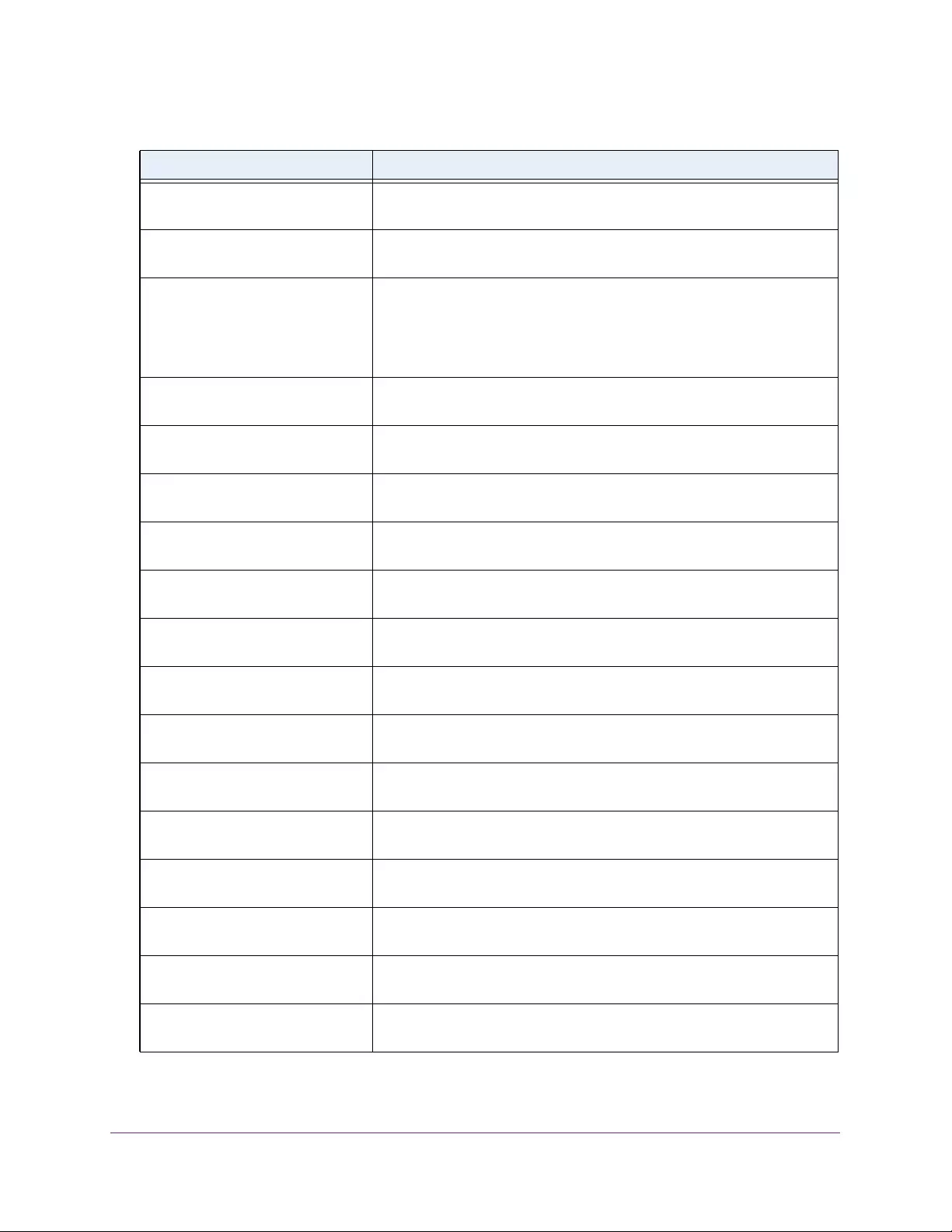
Configuring Routing
197
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
ICMPv6 Group Membership
Reduction Messages Received The number of ICMPv6 Group Membership Reduction messages received
by the interface.
Total ICMPv6 Messages
Transmitted The total number of ICMP messages that this interface attempted to send.
This counter includes all those counted by icmpOutErrors.
ICMPv6 Messages Not Transmitted
Due To Error The number of ICMP messages that this interface did not send due to
problems discovered within ICMP such as a lack of buffers. This value
does not include errors discovered outside the ICMP layer such as the
inability of IPv6 to route the resultant datagram. In some implementations
there might be no types of error that contribute to this counter's value.
ICMPv6 Destination Unreachable
Messages T ransmitted The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages sent by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Messages Prohibited
Administratively T ransmitted Number of ICMP Destination Unreachable/Communication
Administratively Prohibited messages sent.
ICMPv6 Time Exceeded Messages
Transmitted The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages sent by the interface.
ICMPv6 Parameter Problem
Messages T ransmitted The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages sent by the interface.
ICMPv6 Packet Too Big Messages
Transmitted The number of ICMP Packet Too Big messages sent by the interface.
ICMPv6 Echo Request Messages
Transmitted The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages sent by the interface.
ICMPv6 Echo Reply Messages
Transmitted The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages sent by the interface.
ICMPv6 Router Solicit Messages
Transmitted The number of ICMP Neighbor Solicitation messages sent by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Router Advertisement
Messages T ransmitted The number of ICMP Router Advertisement messages sent by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicit Messages
Transmitted The number of ICMP Neighbor Solicitation messages sent by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Neighbor Advertisement
Messages T ransmitted The number of ICMP Neighbor Advertisement messages sent by the
interface.
ICMPv6 Redirect Messages
Transmitted The number of Redirect messages sent.
ICMPv6 Group Membership Query
Messages T ransmitted The number of ICMPv6 Group Membership Query messages sent.
ICMPv6 Group Membership
Response Messages Transmitted The number of ICMPv6 Group Membership Response messages sent.
Table 54. ICMPv6 Statistics information (continued)
Field Description

Configuring Routing
198
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View the IPv6 Neighbor Table
To view or clear the IPv6 Neighbor Table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Neighbor Table.
The IPv6 Neighbor Table page displays.
6. Use the Search menu and field to search for IPv6 routes by IPv6 address or interface
number:
•Search by IPv6 address. Select IPv6 Address from the Search menu. Enter the
128-byte hexadecimal IPv6 address in four-digit groups separated by colons, for
example, 2001:231F:::1. Then click the Go button.
If the address exists, the entry is displayed. An exact match is required.
•Search by Interface. Select Interface from the Search menu. Enter the interface
using the respective naming convention (for example, g1 or l1). Then click the Go
button.
If the address exists, the entry is displayed.
7. To clear the IPv6 neighbors on a selected interface or on all interfaces, click the Clear
button.
8. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Update button.
ICMPv6 Group Membership
Reduction Messages Transmitted The number of ICMPv6 Group Membership Reduction messages sent.
ICMPv6 Duplicate Address Detects The number of duplicate addresses detected by the interface.
Table 54. ICMPv6 Statistics information (continued)
Field Description
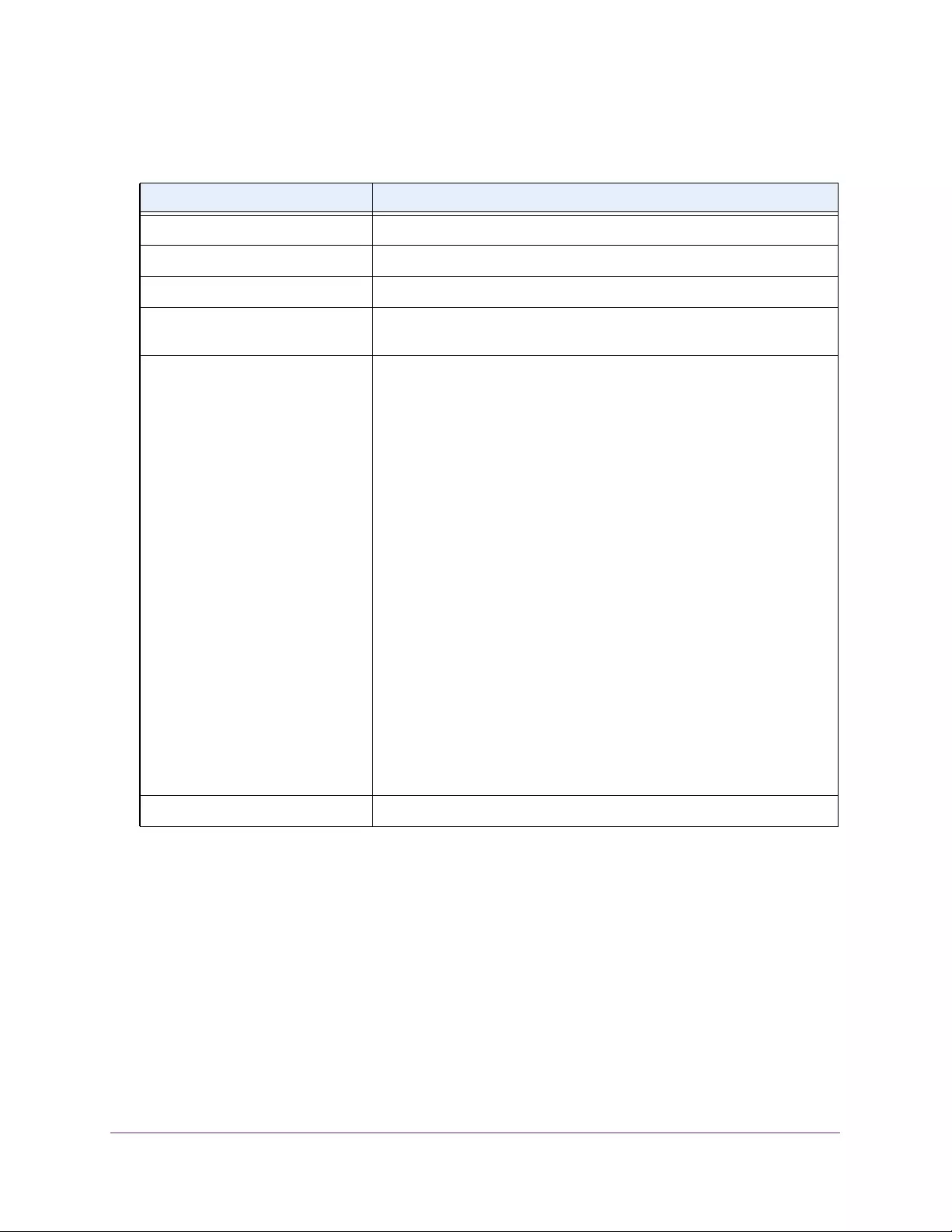
Configuring Routing
199
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Manage Static IPv6 Routes
You can configure static and default routes with a single next hop to any destination. You can
also delete an individual next hop from a static route or an entire static route.
The switch supports a maximum of 32 static routes. The cost of a static route is always 0.
On the switch, routing provides a preference option for the configuration of default routes. A
configured default route is treated exactly a a static route. Therefore, default routes and static
routes contain the same default preference.
The platform supports up to 16 IPv6 static routes and up to 16 VLAN routing interfaces. The
network ports are logical management interfaces. The IP stack’s routing table contains both
Table 55. IPv6 Neighbor Table information
Field Description
Interface The interface whose settings are displayed in the current table row.
IPv6 Address The IPv6 address of the neighbor or interface.
MAC Address The MAC address associated with an interface.
isRtr Indicates whether the neighbor is a router. If the neighbor is a router, the
value is True. If the neighbor is not a router, the value is False.
Neighbor State The state of the neighbor cache entry. Following are the states for
dynamic entries in the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache:
• Incmp. Address resolution is being performed on the entry. A
neighbor solicitation message was sent to the solicited-node multicast
address of the target, but the corresponding neighbor advertisement
message is not yet received.
• Reach. Positive confirmation was received within the last Reachable
Time milliseconds that the forward path to the neighbor was
functioning properly. While in REACH state, the device takes no
special action as packets are sent.
• Stale. More than Reachable Time milliseconds elapsed since the last
positive confirmation was received that the forward path was
functioning properly. While in STALE state, the device takes no action
until a packet is sent.
• Delay. More than Reachable Time milliseconds elapsed since the last
positive confirmation was received that the forward path was
functioning properly. A packet was sent within the last
DELAY_FIRST_PROBE_TIME seconds. If no reachability
confirmation is received within DELAY_FIRST_PROBE_TIME
seconds of entering the DELAY state, send a neighbor solicitation
message and change the state to PROBE.
• Probe. Seeks a reachability confirmation by resending neighbor
solicitation messages every Retrans Timer milliseconds until a
reachability confirmation is received.
Last Updated Time since the address was confirmed to be reachable.

Configuring Routing
200
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
IPv6 routes associated with these management interfaces and IPv6 routes associated with
routing interfaces. Configuration of 127-bit IPv6 prefixes on the routing/host IPv6 interfaces is
supported. You can distinguishes between static routes by specifying a route preference
value. A static route with a lower preference value is a more preferred static route. On a
VLAN routing interface, for example, vlan 10), you can enable IPv4 routing and IPv6 routing
independently.
Add a Static IPV6 Route
To add a static IPv6 route:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Static Route Configuration.
The Configure Routes page displays.
6. In the IPv6 Prefix field, specify the IPv6 network prefix for the configured route.
7. In the Prefix Length field, specify the IPv6 prefix length for the configured route.
8. From the Next Hop IPv6 Address Type menu, select one of the following options:
•Global. Select this option if the IPv6 address is a global IPv6 address.
•Link-Local. Select this option if the next hop IPv6 address is a link-local IPv6
address. You must specify a next hop IPv6 address in the Next Hop IPv6 Address
field.
•Static-Reject. Select this option to create a static-reject route for a destination prefix.
You do not need to specify a next hop IPv6 address.
9. If the selection from the Next Hop IPv6 Address Type menu is Global or Link-Local, enter
the next hop IPv6 address in the Next Hop IPv6 Address field.
10. If the selection from the Next Hop IPv6 Address Type menu is Link-Local, from the
Interface menu, select the interface that connects to the IPv6 next hop.
11. In the Preference field, specify the router preference.

Configuring Routing
201
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
12. Click the Add button.
The route is added.
Change the Preference for a Static IPv6 Route
To change the preference for a static IPv6 route:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Static Route Configuration.
The Configure Routes page displays.
6. Select the check box for the static IPv6 route.
7. In the Preference field, specify another router preference.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Remove Static IPv6 Routes
To remove one or more static IPv6 routes:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Configuring Routing
202
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Static Route Configuration.
The Configure Routes page displays.
6. Select one or more check boxes for static IPv6 routes.
7. Click the Delete button.
The route or routes are removed from the switch.
View the IPv6 Route Table
To view the IPv6 Route Table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Route Table.
The IPv6 Route Table displays.
6. From the Routes Displayed menu, select one of the following options:
•All Routes. Show all active IPv6 routes.
•Best Routes Only. Show only the best active routes.
•Configured Routes Only. Show only the manually configured routes.
7. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Update button.
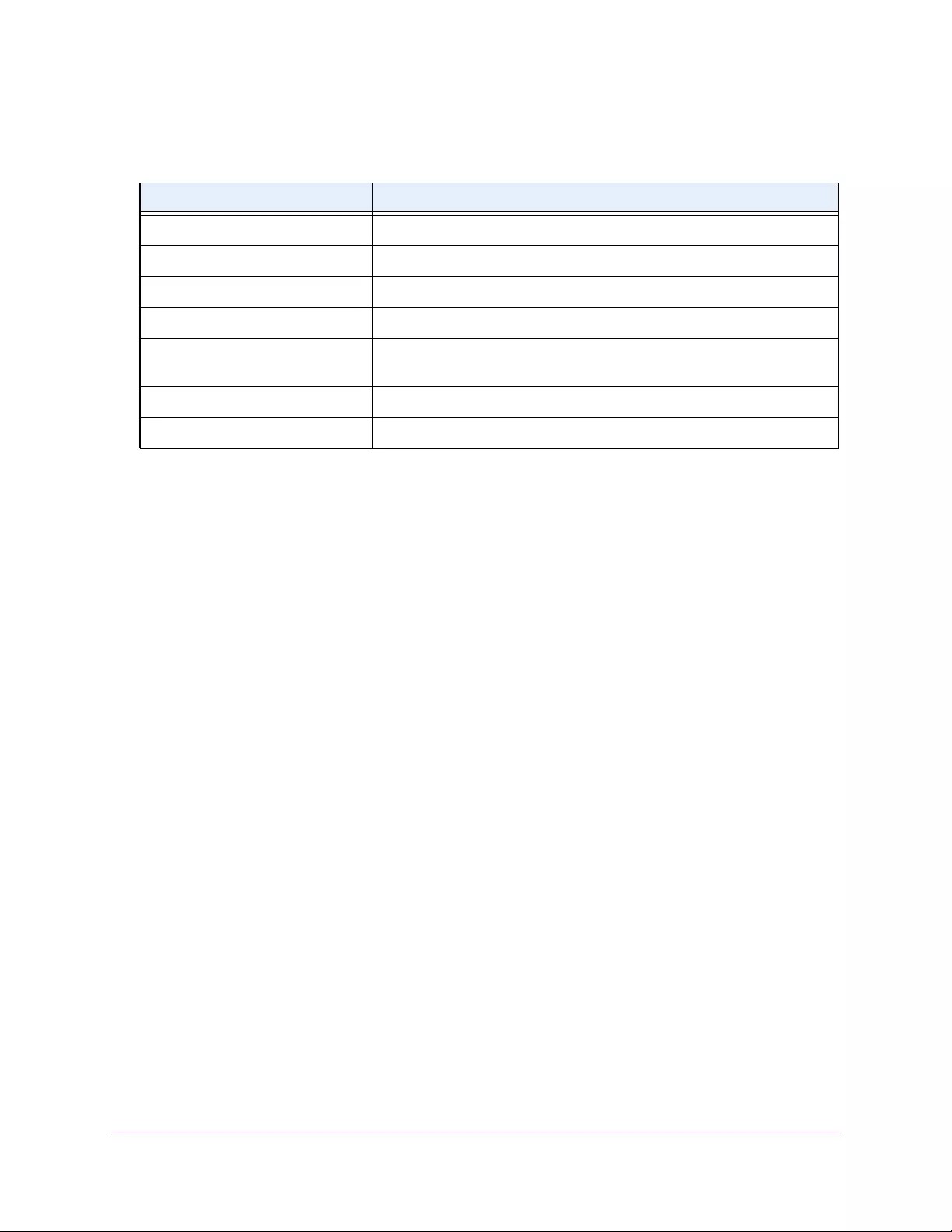
Configuring Routing
203
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Configure IPv6 Route Preferences
You can configure the default preference for each protocol. These values are arbitrary values
in the range of 1 to 255 and are independent of route metrics. Most routing protocols use a
route metric to determine the shortest path known to the protocol, independent of any other
protocol. The switch selects the route with the lowest preference value as the best route to a
destination. When multiple routes to a destination exist, the preference values are used to
determine the preferred route. If these preference values routes are equal, the route with the
best route metric is chosen. To avoid problems with mismatched metrics, you must configure
different preference values for each of the protocols.
Configure the IPv6 route preferences:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing> IPv6 > Advanced > Route Preference.
Table 56. IPv6v Route Table information
Field Description
Number of Routes The total number of active routes in the route table.
IPv6 Prefix The network prefix for the active route.
Prefix Length The prefix length for the active route.
Protocol The type of protocol for the active route.
Next Hop Interface The interface over which the route is active. For a reject route, the next
hop would be a Null0 interface.
Next Hop IP Address The next hop IPv6 address for the active route.
Preference The route preference of the configured route.

Configuring Routing
204
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The IPv6 Route Preference page displays.
6. In the Static field, specify the static route preference value for the switch.
The range is 1 to 255. The default value is 1.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The Local field displays the local preference.
Configure Routing VLANs
You can configure the switch software with some ports supporting VLANs and some
supporting routing. You can also configure the software to allow traffic on a VLAN to be
treated as if the VLAN were a router port.
When a port is enabled for bridging (default) rather than routing, all normal bridge processing
is performed for an inbound packet, which is then associated with a VLAN. Its MAC
Destination Address (MAC DA) and VLAN ID are used to search the MAC address table. If
routing is enabled for the VLAN, and the MAC DA of an inbound unicast packet is that of the
internal bridge-router interface, the packet is routed. An inbound multicast packet is
forwarded to all ports in the VLAN, plus the internal bridge-router interface, if it was received
on a routed VLAN.
Since a port can be configured to belong to more than one VLAN, VLAN routing might be
enabled for all of the VLANs on the port, or for a subset. VLAN Routing can be used to allow
more than one physical port to reside on the same subnet. It could also be used when a
VLAN spans multiple physical networks, or when additional segmentation or security is
required. This section shows how to configure switch software to support VLAN routing. A
port can be either a VLAN port or a router port, but not both. However, a VLAN port can be
part of a VLAN that is itself a router port.
Configure VLAN Routing With the VLAN Routing Wizard
The VLAN Routing Wizard creates a VLAN routing interface, configure the IP address and
subnet mask for the interface, and add selected ports or LAGs to the VLAN. With this wizard,
you can:
•Create a VLAN.
•Add selected ports to the newly created VLAN and remove selected ports from the default
VLAN.
•Optionally, you can create a LAG, add selected ports to a LAG, then add the LAG to the
newly created VLAN.
•Enable tagging on selected ports if the port is in another VLAN. Disable tagging if a
selected port does not exist in another VLAN.
•Exclude ports not selected from the VLAN.
•Enable routing on the VLAN using the IP address and subnet mask entered.

Configuring Routing
205
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To configure VLAN routing using the VLAN routing wizard:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > VLAN > VLAN Routing Wizard.
The following figure show the page for models GC728X and GC728XP. Models GC752X
and GC752XP support 48 Ethernet ports but the same number of LAGs (24).
6. In the Vlan ID field, specify the VLAN Identifier (VID) associated with this VLAN. The VID is
1 to 4093 characters in length.
7. In the IP Address field, define the IP address of the VLAN interface.
8. In the Network Mask field, define the subnet mask of the VLAN interface.

Configuring Routing
206
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
9. In the Ports table, click each port once, twice, or three times to configure one of the following
modes or reset the port to the default settings:
•T (T agged). Select the ports on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN are tagged.
The ports that are selected are included in the VLAN.
•U (Untagged). Select the ports on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN are
untagged. The ports that are selected are included in the VLAN.
By default, the selection is blank, which means that the port is excluded from the VLAN.
10. In the LAG table, click each LAG once, twice, or three times to configure one of the following
modes or reset the LAG to the default settings:
•T (Tagged). Select the LAGs on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN are
tagged. The LAGs that are selected are included in the VLAN.
•U (Untagged). Select the LAGs on which all frames transmitted for this VLAN are
untagged. The LAGs that are selected are included in the VLAN.
By default, the selection is blank, which means that the LAG is excluded from the VLAN.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Manually Manage Routing VLANs
You can view information about existing VLAN routing interfaces on the switch, change the
settings for an existing routing VLAN, change a regular VLAN into a routing VLAN, and delete
a routing VLAN.
View the Existing Routing VLANs and Manually Add a Routing VLAN
You can view the routing VLANs that you added through the VLAN Routing Wizard and
manually add a routing VLAN. You do so by changing a regular VLAN that already exists on
the switch into a routing VLAN.
To view the exiting routing VLANs or manually add a routing VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.

Configuring Routing
207
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > VLAN > VLAN Routing Configuration.
The VLAN Routing Configuration page displays. The table displays any existing routing
VLANs.
6. To add a routing VLAN by changing a regular VLAN into a routing VLAN, do the following:
a. From the VLAN menu, select the VLAN that you want to configure for VLAN routing.
The VLAN menu display all IDs of the VLANs that are configured on the switch.
b. In the IP Address field, enter an IP address for the VLAN routing interface.
c. In the Subnet Mask field, enter a subnet mask for the VLAN routing interface.
d. In the IP MTU field, specify the maximum size of IP packets sent on an interface.
A valid range is from 68 bytes to the link MTU. The default value is 1500. A value of 0
specifies that the value in the IP MTU must be ignored. In that situation, the VLAN
interface uses the link MTU as the IP MTU. The link MTU is the maximum frame size
minus the length of the layer 2 header.
e. Click the Add button.
The VLAN becomes a routing VLAN.
The following table describes the VLAN routing interface status information on the page.
Change an Existing Routing VLAN
To change the settings for an existing routing VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Table 57. VLAN routing interface information
Field Description
Port The port number assigned to the VLAN Routing Interface.
MAC Address The MAC Address assigned to the VLAN Routing Interface.
Routing Mode Shows whether the routing mode is enabled (Enable or Disable).

Configuring Routing
208
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > VLAN > VLAN Routing Configuration.
The VLAN Routing Configuration page displays.
6. From the VLAN list, select the VLAN.
7. Change the settings as needed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Remove a Routing VLAN
When you remove a routing VLAN, the VLAN becomes a regular VLAN.
To remove a routing VLAN:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > VLAN > VLAN Routing Configuration.
The VLAN Routing Configuration page displays.
6. From the VLAN list, select the VLAN.
7. Click the Delete button.
The routing VLAN is removed and the VLAN becomes a regular VLAN.

Configuring Routing
209
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Router Discovery
The Router Discovery protocol is used by hosts to identify operational routers (or routing
interfaces) on the subnet. Router discovery messages can be of two types: router
advertisements and router solicitations. The protocol requires each router to periodically
advertise the IP addresses that it is associated with. Hosts listen for these advertisements
and discover the IP addresses of neighboring routers.
To configure the router discovery parameters:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > Router Discovery.
The Router Discovery Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box for the routing interface.
To configure all routing interfaces, select the check box in the heading row . To configure a
single interface, select the check box associated with the interface. The interface number
displays in the Interface field in the table heading row.
7. From the Advertise Mode menu, select Enable.
Router advertisements are transmitted from the selected interface.
8. In the Advertise Address field. specify the IP address to be used to advertise the switch.
9. In the Maximum Advertise Interval field, specify the maximum time (in seconds) allowed
between router advertisements sent from the interface.
The default is 600 seconds.
10. In the Minimum Advertise Interval field, specify the minimum time (in seconds) allowed
between router advertisements sent from the interface.
The default is 450 seconds.

Configuring Routing
210
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
11. In the Advertise Lifetime field, specify the value (in seconds) to be used as the lifetime field
in router advertisements sent from the interface.
This is the maximum length of time that the advertised addresses are to be considered as
valid router addresses by hosts. The default is 1800 seconds.
12. In the Preference Level field, specify the preference level of the router as a default router
relative to other routers on the same subnet.
Higher numbered addresses are preferred. The default is 0.
13. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Routes and View Routes
You can configure static and default routes and view the routes that the switch learned.
To configure a static or default route:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > Routing Table > Route Configuration.
The Configure Routes page displays. The page also shows the Route Status section.
6. From the Route Type menu, select one of the following types of routes:
•Static. For a static route, you must specify all fields.
•DefaultRoute. For a default route, you cannot specify the Network Address and
Subnet Mask fields.
7. For a static route only, in the Network Address field, specify the IP route prefix for the
destination.
To create a route, a valid routing interface must exist, and the next hop IP Address must
be on the same network as the routing interface.
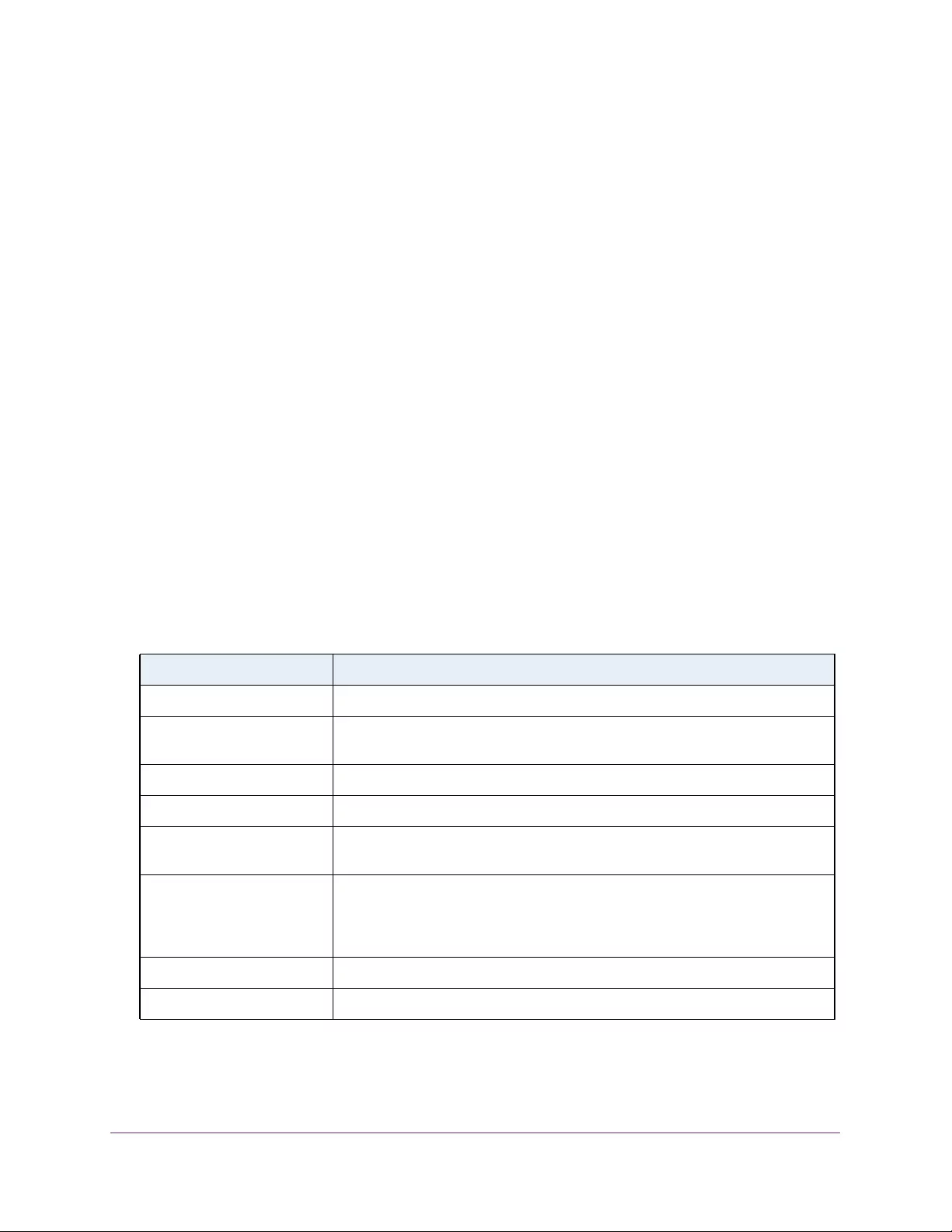
Configuring Routing
211
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
8. For a static route only, in the Subnet Mask field, specify the subnet mask.
Also referred to as the network mask, the mask indicates the portion of the IP address
that identifies the attached network.
9. In the Next Hop IP Address field, specify the next hop IP address.
This is the outgoing router IP address to use when forwarding traffic to the next router (if
any) in the path towards the destination. The next router is always one of the adjacent
neighbors or the IP address of the local interface for a directly attached network. When
creating a route, the next hop IP must be on the same network as the routing interface.
Valid next hop IP addresses are listed in the Route Status table.
10. In the Preference field, specify the preference value for the route.
Among routes to the same destination, the route with the lowest preference value is the
route entered into the forwarding database. By specifying the preference of a static route,
you can control whether a static route is more preferred or less preferred. The preference
also controls whether a static route is more preferred or less preferred than other static
routes to the same destination.
11. As an option, in the Description field, specify a description to help identify the route.
12. Click the Add button.
The route is added.
The Route Status table provides information about the static routes that you manually
configured on the switch and the routes the switch learned dynamically.
Table 58. Routing table information
Field Description
Network Address The IP route prefix for the destination.
Subnet Mask Also referred to as the network mask, the portion of the IP interface address that
identifies the attached network.
Protocol The protocol that created the route. The protocol can be Local or Static.
Route Type Based on the protocol, Connected, Static, or Dynamic.
Next Hop Interface The outgoing router interface that must be used when the switch forwards traffic
to the destination.
Next Hop IP Address The outgoing router IP address that must be used when the switch forwards
traffic to the next router (if any) in the path towards the destination. The next
router is always one of the adjacent neighbors or the IP address of the local
interface for a directly attached network.
Preference A value from 1 to 255.
Metric The administrative cost of the path to the destination.

Configuring Routing
212
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Delete Routes
To delete one or more static routes:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > Routing Table > Route Configuration.
The Configure Routes page displays. The page also shows the Route Status section.
6. Select the check box next to each route to remove.
7. Click the Delete button.
The static route is deleted.
Configure ARP
The address resolution protocol (ARP) associates a layer 2 MAC address with a layer 3 IPv4
address. The switch support both dynamic and manual ARP configuration. With manual ARP
configuration, you can statically add entries into the ARP table.
ARP is a required part of the Internet protocol (IP) and is used to translate an IP address to a
media (MAC) address, defined by a local area network (LAN) such as an Ethernet network.
A device that must send an IP packet must learn the MAC address of the IP destination, or if
the destination is not on the same subnet, of the next hop router. The device achieves this by
broadcasting an ARP request packet, to which the intended recipient responds by sending an
ARP unicast reply that contains its MAC address. Once learned, the MAC address is used in
the destination address field of the Layer 2 header prepended to the IP packet.
The ARP cache is a table maintained locally in each device on the network. ARP cache
entries are learned by examining the source information in the ARP packet payload fields,
regardless of whether it is an ARP request or response. In this way, when an ARP request is
broadcast to all stations on a LAN segment or virtual LAN (VLAN), each recipient can store
the sender’s IP address and MAC address in its ARP cache. The ARP response, which is a
unicast reply, is normally detected only by the device that sends the ARP request. That

Configuring Routing
213
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
device stores the sender’s information in its ARP cache. Newer information always replaces
existing content in the ARP cache.
If you move a device in the network, the device’s MAC address can become associated with
another IP address. Or if you reconfigure, disconnect, or power off the device, the device’ s IP
address can disappear from the network altogether. To prevent such situations from causing
information in the ARP cache to become outdated, each device on the network periodically
updates the entries in its ARP cache with new information from the network. On the switch,
you can set the ageout interval for ARP entries from 15 to 21600 seconds. When the ageout
interval is reached, ARP entries for which the switch did not receive an ARP reply are
removed form the switch ARP cache.
The switch supports 512 ARP entries, which include dynamic and static ARP entries.
To configure and display ARP details, see the following sections:
•View Entries in the ARP Cache on page 213
•Create a Static ARP Entry on page 214
•Configure the Global ARP Settings on page 215
•Remove ARP Entries From the ARP Cache on page 216
View Entries in the ARP Cache
You can view entries in the ARP table.
To display entries in the ARP table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > ARP > Basic > ARP Cache.
The Management VLAN ARP Cache page displays. The page also shows the Routing
VLANs ARP Cache section.
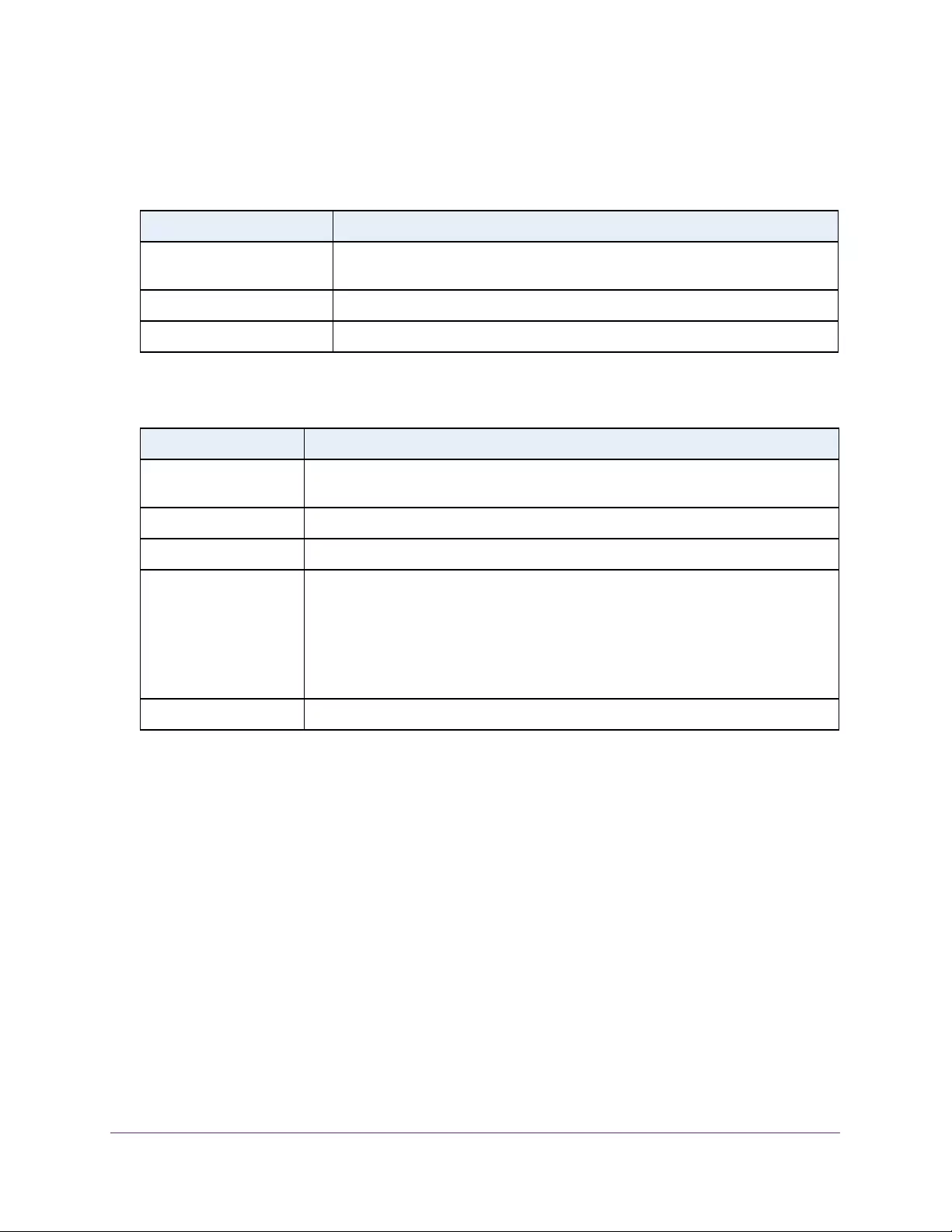
Configuring Routing
214
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table provides information included in the management VLAN ARP cache
section.
The following table provides information included in the routing VLANs ARP cache section.
Create a Static ARP Entry
You can add a static entry to the ARP table.
To add an entry to the ARP table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Table 59. ARP cache information
Field Description
IP Address The associated IP address of a device on a subnet attached to one of the
switch’s existing routing interfaces.
Port The associated interface of the connection.
MAC Address The MAC address of the device.
Table 60. ARP cache information for routing VLANs
Field Description
IP Address The associated IP address of a device on a subnet attached to one of the switch's
existing routing interfaces.
Interface The routing interface associated with the ARP entry.
MAC Address The unicast MAC address of the device.
Type The type of the ARP entry. Possible values are:
• Local. An ARP entry associated with one of the switch’s routing interface’s MAC
addresses.
• Gateway. A dynamic ARP entry for which the IP address is that of a router.
• Static. An ARP entry configured by the user.
• Dynamic. An ARP entry which was learned by the switch
Age Age since the entry was last refreshed in the ARP Table. The format is hh:mm:ss.

Configuring Routing
215
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > ARP > Advanced > ARP Create.
The Static ARP Configuration page displays. The page also shows the Routing VLANs
ARP Cache section.
6. In the IP Address field, specify the IP address to add.
The address must be the IP address of a device on a subnet attached to one of the
switch’s existing routing interfaces.
7. In the MAC Address field, specify the unicast MAC address of the device.
The format is six 2-digit hexadecimal numbers separated by colons, for example
00:06:29:32:81:40.
8. Click the Add button.
The entry is added to the table.
For information about the information in the Routing VLANs ARP Cache table, see Table 60,
ARP cache information for routing VLANs on page 214.
Configure the Global ARP Settings
You can display and change the configuration settings for the ARP table.
To display or change the setting for the ARP table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > ARP > Advanced > Global ARP Configuration.
The Global ARP Configuration page displays.

Configuring Routing
216
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. In the Age Time field, specify the number of seconds for an ARP entry to age out.
7. In the Response Time field, specify the number of seconds that the switch must wait for a
response to an ARP request.
8. In the Retries field, specify the maximum number of times that the switch retries an ARP
request.
9. In the Cache Size field, specify the maximum number of entries for the ARP cache.
10. Next to Dynamic Renew, select Enable t o allow the ARP component to automatically
attempt to renew dynamic ARP entries when they age out.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Remove ARP Entries From the ARP Cache
You can remove certain types of entries from the ARP table.
To remove entries from the ARP table:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Routing > ARP > Advanced > ARP Entry Management.
The ARP Entry Management page displays.
6. From the Remove From Table menu, select the type of ARP entry to be removed.
•All Dynamic Entries
•All Dynamic and Gateway Entries
•Specific Dynamic/Gateway Entry
•Specific Static Entry
•None. This is the default selection.

Configuring Routing
217
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
7. If you select Specific Dynamic/Gateway Entry or Specific Static Entry from the Remove
From Table menu, enter the IP address of the entry that must be removed from the ARP
table.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

218
5
5. Configure Quality of Service
In a switch, each physical port consists of one or more queues for transmitting packets on the
attached network. Multiple queues per port are often provided to give preference to certain
packets over others based on user-defined criteria. When a packet is queued for transmission in
a port, the rate at which it is serviced depends on how the queue is configured and possibly the
amount of traffic present in the other queues of the port. If a delay is necessary, packets get held
in the queue until the scheduler authorizes the queue for transmission. As queues become full,
packets can no longer be held for transmission and are dropped by the switch.
Quality of Service (QoS) is a means of providing consistent, predictable data delivery by
distinguishing packets with strict timing requirements from those that are more tolerant of delay.
Packets with strict timing requirements are given special treatment in a QoS-capable network.
With this in mind, all elements of the network must be QoS capable. The presence of at least one
node that is not QoS capable creates a deficiency in the network path, and the performance of
the entire packet flow is compromised.
This chapter covers the following topics:
•Manage Class of Service
•Manage Differentiated Services

Configure Quality of Service
219
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Manage Class of Service
The Class of Service (CoS) queueing feature lets you directly configure certain aspects of
switch queueing. This provides the desired QoS behavior for dif ferent types of network traf fic
when the complexities of DiffServ are not required. The priority of a packet arriving at an
interface can be used to steer the packet to the appropriate outbound CoS queue through a
mapping table. CoS queue characteristics that affect queue mapping, such as minimum
guaranteed bandwidth or transmission rate shaping, are user configurable at the queue (or
port) level.
Eight queues per port are supported.
Overview of CoS Configuration
You can set the Class of Service trust mode for an interface. Each port in the switch can be
configured to trust one of the packet fields (802.1p or IP DSCP), or to not trust any packet’s
priority designation (untrusted mode). If the port is set to a trusted mode, it uses a mapping
table appropriate for the trusted field being used. This mapping table indicates the CoS
queue to which the packet must be forwarded on the appropriate egress port. Of course, the
trusted field must exist in the packet for the mapping table to be of any use. If this is not the
case, default actions are performed. These actions involve directing the packet to a specific
CoS level configured for the ingress port as a whole, based on the existing port default
priority as mapped to a traffic class by the current 802.1p mapping table.
Alternatively, when a port is configured as untrusted, it does not trust any incoming packet
priority designation and uses the port default priority value instead. All packets arriving at the
ingress of an untrusted port are directed to a specific CoS queue on the appropriate egress
ports, in accordance with the configured default priority of the ingress port. This process is
also used for cases where a trusted port mapping cannot be honored, such as when a non-IP
packet arrives at a port configured to trust the IP DSCP value.
Configure Global CoS Settings
To configure CoS trust mode settings on all interfaces:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
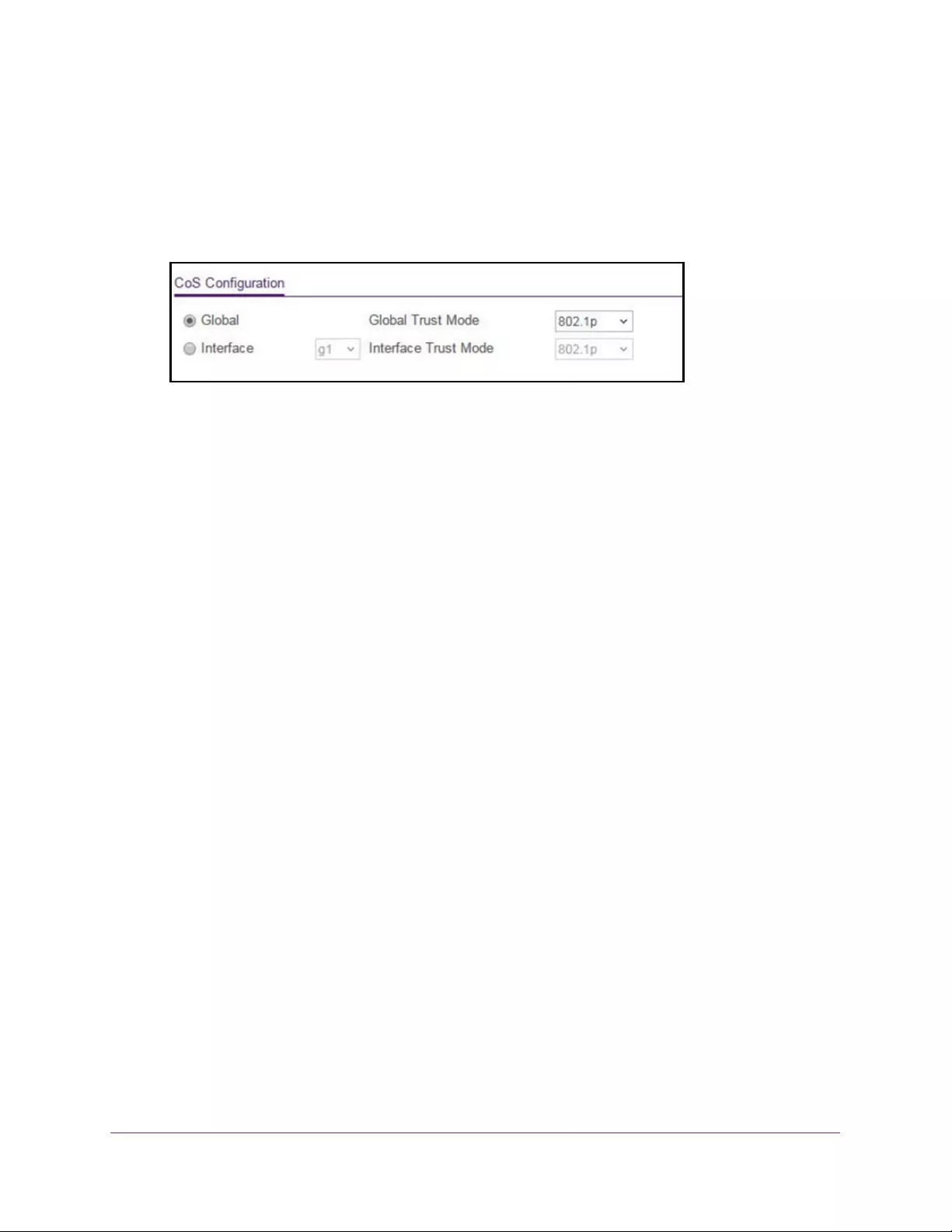
Configure Quality of Service
220
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS> CoS > Basic > CoS Configuration.
6. Either configure the same CoS trust mode settings for all CoS-configurable interfaces or
configure CoS settings per interface.
The default is Global.
•To configure the same CoS trust mode settings for all CoS configurable interfaces, do
the following:
a. Select the Global radio button.
b. From the Global Trust Mode menu, select one of the following trust mode
options for ingress traffic on the switch:
-Untrusted. Do not trust any CoS packet marking at ingress.
-802.1p. The eight priority tags that are specified in IEEE 802.1p are p0 to p7.
The QoS setting lets you map each of the eight priority levels to one of seven
internal hardware priority queues. The default mode is 802.1p.
-DSCP. The six most significant bits of the DiffServ field are called the
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) bits.
•To configure CoS settings per interface, do the following:
a. Select the Interface radio button.
b. From the Interface Trust Mode menu, select one of the following trust mode
options:
-Untrusted. Do not trust any CoS packet marking at ingress.
-802.1p. The eight priority tags that are specified in IEEE 802.1p are p0 to p7.
The QoS setting lets you map each of the eight priority levels to one of seven
internal hardware priority queues. The default mode is 802.1p.
-DSCP. The six most significant bits of the DiffServ field are called the
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) bits.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure Quality of Service
221
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure CoS Interface Settings for an Interface
You can configure the trust mode for one or more interfaces and apply an interface shaping
rate to all interfaces or to a specific interface.
To configure CoS settings for an interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
5. Select QoS > CoS > Advanced > CoS Interface Configuration.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Interface Trust Mode menu, select one of the following trust mode options for
ingress traffic on the selected interfaces:
•Untrusted. Do not trust any CoS packet marking at ingress.

Configure Quality of Service
222
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•802.1p. The eight priority tags that are specified in IEEE 802.1p are p0 to p7. The
QoS setting lets you map each of the eight priority levels to one of seven internal
hardware priority queues. The default value is 802.1p.
•DSCP. The six most significant bits of the DiffServ field are called the Differentiated
Services Code Point (DSCP) bits.
9. In the Interface Shaping Rate field, specify the maximum allowed bandwidth.
The maximum allowed bandwidth is typically used to shape the outbound transmission
rate. This value is controlled independently of any per-queue maximum bandwidth
configuration. It is effectively a second-level shaping mechanism. The default value is 0,
which means that the maximum is unlimited. You can enter values from 0 to 100 in
increments of 1.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure CoS Queue Settings for an Interface
You can define what a particular queue does by configuring switch egress queues.
User-configurable parameters control the amount of bandwidth used by the queue, the queue
depth during times of congestion, and the scheduling of packet transmission from the set of
all queues on a port. Each port contains its own CoS queue-related configuration.
The configuration process is simplified by allowing each CoS queue parameter to be
configured globally or per port. A global configuration change is automatically applied to all
ports in the system.
To configure CoS queue settings for an interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > CoS > Advanced > Interface Queue Configuration.
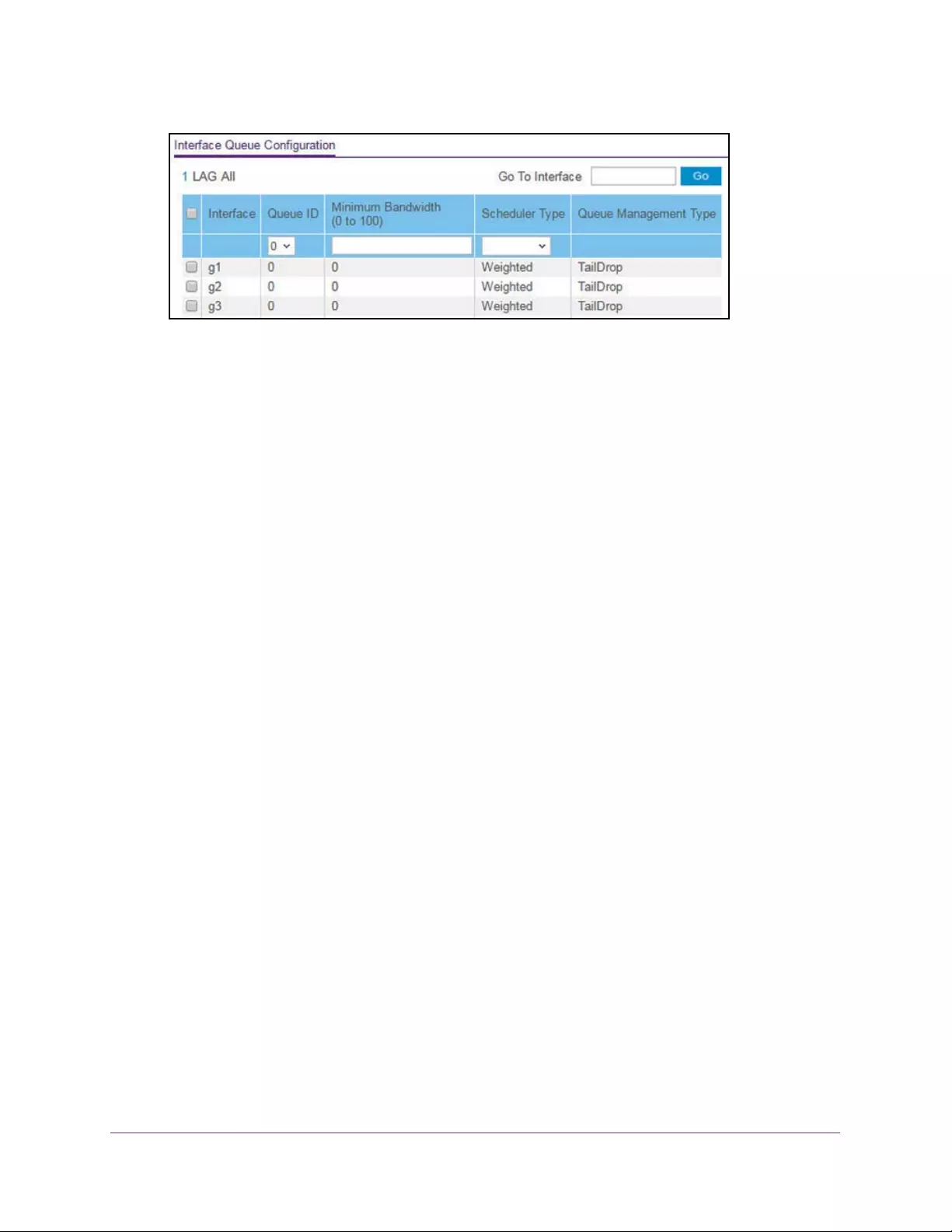
Configure Quality of Service
223
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Queue ID menu, select the queue to be configured.
9. In the Minimum Bandwidth field, specify the minimum guaranteed bandwidth allotted to the
queue.
Setting this value higher than its corresponding maximum bandwidth automatically
increases the maximum to the same value. The default value is 0. The valid range is 0 to
100 in increments of 1. The value 0 means no guaranteed minimum. The sum of the
individual minimum bandwidth values for all queues for the interface cannot exceed the
defined maximum (100).
10. From the Scheduler Type menu, select one of the following options:
•Strict. The interface services traffic with the highest priority on a queue first.
•Weighted. The interface uses weighted round robin to associate a weight to each
queue. This is the default setting.
The Queue Management Type field displays the queue depth management technique
that is used for queues on the interface. By default, this method is Taildrop, irrespective of
your selection from the Scheduler Type menu.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Map 802.1p Priorities to Queues
You can view or change which internal traffic classes are mapped to the 802.1p priority class
values in Ethernet frames that the device receives. The priority-to-traffic class mappings can
be applied globally or per interface. The mapping allows the switch to group various traffic
types (for example, data or voice) based on their latency requirements and give preference to
time-sensitive traffic.

Configure Quality of Service
224
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To map 802.1p priorities to queues:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > CoS > Advanced > 802.1p to Queue Mapping.
6. Select the Global radio button to specify all interfaces (that can be configured for CoS) or
select the Interface radio button to select individual interfaces.
7. In the 802.1p to Queue Mapping table, map each of the eight 802.1p priorities to a queue
(internal traffic class).
The 802.1p Priority row contains traffic class selectors for each of the eight 802.1p
priorities to be mapped. The priority goes from low (0) to high (7). For example, traf fic with
a priority of 0 is for most data traffic and is sent using best effort. Traffic with a higher
priority, such as 7, might be time-sensitive traffic, such as voice or video.
The values in the menu under each priority represent the traffic class. The traffic class is
the hardware queue for a port. Higher traffic class values indicate a higher queue
position. Before traffic in a lower queue is sent, it must wait for traffic in higher queues to
be sent.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
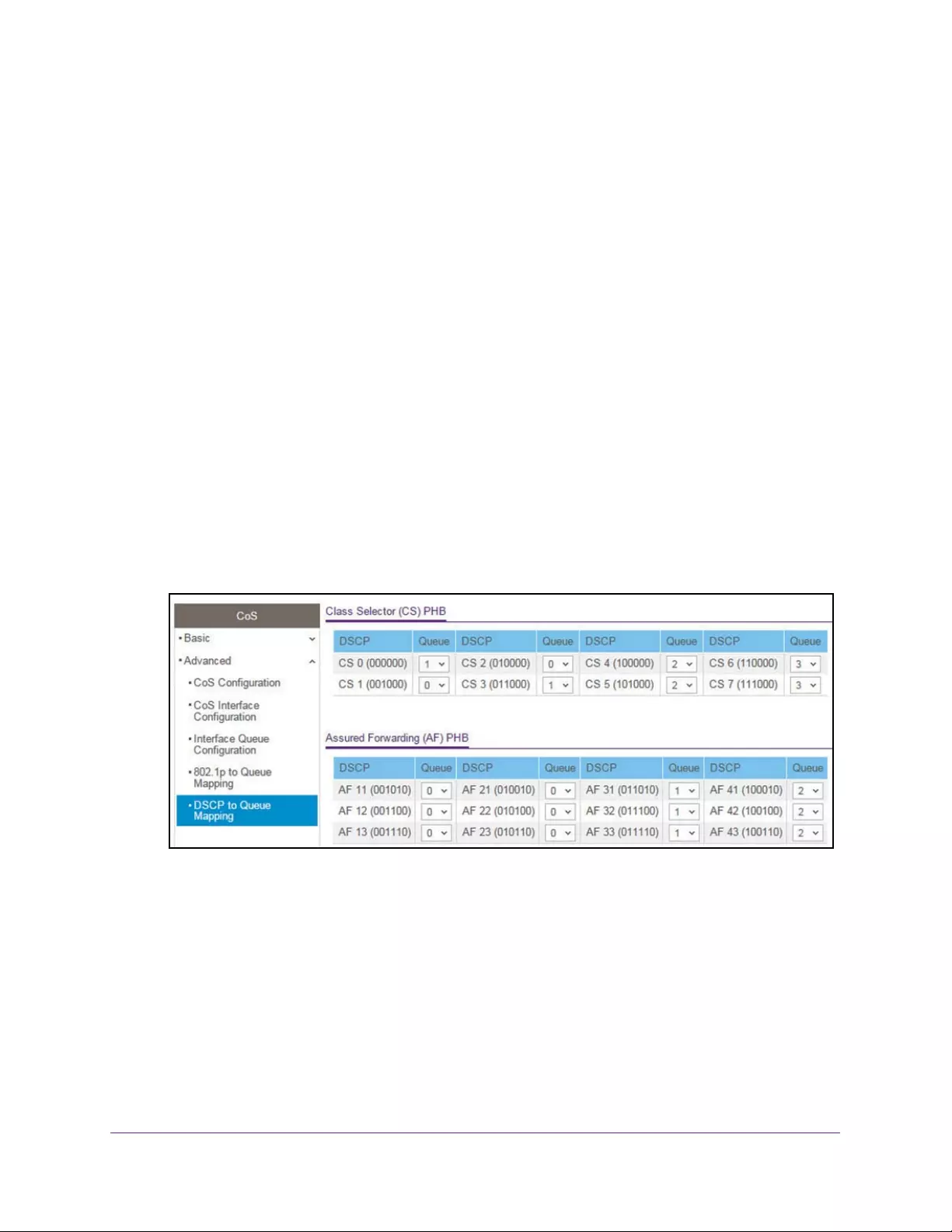
Configure Quality of Service
225
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Map DSCP Values to Queues
You can map an internal traffic class to a DSCP value.
To map DSCP values to queues:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > CoS > Advanced > DSCP to Queue Mapping.
6. For each DSCP value, select from the corresponding Queue menu which internal traffic
class must be mapped to the DSCP value.
The traffic class is the hardware queue for a port. Higher traffic class values indicate a
higher queue position. Before traffic in a lower queue is sent, it must wait for traffic in
higher queues to be sent.
The allowed Per Hop Behavior (PHBs) values, apart from other DSCP experimental
values, are as follows:
•Class Selector (CS) PHB. These values are based on IP precedence.
•Assured Forwarding (AF) PHB. These values define four main levels to sort and
manipulate some flows within the network.

Configure Quality of Service
226
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Expedited Forwarding (EF) PHB. These values are used to prioritize traffic for
real-time applications. In many situations, if the network exceeded traffic and you
need some bandwidth guaranteed for an application, the EF traffic must receive this
rate independently of the intensity of any other traffic attempting to transit the node.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Manage Differentiated Services
The QoS feature contains Differentiated Services (DiffServ) support that allows traffic to be
classified into streams and given certain QoS treatment in accordance with defined per-hop
behaviors.
Standard IP-based networks are designed to provide best effort data delivery service. Best
effort service implies that the network delivers the data in a timely fashion, although it is not
guaranteed. During times of congestion, packets might be delayed, sent sporadically, or
dropped. For typical Internet applications, such as email and file transfer , a slight degradation
in service is acceptable and in many cases unnoticeable. Conversely, any degradation of
service can negatively affect applications with strict timing requirements, such as voice or
multimedia.
Overview of Defining DiffServ
To use DiffServ for QoS, you must first define the following categories and their criteria:
1. Class. Create classes and define class criteria.
2. Policy. Create policies, associate classes with policies, and define policy statements.
3. Service. Add a policy to an inbound interface.
Packets are classified and processed based on defined criteria. The classification criteria are
defined by a class. The processing is defined by a policy’ s attributes. Policy attributes can be
defined on a per-class instance basis, and it is these attributes that are applied when a match
occurs. A policy can contain multiples classes. When the policy is active, the actions taken
depend on which class matches the packet.
Packet processing begins by testing the class match criteria for a packet. A policy is applied
to a packet when a class match within that policy is found.
Configure DiffServ Settings
Packets are filtered and processed based on defined criteria. The filtering criteria is defined
by a class. The processing is defined by a policy's attributes. Policy attributes can be defined
on a per-class instance basis, and it is these attributes that are applied when a match occurs.
The configuration process begins with defining one or more match criteria for a class. Then
one or more classes are added to a policy. Policies are then added to interfaces.
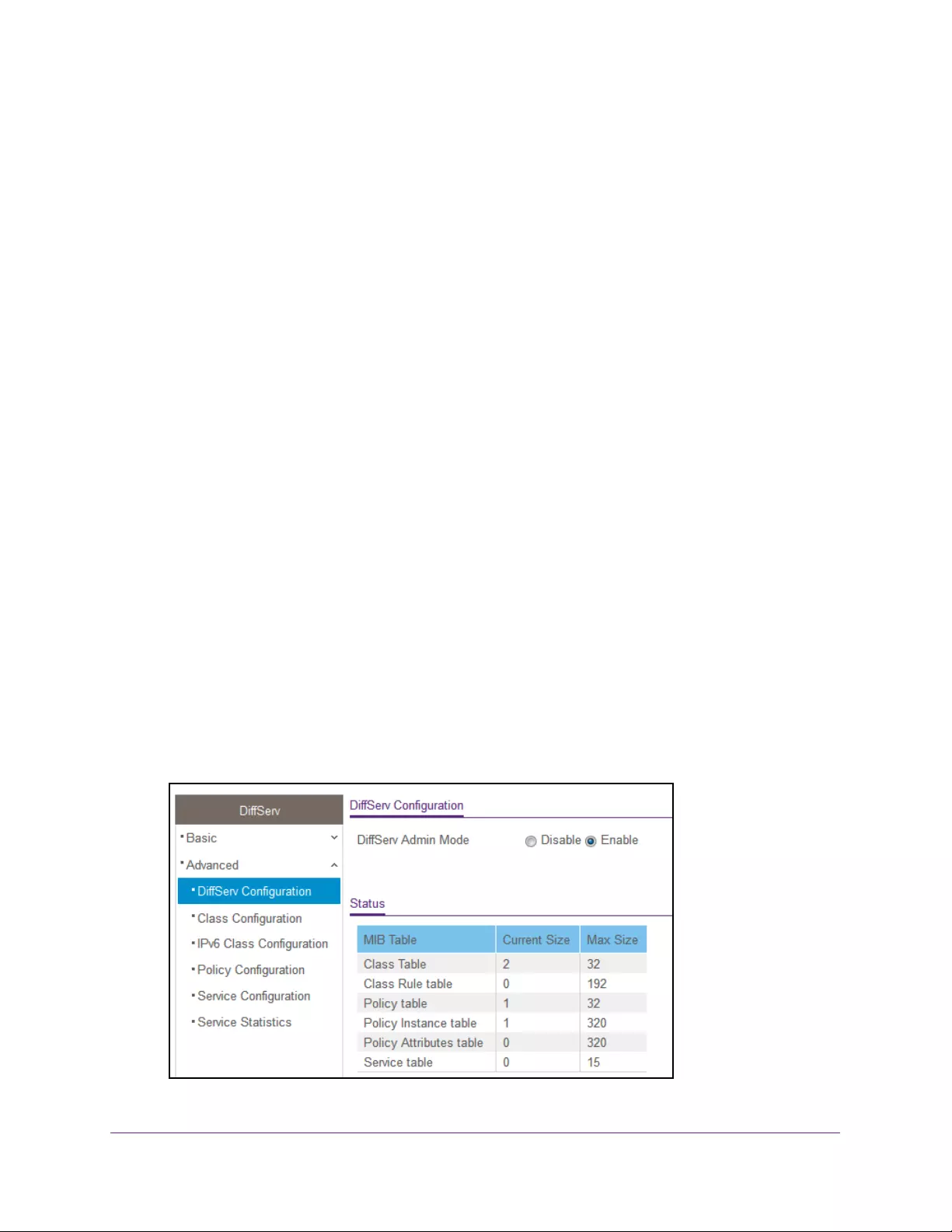
Configure Quality of Service
227
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Packet processing begins by testing the match criteria for a packet. The All class type option
specifies that each match criteria within a class must evaluate to true for a packet to match
that class. The Any class type option specifies that at least one match criteria must evaluate
to true for a packet to match that class. Classes are tested in the order in which they were
added to the policy. A policy is applied to a packet when a class match within that policy is
found.
Configure the Global DiffServ Mode
You can display DiffServ general status group information, which includes the current
administrative mode setting as well as the current and maximum number of rows in each of
the main DiffServ private MIB tables.
To configure the global DiffServ mode:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > DiffServ Configuration.

Configure Quality of Service
228
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Select the administrative mode for DiffServ:
•Enable. Differentiated services are active. This is the default setting.
•Disable. The DiffServ configuration is retained and can be changed but is not active.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the information displayed in the Status table on the DiffServ
Configuration page.
Configure a DiffServ Class
You can add a new DiffServ class name, or rename or delete an existing class. You can also
define the criteria to associate with a DiffServ class. As packets are received, these DiffServ
classes are used to prioritize packets. You can set up multiple match criteria in a class. The
logic is a Boolean logical AND for this criteria. After creating a class, click the class link to the
Class page.
Create and Configure a DiffServ Class
To create and configure a DiffServ class:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Table 61. DiffServ Status information
Field Description
Class Table The number of configured DiffServ classes out of the total allowed on the switch.
Class Rule table The number of configured class rules out of the total allowed on the switch.
Policy table The number of configured policies out of the total allowed on the switch.
Policy Instance table The number of configured policy class instances out of the total allowed on the
switch.
Policy Attributes table The number of configured policy attributes (attached to the policy class instances)
out of the total allowed on the switch.
Service table The number of configured services (attached to the policies on specified interfaces)
out of the total allowed on the switch.
Configure Quality of Service
229
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Class Configuration.
6. In the Class Name field, enter a class name.
The Class Name field also lists all the existing DiffServ class names, from which you can
select one for modification or deletion. The class name can be 1 to 31 alphanumeric
characters in length.
7. From the Class Type menu, select the class type.
The switch supports only the class type value All, which means that all the various match
criteria defined for the class are satisfied for a packet match. All signifies the logical AND
statement of all the match criteria. You can select the class type only when you are
creating a new class. After the class is created, the Class Type field becomes
nonconfigurable.
8. Click the Add button.
The new class is added.
9. After creating the class, click the class name.
The class name is a hyperlink to the page on which you can define the class
configuration.
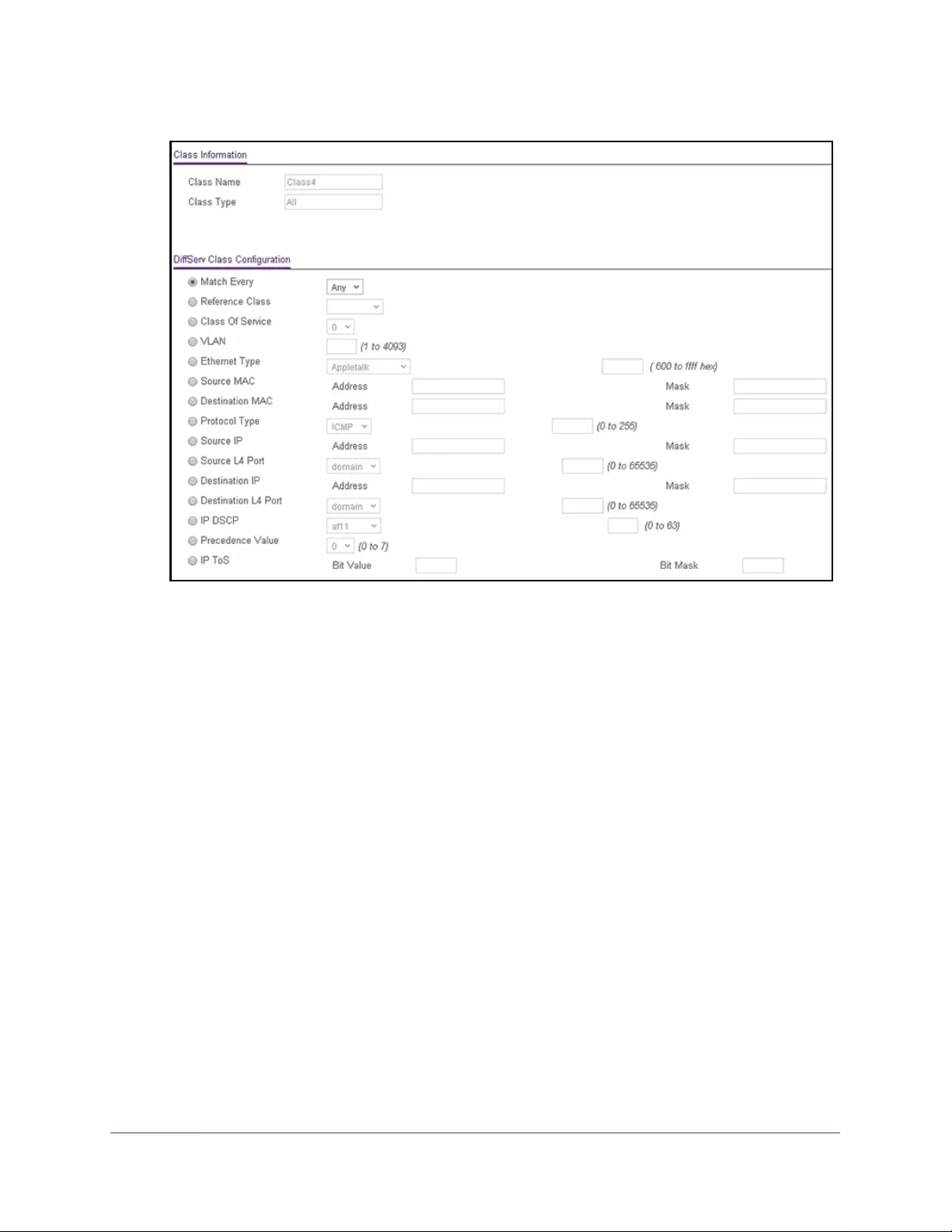
Configure Quality of Service
230
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
10. Define the criteria that must be associated the DiffServ class:
•Match Every. Select this radio button to add a match condition that considers all
packets to belong to the class. The only selection from the Match Every menu is Any.
•Reference Class. Select this radio button to reference another class for criteria. The
match criteria defined in the reference class function as match criteria in addition to
the match criteria that you define for the selected class. After you select the radio
button, the classes that can be referenced are displayed. Select the class to
reference. A class can reference at most one other class of the same type.
•Class of Service. Select this radio button to require the Class of Service (CoS) value
in an Ethernet frame header to match the specified CoS value. This option lists all the
values for the Class of Service match criterion in the range 0 to 7 from which one can
be selected.
•VLAN. Select this radio button to require a packet’s VLAN ID to match a VLAN ID or a
VLAN ID within a continuous range. If you configure a range, a match occurs if a
packet’s VLAN ID is the same as any VLAN ID within the range. The VLAN value is in
the range of 1–4093.
•Ethernet Type. Select this radio button to require the EtherType value in the Ethernet
frame header to match the specified EtherType value. After you select the radio
button, specify the EtherType keyword from the list of common protocols that are
mapped to their Ethertype value.

Configure Quality of Service
231
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Source MAC. Select this radio button to require a packet’s source MAC address to
match the specified MAC address. After you select this radio button, use the following
fields to configure the source MAC address match criteria:
-Address. The source MAC address to match. The source MAC address is
specified as six two-digit hexadecimal numbers separated by colons.
-Mask. The MAC mask, which specifies the bits in the source MAC address to
compare against the Ethernet frame. Use Fs and zeros to configure the MAC
mask. An F means that the bit is checked, and a zero in a bit position means that
the data is not significant. For example, if the MAC address is aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff,
and the mask is ff:ff:00:00:00:00, all MAC addresses with aa:bb:xx:xx:xx:xx result
in a match (where x is any hexadecimal number). Note that this is not a wildcard
mask, which ACLs use.
•Destination MAC. Select this radio button to require a packet’s destination MAC
address to match the specified MAC address. After you select the radio button, use
the following fields to configure the destination MAC address match criteria:
-Address. The destination MAC address to match. The destination MAC address
is specified as six two-digit hexadecimal numbers separated by colons.
-Mask. The MAC mask, which specifies the bits in the destination MAC address to
compare against an Ethernet frame. Use Fs and zeros to configure the MAC
mask. An F means that the bit is checked, and a zero in a bit position means that
the data is not significant. For example, if the MAC address is aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff,
and the mask is ff:ff:00:00:00:00, all MAC addresses with aa:bb:xx:xx:xx:xx result
in a match (where x is any hexadecimal number). Note that this is not a wildcard
mask, which ACLs use.
•Protocol T ype. Select this radio button to require a packet’ s Layer 4 protocol to match
the specified protocol, which you must select from the menu. The menu includes
Other as a selection, which lets you enter a protocol number from 0 to 255.
•Source IP. Select this radio button to require a packet’s source IP address to match
the specified IP address. After you select the radio button, use the following fields to
configure the source IP address match criteria:
-Address. The source IP address format to match in dotted-decimal.
-Mask. The bit mask in IP dotted-decimal format indicating which parts of the
source IP address to use for matching against packet content.
•Source L4 Port. Select this radio button to require a packet’s TCP/UDP source port to
match the specified protocol, which you must select from the menu. The range is 0 to
65535. The menu includes Other as an option for unnamed ports.
•Destination IP. Select this radio button to require a packet’s destination IP address to
match the specified IP address. After you select the radio button, use the following
fields to configure the destination IP address match criteria:
-Address. The destination IP address format to match in dotted-decimal.
-Mask. The bit mask in IP dotted-decimal format indicating which parts of the
destination IP address to use for matching against packet content.

Configure Quality of Service
232
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Destination L4 Port. Select this radio button to require a packet’s TCP/UDP
destination port to match the specified protocol, which you must select from the menu.
The range is 0 to 65535. The menu includes Other as an option for unnamed ports.
•IP DSCP. Select this radio button to require the packet’s IP DiffServ Code Point
(DSCP) value to match the specified IP DSCP keyword code, which you must select
from the menu. The menu includes Other as a selection, which lets you enter an IP
DSCP value from 0 to 63. The DSCP value is defined as the high-order 6 bits of the
Service Type octet in the IP header.
•Precedence Value. Select this radio button to require the packet’s IP precedence
value to match the specified number from 0 to 7, which you must select from the
menu. The IP Precedence field in a packet is defined as the high-order 3 bits of the
Service Type octet in the IP header.
•IP T oS. Select this radio button to require the packet’ s T ype of Service (ToS) bits in the
IP header to match the specified value. The IP ToS field in a packet is defined as all 8
bits of the service type octet in the IP header. After you select the radio button, use
the following fields to configure the ToS match criteria:
-Bits V alue. Enter a two-digit hexadecimal number octet value in the range from 00
to ff to match the bits in a packet’s ToS field.
-Bit Mask. Specify the bit positions that are used for comparison against the IP ToS
field in a packet.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed in the Class
Summary section at the bottom of the DiffServ Advanced Class Configuration page.
Rename an Existing DiffServ Class
To rename an existing DiffServ class:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
Table 62. DiffServ Class Configuration, Class Summary information
Field Description
Match Criteria The configured match criteria for the specified class.
Values The values of the configured match criteria.

Configure Quality of Service
233
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Class Configuration.
The Class Name page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the class name.
7. In the Class Name field, specify the new name.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Change the Criteria for an Existing DiffServ Class
To change the criteria for an existing DiffServ class:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Class Configuration.
The Class Name page displays.
6. Click the class name, which is a hyperlink.
The page on which you can change the class configuration displays.
7. Change the class configuration as needed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure Quality of Service
234
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Delete a DiffServ Class
To delete a DiffServ class:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Class Configuration.
The Class Name page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the class name.
7. Click the Delete button.
The class is removed.
Configure DiffServ IPv6 Class Settings
The IPv6 class configuration feature extends the existing QoS ACL and DiffServ functionality
by providing support for IPv6 packet classification. An Ethernet IPv6 packet is distinguished
from an IPv4 packet by its unique Ethertype value, so all IPv6 classifiers include the
Ethertype field. An IPv6 access list serves the same purpose as its IPv4 counterpart.
Before the introduction of the IPv6 class feature, any DiffServ class definition was assumed
to apply to an IPv4 packet. That is, any match item in a class rule was interpreted in the
context of an IPv4 header. An example is a class rule that specifies an L4 port match value.
With the introduction of the IPv6 match capability, you must specify if this class rule is for IPv4
or for IPv6 packets. To facilitate this distinction, a class configuration parameter is added to
specify whether a class applies to IPv4 or IPv6 packet streams.
The destination and source IPv6 addresses use a prefix length value instead of an individual
mask to qualify them as a subnet addresses or a host addresses. The flow label is a 20-bit
number that is unique to an IPv6 packet, used by end stations to signify some form of Quality
of Service (QoS) handling in routers.

Configure Quality of Service
235
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Packets that match an IPv6 classifier are allowed to be marked using only the 802.1p (CoS)
field or the IP DSCP field in the traffic Class octet. IP precedence is not defined for IPv6. This
is not an appropriate type of packet marking.
IPv6 ACL/DiffServ assignment is appropriate for LAG interfaces. The procedures described
by an ACL or DiffServ policy are equally applicable on a LAG interface.
Create and Configure an IPv6 DiffServ Class
To create and configure an IPv6 DiffServ class:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > IPv6 Class Configuration.
6. Enter a class name in the Class Name field.
The Class Name field also lists all the existing IPv6 class names, from which one can be
selected for modification or deletion.
7. From the Class Type menu, select the class type.
The switch supports only the class type value All, which means that all the various match
criteria defined for the class are satisfied for a packet match. All signifies the logical AND
statement of all the match criteria. You can select the class type only when you are
creating a new class. After the class is created, the Class Type field becomes
nonconfigurable.
8. Click the Add button.
The new class is added.
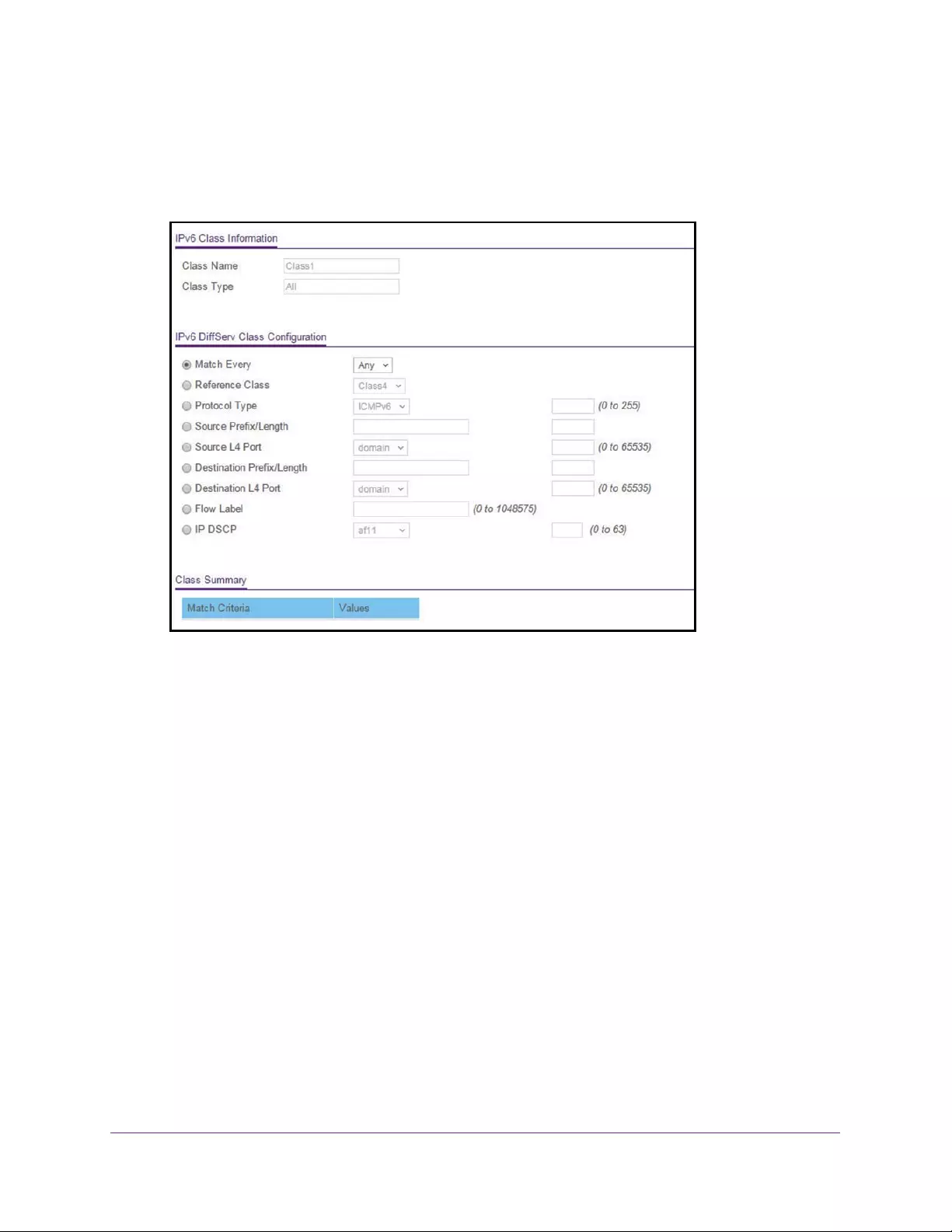
Configure Quality of Service
236
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
9. After creating the class, click the class name.
The class name is a hyperlink to the page on which you can define the class
configuration.
10. Define the criteria that must be associated the IPv6 DiffServ class:
•Match Every. Select this radio button to add a match condition that considers all
packets to belong to the class. The only selection from the Match Every menu is Any.
•Reference Class. Select this radio button to reference another class for criteria. The
match criteria defined in the reference class function as match criteria in addition to
the match criteria that you define for the selected class. After selecting this option, the
classes that can be referenced are displayed. Select the class to reference. A class
can reference at most one other class of the same type.
•Protocol T ype. Select this radio button to require a packet’s Layer 4 protocol to match
the specified protocol, which you must select from the menu. The menu includes
Other as a selection, which lets you enter a protocol number from 0 to 255.
•Source Prefix/Length. Select this radio button to require a packet’s source prefix and
prefix length to match the specified source IPv6 prefix and prefix length. Prefix must
always be specified with the prefix length. The prefix can be in the hexadecimal range
from 0 to FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF and the prefix length can
be in the range from 0 to 128.
•Source L4 Port. Select this radio button to require a packet’s TCP/UDP source port to
match the specified protocol, which you must select from the menu. The range is 0 to
65535. The menu includes Other as an option for unnamed ports.
Configure Quality of Service
237
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Destination Prefix/Length. Select this radio button to require a packet’s destination
prefix and prefix length to match the specified source IPv6 prefix and prefix length.
Prefix must always be specified with the prefix length. The prefix can be in the
hexadecimal range from 0 to FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF and
the prefix length can be in the range from 0 to 128.
•Destination L4 Port. Select this radio button to require a packet’s TCP/UDP
destination port to match the specified protocol, which you must select from the
menu. The range is 0 to 65535. The menu includes Other as an option for unnamed
ports.
•Flow Label. Select this radio button to require a packet’s flow label to match the
specified flow label. The flow label is a 20-bit number that is unique to an IPv6 packet
and that is used by end stations to signify QoS handling in routers. The flow label can
be specified in the range from 0 to 1048575.
•IP DSCP. Select this radio button to require the packet’s IP DiffServ Code Point
(DSCP) value to match the specified IP DSCP keyword code, which you must select
from the menu. The menu includes Other as a selection, which lets you enter an IP
DSCP value from 0 to 63. The DSCP value is defined as the high-order 6 bits of the
Service Type octet in the IP header.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information that is displayed in the Class
Summary section.
Rename an Existing IPv6 DiffServ Class
To rename an existing IPv6 DiffServ class:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Table 63. IPv6 DiffServ class configuration class summary
Field Description
Match Criteria The configured match criteria for the specified class.
Values The values of the configured match criteria.

Configure Quality of Service
238
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > IPv6 Class Configuration.
The Class Name page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the class name.
7. In the Class Name field, specify the new name.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Change the Criteria for an Existing IPv6 DiffServ Class
To change the criteria for an existing IPv6 DiffServ class:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > IPv6 Class Configuration.
The Class Name page displays.
6. Click the class name, which is a hyperlink.
The page on which you can change the class configuration displays.
7. Change the class configuration as needed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure Quality of Service
239
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Delete an IPv6 DiffServ Class
To delete an IPv6 DiffServ class:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > IPv6 Class Configuration.
The Class Name page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the class name.
7. Click the Delete button.
The class is removed.
Configure a DiffServ Policy
You can associate a collection of classes with one or more policies.
Create and Configure a DiffServ Policy
To create and configure a DiffServ policy:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
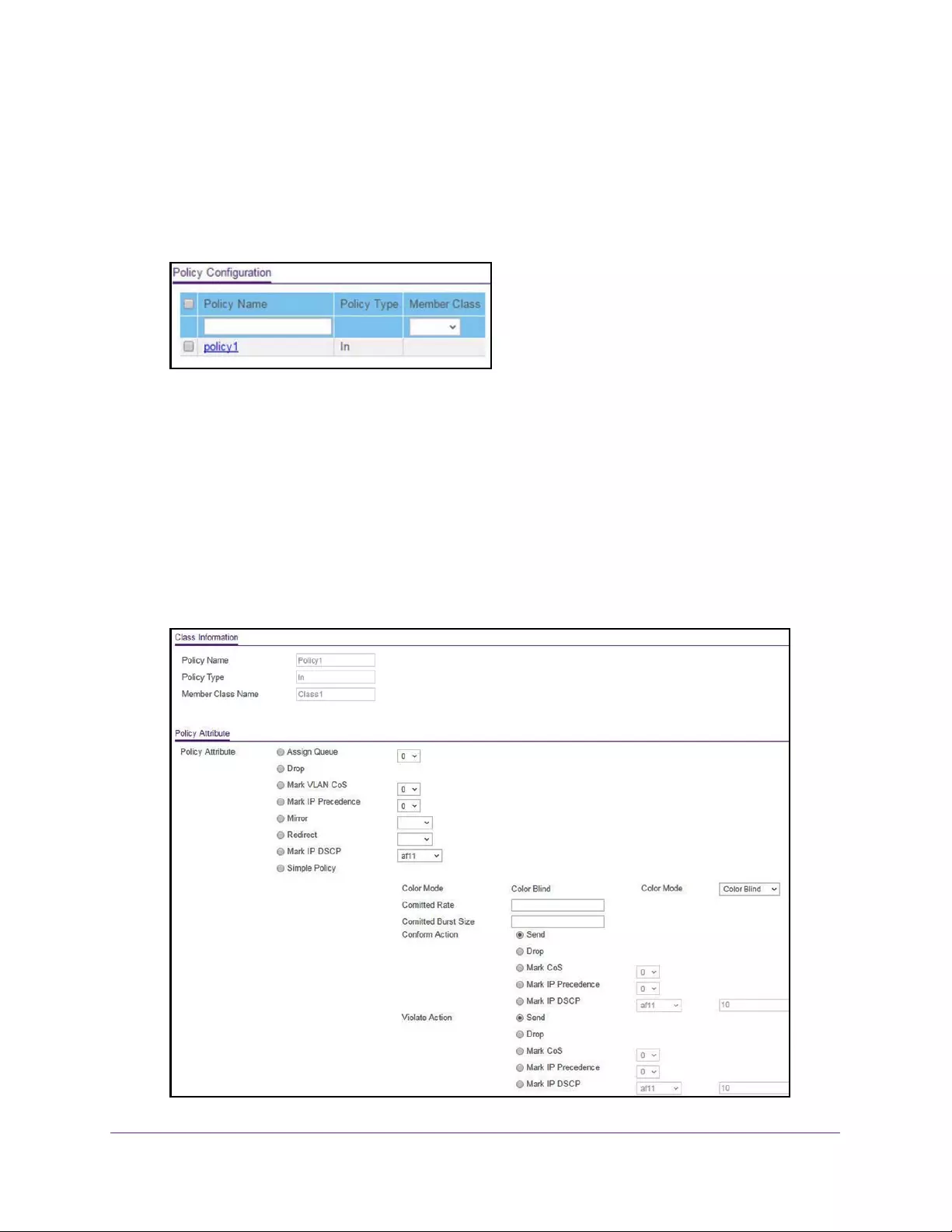
Configure Quality of Service
240
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Policy Configuration.
6. Enter a policy name in the Policy Name field.
You cannot specify the policy type. By default, the policy type is In, indicating that the
policy applies to ingress packets.
7. From the Member Class menu, optionally select an existing class that you want to
associate with the new policy.
8. Click the Add button.
The new policy is added.
9. After creating the policy, click the policy name.
The policy name is a hyperlink to the page on which you can define the policy attributes.

Configure Quality of Service
241
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
10. From the Assign Queue menu, select the queue to which packets of this policy class must
be assigned.
This is an integer value in the range 0 to 7.
11. Configure the policy attributes:
•Drop. Select this radio button to require each inbound packet to be dropped.
•Mark VLAN CoS. Select this radio button to specify the VLAN priority, which you must
select from the menu. The VLAN priority is expressed as an integer value in the range
from 0 to 7.
•Mark IP Precedence. Select this radio button to require packets to be marked with an
IP precedence value before being forwarded. You must select an IP precedence
value from 0 to 7 from the menu.
•Mirror. Select this radio button to require packets to be mirrored to an interface or
LAG, one of which you must select from the menu.
•Redirect. Select this radio button to require packets to be redirected to an interface or
LAG, one of which you must select from the menu.
•Mark IP DSCP. Select this radio button to require packet to be marked with an IP
DSCP keyword code, which you must select from the menu. The menu includes
Other as a selection, which lets you enter an IP DSCP value from 0 to 63. The DSCP
value is defined as the high-order 6 bits of the Service Type octet in the IP header.
•Simple Policy. Select this radio button to define the traffic policing style for the class.
A simple policy uses a single data rate and burst size, resulting in one of two
outcomes: conform or violate. You must define the policy as described in the next
step.
12. If you select the Simple Policy radio button, you can specify the traffic policing style for the
class:
•Color Mode. From the menu, select one of the following options:
-Color Blind. This is the default selection. Color classes do not apply.
-Color Aware. Requires you to select a color class that is valid for use with this
policy instance. After you select Color Aware from the Color Mode menu, the
Color Conform Class menu displays. From this menu you must select a color
class that you already created (see Configure a DiffServ Class on page 228) and
selected as a member class for this policy instance (see Step 7).
Note: A valid color class contains a single, non-excluded match criterion for
the CoS, IP DSCP, or IP Precedence option. The configured option
must not conflict with the classifier of the policy instance itself.
•Committed Rate. Enter the committed rate that is applied to conforming packets by
specifying a value in the range from 1 to 4294967295 Kbps.
•Committed Burst Size. Enter the committed burst size that is applied to conforming
packets by specifying a value in the range from 1 to 128 Kbps.
13. Select the conforming and violating actions.
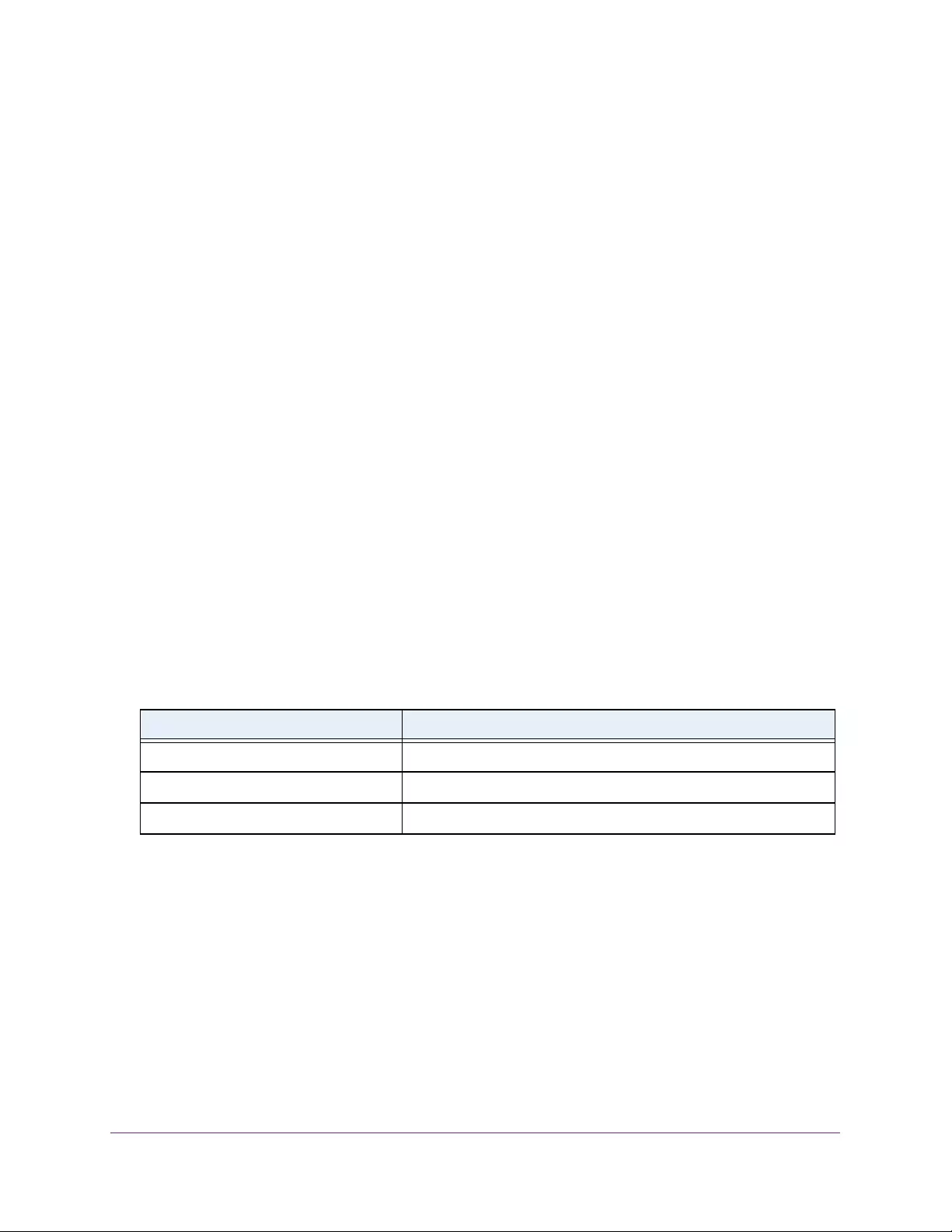
Configure Quality of Service
242
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The Conform Action section and Violate Action section list the actions to be taken on
conforming packets according to the policing metrics. By default, both conforming
packets and violating packets are sent.
In both the Conform Action section and the Violate Action section, select one of the
following actions:
•Send. Packets are forwarded unmodified. This is the default confirming action and the
default violating action.
•Drop. Packets are dropped.
•Mark CoS. Packets are marked by DiffServ with the specified CoS value before being
forwarded. This selection requires that the Mark CoS field is set. You must select a
CoS value from 0 to 7 from the menu.
•Mark IP Precedence. These packets are marked by DiffServ with the specified IP
Precedence value before being forwarded. This selection requires that the Mark IP
Precedence field is set. You must select an IP precedence value from 0 to 7 from the
menu.
•Mark IP DSCP. Packets are marked by DiffServ with the specified DSCP value before
being forwarded. This selection requires that the DSCP field is set. You must select a
DSCP code from the menu. The menu includes Other as a selection, which lets you
enter an IP DSCP value from 0 to 63. The DSCP value is defined as the high-order six
bits of the Service Type octet in the IP header.
14. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Rename an Existing DiffServ Policy
To rename an existing DiffServ policy:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
Table 64. DiffServ policy configuration policy attribute
Field Description
Policy Name The name of the DiffServ policy.
Policy Type The type of the policy, which is always inbound (In).
Member Class Name The name of the class instance within the policy.

Configure Quality of Service
243
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Policy Configuration.
The Policy Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the policy name.
7. In the Policy Name field, specify the new name.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Change the Policy Attributes for an Existing DiffServ Policy
To change the policy attributes for an existing DiffServ policy:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Policy Configuration.
The Policy Configuration page displays.
6. Click the policy name, which is a hyperlink.
The page on which you can change the policy attributes displays.
7. Change the policy attributes as needed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Configure Quality of Service
244
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Remove a Class From an Existing DiffServ Policy
To remove a class from an existing DiffServ policy:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Policy Configuration.
The Policy Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the policy name.
7. From the Member Class menu, select None.
8. Click the Apply button.
The class is removed from the policy.
Delete a DiffServ Policy
To delete a DiffServ policy:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
Configure Quality of Service
245
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Policy Configuration.
The Policy Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the policy name.
7. Click the Delete button.
The policy is removed.
Configure the DiffServ Service Interface
You can activate a policy on an interface.
Attach a DiffServ Policy to an Interface
To attach a DiffServ policy to an interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Service Configuration.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
Configure Quality of Service
246
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Policy Name menu, select a policy name.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Remove a DiffServ Policy From an Interface
To remove a DiffServ policy from an interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Service Configuration.
The Service Interface Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check boxes that are associated with the interfaces from which you want to
remove the policy.
7. From the Policy In Name menu, select None.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Table 65. Service Interface Configuration information
Field Description
Direction Shows the traffic direction of this service interface (either In or Out).
Operational Status Shows the operational status of this service interface (either Up or Down).
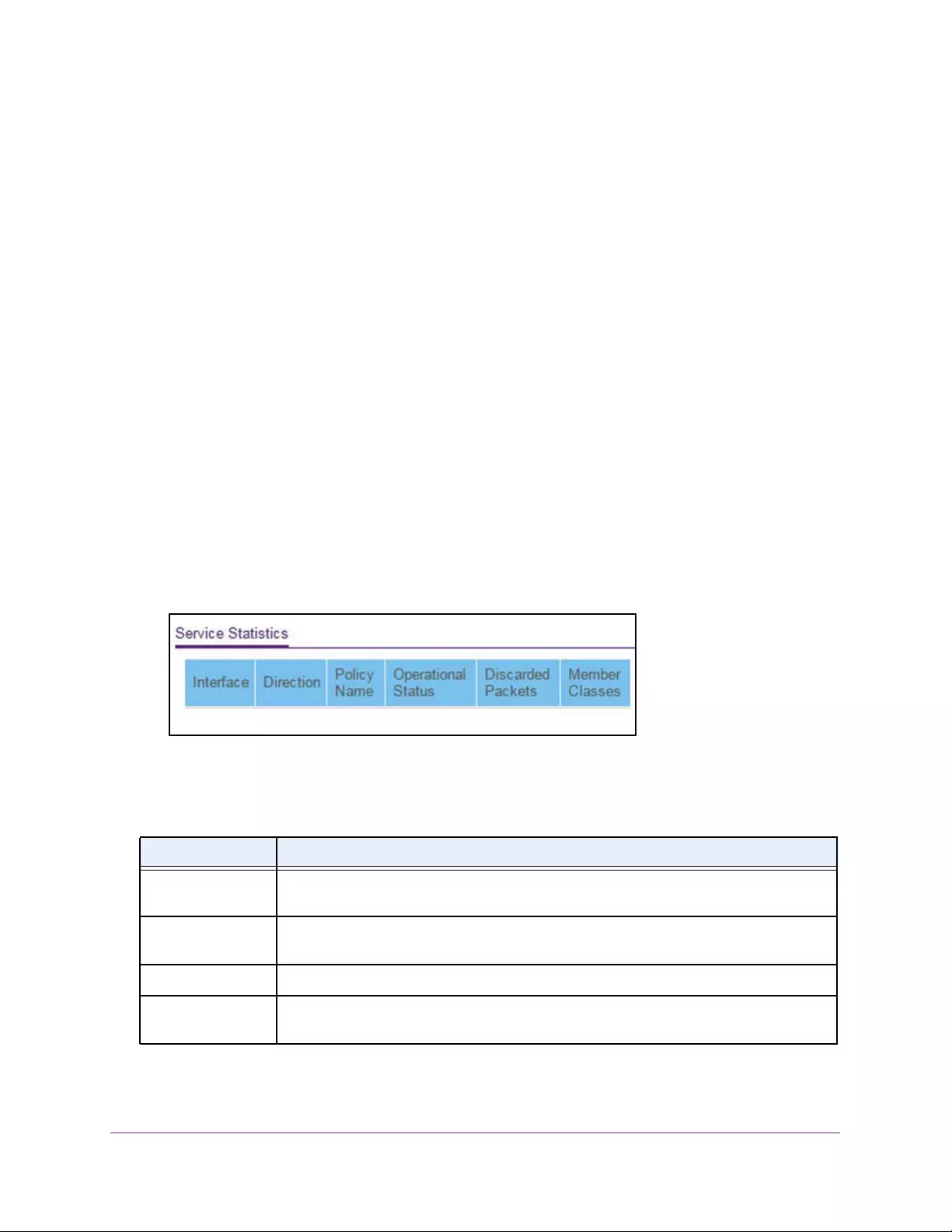
Configure Quality of Service
247
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View DiffServ Service Statistics
You can display service-level statistical information about all interfaces to which DiffServ
policies are attached.
To view the DiffServ service statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > Service Statistics.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the information available on the Service Statistics page.
Table 66. DiffServ Service Statistics information
Field Description
Interface All valid port numbers on the switch with a DiffServ policy that is attached in the inbound
direction.
Direction The traffic direction of interface is inbound (In). This field shows only the direction for
which a DiffServ policy is attached.
Policy Name The name of the policy that is currently attached to the specified interface and direction.
Operational Status The operational status of the policy that is attached to the specified interface and
direction. The value is either Up or Down.

Configure Quality of Service
248
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Discarded Packets The total number of packets that are discarded for all class instances in this service policy
for any reason due to DiffServ treatment. This is the overall count per interface, per
direction. The discarded packets are supported in the inbound direction but not in the
outbound direction.
Member Classes All DiffServ classes that are defined as members of the selected policy name. Select a
member class name to display its statistics. If no class is associated with the selected
policy, then the list is empty.
Table 66. DiffServ Service Statistics information (continued)
Field Description

Manage Device Security
250
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Management Security Settings
You can configure the login password, Remote Authorization Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)
settings, Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) settings, and
authentication lists.
Change the Password
You can change the login password.
To change the login password for the management interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security> Management Security > User Configuration > Change Password.
The Change Password page displays.
6. In the Old Password field, specify the current password for the account created by the user.
The entered password is displayed in dots. Passwords are up to 20 alphanumeric
characters in length, and are case sensitive.
7. In the New Password field, specify the optional new or changed password for the account.
The entered password is displayed in dots. Passwords are up to 20 alphanumeric
characters in length, and are case sensitive.
8. In the Confirm Password field, enter the password again to confirm that you entered it
correctly.
The entered password is displayed in dots.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Manage Device Security
251
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Reset the Password to the Default Password
You can reset the password to the default password, which is password.
If you added the switch to a network on the Insight app before and you change the
management mode back to NETGEAR Insight Mobile App and Insight Cloud Portal, all
Insight-manageable device settings are returned to the last configuration saved on the cloud
server, including the switch password (that is, the password is reset to the Insight network
password).
If you changed the password through the local browser interface and you forget the password
and are unable to log in to switch, press the multifunctional Reset button on the front panel of
the switch for more than five seconds. The device reboots, and all switch settings, including
the password, are reset to the factory default values.
To reset the password to the default password:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security> Management Security > User Configuration > Change Password.
The Change Password page displays.
6. Select the Reset Password check box.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Manage Device Security
252
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
RADIUS Overview
RADIUS servers provide additional security for networks. The RADIUS server maintains a
user database, which contains per-user authentication information. The switch passes
information to the configured RADIUS server, which can authenticate a user name and
password before authorizing use of the network. RADIUS servers provide a centralized
authentication method for the following:
•Web access
•Access control port (802.1X)
Configure the Global RADIUS Server Settings
Use the Global Configuration page to add information about one or more RADIUS servers on
the network.
Consider the maximum delay time when you are configuring RADIUS maximum retransmit
and RADIUS time-out values. If multiple RADIUS servers are configured, the maximum
retransmit period on each server runs out before the next server is attempted. A retransmit
does not occur until the configured time-out period on that server passes without a response
from the RADIUS server. Therefore, the maximum delay in receiving a response from the
RADIUS application equals the retransmit time x time-out period for all configured servers. If
the RADIUS request was generated by a user login attempt, all user interfaces are blocked
until the RADIUS application returns a response.
To configure the global RADIUS server settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Global Configuration.
The RADIUS Configuration page displays.
The Current Server IP Address field is blank if no servers are configured (see Configure a
RADIUS Authentication Server on the Switch on page 254). The switch supports up to
three RADIUS servers. If more than one RADIUS server is configured, the current server

Manage Device Security
253
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
is the server configured as the primary server. If no servers are configured as the primary
server, the current server is the most recently added RADIUS server.
6. In the Max Number of Retransmits field, specify the maximum number of times a request
packet is retransmitted to the RADIUS server.
The valid range is from 1 to 15. The default value is 4.
Consider the maximum delay time when you are configuring RADIUS maximum
retransmit and RADIUS time-out values. If multiple RADIUS servers are configured, the
maximum retransmit period on each server runs out before the next server is attempted.
A retransmit does not occur until the configured time-out period on that server passes
without a response from the RADIUS server. Therefore, the maximum delay in receiving
a response from the RADIUS application equals the retransmit time x time-out period for
all configured servers. If the RADIUS request was generated by a user login attempt, all
user interfaces are blocked until the RADIUS application returns a response.
7. In the Timeout Duration field, specify the time-out value, in seconds, for request
retransmissions.
The valid range is from 1 to 30. The default value is 5.
Consider the maximum delay time when you are configuring RADIUS maximum
retransmit and RADIUS time-out values. If multiple RADIUS servers are configured, the
maximum retransmit period on each server runs out before the next server is attempted.
A retransmit does not occur until the configured time-out period on that server passes
without a response from the RADIUS server. Therefore, the maximum delay in receiving
a response from the RADIUS application equals the retransmit time x time-out period for
all configured servers. If the RADIUS request was generated by a user login attempt, all
user interfaces are blocked until the RADIUS application returns a response.
8. From he Accounting Mode menu, select to disable or enable RADIUS accounting on the
server.
The default is Disabled.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields displayed on the page.
Table 67. RADIUS Configuration information
Field Description
Current Server Address The address of the current server. This field is blank if no servers are configured.
Number of Configured
Authentication Servers The number of configured authentication RADIUS servers. The value can range
from 0 to 32.

Manage Device Security
254
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure a RADIUS Authentication Server on the Switch
Use the RADIUS Server Configuration page to view and configure various settings for a
RADIUS server configured on the switch.
Add a Primary RADIUS Authentication Server to the Switch
To add a primary RADIUS authentication server to the switch and view the RADIUS
authentication server statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Server Configuration.
The Server Configuration page displays.
6. In the Server Address field, specify the IP address of the RADIUS server.
7. In the Authentication Port field, specify the UDP port number the server uses to verify the
RADIUS server authentication.
The valid range is from 1 to 65535. The default value is 1812.
8. From the Secret Configured menu, select Yes.
You must select Yes before you can configure the RADIUS secret. After you add the
RADIUS server, this field indicates whether the shared secret for this server was
configured.
9. In the Secret field, type the shared secret text string used for authenticating and encrypting
all RADIUS communications between the switch and the RADIUS server.
This secret must match the RADIUS encryption.
10. From the Active menu, select Primary.
11. From the Message Authenticator menu, select Enable or Disable to specify whether the
message authenticator attribute for the selected server is enabled.
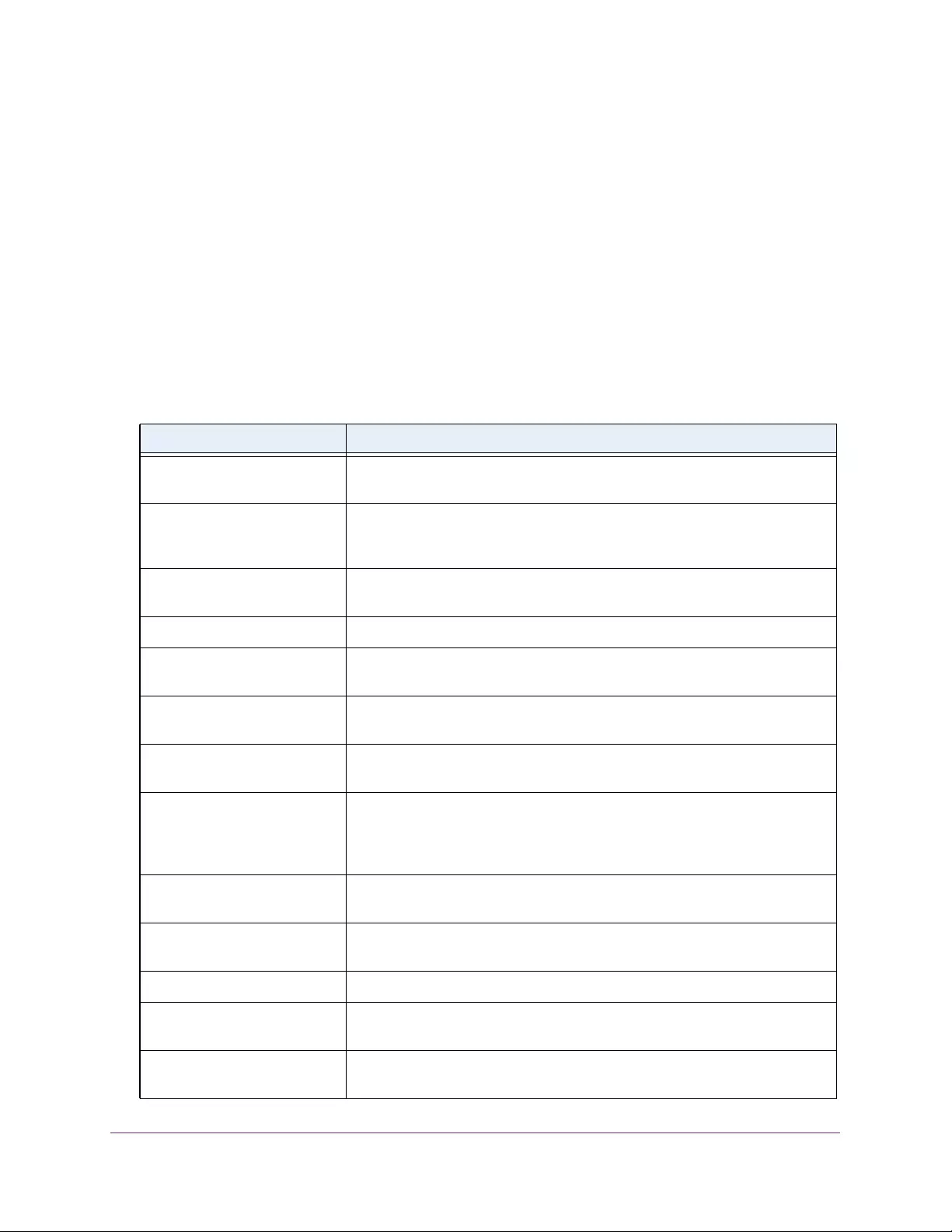
Manage Device Security
255
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The message authenticator adds protection to RADIUS messages by using an MD5 hash
to encrypt each message. The shared secret is used as the key, and if the message fails
to be verified by the RADIUS server, it is discarded.
12. Click the Add button.
The server is added to the switch.
13. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
14. To reset the authentication server and RADIUS statistics to their default values, click the
Clear Counters button.
The following table describes the RADIUS server statistics displayed on the page.
Table 68. RADIUS authentication server statistics information
Field Description
Server Address The address of the RADIUS server or the name of the RADIUS server for
which the statistics are displayed.
Round Trip Time The time interval, in hundredths of a second, between the most recent
access-reply/access-challenge and the access-request that matched it from
this RADIUS authentication server.
Access Requests The number of RADIUS access-request packets sent to this server. This
number does not include retransmissions.
Access Retransmissions The number of RADIUS access-request packets retransmitted to this server.
Access Accepts The number of RADIUS access-accept packets, including both valid and
invalid packets, that were received from this server.
Access Rejects The number of RADIUS access-reject packets, including both valid and invalid
packets, that were received from this server.
Access Challenges The number of RADIUS access-challenge packets, including both valid and
invalid packets, that were received from this server.
Malformed Access Responses The number of malformed RADIUS access-response packets received from
this server. Malformed packets include packets with an invalid length. Bad
authenticators or signature attributes or unknown types are not included in
malformed access-responses.
Bad Authenticators The number of RADIUS access-response packets containing invalid
authenticators or signature attributes received from this server.
Pending Requests The number of RADIUS access-request packets destined for this server that
did not yet time out or receive a response.
Timeouts The number of authentication time-outs to this server.
Unknown Types The number of RADIUS packets of unknown type that were received from this
server on the authentication port.
Packets Dropped The number of RADIUS packets received from this server on the
authentication port and dropped for some other reason.

Manage Device Security
256
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Modify the Settings for a RADIUS Authentication Server on the Switch
To modify the settings for a RADIUS authentication server on the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Server Configuration.
The Server Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the server IP address.
7. Modify the configuration for the selected server.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Remove a RADIUS Authentication Server From the Switch
To a remove a RADIUS authentication server from the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.

Manage Device Security
257
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Server Configuration.
The Server Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the IP address of the server to remove.
7. Click the Delete button.
The RADIUS server is removed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure a RADIUS Accounting Server
Use the Accounting Server Configuration page to view and configure various settings for a
RADIUS accounting servers on the network.
Add a RADIUS Accounting Server to the Switch
To add a RADIUS accounting server to the switch and view the RADIUS accounting
server statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Accounting Server Configuration.
The Accounting Server Configuration page displays.
6. In the Accounting Server Address field, specify the IP address of the RADIUS accounting
server to add.
7. In the Port field, specify the UDP port number the server uses to verify the RADIUS
accounting server authentication. The default UDP port number is 1813.
8. From the Secret Configured menu, select Yes to add a RADIUS secret in the next field.
You must select Yes before you can configure the RADIUS secret. After you add the
RADIUS accounting server, this field indicates whether the shared secret for this server
was configured.
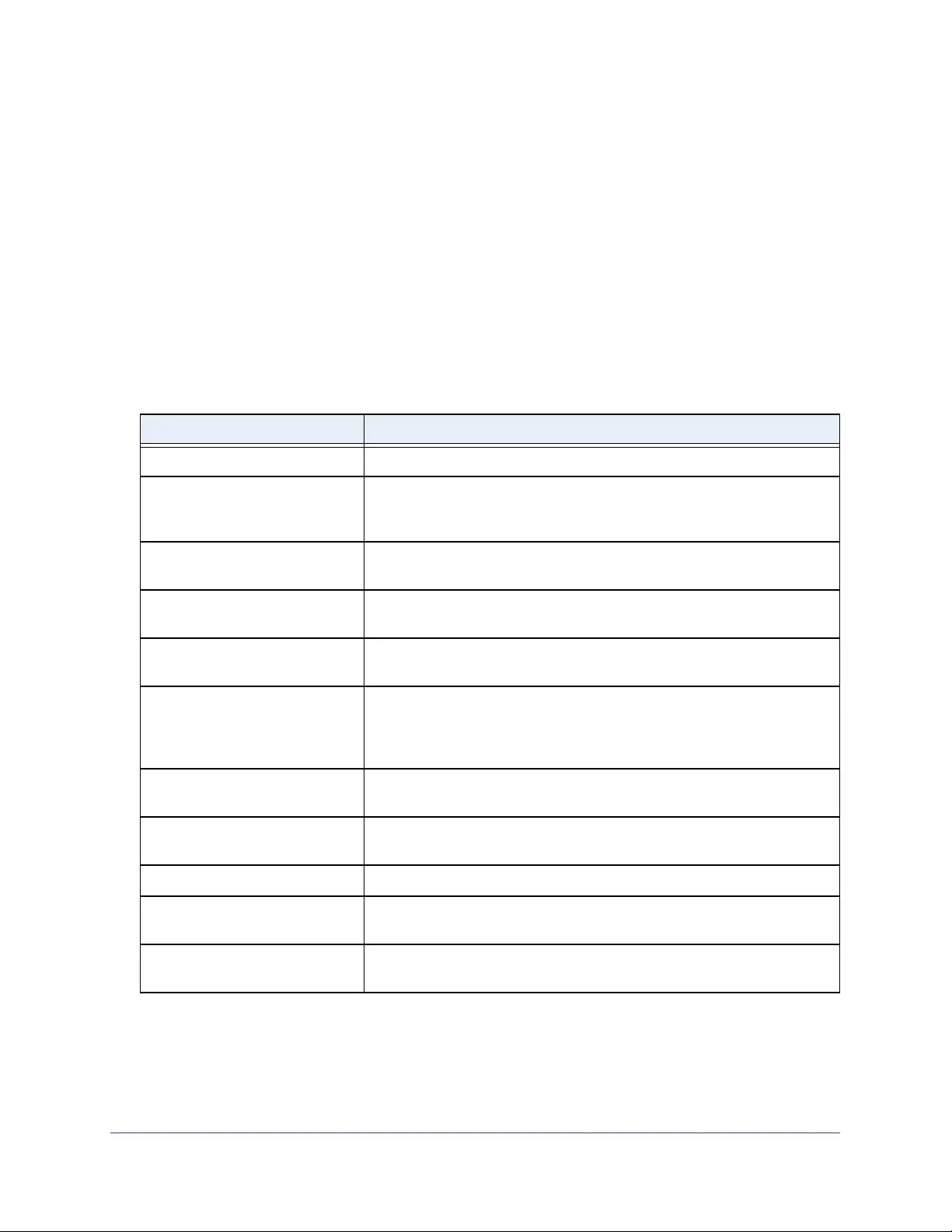
Manage Device Security
258
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
9. In the Secret field, type the shared secret to use with the specified accounting server.
10. From the Accounting Mode menu, select Enable to enable the RADIUS accounting mode.
11. Click the Add button.
The server is added to the switch.
12. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the RADIUS server statistics displayed on the page.
13. To reset the accounting server and RADIUS statistics to their default values, click the Clear
Counters button.
Table 69. RADIUS accounting server statistics information
Field Description
Accounting Server Address The accounting server associated with the statistics.
Round Trip Time (secs) The time interval, in hundredths of a second, between the most recent
accounting-response and the accounting-request that matched it from this
RADIUS accounting server.
Accounting Requests The number of RADIUS accounting-request packets sent not including
retransmissions.
Accounting Retransmissions The number of RADIUS accounting-request packets retransmitted to this
RADIUS accounting server.
Accounting Responses The number of RADIUS packets received on the accounting port from this
server.
Malformed Accounting Responses The number of malformed RADIUS accounting-response packets received
from this server. Malformed packets include packets with an invalid length.
Bad authenticators and unknown types are not included as malformed
accounting responses.
Bad Authenticators The number of RADIUS accounting-response packets that contained invalid
authenticators received from this accounting server.
Pending Requests The number of RADIUS accounting-request packets sent to this server that
did not yet time out or receive a response.
Timeouts The number of accounting time-outs to this server.
Unknown Types The number of RADIUS packets of unknown type that were received from
this server on the accounting port.
Packets Dropped The number of RADIUS packets that were received from this server on the
accounting port and dropped for some other reason.

Manage Device Security
259
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Modify the Settings for a RADIUS Accounting Server on the Switch
To modify the settings for a RADIUS accounting server on the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Accounting Server Configuration.
The Accounting Server Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the server IP address.
7. Modify the configuration for the selected accounting server.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Remove a RADIUS Accounting Server From the Switch
To a remove a RADIUS accounting server from the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.

Manage Device Security
260
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Accounting Server Configuration.
The Accounting Server Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the IP address of the server to remove.
7. Click the Delete button.
The RADIUS accounting server is removed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure TACACS+
TACACS+ provides a centralized user management system, while still retaining consistency
with RADIUS and other authentication processes. TACACS+ provides the following services:
•Authentication. Provides authentication during login and through user names and
user-defined passwords.
•Authorization. Performed at login. When the authentication session is completed, an
authorization session starts using the authenticated user name. The TACACS+ server
checks the user privileges.
The TACACS+ protocol ensures network security through encrypted protocol exchanges
between the device and TACACS+ server.
Configure the Global TACACS+ Settings
You can configure the TACACS+ settings for communication between the switch and the
TACACS+ server that you set up.
To configure the global TACACS+ settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > TACACS+ > TACACS+ Configuration.

Manage Device Security
261
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The TACACS+ Configuration page displays.
6. In the Key String field, specify the authentication and encryption key for TACACS+
communications between the switch and the TACACS+ server.
The valid range is 0–128. The key must match the key configured on the TACACS+
server.
7. In the Connection Timeout field, specify the maximum number of seconds allowed to
establish a TCP connection between the switch and the TACACS+ server.
The valid range is 1–30 seconds. The default is 5 seconds.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure a TACACS+ Server on the Switch
Use the TACACS+ Server Configuration page to configure up to five TACACS+ servers with
which the switch can communicate.
To configure a TACACS+ server on the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security> TACACS+ > TACACS+ Server Configuration.
The TACACS+ Server Configuration page displays.
6. In the TACACS+ Server field, enter the TACACS+ server IP address.
7. In the Priority field, specify the priority for the TACACS+ server.
The priority determines the order in which the TACACS+ servers are contacted when
attempting to authenticate a user. A value of 0 is the highest priority. The valid range is
0–65535.
8. In the Port field, specify the authentication port value for TACAS+ server sessions. It must
be within the range 0–65535. If you do not specify a value, the switch uses the standard
TCP port 49 for sessions with the server.

Manage Device Security
262
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
9. In the Key String field, specify the authentication and encryption key for TACACS+
communications between the device and the TACACS+ server.
The valid range is 0–128. The key must match the key used on the TACACS+ server.
10. In the Connection Timeout field, specify the time that passes before the connection
between the device and the TACACS+ server times out.
The range is 1–30. If you do not specify a value, the switch uses a default value of 5.
11. Click the Add button.
The server is added to the switch.
Configure Authentication Lists
You can configure a default login list that specifies one or more authentication methods to
validate switch or port access for the admin user.
Note: The admin user is assigned to a preconfigured list that is named
defaultList and that you cannot delete.
Configure an HTTP Authentication List
You can configure the default HTTP login list.
To change the HTTP authentication method for the default list:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > Authentication List > HTTP Authentication
List.
The HTTP Authentication List page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the httpList name.

Manage Device Security
263
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
7. From the menu in the 1 column, select the authentication method that must be used first in
the selected authentication login list.
If you select a method that does not time out as the first method, such as Local, no other
method is tried, even if you specified more than one method. User authentication occurs
in the order the methods are selected. Possible methods are as follows:
•Local. The user’s locally stored ID and password are used for authentication. Since
the Local method does not time out, if you select this option as the first method, no
other method is tried, even if you specified more than one method.
•Radius. The user’s ID and password are authenticated using the RADIUS server. If
you select Radius as the first method and an error occurs during the authentication,
the switch uses Method 2 to authenticate the user.
•Tacacs+. The user’s ID and password are authenticated using the TACACS+ server.
If you select Tacacs+ as the first method and an error occurs during the
authentication, the switch attempts user authentication Method 2.
•None. The authentication method is unspecified. This option is available only for
Method 2 and Method 3.
8. From the menu in the 2 column, select the authentication method, if any, that must be used
second in the selected authentication login list.
This is the method that is used if the first method times out. If you select a method that
does not time out as the second method, the third method is not tried.
9. From the menu in the 3 column, select the authentication method, if any, that must be used
third in the selected authentication login list.
10. From the menu in the 4 column, select the method, if any, that must be used fourth in the
selected authentication login list.
This is the method that is used if all previous methods time out.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure an HTTPS Authentication List
You can configure the default login list for secure HTTP (HTTPS).
To configure an HTTPS authentication list:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.

Manage Device Security
264
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > Authentication List > HTTPS Authentication
List.
The HTTPS Authentication List page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the httpsList name.
7. From the menu in the 1 column, select the authentication method that must be used first in
the selected authentication login list.
If you select a method that does not time out as the first method, such as Local, no other
method is tried, even if you specified more than one method. This setting does not display
when you first create a new login list. User authentication occurs in the order the methods
are selected. Possible methods are as follows:
•Local. The user’s locally stored ID and password are used for authentication. Since
the Local method does not time out, if you select this option as the first method, no
other method is tried, even if you specified more than one method.
•Radius. The user’s ID and password are authenticated using the RADIUS server. If
you select Radius as the first method and an error occurs during the authentication,
the switch uses Method 2 to authenticate the user.
•Tacacs+. The user’s ID and password are authenticated using the TACACS+ server.
If you select Tacacs+ as the first method and an error occurs during the
authentication, the switch attempts user authentication Method 2.
•None. The authentication method is unspecified. This option is only available for
Method 2 and Method 3.
8. From the menu in the 2 column, select the authentication method, if any, that must be used
second in the selected authentication login list.
This is the method that is used if the first method times out. If you select a method that does
not time out as the second method, the third method is not tried.
9. From the menu in the 3 column, select the authentication method, if any, that must be used
third in the selected authentication login list.
10. From the menu in the 4 column, select the method, if any, that must be used fourth in the
selected authentication login list.
This is the method that is used if all previous methods time out.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Manage Device Security
265
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure the Dot1x Authentication List
The Dot1x authentication list defines the IEEE 802.1X authentication method used for the
default list. The default list is dot1xList.
To configure the dot1x authentication list:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Management Security > Authentication List > Dot1x Authentication
List.
The Dot1x Authentication List page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the dot1xList name.
7. From the menu in the 1 column, select the method that must be used as the first method in
the selected authentication login list.
The options are as follows:
•Local. The user’s locally stored ID and password are used for authentication.
•None. The user is not authenticated.
•Radius. The user’s ID and password are authenticated using the RADIUS server
instead of locally.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Manage Device Security
266
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Management Access
You can configure HTTP and secure HTTP access to the switch management interface. You
can also configure access control profiles and access rules.
Configure HTTP Settings
You can configure the settings for HTTP access to the switch.
To configure the HTTP server settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Access > HTTP > HTTP Configuration.
The HTTP Configuration page displays.
6. In the HTTP Session Soft Timeout field, specify the number of minutes an HTTP session
can be idle before a time-out occurs.
The value must be in the range of 0–60 minutes. The default value is 5 minutes. The
currently configured value is shown when the web page is displayed.
After the session is inactive for the configured time, you are automatically logged out and
must reenter the password to access the management interface. A value of zero means
that the session does not time out.
7. In the HTTP Session Hard Timeout field, specify the hard time-out for HTTP sessions.
This time-out is unaffected by the activity level of the session. The value must be in the
range of 0–168 hours. value of zero means that the session does not time out. The
default value is 24 hours.
8. In the Maximum Number of HTTP Sessions field, specify the maximum number of HTTP
sessions that can exist at the same time.

Manage Device Security
267
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
HTTPS Configuration
Secure HTTP enables the transmission of HTTP over an encrypted Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) connection. When you manage the switch by using
a web interface, Secure HTTP can help ensure that communication between the
management system and the switch is protected from eavesdroppers and man-in-the-middle
attacks.
You can configure the settings for HTTPS access to the switch.
To configure HTTPS settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Access > HTTPS > HTTPS Configuration.
The HTTPS Configuration page displays.
6. Select the HTTPS Admin Mode Enable or Disable radio button.
This enables or disables the administrative mode of secure HTTP (HTTPS). The
configured value is displayed. The default value is Disable. You can download SSL
certificates only when the HTTPS admin mode is disabled. HTTPS admin mode can be
enabled only if a certificate is present on the device.
7. Select the SSL Version 3 Enable or Disable radio button.
This enables or disables Secure Sockets Layer version 3.0. The configured value is
displayed. The default value is Enable.
8. Select the TLS Version 1 Enable or Disable radio button.
This enables or disables Transport Layer Security version 1.0. The configured value is
displayed. The default value is Enable.

Manage Device Security
268
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
9. In the HTTPS Port field, type the HTTPS port number.
The value must be in the range of 1025 to 65535. Port 443 is the default value. The
configured value is displayed.
10. In the HTTPS Session Soft T imeout (Minutes) field, enter the inactivity time-out for HTTPS
sessions.
The value must be in the range of 1 to 60 minutes. The default value is 5 minutes. The
configured value is displayed.
After the session is inactive for the configured time, you are automatically logged out and
must reenter the password to access the management interface. A value of zero means
that the session does not time out.
11. In the HTTPS Session Hard Timeout (Hours) field, set the hard time-out for HTTPS
sessions.
This time-out is unaffected by the activity level of the session. The value must be in the
range of 1 to 168 hours. The default value is 24 hours.
12. In the Maximum Number of HTTPS Sessions field, enter the maximum allowable number
of HTTPS sessions.
The value must be in the range of 0 to 4. The default value is 4.
13. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Manage Certificates
You can manage certificates.
Generate an SSL Certificate
To generate an SSL certificate:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.

Manage Device Security
269
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Access > HTTPS > Certificate Management.
The Certificate Management page displays.
The Certificate Present field displays whether a certificate is present on the switch.
6. In the Certificate Management area, select Generate Certificates.
7. Click the Apply button.
The switch generates an SSL certificate.
The Certificate Generation Status field shows information about the progress.
Delete an SSL Certificate
To delete an SSL certificate:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Access > HTTPS > Certificate Management.
The Certificate Management page displays.
The Certificate Present field displays Yes.
6. In the Certificate Management area, select Delete Certificates.
7. Click the Apply button.
The certificate is removed.
Download Certificates
You can transfer a certificate file to the switch.
For the web server on the switch to accept HTTPS connections from a management station,
the web server needs a public key certificate. You can generate a certificate externally (for
example, offline) and download it to the switch.

Manage Device Security
270
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Before you download a file to the switch, the following conditions must be true:
•The file to download from the TFTP server is on the server in the appropriate directory.
•The file is in the correct format.
•The switch contains a path to the TFTP server.
To configure the certificate download settings for HTTPS sessions:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Access > HTTPS > Certificate Download.
The Certificate Download page displays.
6. From the File Type menu, select the type of SSL certificate to download, which can be one
of the following:
•SSL Trusted Root Certificate PEM File. SSL Trusted Root Certificate file (PEM
Encoded)
•SSL Server Certificate PEM File. SSL Server Certificate File (PEM Encoded)
•SSL DH Weak Encryption Parameter PEM File. SSL Dif fie-Hellman W eak Encryption
Parameter file (PEM Encoded)
•SSL DH Strong Encryption Parameter PEM File. SSL Diffie-Hellman Strong
Encryption Parameter File (PEM Encoded)
7. From the Server Address Type menu, select IPv4 or DNS to indicate the format of the
TFTP/SFTP/SCP Server Address field.
The default is IPv4.
8. In the TFTP Server IP field, specify the address of the TFTP server.
The address can be an IP address in standard x.x.x.x format or a host name. The host
name must start with a letter of the alphabet. Make sure that the software image or other
file to be downloaded is available on the TFTP server.
9. In the Remote File Path field, enter the path of the file to download.

Manage Device Security
271
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
You can enter up to 96 characters. The default is blank.
10. In the Remote File Name field, enter the name of the file on the TFTP server to download.
You can enter up to 32 characters. The default is blank.
11. Select the Start File Transfer check box.
12. Click the Apply button.
The file transfer starts. A status message displays during the transfer and upon
successful completion of the transfer.
Access Control
Access control allows you to configure a profile and set access rules.
Configure an Access Control Profile
You can set up a security access profile.
To configure an access profile:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Access > Access Control > Access Profile Configuration.
The Access Profile Configuration page displays.
6. In the Access Profile Name field, enter the name of the access profile to be added.
The maximum length is 32 characters.
7. Select one of the following check boxes:
•Activate Profile. Activate an access profile.
•Deactivate Profile. Deactivate an access profile.
•Remove Profile. Remove an access profile. The access profile must be deactivated
before you remove the access profile.
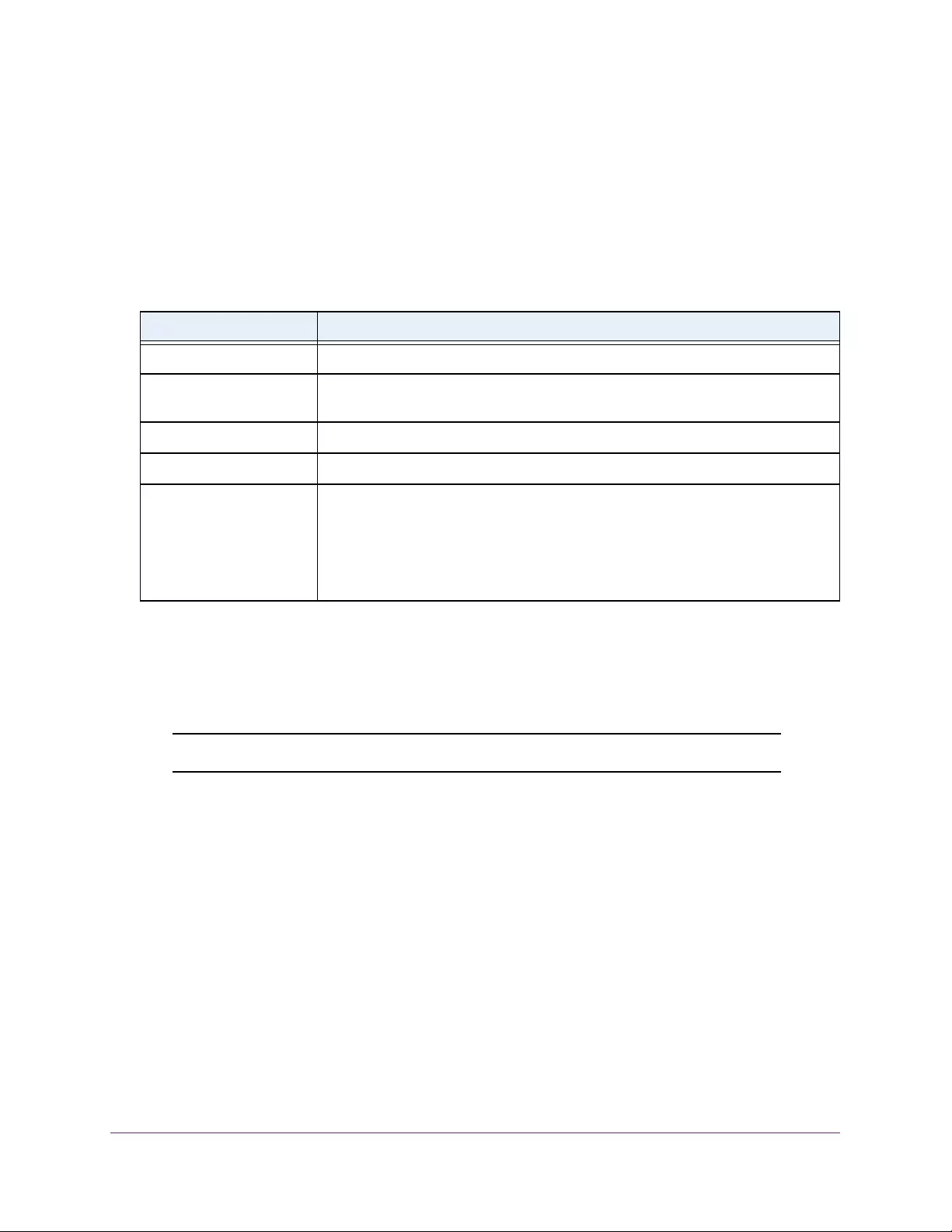
Manage Device Security
272
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The Packets Filtered field displays the number of packets filtered.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
9. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable data that is displayed.
Configure Access Rule Settings
You can add security access rules. You can apply changes an the access rule only when
the access profile is in a deactivated state.
Note: Make sure that you create the access profile before you add rules.
To configure access rules:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Table 70. Access profile configuration profile summary
Field Description
Rule Type The action performed when the rules match.
Service Type The selected service type. The policy is restricted by the selected service type
chosen. The possible methods are HTTP, and secure HTTP (SSL).
Source IP Address Source IP address of the client originating the management traffic.
Mask The subnet mask of the IP Address of the client originating the management traffic.
Priority The priority of the rule. The rules are validated against the incoming management
request in the ascending order of their priorities. If a rule matches, action is
performed and subsequent rules are ignored. For example, if a source IP address
of 10.10.10.10 is configured with priority 1 to permit and source IP address
10.10.10.10 is configured with priority 2 to deny, access is permitted if the profile is
active, and the second rule is ignored.

Manage Device Security
273
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Access > Access Control > Access Rule Configuration.
The Access Rule Configuration page displays.
6. From the Rule Type menu, select Permit or Deny to permit or deny access when the
selected rules are matched.
A Permit rule allows access by traffic that matches the rule criteria. A Deny rule blocks
traffic that matches the rule criteria.
7. From the Service Type menu, select the access method to which the rule is applied.
The policy is restricted by the selected access method. The possible access methods are
TFTP, HTTP, and Secure HTTP (SSL).
8. In the Source IP Address field, enter the source IP address of the client originating the
management traffic.
9. In the Mask field, specify the subnet mask of the client that originates the management
traffic.
10. In the Priority field, assign a priority to the rule.
The rules are validated against the incoming management request in ascending order of
their priorities. If a rule matches, the action is performed and subsequent rules are
ignored. For example, if a source IP 10.10.10.10 is configured with priority 1 to permit and
source IP 10.10.10.10 is configured with priority 2 to deny, access is permitted if the
profile is active, and the second rule is ignored.
11. Click the Add button.
The access rule is added.
Configure Port Authentication
With port-based authentication, when 802.1X is enabled globally and on the port, successful
authentication of any one supplicant attached to the port results in all users being able to use
the port without restrictions. At any time, only one supplicant is allowed to attempt
authentication on a port in this mode. Ports in this mode are under bidirectional control. This
is the default authentication mode.
An 802.1X network includes three components:
•Authenticators. The port that is authenticated before system access is permitted.
•Supplicants. The host connected to the authenticated port requesting access to the
system services.
•Authentication Server. The external server, for example, the RADIUS server that
performs the authentication on behalf of the authenticator , and indicates whether the user
is authorized to access system services.

Manage Device Security
274
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Global 802.1X Settings
You can configure global port access control settings on the switch.
To globally enable all 802.1X features:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Port Authentication > Basic > 802.1X Configuration.
The 802.1X Configuration page displays.
6. Next to Port Based Authentication State, select the Enable radio button.
This enables or disables 802.1X administrative mode on the switch.
Note: If 802.1X is enabled, authentication is performed by a RADIUS server.
This means that the primary authentication method must be RADIUS. To
set the method, select Security > Management Security >
Authentication List and select RADIUS as method 1 for defaultList. For
more information, see Configure Authentication Lists on page 262.
When port-based authentication is globally disabled, the switch does not check for
802.1X authentication before allowing traffic on any ports, even if the ports are configured
to allow only authenticated users.
7. In the VLAN Assignment Mode field, select the Enable radio button.
The default value is Disable.
When enabled, this feature allows a port to be placed into a particular VLAN based on the
result of the authentication or type of 802.1X authentication a client uses when it
accesses the device. The authentication server can provide information to the device
about which VLAN must be assigned the supplicant.
8. Next to Dynamic VLAN Creation Mode, select the Enable radio button.
The default value is Disable.

Manage Device Security
275
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
If RADIUS-assigned VLANs are enabled, the RADIUS server is includes the VLAN ID in
the 802.1X tunnel attributes of its response message to the device. If dynamic VLAN
creation is enabled on the device and the RADIUS-assigned VLAN does not exist, then
the assigned VLAN is dynamically created. This implies that the client can connect from
any port and can get assigned to the appropriate VLAN. This feature gives flexibility for
clients to move around the network without much additional configuration required.
9. Next to EAPOL Flood Mode, select the Enable radio button.
The default value is Disable. Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) over LAN (EAPoL)
flood support is enabled on the switch.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Manage Port Authentication
You can enable and configure port access control on one or more ports.
Configure 802.1X Settings for a Port
To configure 802.1X settings for a port:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Port Authentication > Advanced > Port Authentication.
The Port Authentication page displays.
6. To view more fields, move the horizontal bar at the bottom of the page to the right.
7. Select the check box next to the port.
You can also select multiple check boxes to apply the same settings to the selected ports,
or select the check box in the heading row to apply the same settings to all ports.

Manage Device Security
276
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
8. Specify the following settings:
•Port Control. Defines the port authorization state. The control mode is set only if the
link status of the port is link up. Select one of the following options:
-Auto. The switch automatically detects the mode of the interface.
-Authorized. The switch places the interface into an authorized state without being
authenticated. The interface sends and receives normal traffic without client
port-based authentication.
-Unauthorized. The switch denies the selected interface access by moving the
interface into unauthorized state. The switch cannot provide authentication
services to the client through the interface.
-MAC based. Multiple supplicants connected to the same port are allowed to be
authenticated individually. Each host connected to the port must de authenticated
separately to gain access to the network. The hosts are distinguished by their
MAC addresses.
•MAB. Specify whether to enable or disable MAC-based Authentication Bypass (MAB)
for 802.1x-unaware clients at the specified port. MAB only functions if the port control
mode is MAC-based. By default, MAB is disabled.
•Guest VLAN ID. Specify the VLAN ID for the guest VLAN. The valid range is 0–4093.
The default value is 0. Enter 0 to reset the guest VLAN ID on the interface. The guest
VLAN allows the port to provide a distinguished service to unauthenticated users.
This feature provides a mechanism to allow users access to hosts on the guest VLAN.
•Guest VLAN Period. Specify the number of seconds that the selected port remains in
the quiet state following a failed authentication exchange. The guest VLAN time-out
must be a value in the range of 1–300. The default value is 90.
•Unauthenticated VLAN ID. Specify the VLAN ID of the unauthenticated VLAN for the
selected port. The valid range is 0–3965. The default value is 0. Hosts that fail the
authentication might be denied access to the network or placed on a VLAN created
for unauthenticated clients. This VLAN might be configured with limited network
access.
•Periodic Reauthentication. Select Enable to allow periodic reauthentication of the
supplicant for the specified port.
•Reauthentication Period. Specify the time, in seconds, after which reauthentication
of the supplicant occurs. The reauthentication period must be a value in the range of
1–65535. The default value is 3600. If this field is disabled, connected clients are not
forced to reauthenticate periodically.
•Quiet Period. Specify the number of seconds that the port remains in the quiet state
following a failed authentication exchange. While in the quite state, the port does not
attempt to acquire a supplicant.
•Resending EAP. Specify the EAP retransmit period for the selected port. The
transmit period is the value, in seconds, after which an EAPoL EAP Request/Identify
frame is resent to the supplicant.
•Max EAP Requests. Specify the maximum number of EAP requests for the selected
port. The value is the maximum number of times an EAPoL EAP Request/Identity
message is retransmitted before the supplicant times out.
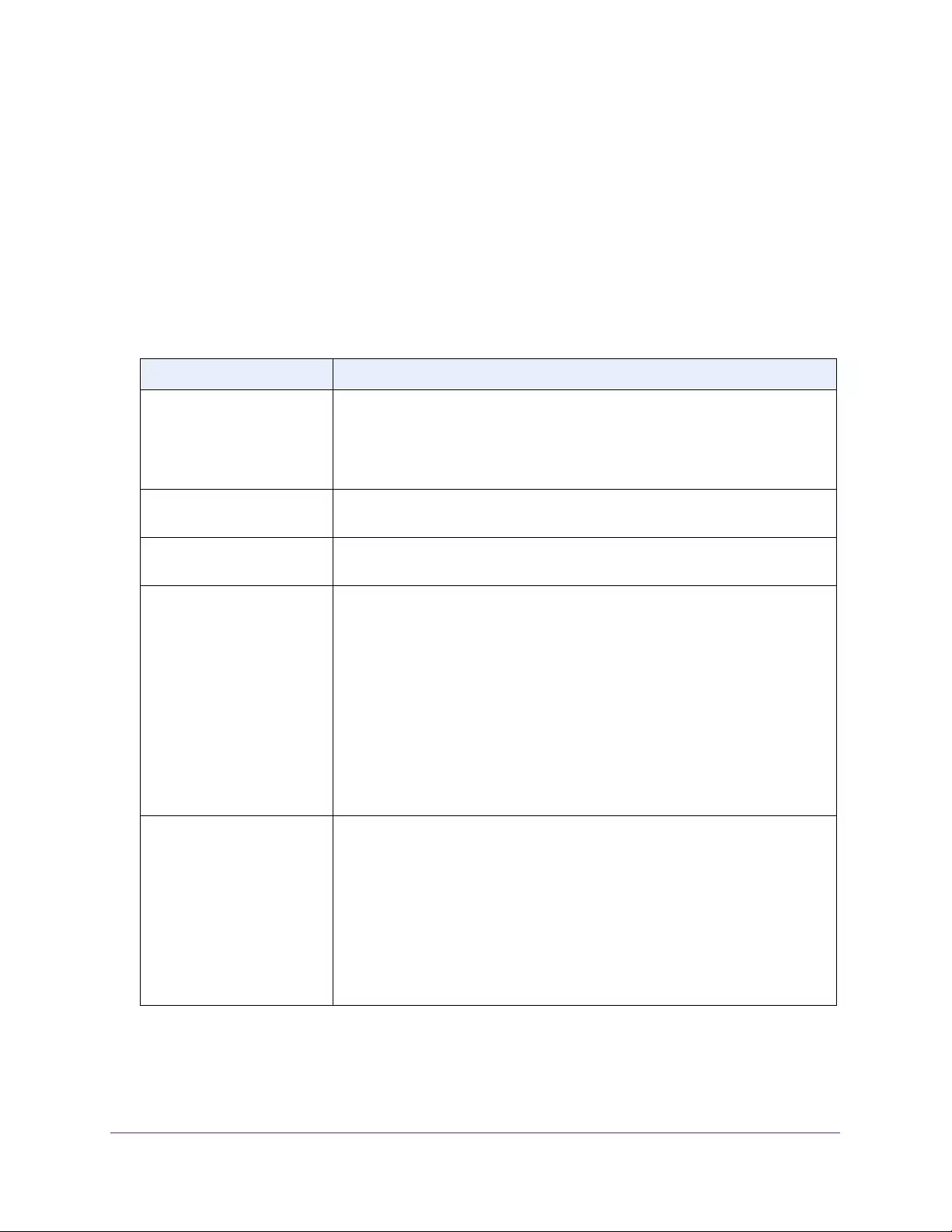
Manage Device Security
277
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Supplicant Timeout. Specify the supplicant time-out for the selected port. The
supplicant time-out is the value, in seconds, after which the supplicant times out.
•Server Timeout. Specify the time that elapses before the switch resends a request to
the authentication server.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the port authentication status information available on the
page.
Table 71. Port authentication status information
Field Description
Control Direction The control direction for the specified port, which is always Both. The control
direction dictates the degree to which protocol exchanges take place between
supplicant and authenticator. The unauthorized controlled port exerts control
over communication in both directions (disabling both incoming and outgoing
frames).
Protocol Version The protocol version associated with the selected port. The only possible value
is 1, corresponding to the first version of the 802.1X specification.
PAE Capabilities The port access entity (PAE) functionality of the selected port. Possible values
are Authenticator or Supplicant.
Authenticator PAE State The current state of the authenticator PAE component. Possible values are as
follows:
Initialize
Disconnected
Connecting
Authenticating
Authenticated
Aborting
Held
ForceAuthorized
ForceUnauthorized
Backend State The current state of the backend authentication component. Possible values are
as follows:
Request
Response
Success
Fail
Timeout
Initialize
Idle

Manage Device Security
278
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Initialize 802.1X on a Port
To initialize 802.1X on a port:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Port Authentication > Advanced > Port Authentication.
The Port Authentication page displays.
6. Select the check box associated with the port to initialize.
7. Click the Initialize button.
802.1X on the selected interface is reset to the initialization state. Traffic sent to and from
the port is blocked during the authentication process. This button is available only if the
control mode is auto. When you click this button, the action is immediate. You do not need
to click the Apply button for the action to occur.
Restart the 802.1X Authentication Process on a Port
To restart the 802.1X authentication process on a port:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.

Manage Device Security
279
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Port Authentication > Advanced > Port Authentication.
The Port Authentication page displays.
6. Select the check box associated with the port to reauthenticate.
7. Click the Reauthenticate button.
The selected port is forced to restart the authentication process.This button is available only
if the control mode is auto. If the button is not selectable, it is grayed out. When you click
this button, the action is immediate. You do not need to click the Apply button for the
action to occur.
View the Port Summary
You can view summary information about the port-based authentication settings for each
port.
To view the port summary:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Port Authentication > Advanced > Port Summary.
The Port Summary page displays.
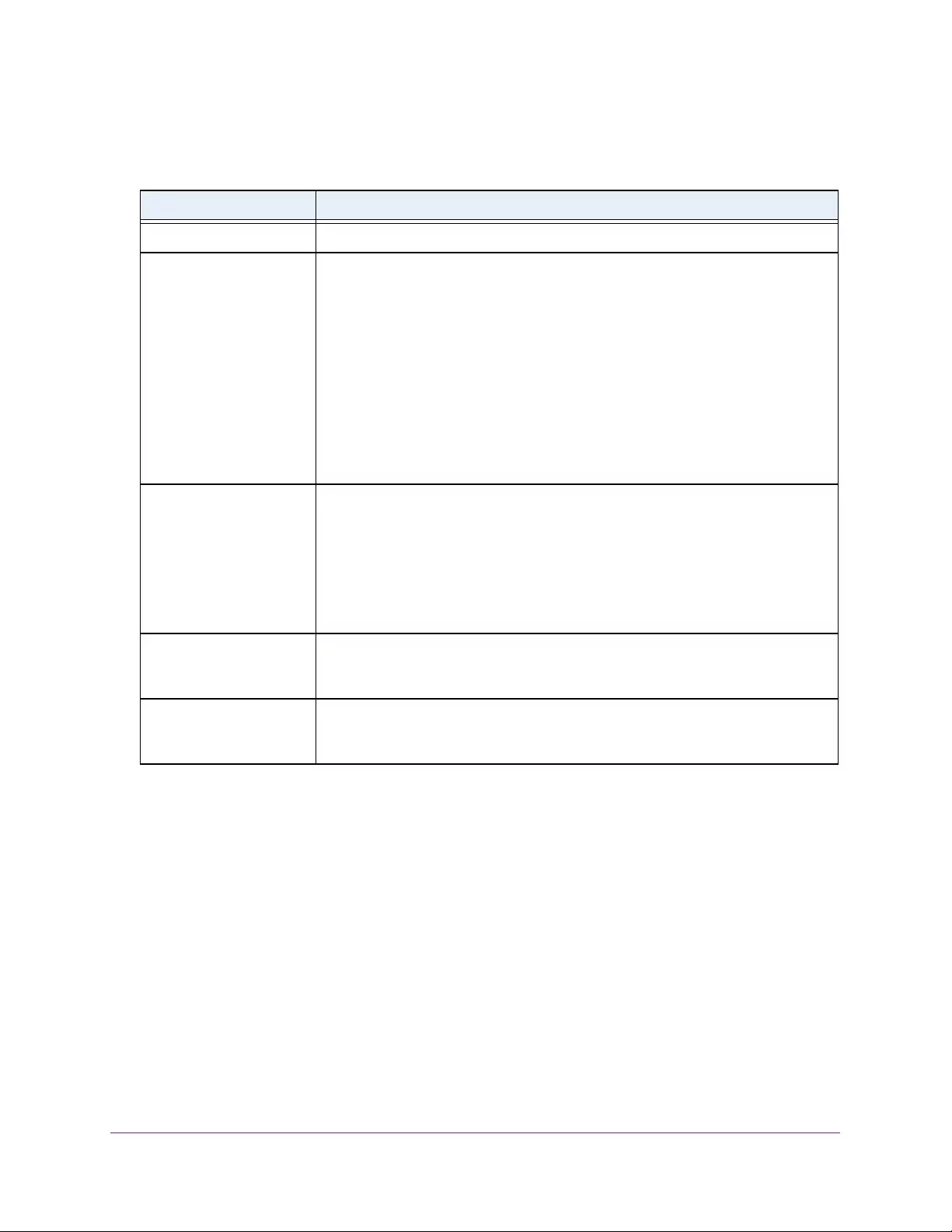
Manage Device Security
280
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the fields on the Port Summary page.
View the Client Summary
You can displays information about supplicant devices that are connected to the local
authenticator ports. If no active 802.1X sessions exist, the table is empty.
To view the client summary:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
Table 72. Port summary
Field Description
Port The port for which the settings are displayed in the current table row.
Control Mode Indicates the configured control mode for the port. Possible values are as follows:
• Auto. The switch sets the port mode based on the authentication exchanges
between the supplicant, authenticator, and the authentication server.
• Force Unauthorized. The switch denies the interface access by moving the
interface into the unauthorized state. The switch cannot provide authentication
services to the client through the interface.
• Force Authorized. The switch places the interface in an authorized state
without the need for authentication. The interface sends and receives normal
traffic without client port-based authentication.
• MAC Based. The switch sets the port mode based on the authentication
exchanges between the supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server on
a per-supplicant basis.
Operating Control Mode The control mode under which the port is actually operating. Possible values are as
follows:
• ForceUnauthorized
• ForceAuthorized
• Auto
• MAC Based
• N/A. If the port is in detached state, it cannot participate in port access control.
Reauthentication Enabled Displays whether reauthentication is enabled on the selected port. The possible
values are true and False. If the value is true, reauthentication occurs. Otherwise,
reauthentication is not allowed.
Port Status The authorization status of the specified port. The possible values are Authorized,
Unauthorized, and N/A. If the port is in detached state, the value is N/A because the
port cannot participate in port access control.
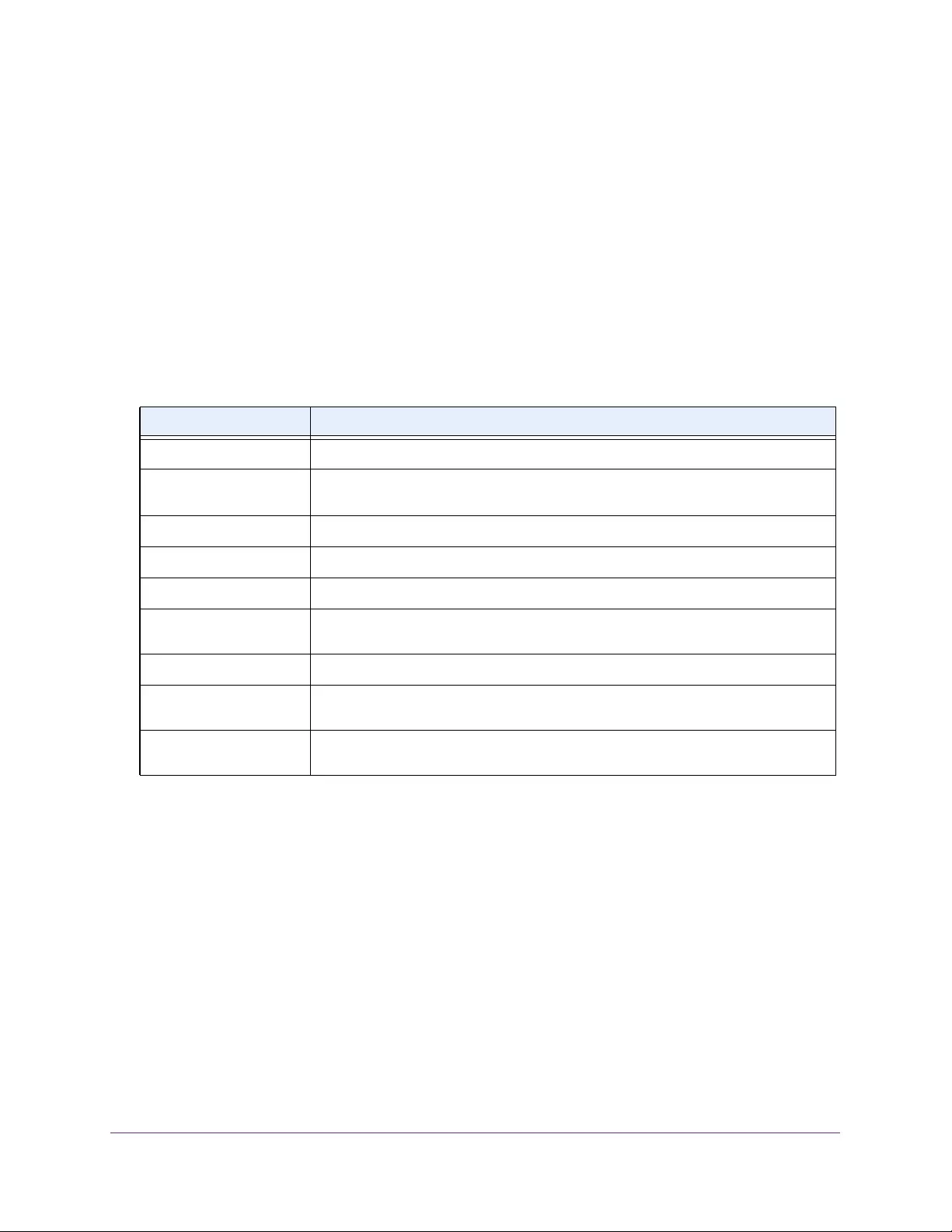
Manage Device Security
281
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Port Authentication > Advanced > Client Summary.
The Client Summary page displays.
The following table describes the fields on the Client Summary page.
Table 73. Client Summary information
Field Description
Port The port to be displayed.
User Name The name the client uses to identify itself as a supplicant to the authentication
server.
Supplicant Mac Address The MAC address of the supplicant that is connected to the port.
Session Time The time in seconds since the supplicant was granted access.
Filter ID The policy filter ID assigned by the authenticator to the supplicant device.
VLAN ID The ID of the VLAN the supplicant was placed in as a result of the authentication
process.
VLAN Assigned The reason why the supplicant was placed in the VLAN.
Session T imeout The reauthentication time-out period set by the RADIUS server to the supplicant
device.
Termination Action The termination action set by the RADIUS server that indicates the action that
occurs when the supplicant session times out.

Manage Device Security
282
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Set Up Traffic Control
You can configure MAC filters, storm control, port security, protected port, and private VLAN
settings.
Manage MAC Filtering
You can create MAC filters that limit the traffic allowed into and out of specified ports on the
switch.
Create a MAC Filter
To create a MAC filter:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > MAC Filter > MAC Filter Configuration.
The MAC Filter Configuration page displays.
6. From the MAC Filter menu, select Create Filter.
If you did not configure any filters, this is the only option available.
7. From the VLAN ID menu, select the VLAN that must be used with the MAC address.
8. In the MAC Address field, specify the MAC address of the filter in the format
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
You cannot define filters for the following MAC addresses:
•00:00:00:00:00:00
•01:80:C2:00:00:00 to 01:80:C2:00:00:0F
•01:80:C2:00:00:20 to 01:80:C2:00:00:21
•FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF

Manage Device Security
283
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
9. In the Port and LAG tables in the Source Port Members section, select the ports and LAGs
that must be included in the inbound filter.
If a packet with the MAC address and VLAN ID that you specify is received on a port that
is not part of the inbound filter, the packet is dropped.
10. In the Port and LAG tables in the Destination Port Members section, select the ports and
LAGs that must be included in the outbound filter.
A packet with the MAC address and VLAN ID that you specify can be transmitted only
from a port that is part of the outbound filter.
Note: Destination ports can be included only in a multicast filter.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete a MAC FIlter
To delete a MAC filter:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > MAC Filter > MAC Filter Configuration.
The MAC Filter Configuration page displays.
6. From the MAC Filter menu, select the filter.
7. Click the Delete button.
The filter is removed.
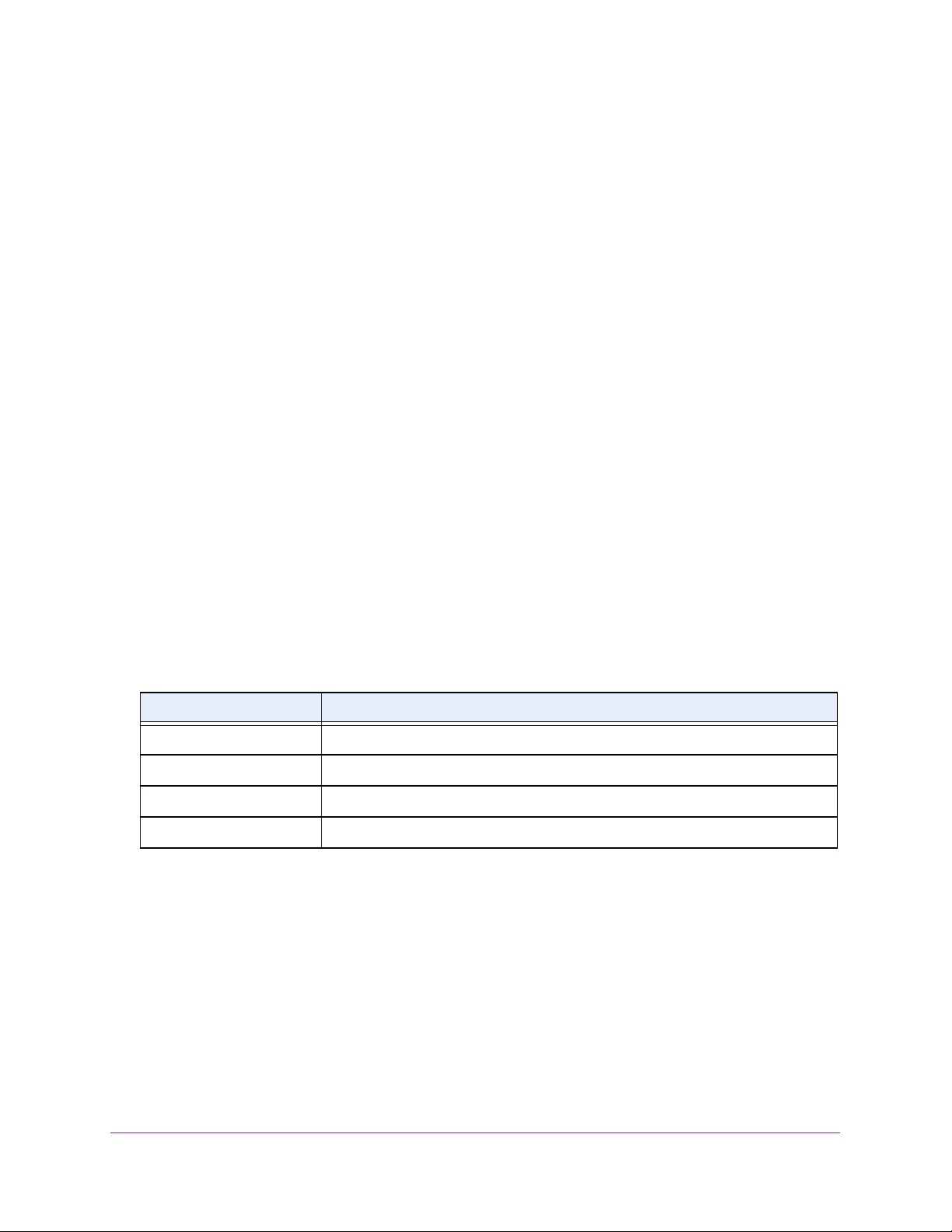
Manage Device Security
284
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View the MAC Filter Summary
You can view the MAC filters that are configured on the switch.
To view the MAC filter summary:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > MAC Filter > MAC Filter Summary.
The MAC Filter Summary page displays.
The following table describes the information displayed on the page.
Configure Storm Control
A broadcast storm is the result of an excessive number of broadcast messages
simultaneously transmitted across a network by a single port. Forwarded message
responses can overload network resources, cause the network to time out, or do both.
The switch measures the incoming packet rate per port for broadcast, multicast, unknown,
and unicast packets and discards packets if the rate exceeds the defined value. You can
enable storm control globally and per interface, by defining the packet type and the rate at
which the packets are transmitted.
Table 74. MAC Filter Summary information
Field Description
MAC Address The MAC address of the filter in the format XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID used with the MAC address to fully identify packets you want filtered.
Source Port Members A list of ports that are used for filtering inbound packets.
Destination Port Members A list of ports that are used for filtering outbound packets.

Manage Device Security
285
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To configure storm control settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Storm Control.
The Storm Control page displays.
6. In the Storm Control section, from the Ingress Control Mode menu, select the mode of
broadcast affected by storm control:
•Disabled. Storm control is disabled. This is the default setting.
•Unknown Unicast. If the rate of incoming unknown Layer 2 unicast traffic (that is,
traffic for which a destination lookup failure occurs) increases beyond the configured
threshold on an interface, the traffic is dropped.
•Multicast. If the rate of incoming Layer 2 multicast traffic increases beyond the
configured threshold on an interface, the traffic is dropped.
•Broadcast. If the rate of incoming Layer 2 broadcast traffic increases beyond the
configured threshold on an interface, the traffic is dropped.
7. In the Storm Control section, if the selection from the Ingress Control Mode menu is not
Disabled, specify whether the ingress control mode is enabled by selecting Enable or
Disable from the Status menu.
8. In the Storm Control section, in the Threshold field, specify the maximum rate at which
unknown packets are forwarded.
The range is a percent of the total threshold between 0–100%. The default is 5%.
9. In the Storm Control section, from the Control Action mode menu, select one of the
following options:
•None. This is the default setting.
•Trap. If the threshold of the configured broadcast storm is exceeded, a trap is sent.
•Shutdown. If the threshold of the configured broadcast storm is exceeded, the port is
shut down.

Manage Device Security
286
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
11. To enable or disable storm control for one or more ports or to specify different threshold and
control action settings for one or more ports, do the following:
a. In the Port Settings section, select one or more interfaces by taking one of the
following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or
type the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the
heading row.
b. In the Port Settings section, if the selection from the Ingress Control Mode menu is
not Disabled, specify whether the ingress control mode is enabled by selecting
Enable or Disable from the Status menu in the table heading.
c. In the Port Settings section, in the Threshold field in the table heading, specify the
maximum rate at which unknown packets are forwarded.
The range is a percent of the total threshold between 0–100%. The default is 5%.
d. In the Port Settings section, from the Control Action mode menu in the table
heading, select one of the following options:
•None. This is the default setting.
•Trap. If the threshold of the configured broadcast storm is exceeded, a trap is
sent.
•Shutdown. If the threshold of the configured broadcast storm is exceeded, the
port is shut down.
12. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Port Security
Port security lets you lock one or more ports on the switch. When a port is locked, only
packets with an allowable source MAC addresses can be forwarded. All other packets are
discarded.
Configure the Global Port Security Mode
To configure the global port security mode:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
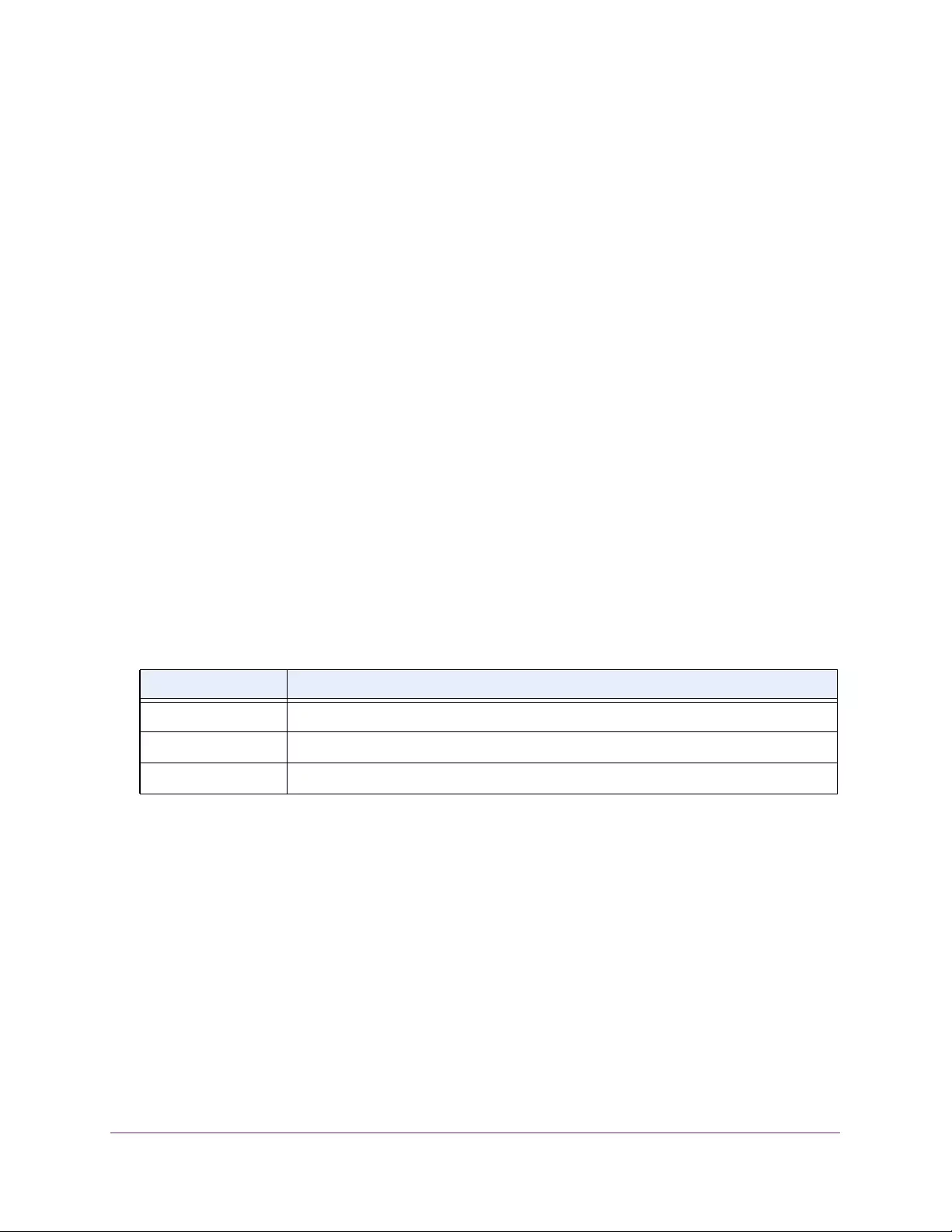
Manage Device Security
287
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Port Security > Port Security Configuration.
The Port Security Configuration page displays.
6. To enable port security on the switch, select the Port Security Mode Enable radio button.
The default is Disable.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
8. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
The Port Security Violations table shows information about violations that occurred on ports
that are enabled for port security.
The following table describes the fields in the Port Security Violations table.
Configure a Port Security Interface
A MAC address can be defined as allowable by one of two methods: dynamically or statically.
Both methods are used concurrently when a port is locked.
Dynamic locking implements a first arrival mechanism for port security. You specify how
many addresses can be learned on the locked port. If the limit was not reached, then a
packet with an unknown source MAC address is learned and forwarded normally. When the
limit is reached, no more addresses are learned on the port. Any packets with source MAC
addresses that were not already learned are discarded. You can effectively disable dynamic
locking by setting the number of allowable dynamic entries to zero.
Static locking allows you to specify a list of MAC addresses that are allowed on a port. The
behavior of packets is the same as for dynamic locking: only packets with an allowable
source MAC address can be forwarded.
Table 75. Port Security Violations information
Field Description
Port The physical interface.
Last Violation MAC The source MAC address of the last packet that was discarded at a locked port.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID corresponding to the last MAC address violation.

Manage Device Security
288
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To configure port security settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Port Security > Interface Configuration.
The Interface Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. Specify the following settings:
•Port Security. Enable or disable the port security feature for the selected interfaces
The default is Disable.
•Max Learned MAC Address. Specify the maximum number of dynamically learned
MAC addresses on the selected interfaces.
•Max Static MAC Address. Specify the maximum number of statically locked MAC
addresses on the selected interfaces.
•Enable Violation Shutdown. Enable or disable shutdown of the selected interfaces if
a packet with a disallowed MAC address is received. The default value is No, which
means that the option is disabled.
•Enable Violation Traps. Enable or disable the sending of new violation traps if a
packet with a disallowed MAC address is received. The default value is No, which
means that the option is disabled.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Manage Device Security
289
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View Learned MAC Addresses and Convert Them to Static MAC Addresses
You can convert a dynamically learned MAC address to a statically locked address.
To view learned MAC addresses for an individual interface or LAG and convert these
MAC addresses to static MAC addresses:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Port Security > Port Security Configuration.
The Port Security Configuration page displays.
6. Make sure that port security is globally enabled.
For more information, see Configure the Global Port Security Mode on page 286.
7. Select Security > Traffic Control > Port Security > Interface Configuration.
The Interface Configuration page displays.
8. Make sure that port security is enabled for the individual interface for which you want to view
the dynamically learned MAC addresses.
For more information, see Configure a Port Security Interface on page 287.
9. Select Security > Traffic Control > Port Security > Security MAC Address.
The Security MAC Address page displays.
10. From the Port List menu, select the individual interface.
The Dynamic MAC Address Table displays the MAC addresses and their associated
VLANs that were learned on the selected port.
Field Description
VLAN ID The VLAN ID corresponding to the MAC address.
MAC Address The MAC addresses learned on a specific port.

Manage Device Security
290
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
11. To convert the dynamically learned MAC address to a statically locked addresses, select the
Convert Dynamic Address to Static check box.
12. Click the Apply button.
The dynamic MAC address entries are converted to static MAC address entries in a
numerically ascending order until the static limit is reached.
The Number of Dynamic MAC Addresses Learned field displays the number of
dynamically learned MAC addresses on a specific port.
13. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
Configure Protected Ports
You can configure the ports as protected or unprotected. If a port is configured as protected,
it does not forward traffic to any other protected port on the switch, but it does forward traffic
to unprotected ports.
To configure protected ports:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Protected Port.
The Protected Port page displays.
6. In the Ports table, click each port that you want to configure as a protected port.
Protected ports are marked with a check mark. No traffic forwarding is possible between
two protected ports.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Manage Device Security
291
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure a Private VLAN
A private VLAN contains switch ports that cannot communicate with each other, but can
access another network. These ports are called private ports. Each private VLAN contains
one or more private ports and a single uplink port or uplink aggregation group. Note that all
traffic between private ports is blocked at all layers, not just Layer 2 traffic, but also traffic
such as FTP, HTTP, and Telnet.
To configure a private VLAN type:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Private VLAN > Private Vlan Type Configuration.
The Private VLAN Type Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box that is associated with the VLAN ID that you want to configure.
7. From the Private VLAN Type menu, select the type of private VLAN. Possible values are as
follows:
•Primary. Sets the private VLAN type as primary.
•Isolated. Sets the private VLAN type as isolated.
•Community. Sets the private VLAN type as community.
•Unconfigured. Sets the private VLAN type as unconfigured. The default is
Unconfigured.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Manage Device Security
292
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Private VLAN Association Settings
To configure private VLAN association:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Private VLAN > Private Vlan Association
Configuration.
The Private VLAN Association page displays.
6. From the Primary VLAN menu, select the primary VLAN ID of the domain.
7. In the Secondary VLAN(s) field, enter the VLAN that you want to associate with the
primary VLAN.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Configure the Private VLAN Port Mode
To configure the private VLAN port mode:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
Table 76. Private VLAN Association information
Field Description
Isolated VLAN The isolated VLAN associated with the selected primary VLAN.
Community VLAN(s) The list of community VLANs associated with the selected primary VLAN.

Manage Device Security
293
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Private VLAN > Private Vlan Port Mode
Configuration.
The Private Vlan Port Mode Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. From the Port VLAN Mode menu, select the switch port mode:
•General. Sets the interfaces in general mode, which is the default selection.
•Host. Sets the interfaces in host mode, which is used for private VLAN
configurations.
•Promiscuous. Sets the interfaces in promiscuous mode, which is used for private
VLAN configurations.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure a Private VLAN Host Interface
To configure a private VLAN host interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.

Manage Device Security
294
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Private VLAN > Private Vlan Host Interface
Configuration.
The Private VLAN Host Interface Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. In the Host Primary VLAN field, enter the primary VLAN ID for the host association mode.
The range of the VLAN ID is 2–4093.
9. In the Host Secondary VLAN field, enter the secondary VLAN ID for host association
mode.
The range of the VLAN ID is 2–4093.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The Operational VLAN(s) field displays the operational VLANs.
Configure a Private VLAN Promiscuous Interface
To configure a private VLAN promiscuous interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Manage Device Security
295
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > Traffic Control > Private VLAN > Private Vlan Promiscuous Interface
Configuration.
The Private VLAN Promiscuous Interface Configuration page displays.
6. To display information for all ports and LAGs, click the All link.
7. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
•To configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the port, or type
the port number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
•To configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
•To configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
8. In the Promiscuous Primary VLAN field, enter the primary VLAN ID for the promiscuous
association mode.
The range of the VLAN ID is 2–4093.
9. In the Promiscuous Secondary VLAN(s) field, enter the secondary VLAN ID for
promiscuous association mode.
This field can accept single a VLAN ID, a range of VLAN IDs, or a combination of both in
sequence separated by a comma. You can specify an individual VLAN ID, such as 10.
You can specify the VLAN range values separated by a hyphen, for example, 10-13. You
can specify the combination of both separated by commas, for example,
12,15,40-43,1000-1005, 2000. The range of VLAN IDs is 2–4093.
Note: The VLAN ID list that you specify replaces the configured secondary
VLAN list in the association.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The Operational VLAN(s) field displays the operational VLANs.
Configure Access Control Lists
Access control lists (ACLs) ensure that only authorized users can access specific resources
while blocking off any unwarranted attempts to reach network resources. ACLs are used to
provide traffic flow control, restrict contents of routing updates, decide which types of traffic
are forwarded or blocked, and above all provide security for the network. The switch’s
software supports IPv4, IPv6, and MAC ACLs.
Manage Device Security
296
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To configure an ACL:
1. Create an IPv4-based or IPv6-based or MAC-based ACL ID.
2. Create a rule and assign it to a unique ACL ID.
3. Define the rules, which can identify protocols, source, and destination IP and MAC
addresses, and other packet-matching criteria.
4. Use the ID number to assign the ACL to a port or to a LAG.
To view ACL configuration examples, see Access Control Lists (ACLs) on page 407.
Use the ACL Wizard to Create a Simple ACL
The ACL Wizard helps you create a simple ACL and apply it to the selected ports easily and
quickly. First, select an ACL type to use when you create an ACL. Then add an ACL rule to
this ACL and apply this ACL on the selected ports. The ACL Wizard allows you to create the
ACL, but does not allow you to modify it. For information about modifying an ACL, see Modify
an ACL Rule on page 299.
Note: The steps in the following procedure describe how you can create an
ACL based on the destination MAC address. If you select a different
type of ACL (for example, an ACL based on a source IPv4), the page
displays different information.
Use the ACL Wizard to create an ACL
To use the ACL Wizard to create an ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > ACL Wizard.
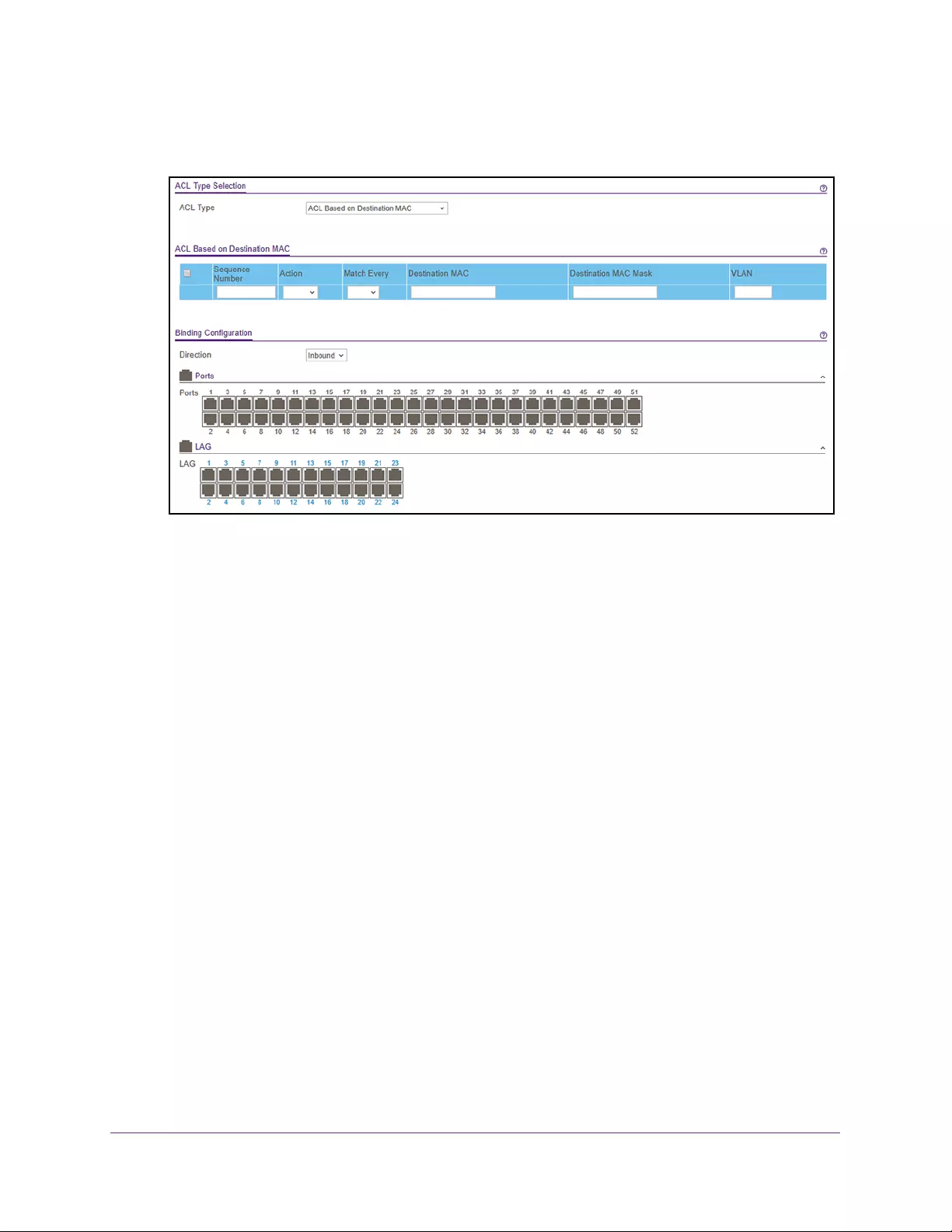
Manage Device Security
297
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following figure show the page for models GC752X and GC752XP. Models GC728X
and GC728XP support 24 Ethernet ports but the same number of LAGs (24).
6. From the ACL Type menu, select the type of ACL.
You can select from the following ACL types:
•ACL Based on Destination MAC. Creates an ACL based on the destination MAC
address, destination MAC mask, and VLAN.
•ACL Based on Source MAC. Creates an ACL based on the source MAC address,
source MAC mask, and VLAN.
•ACL Based on Destination IPv4. Creates an ACL based on the destination IPv4
address and IPv4 address mask.
•ACL Based on Source IPv4. Creates an ACL based on the source IPv4 address and
IPv4 address mask.
•ACL Based on Destination IPv6. Creates an ACL based on the destination IPv6
prefix and IPv6 prefix length.
•ACL Based on Source IPv6. Creates an ACL based on the source IPv6 prefix and
IPv6 prefix length.
•ACL Based on Destination IPv4 L4 Port. Creates an ACL based on the destination
IPv4 Layer 4 port number.
•ACL Based on Source IPv4 L4 Port. Creates an ACL based on the source IPv4
Layer 4 port number.
•ACL Based on Destination IPv6 L4 Port. Creates an ACL based on the destination
IPv6 Layer 4 port number.
•ACL Based on Source IPv6 L4 Port. Creates an ACL based on the source IPv6
Layer 4 port number.
Note: For L4 port options, two rules are created (one for TCP and one for UDP).
Manage Device Security
298
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
7. In the Sequence Number field, enter a whole number in the range of 1 to 2147483647 that
is used to identify the rule.
8. From the Action menu, select Permit or Deny to specify the action that must be taken if a
packet matches the rule’s criteria.
If a packet matches a rule with a permit action, the packet is allowed to continue toward
its destination. If a packet matches a rule with a deny action, the packet is dropped.
9. From the Match Every menu, select one of the following options:
•False. Signifies that packets do not need to match the selected ACL and rule. With
this selection, you can add a destination MAC address, destination MAC mask, and
VLAN.
•True. Signifies that all packets must match the selected ACL and rule and are either
permitted or denied. In this case, since all packets match the rule, you cannot
configure other match criteria.
10. Specify the additional match criteria for the selected ACL type.
The rest of the rule match criteria fields available for configuration depend on the selected
ACL type. For information about the possible match criteria fields, see the following table.
ACL Based On Fields
Destination MAC • Destination MAC. Specify the destination MAC address to compare against
an Ethernet frame. The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. The BPDU keyword
might be specified using a destination MAC address of 01:80:C2:xx:xx:xx.
• Destination MAC Mask. Specify the destination MAC address mask, which
represents the bits in the destination MAC address to compare against an
Ethernet frame. The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. The BPDU keyword
might be specified using a destination MAC mask of 00:00:00:ff:ff:ff.
• VLAN. Specify the VLAN ID to match within the Ethernet frame.
Source MAC • Source MAC. Specify the source MAC address to compare against an
Ethernet frame. The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
• Source MAC Mask. Specify the source MAC address mask, which
represents the bits in the source MAC address to compare against an
Ethernet frame. The valid format is (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx).
• VLAN. Specify the VLAN ID to match within the Ethernet frame.
Destination IPv4 • Destination IP Address. Specify the destination IP address.
• Destination IP Mask. Specify the destination IP address mask.
Source IPv4 • Source IP Address. Specify the source IP address.
• Source IP Mask. Specify the source IP address mask.
Destination IPv6 • Destination Prefix. Specify the destination prefix.
• Destination Prefix Length. Specify the destination prefix length.
Source IPv6 • Source Prefix. Specify the source destination prefix.
• Source Prefix Length. Specify the source prefix length.
Destination IPv4 L4 Port • Destination L4 port (protocol). Specify the destination IPv4 L4 port
protocol.
• Destination L4 port (value). Specify the destination IPv4 L4 port value.
Manage Device Security
299
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
11. For this procedure (in which an ACL based on the destination MAC address is created),
configure the following settings:
a. In the Destination MAC field, specify the destination MAC address that must be
compared against the information in an Ethernet frame.
The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. The BPDU keyword can be specified using a
destination MAC address of 01:80:C2:xx:xx:xx.
b. In the Destination MAC Mask field, specify the destination MAC address mask that
must be compared against the information in an Ethernet frame.
The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. The BPDU keyword can be specified using a
destination MAC mask of 00:00:00:ff:ff:ff.
c. In the VLAN ID field, specify which VLAN must be compared against the information
in an Ethernet frame.
Valid range of values is 1 to 4093. Either a VLAN range or VLAN can be configured.
d. In the Binding Configuration section, from the Direction menu, select the packet
filtering direction for the ACL.
Only the inbound direction is valid.
e. In the Ports and LAG tables in the Binding Configuration section, select the ports
and LAGs to which the ACL must be applied.
f. Click the Add button.
The rule is added to the ACL and is based on the destination MAC.
12. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Modify an ACL Rule
To modify an ACL rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
Source IPv4 L4 Port • Source L4 port (protocol). Specify the source IPv4 L4 port protocol.
• Source L4 port (value). Specify the source IPv4 L4 port value.
Destination IPv6 L4 Port • Destination L4 port (protocol). Specify the destination IPv6 L4 port
protocol.
• Destination L4 port (value). Specify the destination IPv6 L4 port value.
Source IPv6 L4 Port • Source L4 port (protocol). Specify the source IPv6 L4 port protocol.
• Source L4 port (value). Specify the source IPv6 L4 port value.
ACL Based On Fields

Manage Device Security
300
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > ACL Wizard.
The ACL Wizard page displays.
6. Select check box that is associated with the rule.
7. Update the match criteria as needed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete an ACL Rule
To delete an ACL rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > ACL Wizard.
The ACL Wizard page displays.
6. Select check box that is associated with the rule.
7. Click the Delete button.
The rule is removed.
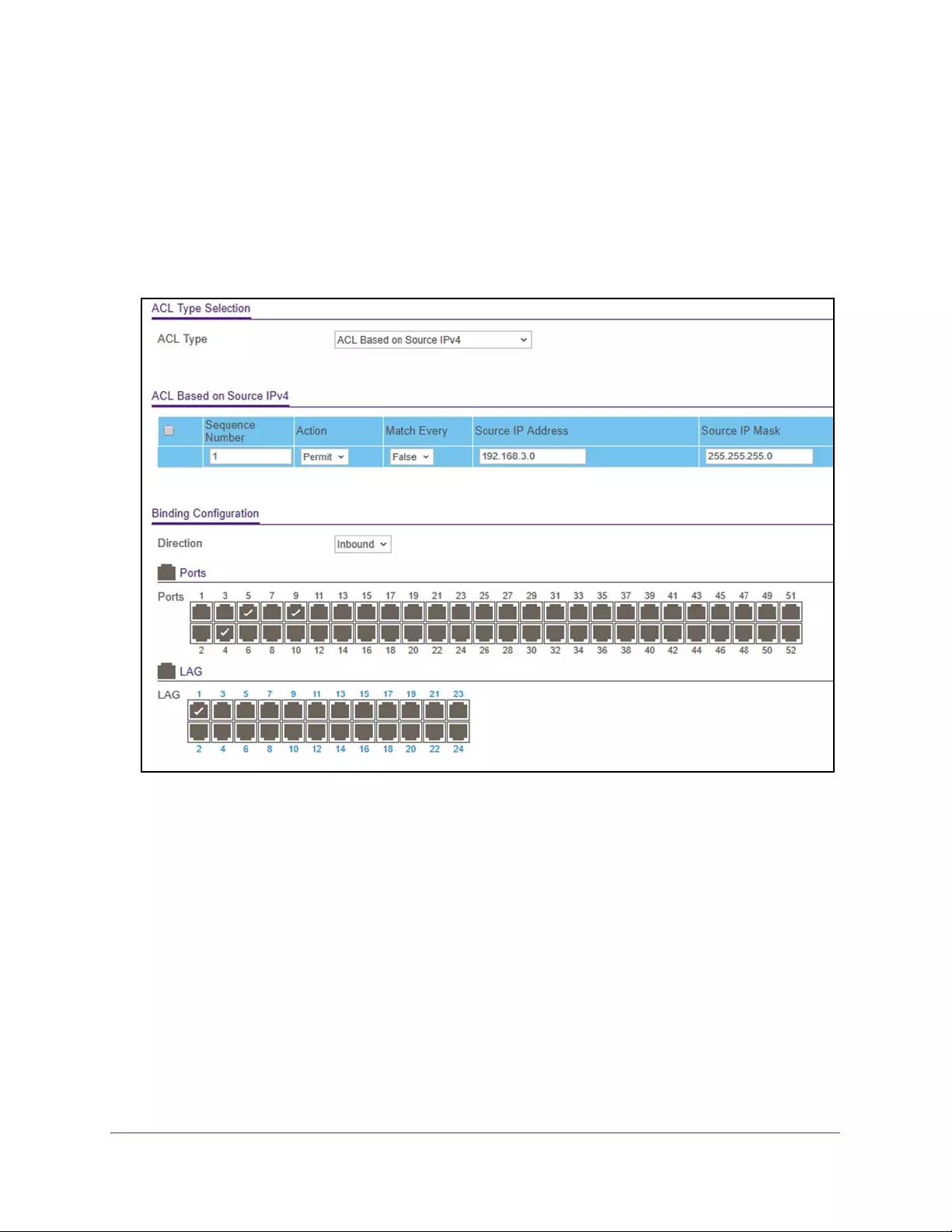
Manage Device Security
301
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
ACL Wizard Example
In the following figure, the ACL rule is configured to check for packet matches on ports 4, 5,
and 9 and on LAG 1. Only the Inbound option is valid. Packets that include a source address
in the 192.168.3.0/16 network are permitted to be forwarded by the interfaces. All other
packets are dropped because every ACL includes an implicit deny all rule as the last rule.
The following figure show the page for models GC752X and GC752XP. Models GC728X and
GC728XP support 24 Ethernet ports but the same number of LAGs (24).
For information about the ACL Wizard, see Use the ACL Wizard to Create a Simple ACL on
page 296.
Configure a Basic MAC ACL
A MAC ACL consists of a set of rules that are matched sequentially against a packet. When a
packet meets the match criteria of a rule, the specified rule action (Permit or Deny) is taken,
and the additional rules are not checked for a match.
Multiple steps are involved in defining a MAC ACL and applying it to the switch:
1. Create the ACL ID.
2. Create a MAC rule.
3. Associate the MAC ACL with one or more interfaces.
You can view or delete MAC ACL configurations in the MAC Binding table (see View or
Delete MAC ACL Bindings in the MAC Binding Table on page 310.

Manage Device Security
302
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Add a MAC ACL
To add a MAC ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC ACL.
The MAC ACL page displays.
The MAC ACL Table displays the number of ACLs currently configured in the switch and
the maximum number of ACLs that can be configured. The current size is equal to the
number of configured IPv4 and IPv6 ACLs plus the number of configured MAC ACLs.
6. In the Name field, specify a name for the MAC ACL.
The name string can include alphabetic, numeric, hyphen, underscore, or space
characters only. The name must start with an alphabetic character.
7. Click the Add button.
The MAC ACL is added.
Each configured ACL displays the following information:
•Rules. The number of rules currently configured for the MAC ACL.
•Direction. The direction of packet traffic affected by the MAC ACL, which can be
Inbound or blank.
Change the Name of a MAC ACL
To change the name of a MAC ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.

Manage Device Security
303
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC ACL.
The MAC ACL page displays.
6. Select check box that is associated with the rule.
7. In the Name field, specify the new name.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete a MAC ACL
To delete a MAC ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC ACL.
The MAC ACL page displays.
6. Select check box that is associated with the rule.
7. Click the Delete button.
The rule is removed.
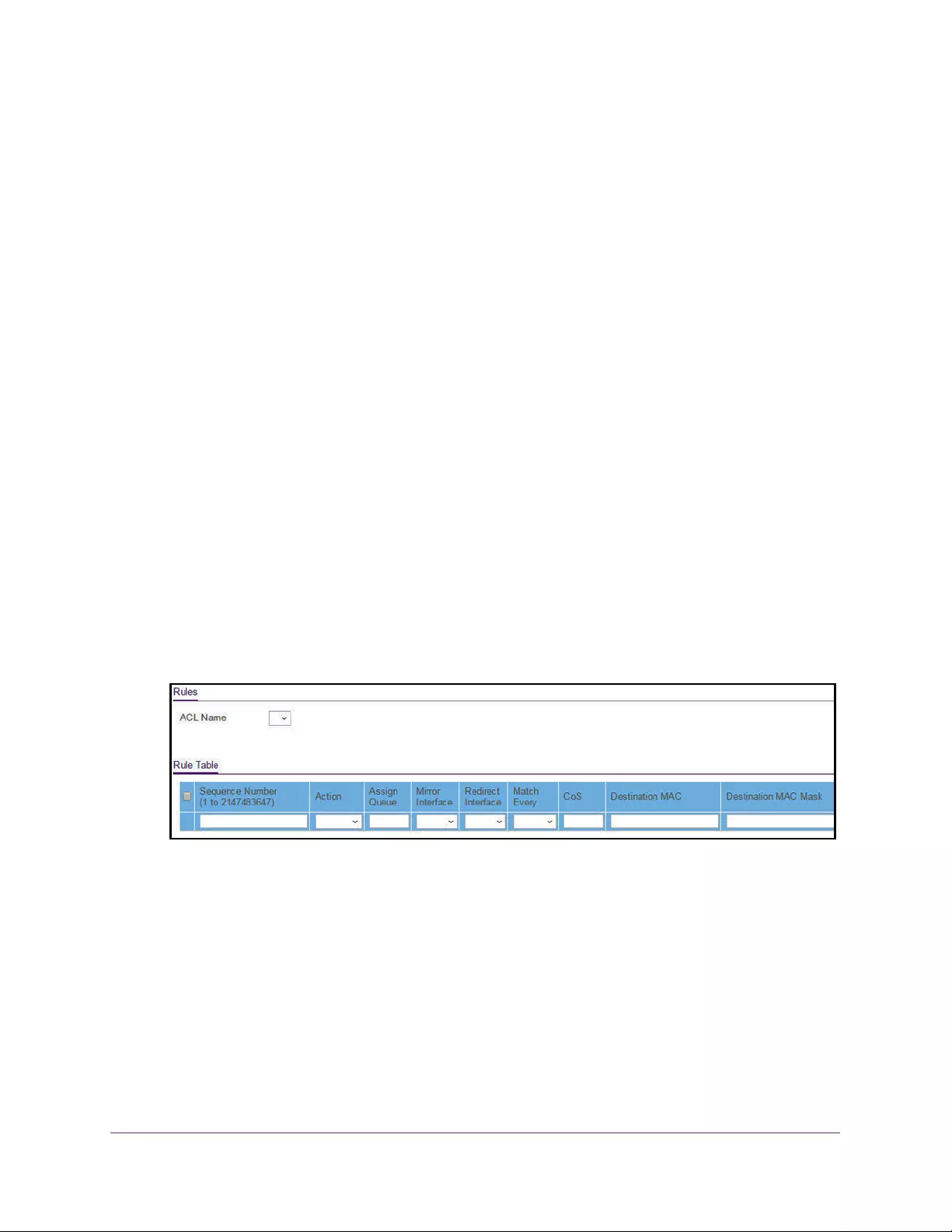
Manage Device Security
304
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure MAC ACL Rules
You can define rules for MAC-based ACLs. The access list definition includes rules that
specify whether traffic matching the criteria is forwarded normally or discarded. A default
deny all rule is the last rule of every list.
Add a Rule to a MAC ACL
To add a rule to a MAC ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC Rules.
The previous figure does not show all columns.
6. From the ACL Name menu, select the MAC ACL.
7. In the Sequence Number field, enter a whole number in the range of 1 to 2147483647 to
identify the rule.
8. From the Action menu, select the action that must be taken if a packet matches the rule’s
criteria:
•Permit. Forwards packets that meet the ACL criteria.
•Deny. Drops packets that meet the ACL criteria.
9. In the Assign Queue field, specify the hardware egress queue identifier that must be used
to handle all packets matching this ACL rule.

Manage Device Security
305
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The valid range of queue IDs is 0 to 7.
10. From the Mirror Interface menu, select the specific egress interface to which the matching
traffic stream must be copied, in addition to being forwarded normally by the switch.
This field cannot be set if a redirect interface is already configured for the ACL rule. This
field is visible for a Permit action.
11. From the Redirect Interface menu, select the egress interface to which the matching traffic
stream must be redirected, bypassing any forwarding decision normally performed by the
switch.
This field cannot be set if a mirror interface is already configured for the ACL rule.
12. From the Match Every menu, select whether each Layer 2 MAC packet must be matched
against the rule:
•True. Each packet must match the selected ACL rule.
•False. Not all packets need to match the selected ACL rule.
13. In the CoS field, specify the 802.1p user priority that must be compared against the
information in an Ethernet frame.
The valid range of values is 0 to 7.
14. In the Destination MAC field, specify the destination MAC address that must be compared
against the information in an Ethernet frame.
The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. The BPDU keyword can be specified using a
destination MAC address of 01:80:C2:xx:xx:xx.
15. In the Destination MAC Mask field, specify the destination MAC address mask that must
be compared against the information in an Ethernet frame.
The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. The BPDU keyword can be specified using a
destination MAC mask of 00:00:00:ff:ff:ff.
The MAC mask specifies which bits in the MAC address must be compared against an
Ethernet frame. You can use Fs and zeros in the MAC mask, which is in a wildcard
format. An F means that the bit is not checked, and a zero in a bit position means that the
data must equal the value given for that bit. For example, if the MAC address is
aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff, and the mask is 00:00:ff:ff:ff:ff, all MAC addresses with
aa:bb:xx:xx:xx:xx result in a match (where x is any hexadecimal number). A MAC mask of
00:00:00:00:00:00 matches a single MAC address.
16. From the EtherType Key menu, select the EtherType value that must be compared against
the information in an Ethernet frame.
The valid values are as follows:
•Appletalk
•ARP
•IBM SNA
•IPv4
•IPv6

Manage Device Security
306
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•IPX
•MPLS multicast
•MPLS unicast
•NetBios
•Novell
•PPPoE
•RARP
•User Value
17. If you select User Value from the EtherType menu, in the EtherType User Value field,
specify the customized EtherType value that must be used when you select User Value
from the EtherType Key menu.
This value must be compared against the information in an Ethernet frame. The valid range
of values is 0x0600 to 0xFFFF.
18. In the Source MAC field, specify the source MAC address that must be compared against
the information in an Ethernet frame.
The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
19. In the Source MAC Mask field, specify the source MAC address mask that must be
compared against the information in an Ethernet frame.
The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
The MAC mask specifies which bits in the MAC address must be compared against an
Ethernet frame. You can use Fs and zeros in the MAC mask, which is in a wildcard
format. An F means that the bit is not checked, and a zero in a bit position means that the
data must equal the value given for that bit. For example, if the MAC address is
aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff, and the mask is 00:00:ff:ff:ff:ff, all MAC addresses with
aa:bb:xx:xx:xx:xx result in a match (where x is any hexadecimal number). A MAC mask of
00:00:00:00:00:00 matches a single MAC address.
20. In the VLAN field, specify the VLAN ID that must be compared against the information in an
Ethernet frame.
The valid range of values is 1 to 4093. Either VLAN range or VLAN can be configured.
21. From the Logging menu, select whether to enable or disable logging.
When set to Enable, logging is enabled for this ACL rule (subject to resource availability
on the switch). If the access list trap flag is also enabled, periodic traps are generated,
indicating the number of times the rule was evoked during the report interval. A fixed
five-minute report interval is used for the switch. A trap is not issued if the ACL rule hit
count is zero for the interval. This field is only supported for a deny action.
22. Click the Add button.
The rule is added.

Manage Device Security
307
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Change the Match Criteria for a MAC Rule
To change the match criteria for a MAC rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC Rules.
The MAC Rules page displays.
6. Select the check box that is associated with the rule.
7. Modify the fields as needed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete a Rule for a MAC ACL
To delete a rule for a MAC:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.

Manage Device Security
308
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC Rules.
The MAC Rules page displays.
6. Select the check box that is associated with the rule.
7. Click the Delete button.
The rule is removed.
Configure MAC Bindings
When an ACL is bound to an interface, all the rules that are defined are applied to the
selected interface. You can assign MAC ACL lists to ACL priorities and interfaces.
To configure MAC bindings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC Binding Configuration.
The following figure show the page for models GC752X and GC752XP. Models GC728X
and GC728XP support 24 Ethernet ports but the same number of LAGs (24).
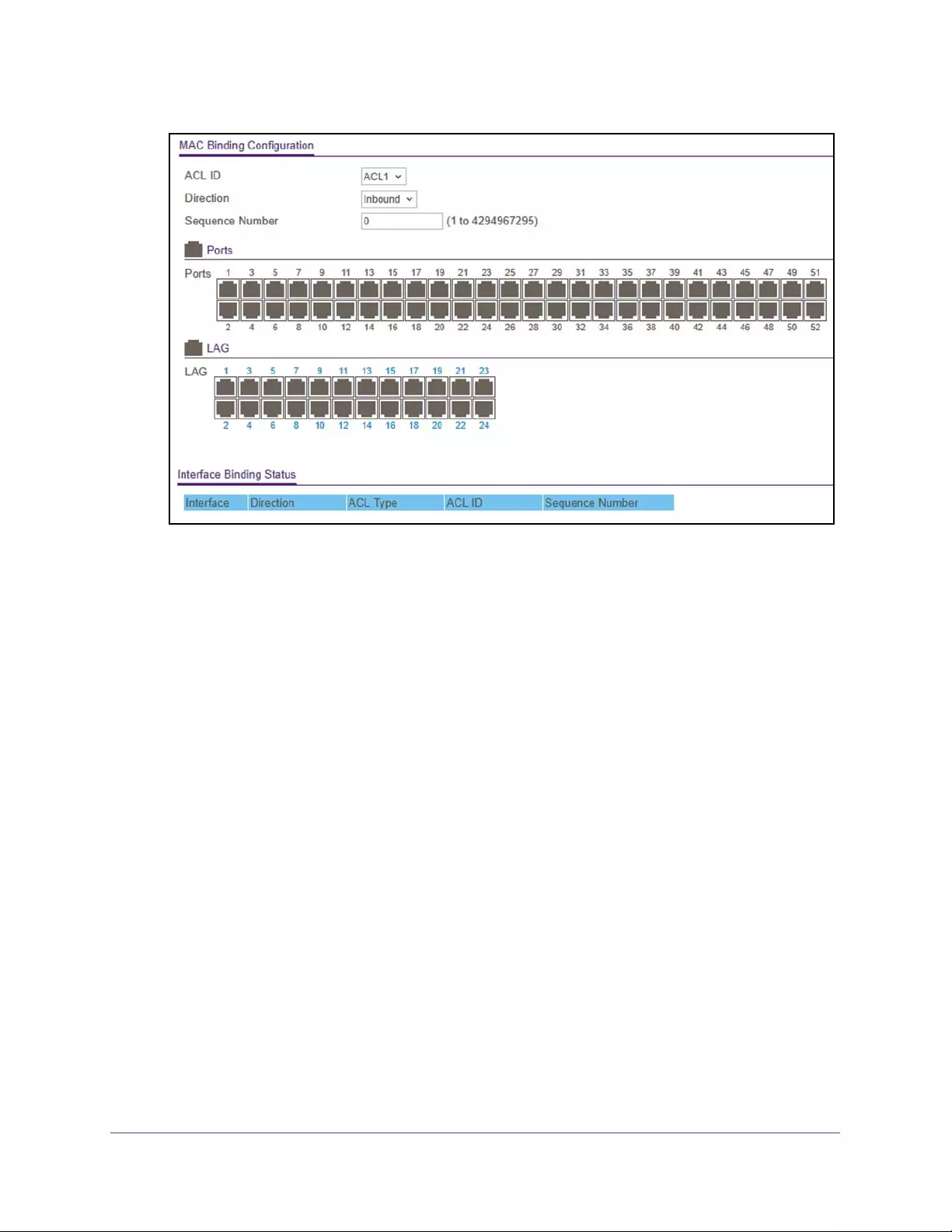
Manage Device Security
309
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. From the ACL ID menu, select an ACL.
The fixed selection from the Direction menu is Inbound, which means that MAC ACL
rules are applied to traffic entering the interface.
7. In the Sequence Number field, optionally specify a number to indicate the order of the
access list relative to other access lists already assigned to the interface and direction.
A low number indicates high precedence order. If a sequence number is already in use
for the interface and direction, the specified access list replaces the currently attached
access list using that sequence number. If you do not specify the sequence number, a
sequence number that is one number greater than the highest sequence number
currently in use for this interface and direction is used. The valid range is 1–4294967295.
8. To add the selected ACL to a port or LAG, in the Ports table or LAG table, click the port or
LAG so that a check mark displays.
You can add the ACL to several ports and LAGs.
The Ports and LAG tables display the available and valid interfaces for ACL binding. All
nonrouting physical interfaces and interfaces participating in LAGs are listed.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
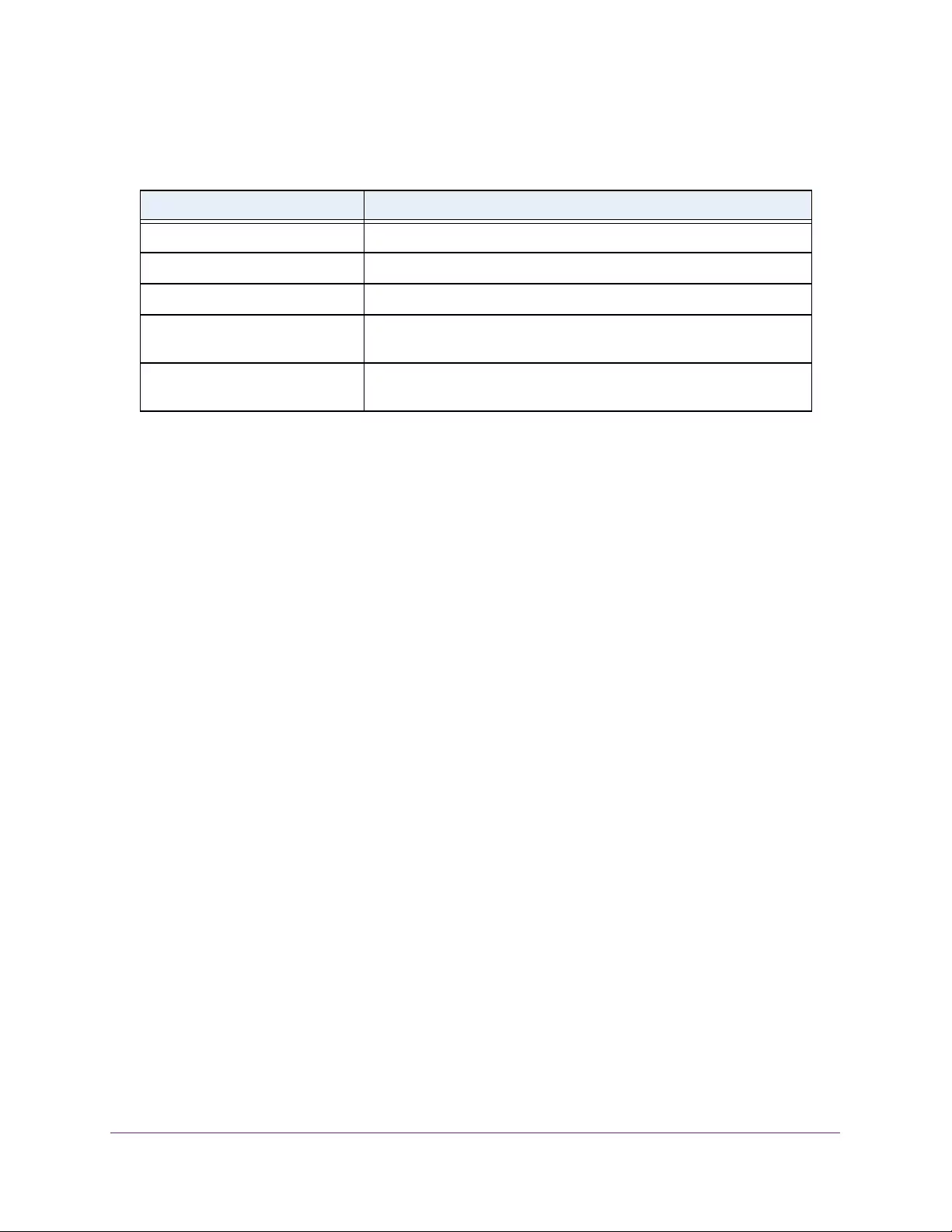
Manage Device Security
310
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the information displayed in the Interface Binding Status table.
View or Delete MAC ACL Bindings in the MAC Binding Table
You can view or delete the MAC ACL bindings in the MAC Binding Table.
To view or delete MAC ACL bindings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC Binding Table.
The MAC Binding Table displays.
6. To delete a MAC ACL-to-interface binding, do the following:
a. Select the check box next to the interface.
b. Click the Delete button.
The binding is removed.
Table 77. Interface Binding Status table
Field Description
Interface The interface of the ACL assigned.
Direction The selected packet filtering direction for the ACL.
ACL Type The type of ACL assigned to the selected interface and direction.
ACL ID The ACL number (for an IP ACL) or ACL name (for a MAC ACL)
identifying the ACL assigned to the selected interface and direction.
Sequence Number The sequence number signifying the order of the specified ACL relative
to other ACLs assigned to the selected interface and direction.
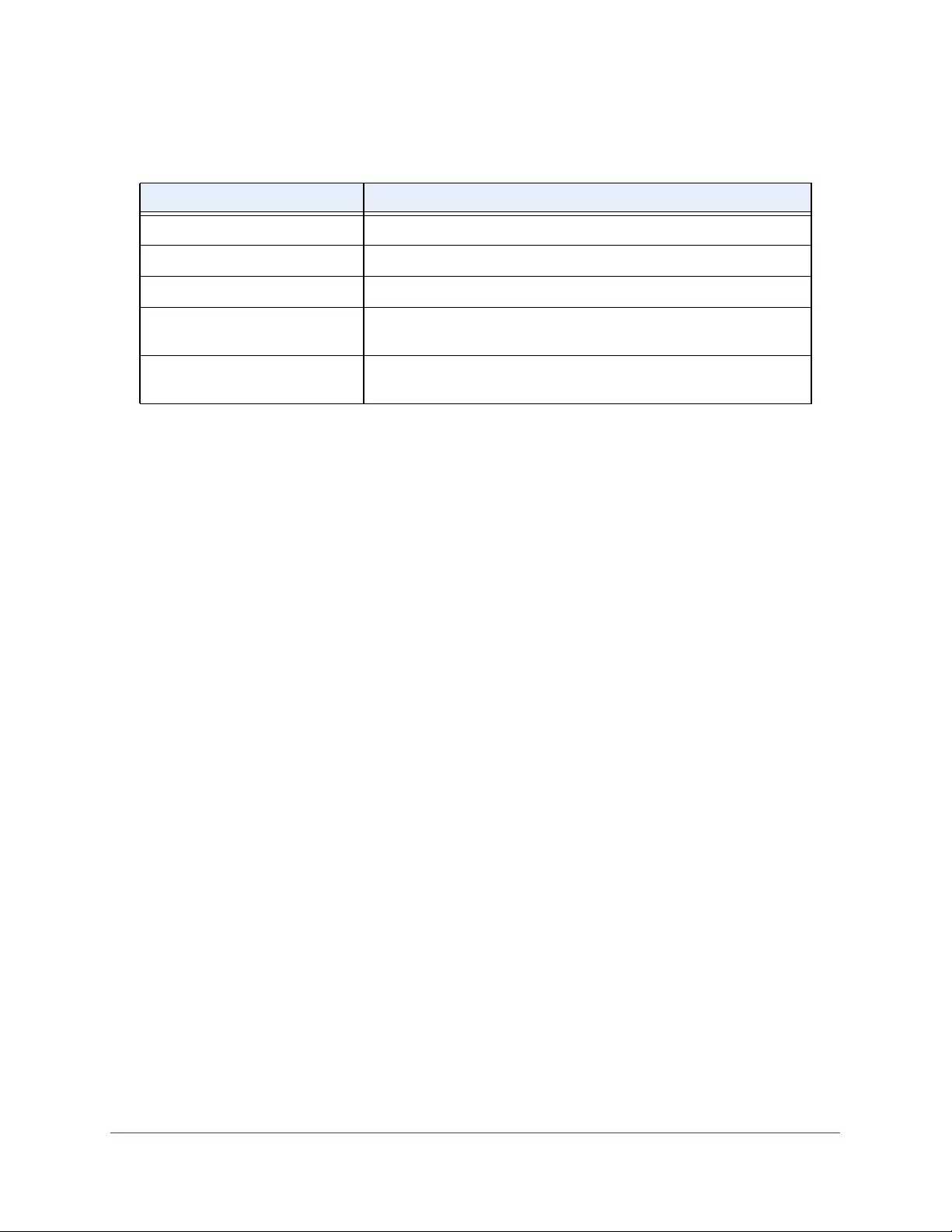
Manage Device Security
311
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the information that is displayed in the MAC Binding Table.
Configure an IP ACL
An IP or IPv6 ACL consists of a set of rules that are matched sequentially against a packet.
When a packet meets the match criteria of a rule, the specified rule action (Permit or Deny) is
taken, and the additional rules are not checked for a match. You must specify the interfaces
to which an IP ACL applies, as well as whether it applies to inbound or outbound traffic.
Add an IP ACL
To add an IP ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP ACL.
The IP ACL Configuration page displays.
The IP ACL page shows the current size of the ACL table compared to the maximum size
of the ACL table. The current size is equal to the number of configured IPv4 and IPv6
ACLs plus the number of configured MAC ACLs. The maximum size is 100.
Table 78. MAC Binding Table
Field Description
Interface The interface of the ACL assigned.
Direction The selected packet filtering direction for the ACL.
ACL Type The type of ACL assigned to the selected interface and direction.
ACL ID The ACL name identifying the ACL assigned to the selected interface
and direction.
Sequence Number The sequence number signifying the order of the specified ACL relative
to other ACLs assigned to the selected interface and direction.

Manage Device Security
312
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The Current Number of ACL field displays the current number of all ACLs configured on
the switch.
The Maximum ACL field displays the maximum number of IP ACLs that can be
configured on the switch.
6. In the IP ACL ID field, specify the ACL ID or IP ACL name, which depends on the IP ACL
type. The IP ACL ID is an integer in the following range:
•1–99. Creates a basic IP ACL, which allows you to permit or deny traf fic from a source
IP address.
•100–199. Creates an extended IP ACL, which allows you to permit or deny specific
types of Layer 3 or Layer 4 traffic from a source IP address to a destination IP
address. This type of ACL provides more granularity and filtering capabilities than the
standard IP ACL.
•IP ACL Name. Create an IPv4 ACL name string that is up to 31 alphanumeric
characters in length. The name must start with an alphabetic character.
Each configured ACL displays the following information:
•Rules. The number of rules currently configured for the IP ACL.
•Type. Identifies the ACL as a basic IP ACL (with an ID from 1 to 99), extended IP ACL
(with an ID from 100 to 199), or a named IP ACL.
7. Click the Add button.
The IP ACL is added to the switch configuration.
Delete an IP ACL
To delete an IP ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP ACL.
The IP ACL Configuration page displays.

Manage Device Security
313
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Select the check box that is associated with the IP ACL.
7. Click the Delete button.
The IP ACL is removed.
Configure Rules for a Basic IP ACL
You can define rules for IP-based standard ACLs (basic ACLs). The access list definition
includes rules that specify whether traffic matching the criteria is forwarded normally or
discarded.
Note: An implicit deny all rule is included at the end of an ACL list. This
means that if an ACL is applied to a packet, and if none of the explicit
rules match, then the final implicit deny all rule applies and the packet
is dropped.
Add a Rule for a Basic IP ACL
To add a rule for a basic IP ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP Rules.

Manage Device Security
314
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
If no rules exist, the Basic ACL Rule Table shows the message No rules have been
configured for this ACL. If one or more rules exist for the ACL, the rules display in the
Basic ACL Rule Table.
6. From the ACL ID menu, select the IP ACL for which you want to add a rule.
For basic IP ACLs, this must be an ID in the range from 1 to 99.
7. Click the Add button.
8. Specify the following match criteria for the rule:
•Sequence Number . Enter an ACL sequence number in the range of 1 to 2147483647
that is used to identify the rule. An IP ACL can contain up to 50 rules.
•Action. Select the ACL forwarding action, which is one of the following:
-Permit. Forward packets that meet the ACL criteria.
-Deny. Drop packets that meet the ACL criteria.
•Egress Queue. If the selection form the Action menu is Permit, you can specify the
hardware egress queue identifier that is used to handle all packets matching this IP
ACL rule. The range of queue IDs is 0 to 7.
•Logging. If the selection form the Action menu is Deny, you can enable logging for
the ACL by selecting the Enable radio button. (Logging is subject to resource
availability in the device.)
If the access list trap flag is also enabled, periodic traps are generated, indicating the
number of times this rule was evoked during the report interval. A fixed five-minute
report interval is used for the switch. A trap is not issued if the ACL rule hit count is
zero for the current interval.
•Match Every. From the Match Every menu, select whether all packets must match
the selected IP ACL rule:
-Enable. All packets must match the selected IP ACL rule and are either permitted
or denied.
-Disable. Not all packets need to match the selected IP ACL rule.

Manage Device Security
315
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Mirror Interface. From the Mirror Interface menu, select the specific egress
interface to which the matching traffic stream must be copied, in addition to being
forwarded normally by the switch.
This field cannot be set if a redirect interface is already configured for the IP ACL rule.
This field is visible for a Permit action.
•Redirect Interface. From the Redirect Interface menu, select the egress interface to
which the matching traffic stream must be redirected, bypassing any forwarding
decision normally performed by the switch.
This field cannot be set if a mirror interface is already configured for the IP ACL rule.
•Src IP Address. Enter an IP address using dotted-decimal notation to be compared
to a packet’s source IP address as a match criterion for the selected IP ACL rule.
•Src IP Mask. Specify the IP mask in dotted-decimal notation to be used with the
source IP address value.
Wildcard masks determine which bits are used and which bits are ignored. A wildcard
masking for an ACL functions differently from a subnet mask. A wildcard mask is in
essence the inverse of a subnet mask. For example, to apply the rule to all hosts in
the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet, enter 0.0.0.255 in the Source IP Mask field. A wildcard
mask of 255.255.255.255 indicates that no bit is important. A wildcard mask of 0.0.0.0
indicates that all of the bits are important.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Modify the Match Criteria for a Basic IP ACL Rule
To modify the match criteria for a basic IP ACL rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP Rules.
The IP Rules page displays.

Manage Device Security
316
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. From the ACL ID menu, select the ACL that includes the rule that you want to modify.
7. In the Basic ACL Rule Table, click the rule.
The rule is a hyperlink. The Standard ACL Rule Configuration page displays.
8. Modify the basic IP ACL rule criteria.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete a Basic IP ACL RUle
To delete a basic IP ACL rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP Rules.
The IP Rules page displays.
6. From the ACL ID menu, select the ACL that includes the rule that you want to modify.
7. In the Basic ACL Rule Table, select the check box that is associated with the rule.
8. Click the Delete button.
The rule is removed.
Configure Rules for an Extended IP ACL
You can define rules for IP-based extended ACLs. The access list definition includes rules
that specify whether traffic matching the criteria is forwarded normally or discarded.
Note: An implicit deny all rule is included at the end of an ACL list. This means
that if an ACL is applied to a packet and if none of the explicit rules match,
then the final implicit deny all rule applies and the packet is dropped.
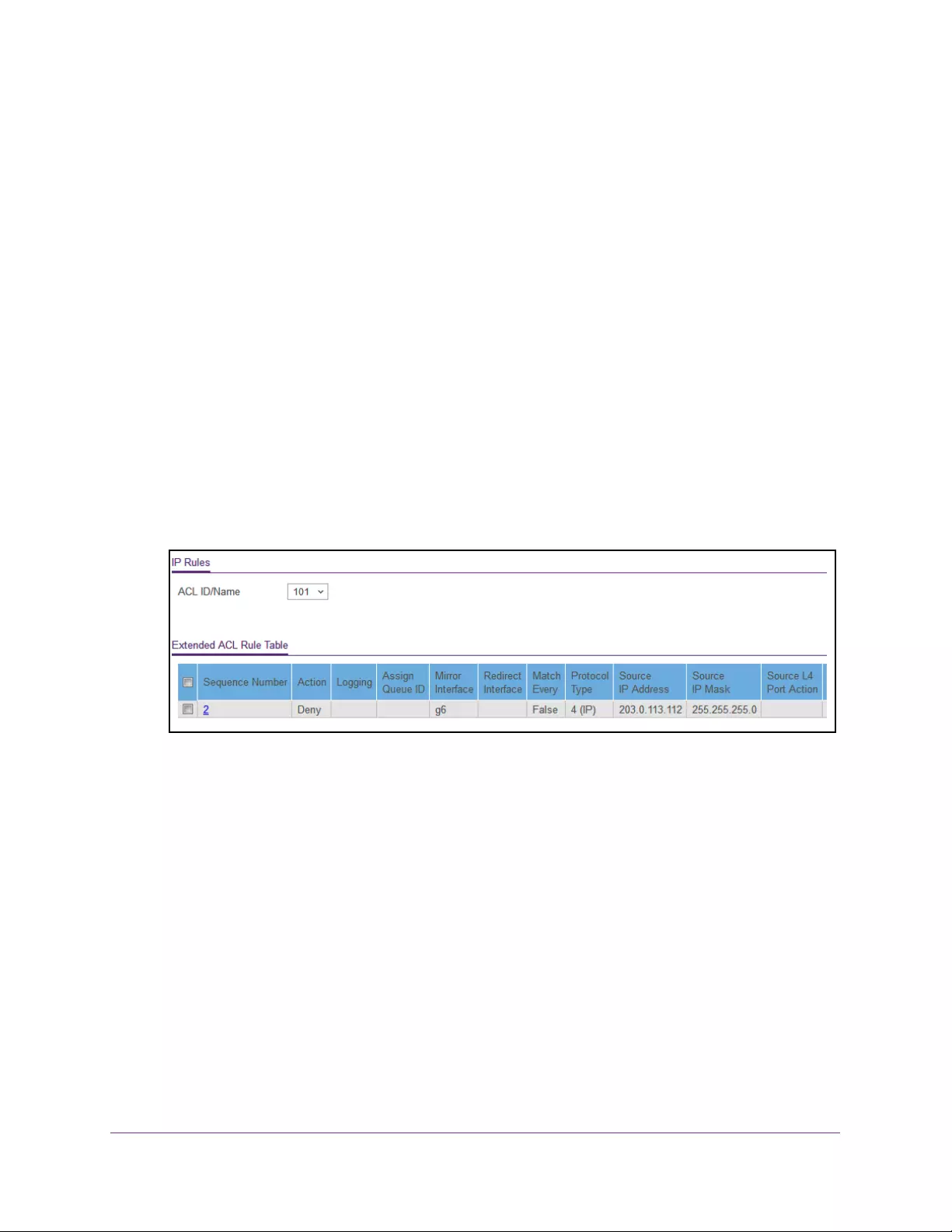
Manage Device Security
317
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Add a Rule for an Extended IP ACL
To add a rule for an extended IP ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP Extended Rules.
The previous figure does not show all columns.
If no rules exists, the Extended ACL Rule Table shows the message No rules have been
configured for this ACL. If one or more rules exist for the ACL, the rules display in the
Extended ACL Rule Table.
6. From the ACL ID/Name menu, select the IP ACL for which you want to add a rule.
For extended IP ACLs, this must be an ID in the range from 101 to 199 or a name.
7. Click the Add button.
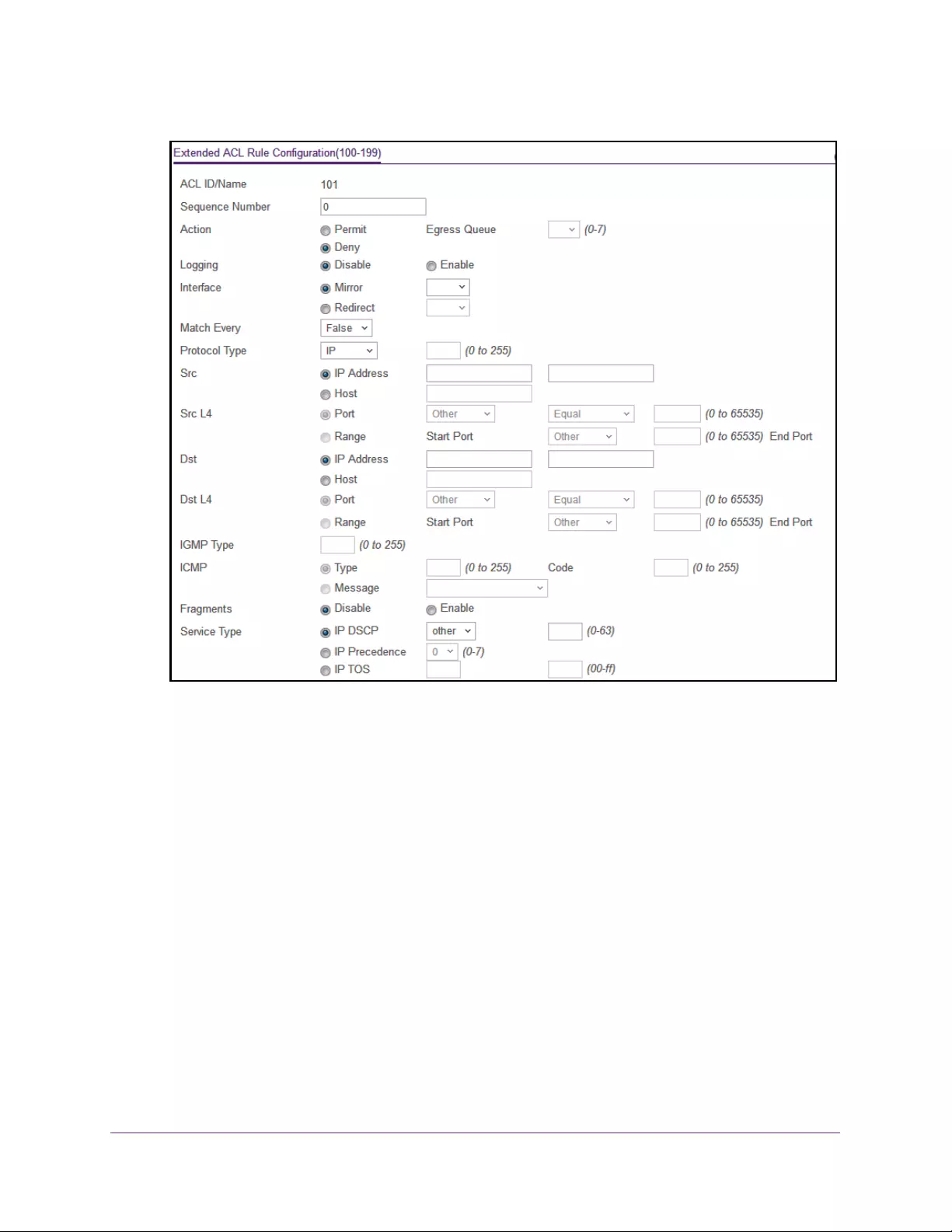
Manage Device Security
318
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The previous figure does not show the rightmost fields.
8. Configure the following match criteria for the rule:
•Sequence Number. Enter a whole number in the range of 1 to 2147483647 that is
used to identify the rule. An extended IP ACL can contain up to 50 rules.
•Action. Select the ACL forwarding action, which is one of the following:
-Permit. Forward packets that meet the ACL criteria.
-Deny. Drop packets that meet the ACL criteria.
•Egress Queue. If the selection from the Action menu is Permit, select the hardware
egress queue identifier that is used to handle all packets matching this IP ACL rule.
The range of queue IDs is 0 to 7.
•Logging. If the selection form the Action menu is Deny, you can enable logging for
the ACL by selecting the Enable radio button. (Logging is subject to resource
availability in the device.)
If the access list trap flag is also enabled, periodic traps are generated, indicating the
number of times this rule was evoked during the report interval. A fixed five-minute
report interval is used for the switch. A trap is not issued if the ACL rule hit count is
zero for the current interval.

Manage Device Security
319
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Interface. For a Permit action, use either a mirror interface or a redirect interface:
-Select the Mirror Interface radio button and use the menu to specify the egress
interface to which the matching traffic stream is copied, in addition to being
forwarded normally by the device.
-Select the Redirect Interface radio button and use the menu to specify the
egress interface to which the matching traffic stream is forced, bypassing any
forwarding decision normally performed by the device.
•Match Every. From the Match Every menu, select whether all packets must match
the selected IP ACL rule:
-False. Not all packets need to match the selected IP ACL rule. You can configure
other match criteria on the page.
-True. All packets must match the selected IP ACL rule and are either permitted or
denied. In this case, you cannot configure other match criteria on the page.
•Protocol Type. From the menu, select a protocol that a packet’s IP protocol must be
matched against: IP, ICMP, IGMP, TCP, UDP, EIGRP, GRE, IPINIP, OSPF, PIM, or
Other. If you select Other, specify enter a protocol number from 0 to 255.
•Src. In the Src field, enter a source IP address, using dotted-decimal notation, to be
compared to a packet’s source IP address as a match criterion for the selected IP
ACL rule:
-If you select the IP Address radio button, enter an IP address or an IP address
range. You can enter a relevant wildcard mask to apply this criteria. If this field is
left empty, it means any.
-If you select the Host radio button, the wildcard mask is configured as 0.0.0.0. If
this field is left empty, it means any.
The wildcard mask determines which bits are used and which bits are ignored. A
wildcard mask of 0.0.0.0 indicates that none of the bits are important. A wildcard of
255.255.255.255 indicates that all of the bits are important.
•Src L4. The options are available only when the protocol is set to TCP or UDP. Use the
source L4 port option to specify relevant matching conditions for L4 port numbers in
the extended ACL rule.
You can select either the Port radio button or the Range radio button:
-Port radio button. If you select the Port radio button, you can either enter the
port number yourself or select one of the following protocols from the menu:
•The source IP TCP port protocols are domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata, www-http,
smtp, telnet, pop2, pop3, and bgp.
•The source IP UDP port protocols are domain, echo, snmp, ntp, rip, time,
who, and tftp.
Each of these values translates into its equivalent port number, which is used as
both the start and end of the port range.
Select Other from the menu to enter a port number. If you select Other from the
menu but leave the field blank, it means any.

Manage Device Security
320
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The relevant matching conditions for L4 port numbers are as follows:
•Equal. IP ACL rule matches only if the Layer 4 source port number is equal to
the specified port number or port protocol.
•Not Equal. IP ACL rule matches only if the Layer 4 source port number is not
equal to the specified port number or port protocol.
•Less Than. IP ACL rule matches if the Layer 4 source port number is less
than the specified port number.
•Greater Than. IP ACL rule matches if the Layer 4 source port number is
greater than the specified port number.
-Range radio button. If you select the Range radio button, the IP ACL rule
matches only if the Layer 4 source port number is within the specified port range.
The starting port, ending port, and all ports in between are a part of the Layer 4
port range.
The Start Port and End Port fields identify the first and last ports that are part of
the port range. The values can range from 0 to 65535.
You can either enter the port range yourself or select one of the following
protocols from the menu:
•The destination IP TCP port protocols are domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata,
www-http, smtp, telnet, pop2, pop3, and bgp.
•The destination IP UDP port protocols are domain, echo, snmp, ntp, rip,
time, who, and tftp.
Each of these values translates into its equivalent port number, which is used as
both the start and end of the port range.
Select Other from the menu to enter a port number. If you select Other from the
menu but leave the field blank, it means any.
The wildcard mask determines which bits are used and which bits are ignored. A
wildcard mask of 0.0.0.0 indicates that none of the bits are important. A wildcard
of 255.255.255.255 indicates that all of the bits are important.
•Dst. In the Dst field, enter a destination IP address, using dotted-decimal notation, to
be compared to a packet’s destination IP address as a match criterion for the selected
IP ACL rule:
-If you select the IP Address radio button, enter an IP address with a relevant
wildcard mask to apply this criteria. If this field is left empty, it means any.
-If you select the Host radio button, the wildcard mask is configured as 0.0.0.0. If
this field is left empty, it means any.
The wildcard mask determines which bits are used and which bits are ignored. A
wildcard mask of 0.0.0.0 indicates that none of the bits are important. A wildcard of
255.255.255.255 indicates that all of the bits are important.

Manage Device Security
321
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Dst L4. The options are available only when the protocol is set to TCP or UDP. Use the
destination L4 port option to specify relevant matching conditions for L4 port numbers
in the extended ACL rule.
You can select either the Port radio button or the Range radio button:
-Port radio button. If you select the Port radio button, you can either enter the
port number yourself or select one of the following protocols from the menu.
•The destination IP TCP port protocols are domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata,
www-http, smtp, telnet, pop2, pop3, and bgp.
•The destination IP UDP port protocols are domain, echo, snmp, ntp, rip,
time, who, and tftp.
Each of these values translates into its equivalent port number, which is used as
both the start and end of the port range.
Select Other from the menu to enter a port number. If you select Other from the
menu but leave the field blank, it means any.
The relevant matching conditions for L4 port numbers are as follows:
•Equal. The IP ACL rule matches only if the Layer 4 destination port number is
equal to the specified port number or port protocol.
•Not Equal. The IP ACL rule matches only if the Layer 4 destination port
number is not equal to the specified port number or port protocol.
•Less Than. The IP ACL rule matches if the Layer 4 destination port number is
less than the specified port number.
•Greater Than. The IP ACL rule matches if the Layer 4 destination port
number is greater than the specified port number.
-Range radio button. If you select the Range radio button, the IP ACL rule
matches only if the Layer 4 destination port number is within the specified port
range. The starting port, ending port, and all ports in between are a part of the
Layer 4 port range.
The Start Port and End Port fields identify the first and last ports that are part of
the port range. They values can range from 0 to 65535.
You can either select the enter the port range yourself or select one of the
following protocols from the menu:
•The destination IP TCP port range names are domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata,
www-http, smtp, telnet, pop2, pop3, and bgp.
•The destination IP UDP port range names are domain, echo, snmp, ntp, rip,
time, who, and tftp.
Each of these values translates into its equivalent port number, which is used as
both the start and end of the port range.
Select Other from the menu to enter a port number. If you select Other from the
menu but leave the field blank, it means any.

Manage Device Security
322
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The wildcard mask determines which bits are used and which bits are ignored. A
wildcard mask of 0.0.0.0 indicates that none of the bits are important. A wildcard
of 255.255.255.255 indicates that all of the bits are important.
•IGMP Type. If you specify the IGMP type, the IP ACL rule matches the specified
IGMP message type. Possible values are in the range 0 to 255. If this field is left
empty, it means any.
•ICMP. Select either the Type or Message radio button:
-If you select the Type radio button, note the following:
•The Type and Code fields are enabled only if the protocol is ICMP. Use these
fields to specify a match condition for ICMP packets:
•The IP ACL rule matches the specified ICMP message type. Possible type
numbers are in the range from 0 to 255.
•If you specify information in the Message field, the IP ACL rule matches the
specified ICMP message code. Possible values for the code can be in the
range from 0 to 255.
•If these fields are left empty, it means any.
-If you select the Message radio button, select the type of the ICMP message to
match with the selected IP ACL rule. Specifying a type of message implies that
both the ICMP type and ICMP code are specified. The ICMP message is decoded
into the corresponding ICMP type and ICMP code within the ICMP type.
The IPv4 ICMP message types are echo, echo-reply, host-redirect,
mobile-redirect, net-redirect, net-unreachable, redirect, packet-too-big,
port-unreachable, source-quench, router-solicitation, router-advertisement,
ttl-exceeded, time-exceeded, and unreachable.
•Fragments. Either select the Enable radio button to allow initial fragments (that is,
the fragment bit is asserted) or leave the default Disable radio button selected to
prevent initial fragments from being used.
This option is not valid for rules that match L4 information such as a TCP port number,
because that information is carried in the initial packet.
•Service Type. Select a service type match condition for the extended IP ACL rule.
The possible options are IP DSCP, IP precedence, and IP T OS, which are alternative
methods to specify a match criterion for the same service type field in the IP header.
Each method uses a different user notation. After you make a selection, you can
specify the appropriate values:
-IP DSCP. This is an optional configuration. Specify the IP DiffServ Code Point
(DSCP) field. The DSCP is defined as the high-order 6 bits of the service type
octet in the IP header. Enter an integer from 0 to 63. To select the IP DSCP, select
one of the DSCP keywords from the menu. To specify a numeric value, select
Other and a field displays in which you can enter numeric value of the DSCP.
-IP Precedence. This is an optional configuration. The IP precedence field in a
packet is defined as the high-order 3 bits of the service type octet in the IP header .
Enter an integer from 0 to 7.

Manage Device Security
323
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
-IP TOS. This is an optional configuration. The IP ToS field in a packet is defined
as all 8 bits of the service type octet in the IP header. The ToS bits value is a
hexadecimal number that is composed of numbers 00 to 09 and AA to FF. The
ToS mask value is a hexadecimal number that is composed of numbers 00 to FF.
The ToS mask denotes the bit positions in the ToS bits value that are used for
comparison against the IP ToS field in a packet.
For example, to check for an IP ToS value for which bit 7 is set and is the most
significant value, for which bit 5 is set, and for which bit 1 is cleared, use a ToS
bits value of 0xA0 and a ToS mask of 0xFF.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Modify the Match Criteria for an Extended IP ACL Rule
To modify the match criteria for an existing extended IP ACL rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP Extended Rules.
The IP Rules page displays.
6. From the ACL ID menu, select the ACL that includes the rule that you want to modify.
7. In the Extended ACL Rule Table, click the rule.
The rule is a hyperlink. The Extended ACL Rule Configuration page displays.
8. Modify the extended IP ACL rule criteria.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Manage Device Security
324
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Delete an Extended IP ACL Rule
To delete an extended IP ACL rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP Extended Rules.
The IP Rules page displays.
6. From the ACL ID menu, select the ACL that includes the rule that you want to delete.
7. In the Extended ACL Rule Table, select the check box that is associated with the rule.
8. Click the Delete button.
The rule is removed.
Configure an IPv6 ACL
An IP or IPv6 ACL consists of a set of rules that are matched sequentially against a packet.
When a packet meets the match criteria of a rule, the specified rule action (Permit or Deny) is
taken, and the additional rules are not checked for a match.
Add an IPv6 ACL
To add an IPv6 ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
Manage Device Security
325
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IPv6 ACL.
The IPV6 Configuration page displays.
6. In the IPv6 ACL field, specify a name to identify the IPv6 ACL.
This is the IPv6 ACL name string, which includes up to 31 alphanumeric characters only.
The name must start with an alphabetic character.
7. Click the Add button.
The IPv6 ACL is added.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Delete an IPv6 ACL
To delete an IPv6 ACL:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
Table 79. IPv6 Configuration and IPv6 ACL Table information
Field Description
Current Number of ACL The current number of the IP ACLs configured on the switch.
Maximum ACL The maximum number of IP ACLs that can be configured on the switch.
Rules The number of the rules associated with the IP ACL.
Type The type is IPv6 ACL.

Manage Device Security
326
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IPv6 ACL.
The IPv6 Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box that is associated with the IPv6 ACL.
7. Click the Delete button.
The IPv6 ACL is removed.
Configure Rules for an IPv6 ACL
You can define rules for IPv6 ACLs. The access list definition includes rules that specify
whether traffic matching the criteria is forwarded normally or discarded.
Note: An implicit deny all rule is included at the end of an ACL list. This
means that if an ACL is applied to a packet and if none of the explicit
rules match, then the final implicit deny all rule applies and the packet
is dropped.
Add a Rule for an IPv6 ACL
Add a rule for an ACL IPv6:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IPv6 Rules.
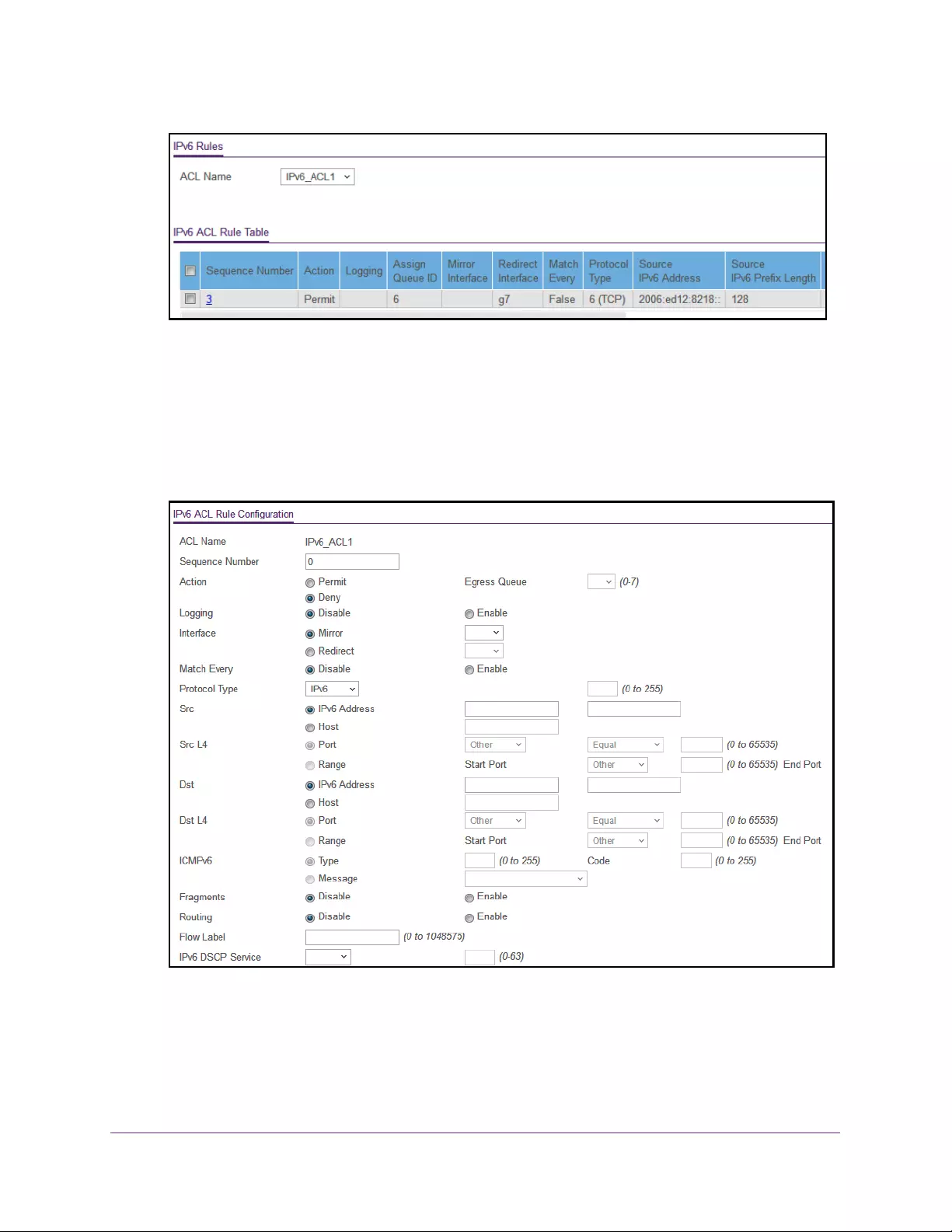
Manage Device Security
327
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The previous figure does not show all columns.
If no rules exists, the IPv6 ACL Rule Table shows the message No rules have been
configured for this ACL. If one or more rules exist for the ACL, the rules display in the
IPv6 ACL Rule Table.
6. From the ACL Name menu, select the IPv6 ACL for which you want to add a rule.
7. Click the Add button.
The previous figure does not show the rightmost fields.
8. Configure the following match criteria for the rule:
•Sequence Number. Enter a whole number in the range of 1 to 2147483647 that is
used to identify the rule. An extended IP ACL can contain up to 50 rules.

Manage Device Security
328
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Action. Select the ACL forwarding action by selecting one of the following radio
buttons:
-Permit. Forward packets that meet the ACL criteria.
-Deny. Drop packets that meet the ACL criteria.
•Egress Queue. If you select the Permit radio button, select the hardware egress
queue identifier that is used to handle all packets matching this IPv6 ACL rule. The
range of queue IDs is 0 to 7.
•Logging. If you select the Deny radio button, you can enable logging for the ACL by
selecting the Enable radio button. (Logging is subject to resource availability in the
device.)
If the access list trap flag is also enabled, periodic traps are generated, indicating the
number of times this rule was evoked during the report interval. A fixed five-minute
report interval is used for the switch. A trap is not issued if the ACL rule hit count is
zero for the current interval.
•Interface. For a Permit action, use either a mirror interface or a redirect interface:
-Select the Mirror Interface radio button and use the menu to specify the egress
interface to which the matching traffic stream is copied, in addition to being
forwarded normally by the device.
-Select the Redirect Interface radio button and use the menu to specify the
egress interface to which the matching traffic stream is forced, bypassing any
forwarding decision normally performed by the device.
•Match Every. Select whether all packet must match the selected IPv6 ACL rule:
-Disable. Not all packets need to match the selected IPv6 ACL rule. You can
configure other match criteria on the page.
-Enable. All packets must match the selected IPv6 ACL rule and are either
permitted or denied. In this case, you cannot configure other match criteria on the
page.
•Protocol Type. Specify the IPv6 protocol type in one of the following ways:
-From the Protocol Type menu, select IPv6, ICMPv6, TCP, or UDP.
-From the Protocol Type menu, select Other, and in the associated field, specify
an integer ranging from 0 to 255. This number represents the IPv6 protocol.
•Src. In the Src field, enter a source IPv6 address or source IPv6 address range to be
compared to a packet’s source IPv6 address as a match criterion for the selected
IPv6 ACL rule:
-If you select the IPv6 Address radio button, enter an IPv6 address or IPv6 range
to apply this criteria. If this field is left empty, it means any.
-If you select the Host radio button, enter a host source IPv6 address to match the
specified IPv6 address. If this field is left empty, it means any.
The source IPv6 address argument must be in the form documented in RFC 2373
where the address is specified in hexadecimal numbers using 16-bit values between
colons.

Manage Device Security
329
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Src L4. The options are available only when the protocol is set to TCP or UDP. Use the
source L4 port option to specify relevant matching conditions for L4 port numbers in
the extended ACL rule.
You can select either the Port radio button or the Range radio button:
-Port radio button. If you select the Port radio button, you can either enter the
port number yourself or select one of the following protocols from the menu:
•The source IP TCP port protocols are domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata, www-http,
smtp, telnet, pop2, pop3, and bgp.
•The source IP UDP port protocols are domain, echo, snmp, ntp, rip, time,
who, and tftp.
Each of these values translates into its equivalent port number, which is used as
both the start and end of the port range.
Select Other from the menu to enter a port number. If you select Other from the
menu but leave the field blank, it means any.
The relevant matching conditions for L4 port numbers are as follows:
•Equal. The IPv6 ACL rule matches only if the Layer 4 source port number is
equal to the specified port number or port protocol.
•Not Equal. The IPv6 ACL rule matches only if the Layer 4 source port number
is not equal to the specified port number or port protocol.
•Less Than. The IPv6 ACL rule matches if the Layer 4 source port number is
less than the specified port number.
•Greater Than. The IPv6 ACL rule matches if the Layer 4 source port number
is greater than the specified port number.
-Range radio button. If you select the Range radio button, the IPv6 ACL rule
matches only if the Layer 4 source port number is within the specified port range.
The starting port, ending port, and all ports in between are a part of the Layer 4
port range.
The Start Port and End Port fields identify the first and last ports that are part of
the port range. They values can range from 0 to 65535.
You can either enter the port range yourself or select one of the following
protocols from the menu:
•The source IP TCP port protocols are domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata, www-http,
smtp, telnet, pop2, pop3, and bgp.
•The source IP UDP port protocols are domain, echo, snmp, ntp, rip, time,
who, and tftp.
Each of these values translates into its equivalent port number, which is used as
both the start and end of the port range.
Select Other from the menu to enter port numbers. If you select Other from the
menu but leave the fields blank, it means any.

Manage Device Security
330
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Dst. In the Dst field, enter a destination IPv6 address to be compared to a packet’s
destination IPv6 address as a match criterion for the selected IPv6 ACL rule:
-If you select the IPv6 Address radio button, enter an IPv6 address to apply this
criteria. If this field is left empty, it means any.
-If you select the Host radio button, enter a host source IPv6 address to match the
specified IPv6 address. If this field is left empty, it means any.
The source IPv6 address argument must be in the form documented in RFC 2373
where the address is specified in hexadecimal numbers using 16-bit values between
colons.
•Dst L4. The options are available only when the protocol is set to TCP or UDP. Use the
destination L4 port option to specify relevant matching conditions for L4 port numbers
in the extended ACL rule.
You can select either the Port radio button or the Range radio button:
-Port radio button. If you select the Port radio button, you can either enter the
port number yourself or select one of the following protocols from the menu:
•The destination IP TCP port protocols are domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata,
www-http, smtp, telnet, pop2, pop3, and bgp.
•The destination IP UDP port protocols are domain, echo, snmp, ntp, rip,
time, who, and tftp.
Each of these values translates into its equivalent port number, which is used as
both the start and end of the port range.
Select Other from the menu to enter a port number. If you select Other from the
menu but leave the field blank, it means any.
The relevant matching conditions for L4 port numbers are as follows:
•Equal. The IPv6 ACL rule matches only if the Layer 4 destination port number
is equal to the specified port number or port protocol.
•Not Equal. The IPv6 ACL rule matches only if the Layer 4 destination port
number is not equal to the specified port number or port protocol.
•Less Than. The IPv6 ACL rule matches if the Layer 4 destination port number
is less than the specified port number.
•Greater Than. The IPv6 ACL rule matches if the Layer 4 destination port
number is greater than the specified port number.
-Range radio button. If you select the Range radio button, the IPv6 ACL rule
matches only if the Layer 4 destination port number is within the specified port
range. The starting port, ending port, and all ports in between are a part of the
Layer 4 port range.
The Start Port and End Port fields identify the first and last ports that are part of
the port range. They values can range from 0 to 65535.

Manage Device Security
331
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
You can either enter the port range yourself or select one of the following
protocols from the menu:
•The destination IP TCP port protocols are domain, echo, ftp, ftpdata,
www-http, smtp, telnet, pop2, pop3, and bgp.
•The destination IP UDP port protocols are domain, echo, snmp, ntp, rip,
time, who, and tftp.
Each of these values translates into its equivalent port number, which is used as
both the start and end of the port range.
Select Other from the menu to enter port numbers. If you select Other from the
menu but leave the fields blank, it means any.
•ICMPv6. Select either the Type or Message radio button:
-Type radio button. If you select the Type radio button, note the following:
•The Type and Message fields are enabled only if the protocol is ICMPv6. Use
these fields to specify a match condition for ICMPv6 packets.
•The IPv6 ACL rule matches the specified ICMPv6 message type. Possible
type numbers are in the range from 0 to 255.
•If you specify information in the Message field, the IPv6 ACL rule matches the
specified ICMPv6 message code. Possible values for code can be in the
range from 0 to 255.
•If these fields are left empty, it means any.
-Message radio button. If you select the Message radio button, select the type of
the ICMPv6 message to match with the selected IPv6 ACL rule. Specifying a type
of message implies that both the ICMPv6 type and ICMPv6 code are specified.
The ICMPv6 message is decoded into the corresponding ICMPv6 type and
ICMPv6 code within the ICMP type.
The ICMPv6 message types are destination-unreachable, echo-reply,
echo-request, header, hop-limit, mld-query, mld-reduction, mld-report,
nd-na, nd-ns, next-header, no-admin, no-route, packet-too-big,
port-unreachable, router-solicitation, router-advertisement,
router-renumbering, time-exceeded, and unreachable.
•Fragments. Either select the Enable radio button to allow initial fragments (that is,
the fragment bit is asserted) or leave the default Disable radio button selected to
prevent initial fragments from being used.
This option is not valid for rules that match L4 information such as TCP port number,
because that information is carried in the initial packet.
•Routing. Either select the Enable radio button to match packets that include a
routing extension header or leave the default Disable radio button selected to ignore
the routing extension headers in packets.
•Flow Label. The Flow Label field is enabled only if selection from the Protocol Type
menu is ICMPv6. The flow label is 20-bit number that is unique to an IPv6 packet and

Manage Device Security
332
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
that is used by end stations to signify Quality of Service handling in routers. The flow
label can specified within the range 0 to 1048575.
•IPv6 DSCP Service. Specify the IP DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) field. This is an
optional configuration.
The DSCP is defined as the high-order 6 bits of the service type octet in the IPv6
header. Enter an integer from 0 to 63. To select the IPv6 DSCP, select one of the
DSCP keywords. To specify a numeric value, select Other and enter the numeric
value of the DSCP.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Modify the Match Criteria for an IPv6 ACL Rule
To modify the match criteria for an IPv6 ACL rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IPv6 Rules.
The IPv6 Rules page displays.
6. From the ACL Name menu, select the ACL that includes the rule that you want to modify.
7. In the IPv6 ACL Rule Table, click the rule.
The rule is a hyperlink. The IPv6 ACL Rule Configuration page displays.
8. Modify the IPv6 ACL rule criteria.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.

Manage Device Security
333
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Delete an IPv6 ACL Rule
To delete an IPv6 ACL rule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IPv6 Rules .
The IPv6 Rules page displays.
6. From the ACL Name menu, select the ACL that includes the rule that you want to delete.
7. In the IPv6 ACL Rule Table, select the check box that is associated with the rule.
8. Click the Delete button.
The rule is removed.
Configure IP ACL Interface Bindings
When an ACL is bound to an interface, all the rules that are defined are applied to the
selected interface. You can assign ACL lists to ACL priorities and interfaces.
If resources on the switch are insufficient, an attempt to bind an ACL to an interface fails. You
cannot bind an IPv4 ACL and an IPv6 ACL to the same interface.
To bind an IP ACL to one or more interfaces:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
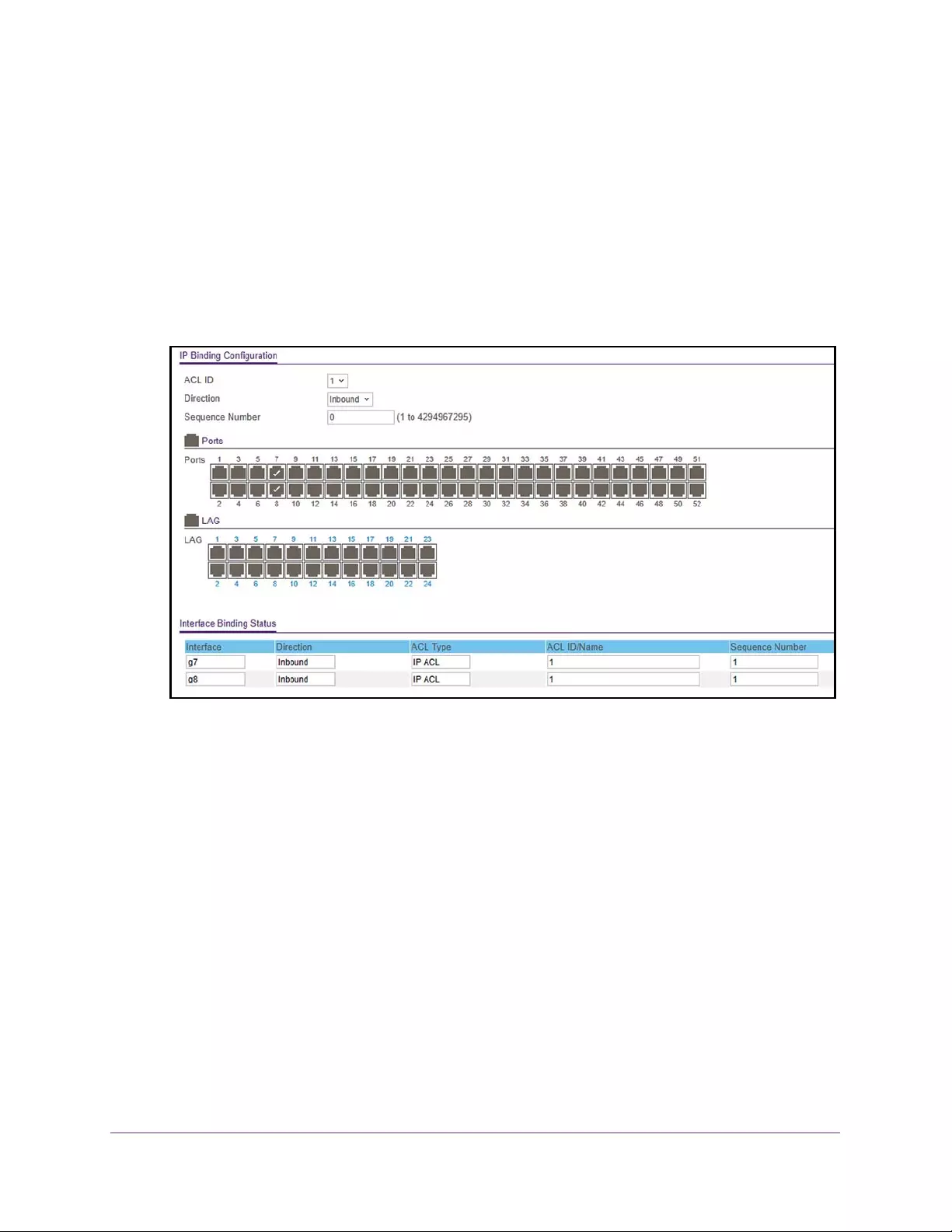
Manage Device Security
334
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > IP Binding Configuration.
The following figure show the page for models GC752X and GC752XP. Models GC728X
and GC728XP support 24 Ethernet ports but the same number of LAGs (24).
6. From the ACL ID menu, select an existing IP ACL for you which you want to add an IP ACL
interface binding.
The fixed selection from the Direction menu is Inbound, which means that MAC ACL
rules are applied to traffic entering the interface.
7. In the Sequence Number field, optionally specify a number to indicate the order of the
access list relative to other access lists already assigned to this interface and direction.
A low number indicates high precedence order. If a sequence number is already in use
for this interface and direction, the specified access list replaces the currently attached
access list using that sequence number. If you do not specify the sequence number
(meaning that the value is 0), a sequence number that is one number greater than the
highest sequence number currently in use for this interface and direction is used. The
valid range is 1–4294967295.
8. To add the selected ACL to a port or LAG, in the Ports table or LAG table, click the port or
LAG so that a check mark displays.
You can add the ACL to several ports and LAGs.
Manage Device Security
335
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The Ports and LAG tables display the available and valid interfaces for ACL binding. All
nonrouting physical interfaces, VLAN interfaces, and interfaces participating in LAGs are
listed.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
View or Delete IP ACL Bindings in the IP ACL Binding Table
You can view or delete the IP ACL bindings.
To view or delete IP ACL bindings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL > Advanced > Binding Table.
The IP ACL Binding Table displays.
Table 80. IP Binding Status table
Field Description
Interface The selected interface.
Direction The selected packet filtering direction for the ACL.
ACL Type The type of ACL assigned to the selected interface and direction.
ACL ID/Name The ACL number (for an IP ACL) or ACL name (for a named IP ACL or
IPv6 ACL) identifying the ACL assigned to the selected interface and
direction.
Sequence Number The sequence number signifying the order of specified ACL relative to
other ACLs assigned to the selected interface and direction.

Manage Device Security
336
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. To delete an IP ACL-to-interface binding, do the following:
a. Select the check box next to the interface.
b. Click the Delete button.
The binding is removed.
The following table describes the information displayed in the IP ACL Binding Table.
Configure VLAN ACL Bindings
You can associate an ACL with a VLAN. When an ACL is associated with a VLAN, it is
applied to all interfaces that are members of the VLAN.
To configure VLAN ACL bindings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Security > ACL> Advanced > VLAN Binding Configuration.
The VLAN Binding Configuration page displays.
Table 81. IP ACL Binding Table
Field Description
Interface The interface.
Direction The selected packet filtering direction for the ACL.
ACL Type The type of ACL assigned to the selected interface and direction.
ACL ID/Name The ACL number (for an IP ACL) or ACL name (for a named IP ACL or
IPv6 ACL) identifying the ACL assigned to the selected interface and
direction.
Sequence Number The sequence number signifying the order of the specified ACL relative
to other ACLs assigned to the selected interface and direction.

Manage Device Security
337
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. In the VLAN ID field, enter the VLAN ID to which the binding must apply.
7. From the Direction menu, select the packet filtering direction.
8. In the Sequence Number field, enter an optional sequence number.
You can specify an optional sequence number to indicate the order of this access list
relative to other access lists that are already assigned to the VLAN ID and selected
direction. A lower number indicates a higher precedence order. If a sequence number is
already in use for the VLAN ID and selected direction, the specified access list replaces
the currently attached ACL using that sequence number. If you do not specify a sequence
number (the value is 0), a sequence number that is one greater than the highest
sequence number currently in use for the VLAN ID and selected direction is used. The
valid range is 1 to 4294967295.
9. From the ACL Type menu, select the type of ACL.
Valid ACL types include IP ACL, MAC ACL, and IPv6 ACL.
10. From the ACL ID list, select the ID or name of the ACL that must be bound to the specified
VLAN.
11. Click the Add button.
The VLAN ACL binding is added.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
339
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Reboot the Switch
You can reboot the switch from the local browser interface.
Note: The switch provides a recessed multi-function Reset button that lets
you reboot (power-cycle) the switch. To reboot the switch, press the
Reset button on the front panel for about two seconds. (Do not press
the button for more than five seconds!) The switch restarts but retains
its custom settings.
To reboot the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Reset > Device Reboot.
6. The Device Reboot page displays.
7. Select the check box.
8. Click the Apply button.
The switch reboots.
Reset the Switch to Its Factory Default Settings
You can reset the system configuration to the factory default values. All changes that you
made are lost. If the IP address changes, your web session might disconnect.
If you added the switch to a network on the Insight app before, all Insight-manageable device
settings are returned to the last configuration saved on the cloud server, including the switch
password (that is, the password is reset to the Insight network password). Otherwise, the IP
address is reset to 192.168.0.239, the DHCP client is enabled, and the password is reset to

Perform Maintenance Tasks
340
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
password. The default management mode is reset to NETGEAR Insight Mobile App and
Insight Cloud Portal.
For information about reconnecting to the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
For information about changing the management mode, see Change the Management Mode
of the Switch on page 20.
Note: The switch provides a recessed multi-function Reset button that lets
you return the switch to its factory default settings, causing all custom
settings to be erased. The factory default settings function of the
Reset button is available only after you use the NETGEAR Insight
app to remove the switch from your network. After you use the
NETGEAR Insight app to remove the switch from your network, press
the Reset button on the front panel for at least five seconds. The
switch restarts and returns to its factory default settings.
To reset the switch to the factory default settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Reset > Factory Default.
The Factory Default page displays.
6. Select the check box.
7. Click the Apply button.
A confirmation pop-up window opens.
8. Click the OK button to confirm.
All configuration settings are reset to their factory default values. All changes that you
made are lost, even if you saved the configuration.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
341
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Export a File From the Switch
You can export configuration (ASCII or log ASCII) files from the switch to a file server by
using TFTP or HTTP or to a USB storage device.
The following sections describe how you can export a file from the switch:
•Export a File to the TFTP Server on page 341
•Use an HTTP Sessions to Export a File on page 342
•Export a File to a USB Storage Device on page 343
Export a File to the TFTP Server
You can upload (export) configuration (ASCII or log ASCII) files from the switch to a TFTP
server on the network.
To export a file from the switch to a TFTP server:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Export > TFTP File Export.
The TFTP File Export page displays.
6. From the File Type menu, select the type of file:
•Text Configuration. A text-based configuration file enables you to edit a configured
text file (startup-config) offline as needed. The most common usage of
text-based configuration is to upload a working configuration from a device, edit it
offline to personalize it for another similar device (for example, change the device
name or IP address), and download it to that device.
•Error Log. The system error (persistent) log, also referred to as the event log.
•Trap Log. The trap log with the system trap records.
•Buffered Log. The system buffered (in-memory) log.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
342
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Tech Support. The tech support file is a text-base file that contains a variety of
hardware, software, and configuration information that can assist in device and
network troubleshooting.
•Crash Logs. Specify the crash logs to retrieve them.
7. From the Server Address Type menu, select the format for the Server Address field:
•IPv4. Indicates that the TFTP server address is an IP address in dotted-decimal
format. This is the default setting.
•DNS. Indicates that the TFTP server address is a host name.
8. In the Server Address field, enter the IP address of the server in accordance with the
format indicated by the server address type.
The default is the IPv4 address 0.0.0.0.
9. In the Transfer File Path field, specify the path on the TFTP server where you want to save
the file.
You can enter up to 32 characters. Include the backslash at the end of the path. A path
name with a space is not accepted. Leave this field blank to save the file to the root TFTP
directory.
10. In the Transfer File Name field, specify a destination file name for the file to be uploaded.
You can enter up to 32 characters. The transfer fails if you do not specify a file name. For
an archive transfer, use a .stk file extension.
11. Select the Start File Transfer check box.
12. Click the Apply button.
The file transfer begins.
The page displays information about the file transfer progress. The page refreshes
automatically when the file transfer completes (or if it fails).
Use an HTTP Sessions to Export a File
You can upload (export) files of various types from the switch to a management system
through an HTTP session by using your web browser.
To export a file from the switch to another system by using HTTP:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
343
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Export > HTTP File Export.
The HTTP File Export page displays.
6. From the File Type menu, select the type of file:
•Text Configuration. A text-based configuration file enables you to edit a configured
text file (startup-config) offline as needed. The most common usage of
text-based configuration is to upload a working configuration from a device, edit it
offline to personalize it for another similar device (for example, change the device
name or IP address), and download it to that device.
•Tech Support. The tech support file is a text-base file that contains a variety of
hardware, software, and configuration information that can assist in device and
network troubleshooting.
•Crash Logs. Specify crash logs to retrieve them.
7. Click the Apply button.
The file transfer begins.
The page displays information about the file transfer progress. The page refreshes
automatically when the file transfer completes (or if it fails).
Export a File to a USB Storage Device
You can upload (export) files of various types from the switch to a USB storage device.
To export a file from the switch to a USB storage device:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
344
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
5. Select Maintenance > Export > USB File Export.
The Export File to USB page displays.
The default and only possible selection from the File Type menu is Text Configuration.
A text-based configuration file enables you to edit a configured text file
(startup-config) offline as needed. The most common usage of text-based
configuration is to upload a working configuration from a device, edit it offline to
personalize it for another similar device (for example, change the device name or IP
address), and download it to that device.
6. In the File Path field, enter the path for the file to export.
You can enter up to 139 characters.
7. In the USB File field, specify the name for the file to export.
You can enter up to 32 characters.
8. Click the Apply button.
The file transfer begins.
The page displays information about the file transfer progress. The page refreshes
automatically when the file transfer completes (or if it fails).
Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch
Note: You can manually check for the latest software (firmware) version by
visiting downloadcenter.netgear.com, download the software to a
TFTP server, computer, or USB storage device, and then download
the software to the switch. If release notes are available with the new
software, read the release notes to find out if you must reconfigure the
switch after upgrading the software.
You can download system files from a TFTP server, over an HTTP session, or from a USB
storage device.
The following sections describe how you can download a file to the switch:
•Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using TFTP on page 345
•Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using HTTP on page 347
•Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using a USB Device on page 349

Perform Maintenance Tasks
345
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using
TFTP
You can upgrade software and download the image file, the configuration files, and SSL files
from a TFTP server to the switch.
Before you download a file to the switch, the following conditions must be true:
•The file to download from the TFTP server is on the server in the appropriate directory.
•The file is in the correct format.
•The switch contains a path to the TFTP server.
To upgrade software or download a file from a TFTP server to the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Upgrade > TFTP File Upgrade.
The TFTP File Upgrade page displays.
6. From the File Type menu, select the type of file:
•Software. The system software image, which is saved in one of two flash sectors
called images (image1 and image2). The active image stores the active copy, while
the other image stores a second copy. The device boots and runs from the active
image. If the active image is corrupted, the system automatically boots from the
nonactive image. This is a safety feature for faults occurring during the boot upgrade
process. The default setting is Software.
•Text Configuration. A text-based configuration file enables you to edit a configured
text file (startup-config) offline as needed. The most common usage of
text-based configuration is to upload a working configuration from a device, edit it
offline to personalize it for another similar device (for example, change the device
name or IP address), and download it to that device.
•SSH-1 RSA Key File. SSH-1 Rivest-Shamir-Adelman (RSA) Key file.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
346
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•SSH-2 RSA Key PEM File. SSH-2 Rivest-Shamir-Adelman (RSA) Key File (PEM
Encoded).
•SSH-2 DSA Key PEM File. SSH-2 Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) Key File (PEM
Encoded).
•SSL Trusted Root Certificate PEM File. SSL Trusted Root Certificate File (PEM
Encoded).
•SSL Server Certificate PEM File. SSL Server Certificate File (PEM Encoded).
•SSL DH Weak Encryption Parameter PEM File. SSL Diffie-Hellman Weak
Encryption Parameter File (PEM Encoded).
•SSL DH Strong Encryption Parameter PEM File. SSL Diffie-Hellman Strong
Encryption Parameter File (PEM Encoded).
7. If the selection from the File Type menu is Software, the Image Name menu is displayed
and you must select the software image that must be downloaded to the switch:
•image1. Select image1 to upload image1.
•image2. Select image2 to upload image2.
Note: We recommended that you do not overwrite the active image. If you do
so, the switch displays a warning that you are trying to overwrite the
active image.
8. From the Transfer Mode menu, select the protocol for the file transfer:
•TFTP. Trivial File Transfer Protocol.
•SFTP. Secure File Transfer Protocol.
•SCP. Secure Copy Protocol.
•FTP. File Transfer Protocol.
9. From the Server Address Type menu, select the format for the TFTP Server IP field:
•IPv4. Indicates that the TFTP server address is an IP address in dotted-decimal
format. This is the default setting.
•DNS. Indicates that the TFTP server address is a host name.
10. In the TFTP Server IP field, enter the IP address of the TFTP server indicated by the server
address type.
The default is the IPv4 address 0.0.0.0.
11. In the Transfer File Path field, specify the path on the TFTP server where the file is located.
Enter up to 160 characters. Include the backslash at the end of the path. A path name
with a space is not accepted. Leave this field blank to save the file to the root TFTP
directory.
12. In the Remote File Name field, specify the name of the file to download from the TFTP
server.
The file path cannot include the following symbols: ' \:*?”<>| '. You can enter up to
32 characters. A file name with a space is not accepted.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
347
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
13. If you selected SFTP or SCP from the Transfer Mode menu, specify the following
credentials:
•User Name. The user name to log in the server.
•Password. The password to log in the server.
14. Select the Start File Transfer check box.
15. Click the Apply button.
The file transfer begins.
The page displays information about the progress of the file transfer. The page refreshes
automatically when the file transfer completes (or if it fails).
To activate a software image that you downloaded to the switch, see Manage Software
Images on page 350.
Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using
HTTP
You can upgrade software and download the image file, the configuration files, and SSL files
to the switch through an HTTP session by using your web browser.
To upgrade the software or download a file to the switch using HTTP:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Upgrade > HTTP File Upgrade.
The HTTP File Upgrade page displays.
6. From the File Type menu, select the type of file:
•Software. The system software image, which is saved in one of two flash sectors
called images (image1 and image2). The active image stores the active copy, the
other image stores a second copy. The device boots and runs from the active image.
If the active image is corrupted, the system automatically boots from the nonactive

Perform Maintenance Tasks
348
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
image. This is a safety feature for faults occurring during the boot upgrade process.
The default setting is Software.
•Text Configuration. A text-based configuration file enables you to edit a configured
text file (startup-config) offline as needed. The most common usage of
text-based configuration is to upload a working configuration from a device, edit it
offline to personalize it for another similar device (for example, change the device
name, serial number, IP address), and download it to that device.
•SSH-1 RSA Key File. SSH-1 Rivest-Shamir-Adelman (RSA) Key file.
•SSH-2 RSA Key PEM File. SSH-2 Rivest-Shamir-Adelman (RSA) Key File (PEM
Encoded).
•SSH-2 DSA Key PEM File. SSH-2 Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) Key File (PEM
Encoded).
•SSL Trusted Root Certificate PEM File. SSL Trusted Root Certificate File (PEM
Encoded).
•SSL Server Certificate PEM File. SSL Server Certificate File (PEM Encoded).
•SSL DH Weak Encryption Parameter PEM File. SSL Diffie-Hellman Weak
Encryption Parameter File (PEM Encoded).
•SSL DH Strong Encryption Parameter PEM File. SSL Diffie-Hellman Strong
Encryption Parameter File (PEM Encoded).
7. If the selection from the File Type menu is Software, the Image Name menu is displayed
and you must select the software image that must be downloaded to the switch:
•image1. Select image1 to download image1.
•image2. Select image2 to download image2.
Note: We recommended that you do not overwrite the active image. If you do
so, the switch displays a warning that you are trying to overwrite the
active image.
8. Next to Select File, click the Browse button and locate the file that you want to download.
The file name can contain up to 80 characters.
9. Click the Apply button.
The file transfer begins.
The page displays information about the progress of the file transfer. The page refreshes
automatically when the file transfer completes (or if it fails).
Note: After a file transfer is started, wait until the page refreshes. When the
page refreshes, the option to select a file is no longer available,
indicating that the file transfer is complete.
To activate a software image that you downloaded to the switch, see Manage Software
Images on page 350.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
349
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Note: After a text configuration file is downloaded, the switch applies the
configuration automatically.
Upgrade the Software or Download a File to the Switch Using
a USB Device
You can upgrade the software and download files of various types from a USB storage device
to the switch.
To upgrade the software or download a file a from a USB storage device to the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Export > USB File Export.
The Upgrade File From USB page displays.
6. From the File Type menu, select the type of file:
•Software. The system software image, which is saved in one of two flash sectors
called images (image1 and image2). The active image stores the active copy, the
other image stores a second copy. The device boots and runs from the active image.
If the active image is corrupted, the system automatically boots from the nonactive
image. This is a safety feature for faults occurring during the boot upgrade process.
The default setting is Software.
•Text Configuration. A text-based configuration file enables you to edit a configured
text file (startup-config) offline as needed. The most common usage of
text-based configuration is to upload a working configuration from a device, edit it
offline to personalize it for another similar device (for example, change the device
name or IP address), and download it to that device.
Perform Maintenance Tasks
350
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
7. If the selection from the File Type menu is Software, the Image Name menu is displayed
and you must select the software image that must be downloaded to the switch:
•image1. Select image1 to download image1.
•image2. Select image2 to download image2.
Note: We recommended that you do not overwrite the active image. If you do
so, the switch displays a warning that you are trying to overwrite the
active image.
8. In the File Path field, enter the path for the file to download.
You can enter up to 146 characters.
9. In the USB File field, specify the name for the file to download.
You can enter up to 32 characters. The transfer fails if you do not specify a filename.
10. Click the Apply button.
The file transfer begins.
The page displays information about the progress of the file transfer. The page refreshes
automatically when the file transfer completes (or if it fails).
To activate a software image that you downloaded to the switch, see Manage Software
Images on page 350.
Note: After a text configuration file is downloaded, the switch applies the
configuration automatically.
Manage Software Images
The system maintains two versions of the switch software in permanent storage. One image
is the active image, and the second image is the backup image. The active image is loaded
during subsequent switch restarts. This feature reduces switch down time when you are
upgrading or downgrading the switch software.
A legacy software version can ignore (that is, might not load) a configuration file that is
created by a newer software version. When a configuration file created by the newer software
version is discovered by the system running an older version of the software, the system
displays an appropriate warning.
The following sections describe how you can manage the images:
•Copy an Image on page 351
•Configure Dual Image Settings on page 351

Perform Maintenance Tasks
351
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Copy an Image
You can copy an image from one location (primary or backup) to another.
To copy an image:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Image Management > Copy.
The Copy page displays.
6. Select the Source Image image1 or image2 radio button to specify the image to be copied.
7. Select the Destination Image image1 or image2 radio button to specify the destination
image.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Dual Image Settings
The Dual Image feature allows the switch to retain two images in permanent storage. You
can select which image to load during the next boot cycle, configure an image description, or
delete an image. This feature reduces switch down time when you are upgrading or
downgrading the software image.
Change the Image That Loads During the Boot Process
To change the image that loads during the boot process:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
352
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Image Management > Dual Image > Dual Image Configuration.
The Dual Image Configuration page displays.
6. From the Image Name menu, select the image that is not the image displayed in the
Current-active field.
The Current-active field displays the name of the active image.
7. To specify a name for the selected image, enter one in the Image Description field.
8. Select the Activate Image check box.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Note: After activating an image, you must perform a system reset of the
switch to run the new code. The switch continues running the image
shown in the Current-active field until the switch reboots.
Delete an Image
To delete an image:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
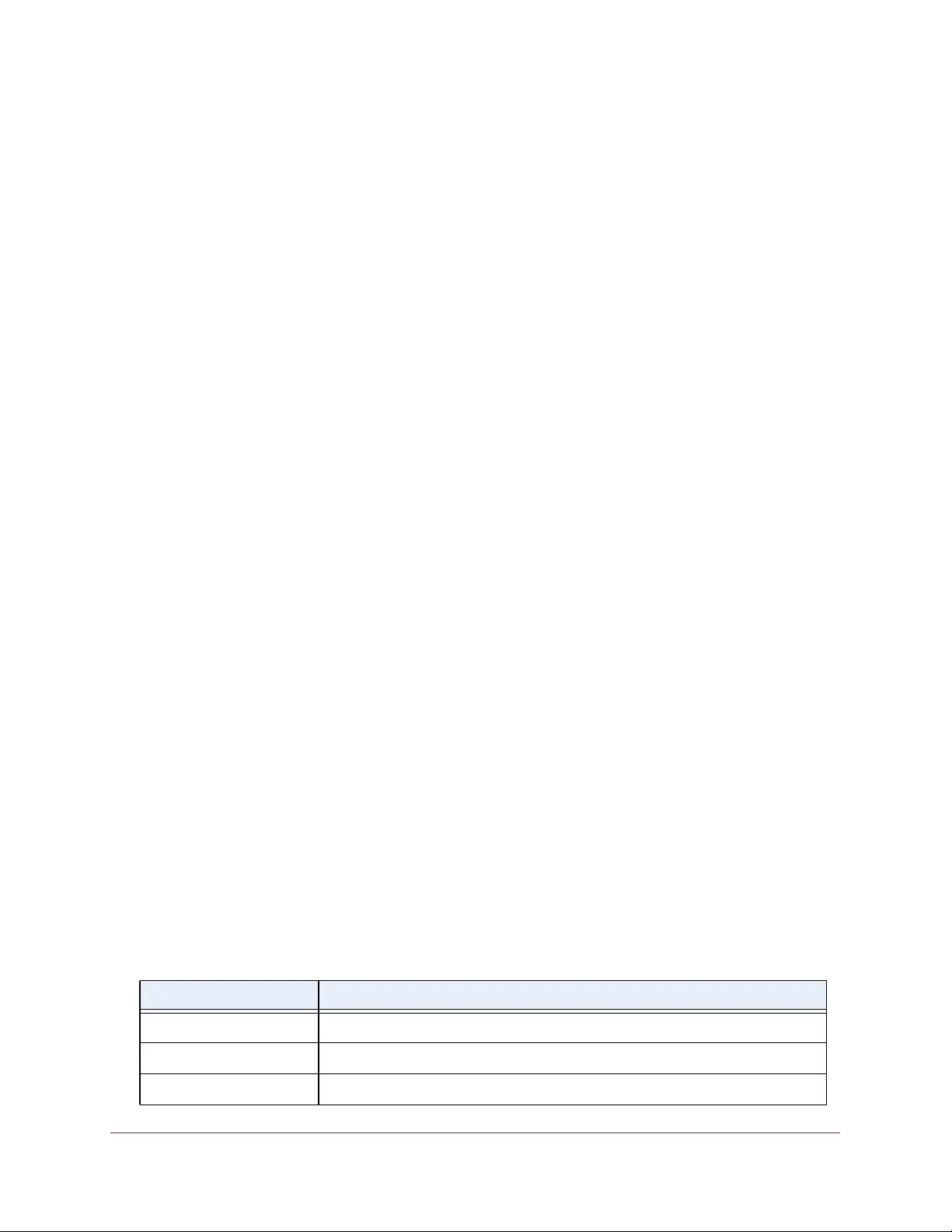
Perform Maintenance Tasks
353
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Image Management > Dual Image > Dual Image Configuration.
The Dual Image Configuration page displays.
6. From the Image Name menu, select the image that is not the image displayed in the
Current-active field.
The Current-active field displays the name of the active image. You cannot delete the
active image.
7. Select the Delete Image check box.
8. Click the Apply button.
The image is removed.
View the Dual Image Status
You can view information about the active and backup images on the switch.
To view dual image status information:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Image Management > Dual Image > Dual Image Status.
The Dual Image Status page displays.
The following table describes the information available on the page.
Table 82. Dual Image Status information
Field Description
Image1 Ver The version of the image1 code file.
Image2 Ver The version of the image2 code file.
Current-active The currently active image on this switch.
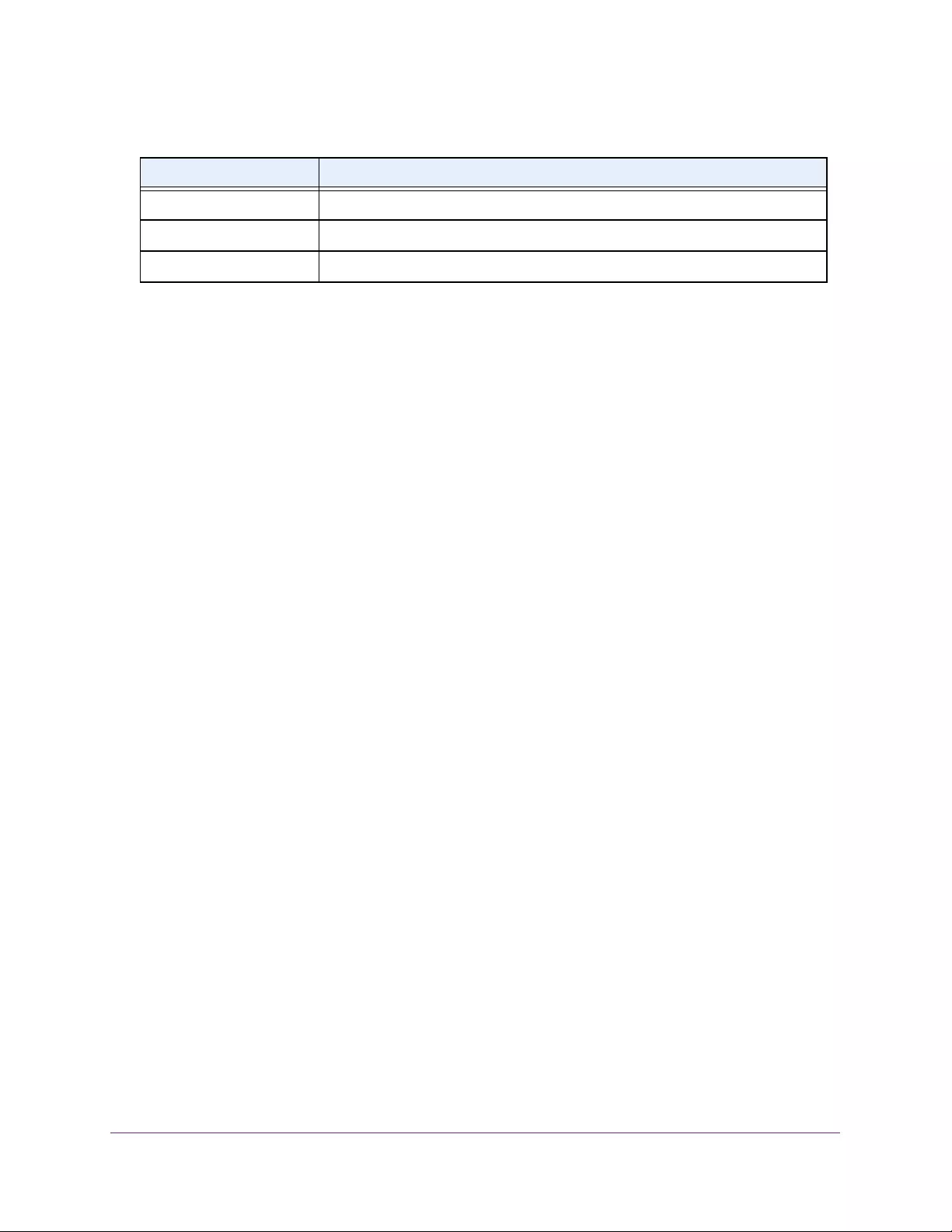
Perform Maintenance Tasks
354
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Perform Troubleshooting Tasks
You can send a ping or a traceroute.
The following sections describe how you can troubleshoot the switch and the network:
•Send an IPv4 Ping on page 354
•Send an IPv6 Ping on page 355
•Send an IPv4 Traceroute on page 357
•Send an IPv6 Traceroute on page 358
•Enable Remote Diagnostics on page 360
•Configure Memory Dump Settings and Perform a Full Memory Dump on page 360
Send an IPv4 Ping
You can configure the switch to send a ping request to a specified IP address. You can use
this to check whether the switch can communicate with a particular IP station. When you click
the Apply button, the switch sends a specified number of ping requests and the results are
displayed.
If a reply to the ping is not received, the following message displays:
Tx = Count, Rx = 0 Min/Max/Avg RTT = 0/0/0 msec
If a reply to the ping is received, the following message displays:
Reply From a.b.c.d: icmp_seq = 0. time= xyz usec.
Reply From a.b.c.d: icmp_seq = 1. time= abc usec.
Reply From a.b.c.d: icmp_seq = 2. time= def usec.
Tx = count, Rx = count Min/Max/Avg RTT = xyz/abc/def msec
To send an IPv4 ping:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
Next-active The image to be used on the next restart of this switch.
Image1 Description The description associated with the image1 code file.
Image2 Description The description associated with the image2 code file.
Table 82. Dual Image Status information (continued)
Field Description

Perform Maintenance Tasks
355
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Troubleshooting > Ping IPv4.
The Ping Details page displays.
6. In the IP Address/Host Name field, enter the IP address or host name of the device that
must be pinged.
7. In the Count field, enter the number of echo requests that must be sent.
The default value is 3. The range is 1 to 15.
8. In the Interval field, enter the time between ping packets in seconds.
The default value is 3 seconds. The range is 1 to 60.
9. In the Size field, enter the size of the ping packet. The default value is 0 bytes. The range is
0 to 13000.
10. From the Source menu, select the IP address or interface that must be used to send echo
request packets:
•None. The source address of the ping packet is the address of the default egress
interface.
•IP Address. The source IP address that must be used when echo request packets
are sent. With this selection, the IP Address field displays and you must enter the IP
address that must be used as the source.
•Interface. The interface that must be used when echo request packets are sent. With
this selection, the Interface menu displays and you must select an interface as the
source.
11. Click the Apply button.
The specified address is pinged. The results are displayed below the configurable data in
the Results field.
Send an IPv6 Ping
This page is used to send a ping request to a specified host name or IPv6 address. You can
use this to check whether the switch can communicate with a particular IPv6 station. When
you click the Apply button, the switch sends a specified number of ping requests and the
results are displayed below the configurable data. The output displays the following:
Send count=n, Receive count=n from (IPv6 Address). Average round trip time = n ms.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
356
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To send an IPv6 ping:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Troubleshooting > Ping IPv6.
The Ping IPv6 page displays.
6. From the Ping menu, select the type of ping:
•Global. Pings a global IPv6 address.
•Link Local. Pings a link-local IPv6 address over a specified interface. With this
selection, the Interface menu displays, and you must select the interface.
7. In the IPv6 Address/Hostname field, enter the IPv6 address or host name of the station
that must be pinged.
The format is xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx. The maximum number of
characters is 255.
8. In the Count field, enter the number of echo requests that must be sent.
The range is 1 to 15. The default value is 3.
9. In the Interval field, enter the time in seconds between ping packets.
The range is 1 to 60. The default value is 3.
10. In the Datagram Size field, enter the datagram size.
The valid range is 0 to 13000. The default value is 0 bytes.
11. From the Source menu, select the IP address or interface that must be used to send echo
request packets:
•None. The source address of the ping packet is the address of the default egress
interface.
•IPv6 Address. The source IP address that must be used when echo request packets
are sent. With this selection, the IPv6 Address field displays and you must enter the
IPv6 address that must be used as the source.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
357
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Interface. The interface that must be used when echo request packets are sent. With
this selection, the Interface menu displays and you must select an interface as the
source.
12. Click the Apply button.
The specified address is pinged. The results are displayed below the configurable data in
the Results field.
Send an IPv4 Traceroute
You can configure the switch to send a traceroute request to a specified IP address or host
name. You can use this to discover the paths that packets take to a remote destination. Once
you click the Apply button, the switch sends a traceroute and the results are displayed below
the configurable data.
If a reply to the traceroute is received, the following message displays:
1 e.f.g.h 9869 usec 9775 usec 10584 usec
2 0.0.0.0 0 usec * 0 usec * 0 usec *
3 0.0.0.0 0 usec * 0 usec * 0 usec *
Hop Count = j Last TTL = k Test attempt = m Test Success = n.
To send an IPv4 traceroute:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Troubleshooting > Traceroute IPv4.
The Traceroute page displays.
6. In the IP Address/Hostname field, enter the IP address or host name of the device for
which the path must be discovered.
7. In the Probes Per Hop field, enter the number of probes per hop.
The default value is 3. The range is 1 to 10.
8. In the Max TTL field, enter the maximum time to live (TTL) for the destination.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
358
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default value is 30. The range is 1 to 255.
9. In the Init TTL field, enter the initial TTL to be used.
The default value is 1. The range is 1 to 255.
10. In the MaxFail field, enter the maximum number of failures allowed in the session.
The default value is 5. The range is 1 to 255.
11. In the Interval field, enter the time between probes in seconds.
The default value is 3. The range is 1 to 60.
12. In the Port field, enter the UDP destination port for the probe packets.
The default value is 33434. The range is 1–65535.
13. In the Size field, enter the size of the probe packets.
The default value is 0. The range is 0 to 39936.
14. From the Source menu, select the IP address or interface that must be used to send echo
request packets:
•None. The source address for the traceroute is the address of the default egress
interface.
•IP Address. The source IP address that must be used for the traceroute. With this
selection, the IP Address field displays and you must enter the IP address that must
be used as the source.
•Interface. The interface that must be used for the traceroute. With this selection, the
Interface menu displays and you must select an interface as the source.
15. Click the Apply button.
A traceroute request is sent to the specified IP address or host name. The results are
displayed below the configurable data in the Results field.
Send an IPv6 Traceroute
You can configure the switch to send a traceroute request to a specified IPv6 address or host
name. You can use this to discover the paths that packets take to a remote destination. Once
you click the Apply button, the switch sends a traceroute and the results are displayed below
the configurable data.
If a reply to the traceroute is received, the following message displays:
1 a:b:c:d:e:f:g 9869 usec 9775 usec 10584 usec
2 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 0 usec * 0 usec * 0 usec *
Hop Count = p Last TTL = q Test attempt = r Test Success = s.
To send an IPv6 traceroute:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
359
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Troubleshooting > Traceroute IPv6.
The Traceroute IPv6 page displays.
6. In the IPv6 Address/Host Name field, enter the IPv6 address or host name of the device for
which the path must be discovered.
7. In the Probes Per Hop field, enter the number of probes per hop.
The default value is 3. The range is 1 to 10.
8. In the Max TTL field, enter the maximum time to live (TTL) for the destination.
The default value is 30. The range is 1 to 255.
9. In the Init TTL field, enter the initial TTL to be used.
The default value is 1. The range is 1 to 255.
10. In the MaxFail field, enter the maximum number of failures allowed in the session.
The default value is 5. The range is 1 to 255.
11. In the Interval field, enter the time between probes in seconds.
The default value is 3. The range is 1 to 60.
12. In the Port field, enter the UDP destination port for the probe packets.
The default value is 33434. The range is 1–65535.
13. In the Size field, enter the size of the probe packets.
The default value is 0. The range is 0 to 39936.
14. From the Source menu, select the IP address or interface that must be used to send echo
request packets:
•None. The source address for the traceroute is the address of the default egress
interface.
•IP Address. The source IP address that must be used for the traceroute. With this
selection, the IPv6 Address field displays and you must enter the IPv6 address that
must be used as the source.
•Interface. The interface that must be used for the traceroute. With this selection, the
Interface menu displays and you must select an interface as the source.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
360
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
15. Click the Apply button.
A traceroute request is sent to the specified IP address or host name. The results are
displayed below the configurable data in the Results field.
Enable Remote Diagnostics
You can enable or disable the option to access the switch remotely. When remote access is
enabled, you can perform diagnostics services.
To enable remote diagnostics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Troubleshooting > Remote Diagnostics.
The Remote Diagnostics page displays.
6. Select the Enable radio button.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure Memory Dump Settings and Perform a Full Memory
Dump
You can perform a full memory dump to retrieve the core dump for the purpose of
troubleshooting.
To configure the memory dump settings, test a memory dump to a USB device, and
perform a full memory dump:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
361
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Maintenance > Troubleshooting > Full Memory Dump.
The Full Memory Dump Configuration page displays.
6. From the Protocol menu, select the protocol that must be used to save the core dump file:
•None. Disable the core dump. This is the default setting.
•USB. Sets the USB protocol.
7. In the File Path field, enter the path where the core dump file must be saved on the USB
device.
The form of the full file path is /mnt/usb-storage/<dir>. The file path must consist of
-, _, / and alphanumeric characters. Up to 64 characters can be used. The default is /.
8. In the File Name field, specify the core dump file name. Up to 15 characters can be used.
The file name must consists of -, _, and alphanumeric characters. The default is core. The
form of the file name is as follows:
<file-name-prefix>_<Host_Name>.bin (timestamp disabled) or
<file-name-prefix>_<MAC_Address>_<Time_Stamp>.bin (host name disabled)
9. To append a host name to the core dump file name, select the Hostname check box.
If you do not select the Hostname check box, the system MAC address is included in the
file name. By default, the check box is not enabled.
10. Select the Time-stamp check box to append a timestamp to the core dump file name.
This check box is selected by default.
11. To let the switch dump the switch chip register in the case of an exception, select the Switch
Register Dump check box.
When this option is enabled, all switch memories and switch registers are dumped to a
file with a prefix of reg. This option is disabled by default.
12. To test if a core dump can be written to the USB device (available only if you specified USB
as the protocol), do the following:
a. Select the Write Core Test check box.

Perform Maintenance Tasks
362
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
CAUTION:
Make sure that the Write Core check box is cleared when you click the
Apply button. Otherwise, the switch reboots.
b. Click the Apply button.
A pop-up window opens and displays the test results. You can verify if the configured
settings are correct and if the USB device is accessible. The core dump file name that
you entered in the File Name field is used as the destination.
13. To write a core dump to the USB device (available only if you specified USB as the protocol),
do the following:
a. Select the Write Core check box.
CAUTION:
The switch reboots after you click the Apply button.
b. Click the Apply button.
The core dump is written to the USB device and the switch reboots.
14. To save the configuration settings, select the Save Current Settings check box.
By default, this check box is selected. You can clear the check box only if you first select
the Write Core check box.
CAUTION:
Make sure that the Write Core check box is cleared when you click the
Apply button. Otherwise, the switch reboots.
15. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
363
8
8. Manage Power over Ethernet
This chapter covers the following topics:
•PoE Overview
•Device Class Power Requirements
•Power Allocation and Power Budget
•Configure the Global PoE Settings
•Manage and View the PoE+ Port Configuration
•Reset One or More PoE+ Ports
•Set Up PoE Timer Schedules
Note: This chapter applies to models GC728XP and GC752XP.
Models GC728X and GC752X do not support Power over Ethernet.

Manage Power over Ethernet
364
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
PoE Overview
Model GC728XP includes 24 PoE plus (PoE+) ports.
Model GC752XP includes 48 PoE+ ports
The following table shows the capacity for each model.
By default, supplied power is prioritized in ascending port order, up to the total power budget
of the device. If the power requirements for the attached devices exceed the total power
budget of the switch, the power to the device on the highest-numbered PoE+ port is disabled
to make sure that the devices connected to the higher-priority, lower-numbered PoE+ ports
are supported first. You can manually change the prioritization scheme by changing the port
priority (see Manage and View the PoE+ Port Configuration on page 368).
It is important to note that although a device is listed as an 802.3at (PoE+) powered or
802.3af (PoE) powered device, it might not require the maximum power limit that is specified.
Many devices require less power, allowing all PoE ports to be active simultaneously, when
the devices correctly report their PoE class to the switch.
Device Class Power Requirements
PoE and PoE+ use Ethernet cables to supply power to PoE-capable devices on the network,
such as WiFi access points, IP cameras, VoIP phones, and switches. The switch is compliant
with the IEEE 802.3at standard (PoE+) and backward compatible with the IEEE 802.3af
standard (PoE). The switch can pass power through to any powered device (PD) that
supports these standards. PoE and PoE+ let you power such devices without the need for a
separate power supply.
The switch supports a Plug-and-Play process by which it detects the type of device that is
connected to one of its PoE+ ports and whether that device needs power and how much so
that the switch can provide the correct power the device.
During the Plug-and-Play process, the connected device can provide its Class response to
the switch in many ways, depending on how the vendor programmed the device.
Table 83. PoE capacities for each model
Model Maximum PoE Power
Per Port Maximum Power Budget
Across All Active PoE Ports
GC728X PoE is not supported PoE is not supported
GC728XP 30W PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at) 390W
GC752X PoE is not supported PoE is not supported
GC752XP 30W PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at) 505W
Manage Power over Ethernet
365
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table shows the device classes for PoE+ devices adhering to the IEEE 802.3at
standard. The device classes for PoE devices adhering to the IEEE 802.3af standard are
identical with the exception that Device Class 4 is not supported.
Power Allocation and Power Budget
The switch is a smart switch in that it can allocate the required power to a connected device
by using a prioritization scheme: By default, power is supplied in ascending port order (that
is, lower port numbers are served first) until the power budget is consumed and insufficient
power remains to allocate to the next device. When less than 7W of PoE power is available
on a port, the port PoE LED lights yellow, and the attached device does not receive power
from the port. However, the switch continues to send data through the port connection.
You can manually change the prioritization scheme by changing the port priority (see Manage
and View the PoE+ Port Configuration on page 368).
The switch is also a smart switch in that it can override the IEEE power classification of a
powered device (PD): If the PD consumes less power than required by its power
classification, the switch provides only the power that the PD consumes instead of the power
that is required by the PD’s power classification.
If some PoE+ ports are in use and deliver power, you can calculate the available power
budget for the other PoE+ ports by subtracting the consumed (that is, delivered power) from
the total available power budget. (For information about the total available power budget, see
PoE Overview on page 364.)
An example:
Port 1 delivers 4.4W to a PD. The available power budget is 385.6W (390W–4.4W).
Another example:
A Class 4 PD is attached to Port 1, a Class 2 PD to Port 2, and another Class 4 PD to Port 3.
However, the PDs consume less power than defined by their classes: The PD attached to
Port 1 consumes 7.3W, the PD attached to Port 2 consumes 4.7W, and the PD attached to
Port 3 consumes 8.9W. So even though the switch provides power to two Class 4 devices
and one Class 3 device, the available power budget is 369.1W (390W–7.3–4.7–8.9W).
Table 84. PoE and PoE+ device class power allocation
Device
Class Standard Range of Power
Delivered to the
Powered Device
Minimum Output at
PoE Switch Port
(Minimum Allocated)
Maximum Output at
PoE Switch Port
(Maximum Allocated)
0 PoE and PoE+ 0.44W–12.95W 15.4W 16.2W
1 PoE and PoE+ 0.44W–3.84W 4.0W 4.2W
2 PoE and PoE+ 3.84W–6.49W 7.0W 7.4W
3 PoE and PoE+ 6.49W–12.95W 15.4W 16.2W
4 PoE+ only 12.95W–25.5W 30.0W 31.6W
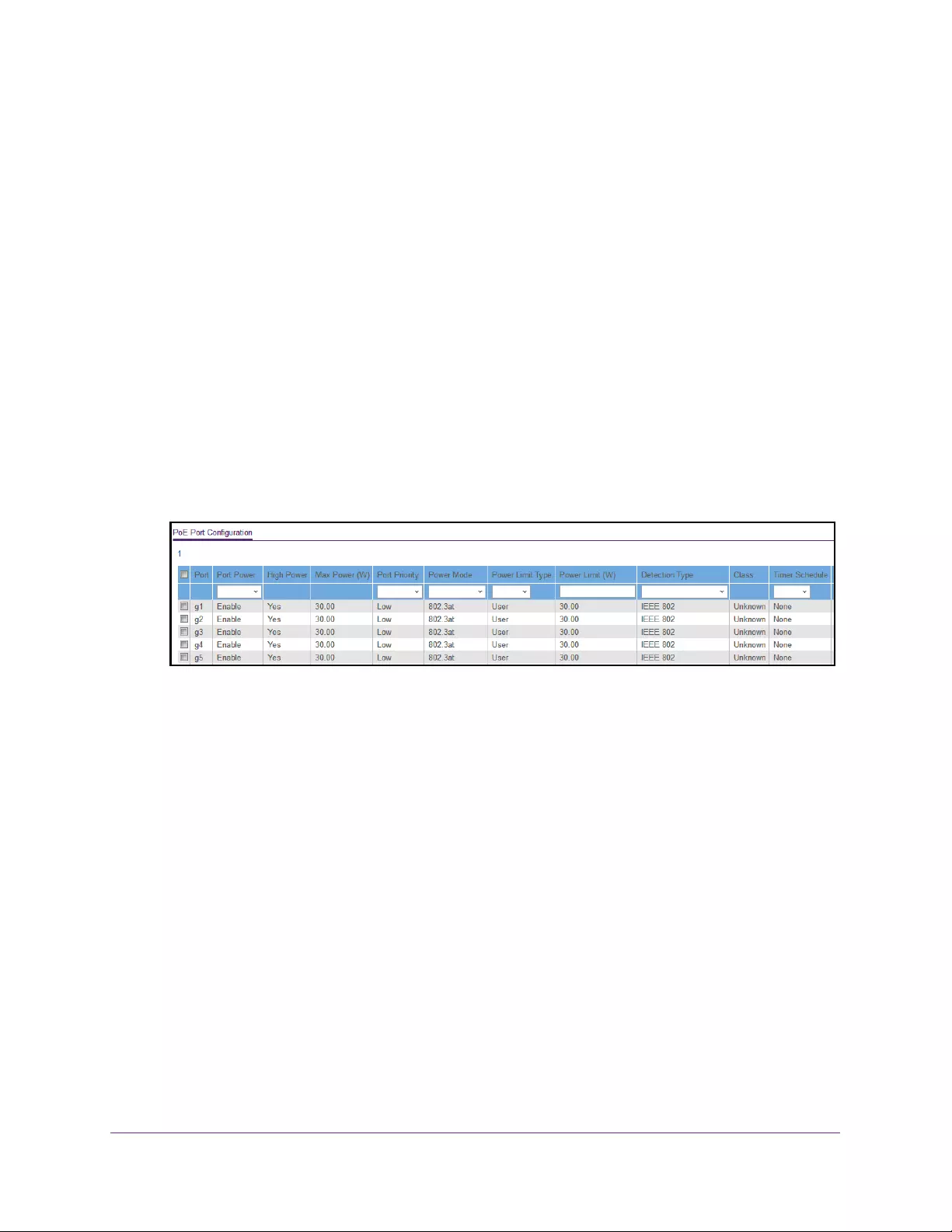
Manage Power over Ethernet
366
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
To determine the delivered power by PoE+ ports:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > PoE > Advanced > PoE Port Configuration.
The previous figure does not show all columns on the page.
The delivered power is stated in the Output Power (mW) column (which is not shown in
the previous figure).
Configure the Global PoE Settings
To configure the global PoE settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
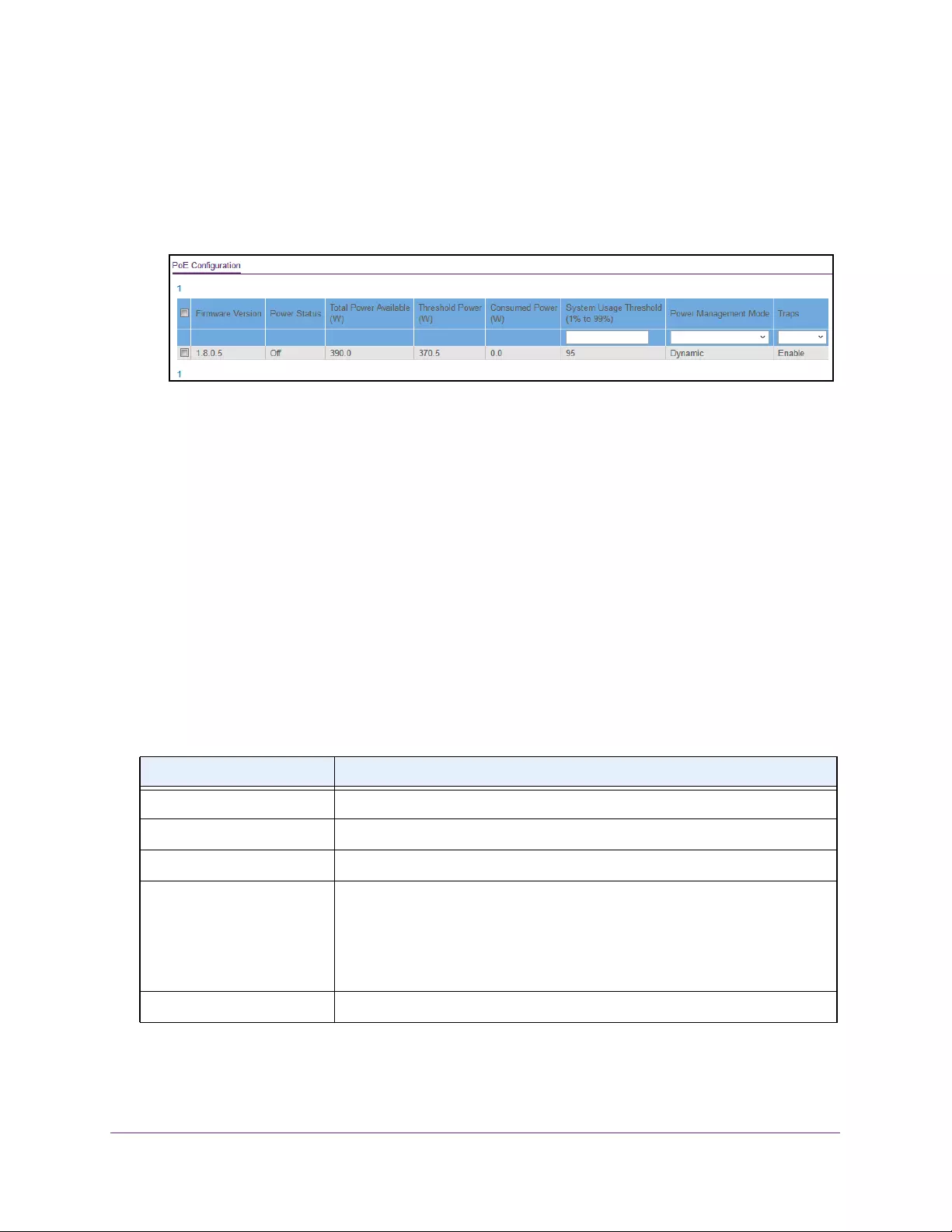
Manage Power over Ethernet
367
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > PoE > Basic > PoE Configuration.
6. In the System Usage Threshold field, enter a number from 1 to 99 to set the threshold
level at which a trap is sent if the consumed power exceeds the threshold power.
7. From the Power Management mode menu, select the power management algorithm that
the switch uses to deliver power to the requesting powered devices (PDs):
•Static. Specifies that the power allocated for each port depends on the type of power
threshold configured on the port.
•Dynamic. Specifies that the power consumption on each port is measured and
calculated in real time.
8. To active the PoE traps, from the Traps menu, select Enable.
Selecting Disable deactivates the PoE traps. The default setting is Enabled.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your setting are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields on the page.
Table 85. PoE Configuration fields
Field Description
Firmware Version The firmware version of the PoE firmware component.
Power Status The power status.
Total Power Available (W) The maximum amount of power in watts that the switch can deliver to all ports.
Threshold Power (W) If the consumed power is below the threshold power, the switch can power up
another port. The consumed power can be between the nominal and threshold
power. The threshold power is displayed in watts.
Note: The threshold power value is determined by the value that you enter in the
System Usage Threshold field.
Consumed Power (W) The total amount of power in watts that is being delivered to all ports.

Manage Power over Ethernet
368
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Manage and View the PoE+ Port Configuration
Depending on the model, the switch includes 24 or 48 PoE+ ports.
To manage and view the PoE+ port settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > PoE > Advanced > PoE Port Configuration.
The previous figure does not show all columns on the page.
6. Select the check boxes for the PoE+ ports that you want to configure or select the check box
in the heading to configure all PoE+ ports.
7. Configure the settings as described in the following table.
Manage Power over Ethernet
369
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The settings that you configure apply to all selected PoE+ ports.
Menu Item Description
Port Power Select the administrative mode of the port:
• Enable. The port’s capacity to deliver power is enabled. This is the default
setting.
• Disable. The port’s capacity to deliver power is disabled.
Port Priority The port priority determines which ports can still deliver power after the total
power delivered by the switch exceeds the total power budget of 390W. (In such a
situation, the switch might not be able to deliver power to all connected devices.)
If the same priority applies to two ports, the lower-numbered port receives higher
priority.
Select one of the following priorities:
• Low. Low priority. This is the default setting.
• Medium. Medium priority.
• High. High priority.
• Critical. Critical priority.
Power Mode Select the one of the following power modes:
• 802.3af. The port is powered in and limited to the IEEE 802.3af mode. A PD
that requires IEEE 802.3at does not receive power if the port functions in
IEEE 802.3af mode.
• Legacy. The port is powered using high-inrush current, which is used by
legacy PDs that require more than 15W to power up.
• Pre-802.3at. The port is initially powered in the IEEE 802.3af mode and,
before 75 msec pass, is switched to the high-power IEEE 802.3at mode.
Select this mode if the PD does not perform Layer 2 classification or if switch
performs 2-event Layer 1 classification.
• 802.3at. The port is powered in the IEEE 802.3at mode. This is the default
mode. In this mode, if the switch detects that the attached PD is not a Class
4 device, the PD does not receive power from the switch.
Power Limit Type The power limit type controls the maximum power that a port can deliver. Select
one of the following types:
• None. The port draws up to Class 0 maximum power in low power mode and
up to Class 4 maximum power in high power mode.
• Class. The port power limit is equal to the class of the attached PD.
• User. The port power limit is equal to the value that is specified in the
Power Limit (W) field. This is the default setting.
Note: If a PD does not report its class correctly, use of these options can preserve
additional PoE power by preventing the switch from delivering more power than the
PD requires. However, depending on which option you select, a PD that does not
report its class correctly might not power up at all.
Power Limit (W) Enter the maximum power (in watts) that the port can deliver.
The range is 3.0–30.0W, with 0.1W steps. The default is 30W.
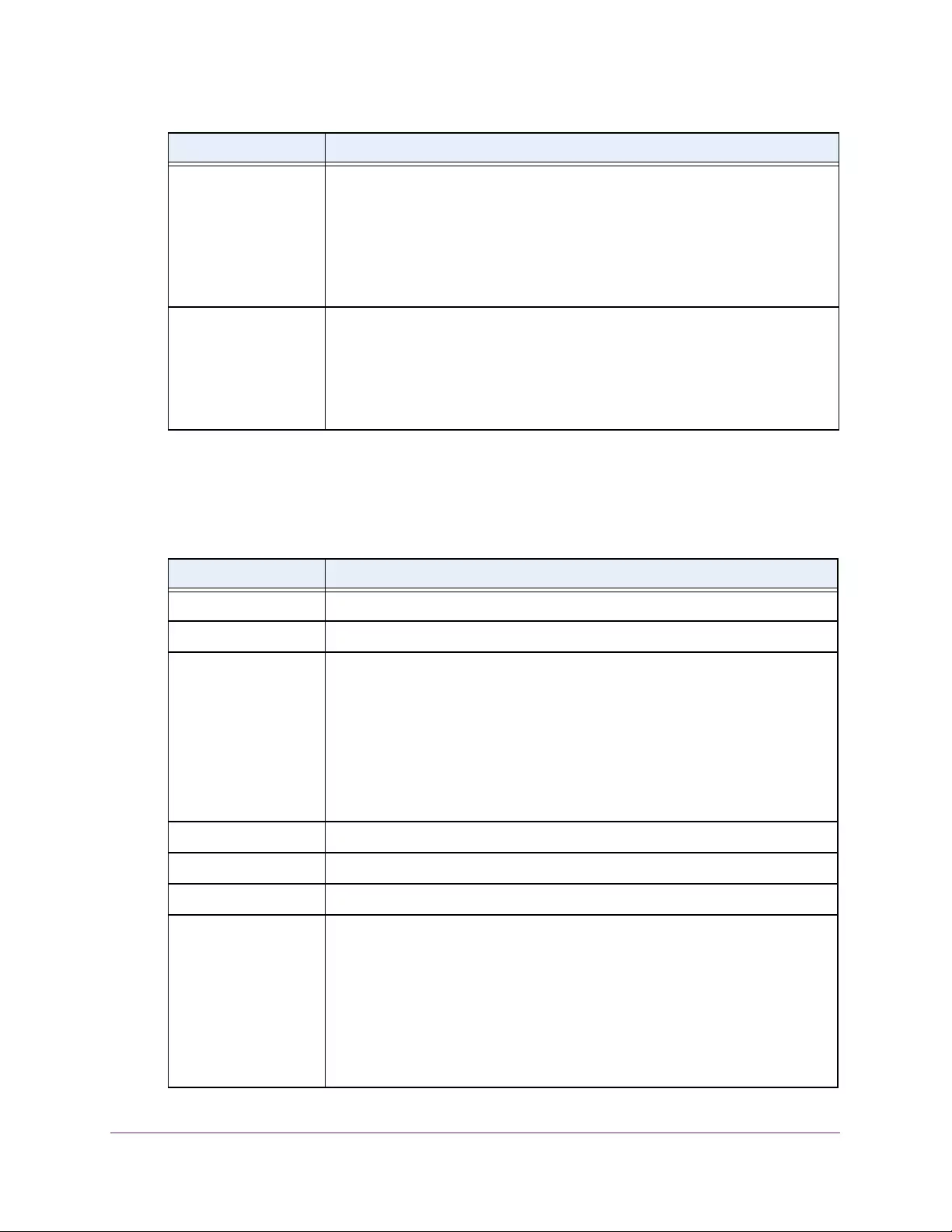
Manage Power over Ethernet
370
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable fields on the PoE Port Configuration
page.
Detection Type The detection type specifies how the port detects the attached PD. Select one of
the following types:
• IEEE 802. The port performs a 4-point resistive detection. This is the default
setting.
• 4pt 802.3af + Legacy. The port performs a 4-point resistive detection, and if
required, continues with legacy detection.
• Legacy. The port performs legacy detection.
Timer Schedule If you set up a PoE timer schedule, you can assign it to the port by selecting the
schedule from the Timer Schedule menu.
For information about PoE timer schedules, see Set Up PoE Timer Schedules on
page 372. By default, the selection from the menu is None.
If you want to remove a previously assigned timer schedule, select None from the
Timer Schedule menu.
Field Description
High Power If a port supports High Power mode, the field displays Yes.
Max Power (W) The maximum power in watts that the port can provide.
Class The class defines the range of power a powered device (PD) is drawing from the
switch. The class definitions are as follows:
• 0: 0.44–16.2W
• 1: 0.44–4.2W
• 2: 0.44–7.4W
• 3: 0.44–16.2W
• 4: 0.44–31.6W
• Unknown. The class cannot be detected, or no PD is attached to the port.
Output Voltage (Volts) The voltage that is delivered to the PD in volts.
Output Current (mA) The current that is delivered to the PD in mA.
Output Power (W) The power that is delivered to the PD in watts.
Status The operational status of the port. The possible values are as follows:
• Disabled. No power is delivered.
• Delivering Power. Power is being drawn by the PD.
• Requesting Power. The port is requesting power.
• Fault. A problem occurred with the power.
• Test. The port is in test mode.
• Other Fault. The port is idle because of an error condition.
• Searching. The port is not in one of the other states in this list.
Menu Item Description

Manage Power over Ethernet
371
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Reset One or More PoE+ Ports
You can forcibly reset one or more PoE+ ports on the switch. I f a PoE device is attached to the
port, the device restarts. Resetting a PoE+ port does not affect its data link, so if a non-PoE
device is attached to the port, the device is not affected and does not restart.
To reset one or more PoE+ ports:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > PoE > Advanced > PoE Port Configuration.
The PoE Port Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check boxes for the PoE+ ports that you want to reset or select the check box in
the heading to reset all PoE+ ports.
7. Click the Power Cycle Port(s) button.
The ports are reset.
Fault Status The error description when the PoE port is in a fault state. The possible values are
as follows:
• No Error. The port is not in any error state and can provide power.
• MPS Absent. The port detected the absence of the main power supply,
preventing the port from providing power.
• Short. The port detected a short circuit condition, preventing the port from
providing power.
• Overload. The PD that is connected to the port attempts to draw more power
than allowed by the port’s settings, preventing the port from providing power
at all.
• Power Denied. The port was denied power because of a shortage of power
or because of an administrative condition. In this condition, the port cannot
provide power.
Field Description

Manage Power over Ethernet
372
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Set Up PoE Timer Schedules
The switch lets you define multiple timer schedules that you can use for PoE power delivery
to attached PDs.
After you create a timer schedule, you can associate it with one or more PoE+ ports (see
Manage and View the PoE+ Port Configuration on page 368). You can use a separate timer
schedule for each PoE+ port.
After you associate a timer schedule with a PoE+ port, the start date and time force the PoE+
port to stop delivering power and the stop date and time enable the PoE+ port to start
delivering power.
You can create absolute schedules, which apply to specific dates and times, and you can
create recurring schedules.
Create a PoE Timer Schedule
The maximum number of timer schedules that you can add is 100.
To create a PoE timer schedule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Timer Schedule > Basic > Global Configuration.
The Timer Schedule Name page displays.
6. In the Timer Schedule Name field, specify the name for a timer schedule.
7. Click the Add button.
The timer schedule is added to the table on the Timer Schedule Name page and is
assigned an ID.

Manage Power over Ethernet
373
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Specify the Settings for an Absolute PoE Timer Schedule
An absolute timer schedule applies to specific dates and times. The schedule is executed
once only.
To specify the settings for a PoE timer schedule that uses specific dates and times:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Timer Schedule > Advanced > Timer Schedule Configuration.
The Timer Schedule Configuration page displays.
6. In the Timer Schedule Selection section, make your selections from the following menus:
a. Timer Schedule Name. Select the name of the timer schedule that you want to
configure.
You can select only names of schedules that you created (see Create a PoE Timer
Schedule on page 372).
b. Timer Schedule Type. Select Absolute.
The fields in the Timer Schedule Configuration section might adjust to let you configure
a timer schedule for specific dates and times.
c. Timer Schedule Entry. To add a new entry, select new.
Selecting an existing entry lets you make changes to that entry.
7. In the Timer Schedule Configuration section, specify the times and dates:
a. In the Time Start field, enter the time of day in the HH:MM format to specify when the
timer schedule must start.
b. In the Time End field, enter the time of day in the HH:MM format to specify when the
timer schedule must stop.
c. Next to the Date Start field, click the calendar icon and use the menus in the pop-up
window to enter the date in the DD-Mon-YYYY format to specify when the timer
schedule must start.

Manage Power over Ethernet
374
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
d. Next to the Date End field, click the calendar icon and use the menus in the pop-up
window to enter the date in the DD-Mon-YYYY format to specify when the timer
schedule must stop.
8. Click the Add button.
The entry for the timer schedule is added.
Specify the Settings for a Recurring PoE Timer Schedule
A recurring schedule allows you to set up a single schedule that starts at a particular date and
that recurs either with a specific end date or indefinitely.
For a single recurring PoE timer schedule, you can add a daily, weekly , and monthly schedule
configuration. That is, these schedule configurations are not mutually exclusive but
complement each other.
To specify the settings for a PoE timer schedule that uses a recurring pattern:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System> Timer Schedule > Advanced > Timer Schedule Configuration.
The Timer Schedule Configuration page displays.
6. In the Timer Schedule Selection section, make your selections from the following menus:
a. Timer Schedule Name. Select the name of the timer schedule that you want to
configure.
You can select only names of schedules that you created (see Create a PoE Timer
Schedule on page 372).
b. Timer Schedule Type. Select Periodic.
The fields in the Timer Schedule Configuration section might adjust to let you configure
a timer schedule with a recurrence pattern.
c. Timer Schedule Entry. To add a new entry, select new.

Manage Power over Ethernet
375
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Selecting an existing entry lets you make changes to that entry.
7. In the Timer Schedule Configuration section, specify the recurrence pattern:
a. In the Time Start field, enter the time of day in the HH:MM format to specify when the
timer schedule must start.
b. In the Time End field, enter the time of day in the HH:MM format to specify when the
timer schedule must stop.
c. Next to the Date Start field, click the calendar icon and use the menus in the pop-up
window to enter the date in the DD-Mon-YYYY format to specify when the timer
schedule must start.
d. Either select the No End Date radio button or select the End Date radio button, and
next to the End Date field, click the calendar icon and use the menus in the pop-up
window to enter the date in the DD-Mon-YYYY format to specify when the timer
schedule must stop.
e. From the Recurrence Pattern menu, select the pattern:
•Daily. The timer schedule works with daily recurrence. The fields adjust.
Either select the Every Weekday radio button to let the schedule operate from
Monday through Friday or select the Every Day(s) radio button and enter a
number from 1 to 255 in the field.
In the latter case, the schedule is triggered every specified number of days.
•Weekly. The timer schedule works with weekly recurrence. The fields adjust.
In the Every Week(s) field, enter a number from 1 to 255 to specify that the
schedule must be triggered every specified number of weeks.
Select a single Week Day check box, multiple check boxes, or all check boxes to
specify the day or days of the week that the schedule must operate.
•Monthly. The timer schedule works with monthly recurrence. The fields adjust.
In the Day field, enter a number from 1 to 31 to specify the day of the month when
the schedule must be triggered.
In the Every Month(s) field, enter a number from 1 to 255 to specify that the
schedule must be triggered every specified number of months.
8. Click the Add button.
The entry for the timer schedule is added.
Change the Settings for a Recurring PoE Timer Schedule Entry
You can change the settings for an existing recurring PoE timer schedule entry. (You cannot
do this for an existing absolute PoE timer schedule.)
To change the settings for an existing recurring PoE timer schedule entry:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.

Manage Power over Ethernet
376
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Timer Schedule > Advanced > Timer Schedule Configuration.
The Timer Schedule Configuration page displays.
6. From the Timer Schedule Name menu, select the schedule name.
7. From the Timer Schedule Type menu, select the schedule type.
8. From the Timer Schedule Entry menu, select the schedule entry.
9. Make the changes to the schedule entry.
For more information, see Specify the Settings for a Recurring PoE Timer Schedule on
page 374.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete a PoE Timer Schedule Entry
You can delete a PoE timer schedule entry that you no longer need.
To delete a PoE timer schedule entry:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.

Manage Power over Ethernet
377
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Timer Schedule > Advanced > Timer Schedule Configuration.
The Timer Schedule Configuration page displays.
6. From the Timer Schedule Name menu, select the schedule name.
7. From the Timer Schedule Type menu, select the schedule type.
8. From the Timer Schedule Entry menu, select the schedule entry.
9. Click the Delete button.
The entry is deleted.
Delete a PoE Timer Schedule
You can delete a PoE timer schedule that you no longer need. All entries that are part of the
PoE timer schedule are also deleted.
To delete a PoE timer schedule:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired connection to connect your computer to the network, or
connect directly to a switch that is off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select System > Timer Schedule > Basic > Global Configuration.
The Timer Schedule Name page displays.
6. Select the check box for the schedule that you want to delete.
7. Click the Delete button.
The schedule is deleted.

Monitor the System
379
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Monitor the Switch and the Ports
The following sections describe how you can view a variety of information about the amount
and type of traffic that is transmitted from and received on the switch:
•View or Clear the Switch Statistics on page 379
•View or Clear Port Statistics on page 381
•View or Clear Detailed Port Statistics on page 383
•View or Clear EAP Statistics on page 389
•Perform a Cable Test on page 391
View or Clear the Switch Statistics
You can view or clear detailed statistical information about the traffic that the switch handles.
To view or clear the switch statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Ports > Switch Statistics.
The Switch Statistics page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
7. To clear all the statistics counters, click the Clear button.
All switch summary and detailed statistics are reset to default values. However, the
discarded packets counters cannot be cleared.
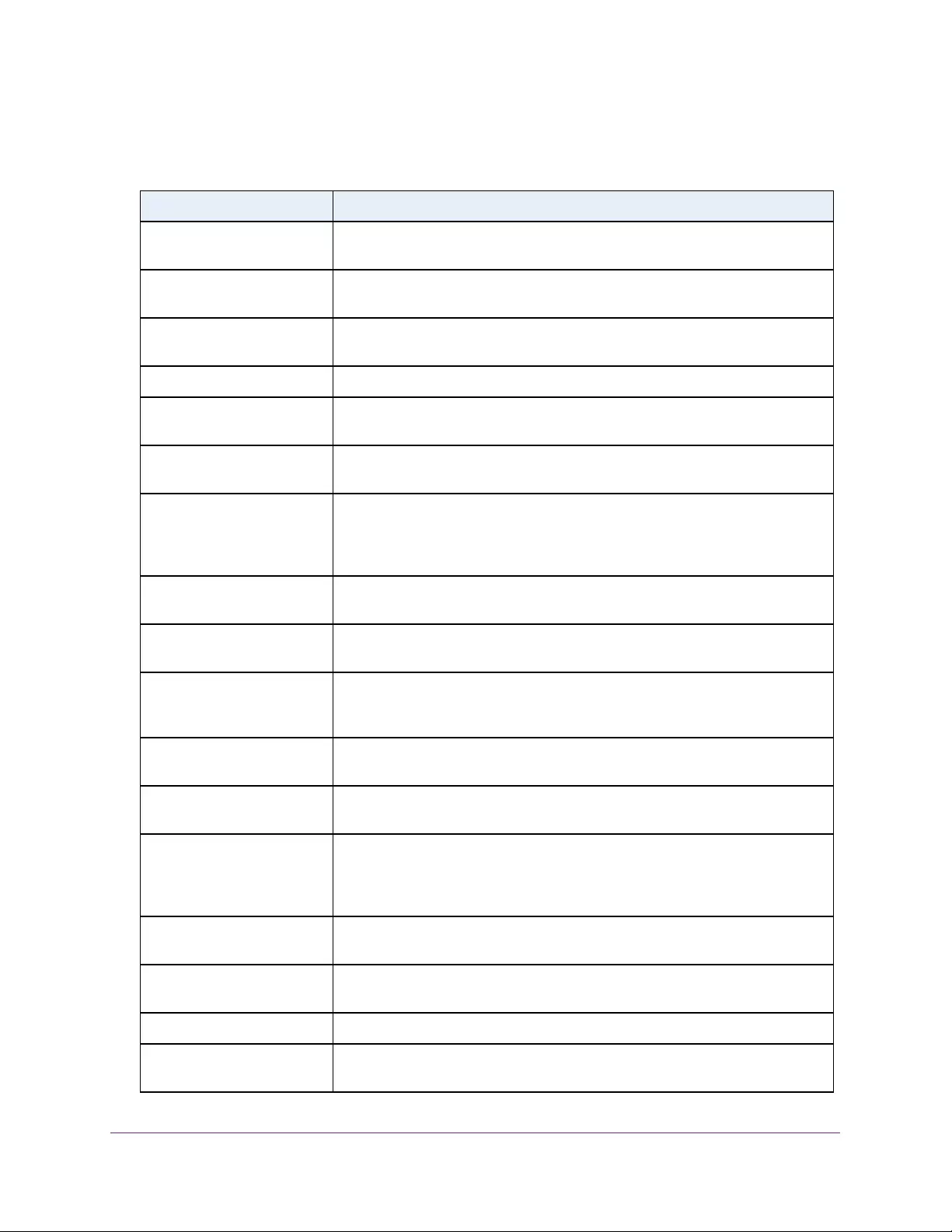
Monitor the System
380
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the switch statistics displayed on the page.
Table 86. Switch statistics
Field Description
ifIndex The interface index of the interface table entry associated with the processor of
this switch.
Octets Received The total number of octets of data received by the processor (excluding framing
bits, but including FCS octets).
Packets Received Without
Errors The total number of packets (including broadcast packets and multicast
packets) received by the processor.
Unicast Packets Received The number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
Multicast Packets Received The total number of packets received that were directed to a multicast address.
This number does not include packets directed to the broadcast address.
Broadcast Packets Received The total number of packets received that were directed to the broadcast
address. This does not include multicast packets.
Receive Packets Discarded The number of inbound packets that were discarded, even though no errors
were detected, to prevent the packets from being delivered to a higher-layer
protocol. A possible reason for discarding a packet could be to free buffer
space.
Octets Transmitted The total number of octets transmitted from the interface, including framing
characters.
Packets T ransmitted Without
Errors The total number of packets transmitted from the interface.
Unicast Packets Transmitted The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested to be
transmitted to a subnetwork-unicast address, including the packets that were
discarded or not sent.
Multicast Packets
Transmitted The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted
to a multicast address, including the packets that were discarded or not sent.
Broadcast Packets
Transmitted The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted
to the broadcast address, including the packets that were discarded or not sent.
Transmit Packets Discarded The number of outbound packets that were discarded, even though no errors
were detected, to prevent the packets from being delivered to a higher-layer
protocol. A possible reason for discarding a packet could be to free buffer
space.
Most Address Entries Ever
Used The highest number of Forwarding Database Address Table entries that were
learned by the switch since the most recent reboot.
Address Entries in Use The number of learned and static entries in the Forwarding Database Address
Table for the switch.
Maximum VLAN Entries The maximum number of VLANs allowed on the switch.
Most VLAN Entries Ever
Used The largest number of VLANs that were active on the switch since the last
reboot.
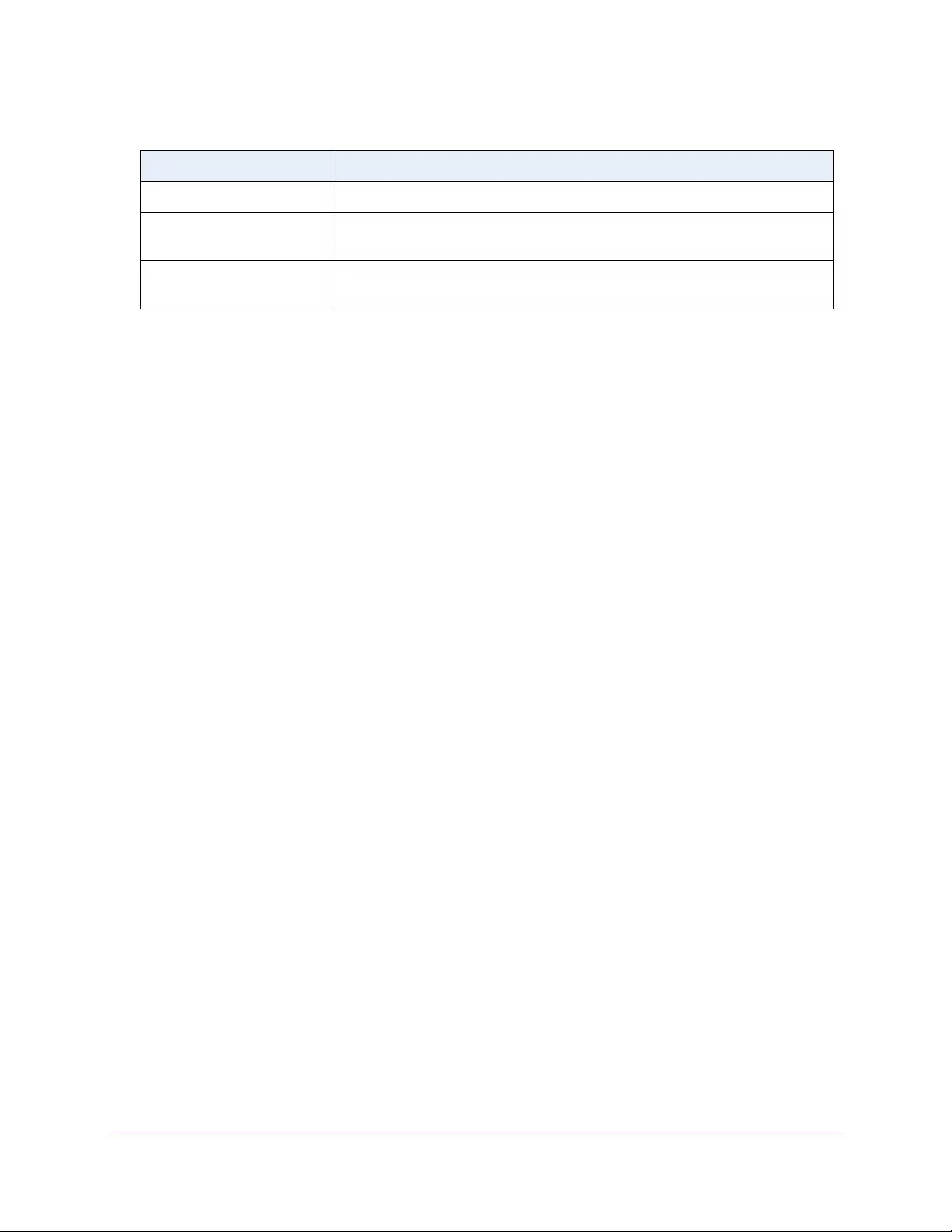
Monitor the System
381
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View or Clear Port Statistics
You can view a summary of per-port traffic statistics on the switch.
To view port statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Ports > Port Statistics.
The Status page displays.
6. Select whether to display physical interfaces, link aggregation groups (LAGs), or both by
clicking one of the following links above the table heading:
•1 (or the unit ID of the switch). Only physical interfaces are displayed. This is the
default setting.
•LAGS. Only link aggregation groups are displayed.
•All. Both physical interfaces and link aggregation groups are displayed.
To locate an interface quickly, type the interface number using the respective naming
convention (for example, g1 or l1) in the Go To Interface field above or below the table and
click the Go button. See Interface Naming Conventions on page 12 for more information.
The entry corresponding to the specified interface is selected.
Static VLAN Entries The number of active VLAN entries that were created statically on the switch.
VLAN Deletes The number of VLANs that were created and then deleted on the switch since
the last reboot.
Time Since Counters Last
Cleared The elapsed time, in days, hours, minutes, and seconds, since the statistics for
the switch were last cleared.
Table 86. Switch statistics (continued)
Field Description
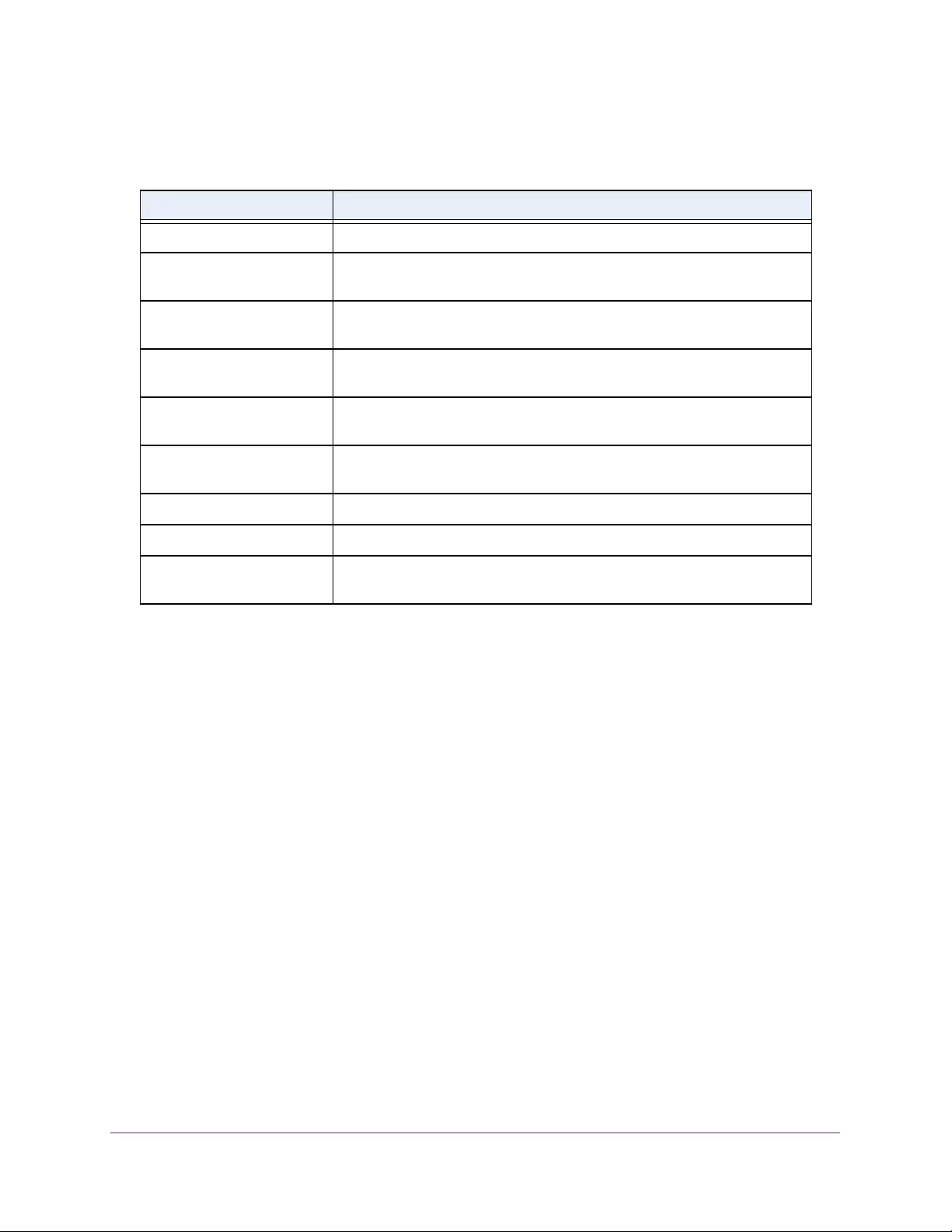
Monitor the System
382
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the per-port statistics displayed on the page.
Reset Counters for All Interfaces on the Switch
To reset the counters for all interfaces on the switch:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Ports > Port Statistics.
The Status page displays.
Table 87. Port statistics
Field Description
Interface The interface for which the statistics are displayed.
Total Packets Received
Without Errors The total number of packets received that were without errors.
Packets Received With Error The number of inbound packets that contained errors, preventing them from
being delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
Broadcast Packets Received The total number of well-formed packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. This number does not include multicast packets.
Packets T ransmitted Without
Errors The number of frames that were transmitted without errors.
Transmit Packet Errors The number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of
errors.
Collision Frames The best estimate of the total number of collisions.
Link Down Events The total number of link-down events.
Time Since Counters Last
Cleared The elapsed time in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since the statistics
were cleared.

Monitor the System
383
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Select the check box in the heading of the table.
7. Click the Clear button.
All counters are reset to 0.
Reset Counters for a Specific Interface
To reset the counters for a specific interface:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Ports > Port Statistics.
The Status page displays.
6. Select the check box next to the interface for which you want to clear the counters.
You can also type the interface number using the respective naming convention (for
example, g1 or l1) in the Go To Interface field above or below the table and click the Go
button. See Interface Naming Conventions on page 12 for more information. The entry
corresponding to the specified interface is selected.
7. Click the Clear button.
The counters for the interface are reset to 0.
View or Clear Detailed Port Statistics
You can view a variety of per-port traffic statistics.
To view detailed port statistics or clear the statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
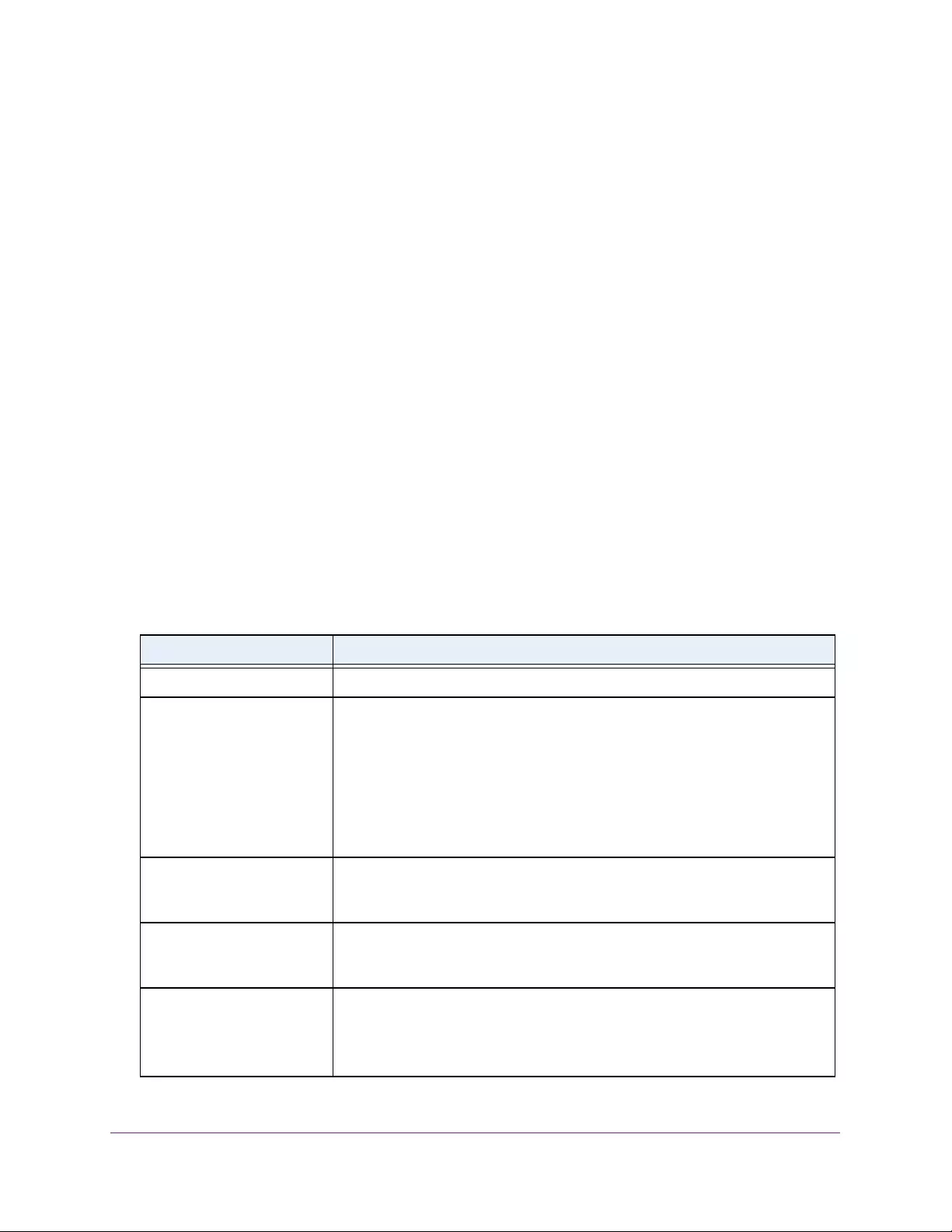
Monitor the System
384
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Ports > Port Detailed Statistics.
The Port Detailed Statistics page displays.
6. From the Interface menu, select the interface for which you want to view the statistics.
7. From the MST ID menu, select the MST ID associated with the interface (if available).
8. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
9. To clear all the counters, click the Clear button.
This resets all statistics for this port to the default values.
The following table describes the detailed port information displayed on the page. To view
information about a different port, select the port number from the Interface menu.
Table 88. Detailed port statistics
Field Description
ifIndex The interface index (ifIndex) for which the statistics are displayed.
Port Type For normal ports this field displays Normal. Otherwise, the possible values are
as follows:
• Mirrored. This port is a participating in port mirroring as a mirrored port. For
more information, see Configure Port Mirroring on page 402.
• Probe. This port is a participating in port mirroring as the probe port. For
more information, see Configure Port Mirroring on page 402.
• Trunk Member. The port is a member of a link aggregation trunk, which is
also referred to as a Link Aggregation Group (LAG).
Port Channel ID If the port is a member of a port channel, which is also referred to as a Link
Aggregation Group (LAG), the port channel’s interface ID and name are shown.
Otherwise, Disable is shown.
Port Role Each MST bridge port that is enabled is assigned a port role for each spanning
tree. The port role is one of the following values: Root, Designated, Alternate,
Backup, Master, or Disabled.
STP Mode The Spanning T ree Protocol administrative mode that is associated with the port
or port channel. The possible values are as follows:
• Enable. Spanning tree is enabled for this port.
• Disable. Spanning tree is disabled for this port.
Monitor the System
385
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
STP State The port's current Spanning Tree state. This state controls what action a port
takes on receipt of a frame. If the bridge detects a malfunctioning port, it places
that port into the broken state. The states are defined in IEEE 802.1D:
• Disabled
• Blocking
• Listening
• Learning
• Forwarding
• Broken
Admin Mode The port control administration state:
• Enable. The port can participate in the network (default).
• Disable. The port is administratively down and does not participate in the
network.
Flow Control Mode Indicates whether flow control is enabled or disabled for the port. This field is not
valid for LAG interfaces.
LACP Mode The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) administration state, which is one
of the following:
• Enable. The port is allowed to participate in a LAG, which is the default
mode.
• Disable. The port cannot participate in a LAG.
Physical Mode The port speed and duplex mode. In autonegotiation mode, the duplex mode
and speed are set by the autonegotiation process.
Physical Status The port speed and duplex mode.
Link Status Indicates whether the link is up or down.
Link Trap Indicates whether or not the port sends a trap when link status changes:
• Enable. The switch sends a trap when the link status changes.
• Disable. The switch does not send a trap when the link status changes.
Packets RX and TX 64 Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 65-127
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were between 65 and 127 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 128-255
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were between 128 and 255 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 256-511
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were between 256 and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits
but including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX 512-1023
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were between 512 and 1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing
bits but including FCS octets).
Table 88. Detailed port statistics (continued)
Field Description
Monitor the System
386
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Packets RX and TX
1024-1518 Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were between 1024 and 1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing
bits but including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX
1519-2047 Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were between 1519 and 2047 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing
bits but including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX
2048-4095 Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were between 2048 and 4095 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing
bits but including FCS octets).
Packets RX and TX
4096-9216 Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted
that were between 4096 and 9216 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing
bits but including FCS octets).
Octets Received The total number of octets of data (including those in bad packets) received on
the network (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets). This number can
be used as a reasonable estimate of Ethernet utilization. If greater precision is
required, sample the etherStatsPkts and etherStatsOctets objects before and
after a common interval.
Packets Received 64 Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
64 octets in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets Received 65-127
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
65 and 127 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets Received 128-255
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
128 and 255 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets Received 256-511
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
256 and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets Received 512-1023
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
512 and 1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS octets).
Packets Received 1024-1518
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
1024 and 1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS octets).
Packets Received > 1518
Octets The total number of packets received that were longer than 1518 octets
(excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were otherwise well
formed.
Total Packets Received
Without Errors The total number of packets received that were without errors.
Unicast Packets Received The number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
Table 88. Detailed port statistics (continued)
Field Description
Monitor the System
387
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Multicast Packets Received The total number of well-formed packets received that were directed to a
multicast address. This number does not include packets directed to the
broadcast address.
Broadcast Packets Received The total number of well-formed packets received that were directed to the
broadcast address. This does not include multicast packets.
Receive Packets Discarded The number of inbound packets that were discarded, even though no errors
were detected, to prevent the packets from being delivered to a higher-layer
protocol. A possible reason for discarding a packet could be to free buffer space.
Total Packets Received with
MAC Errors The total number of inbound packets that contained errors, preventing them
from being delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
Jabbers Received The total number of packets received that were longer than 1518 octets
(excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets), and included either a bad
frame check sequence (FCS) with an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a
bad FCS with a nonintegral number of octets (alignment error).
This definition of a jabber is different from the definition in IEEE-802.3 section
8.2.1.5 (10BASE5) and section 10.3.1.4 (10BASE2). These documents define
jabber as the condition in which any packet exceeds 20 ms. The allowed range
to detect jabbers is between 20 ms and 150 ms.
Fragments Received The total number of packets received that were less than 64 octets in length with
ERROR CRC (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Undersize Received The total number of packets received that were less than 64 octets in length with
GOOD CRC (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Alignment Errors The total number of packets received with a length (excluding framing bits, but
including FCS octets) of between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but included a
bad frame check sequence (FCS) with a nonintegral number of octets.
Rx FCS Errors The total number of packets received with a length (excluding framing bits, but
including FCS octets) of between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but included a
bad frame check sequence (FCS) with an integral number of octets.
Overruns The total number of frames discarded because the port was overloaded with
incoming packets, and could not keep up with the inflow.
Total Received Packets Not
Forwarded The number of valid frames received that were discarded (that is, filtered) by the
forwarding process.
802.3x Pause Frames
Received The number of MAC control frames received with an opcode indicating the
PAUSE operation. This counter does not increment when the interface is
operating in half-duplex mode.
Unacceptable Frame Type The number of frames discarded from this port due to being an unacceptable
frame type.
Total Packets Transmitted
(Octets) The total number of octets of data (including those in bad packets) transmitted
on the network (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets). This object can
be used as a reasonable estimate of Ethernet utilization. If greater precision is
required, sample the etherStatsPkts and etherStatsOctets objects after a
common interval.
Table 88. Detailed port statistics (continued)
Field Description
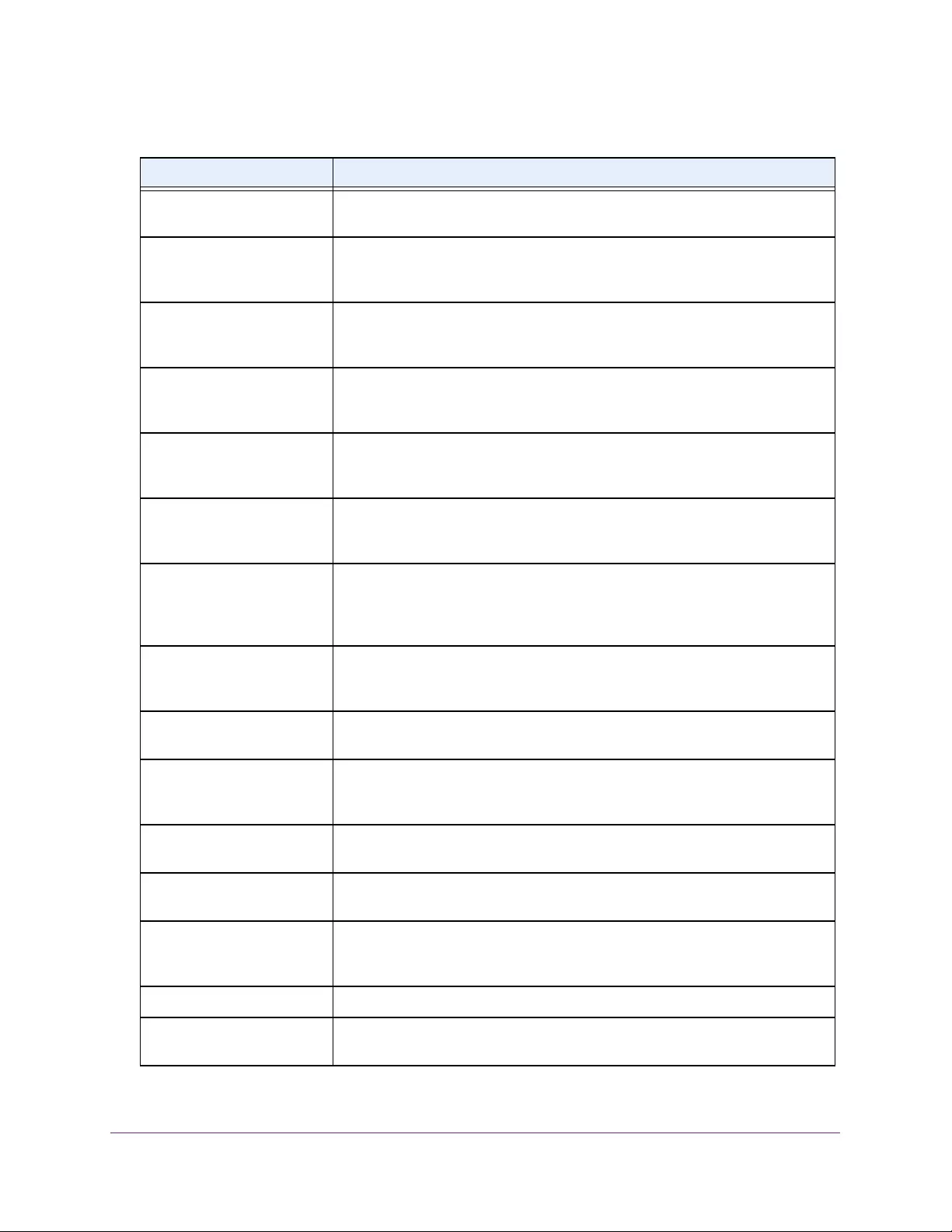
Monitor the System
388
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Packets T ransmitted 64
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
64 octets in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Packets T ransmitted 65-127
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
65 and 127 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets Transmitted 128-255
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
128 and 255 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets T ransmitted 256-51 1
Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
256 and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS
octets).
Packets T ransmitted
512-1023 Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
512 and 1023 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS octets).
Packets T ransmitted
1024-1518 Octets The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between
1024 and 1518 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS octets).
Packets Transmitted > 1518
Octets The total number of packets transmitted that were longer than 1518 octets
(excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were otherwise well
formed. This counter supports a maximum increment rate of 815 counts per sec
at 10 Mb/s.
Maximum Frame Size The maximum Ethernet frame size the interface supports or is configured to use,
including Ethernet header, CRC, and payload. The possible range is 1518 to
9216. The default maximum frame size is 1518.
Total Packets Transmitted
Successfully The number of frames that were transmitted.
Unicast Packets Transmitted The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted
to a subnetwork-unicast address, including the packets that were discarded or
not sent.
Multicast Packets
Transmitted The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted
to a multicast address, including the packets hat were discarded or not sent.
Broadcast Packets
Transmitted The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted
to the broadcast address, including the packets that were discarded or not sent.
Transmit Packets Discarded The number of outbound packets that were discarded, even though no errors
were detected, preventing the packets from being delivered to a higher-layer
protocol. A possible reason for discarding a packet could be to free buffer space.
Total Transmit Errors The sum of single, multiple, and excessive collisions.
Total T ransmit Packets
Discarded The sum of single collision frames discarded, multiple collision frames
discarded, and excessive frames discarded.
Table 88. Detailed port statistics (continued)
Field Description
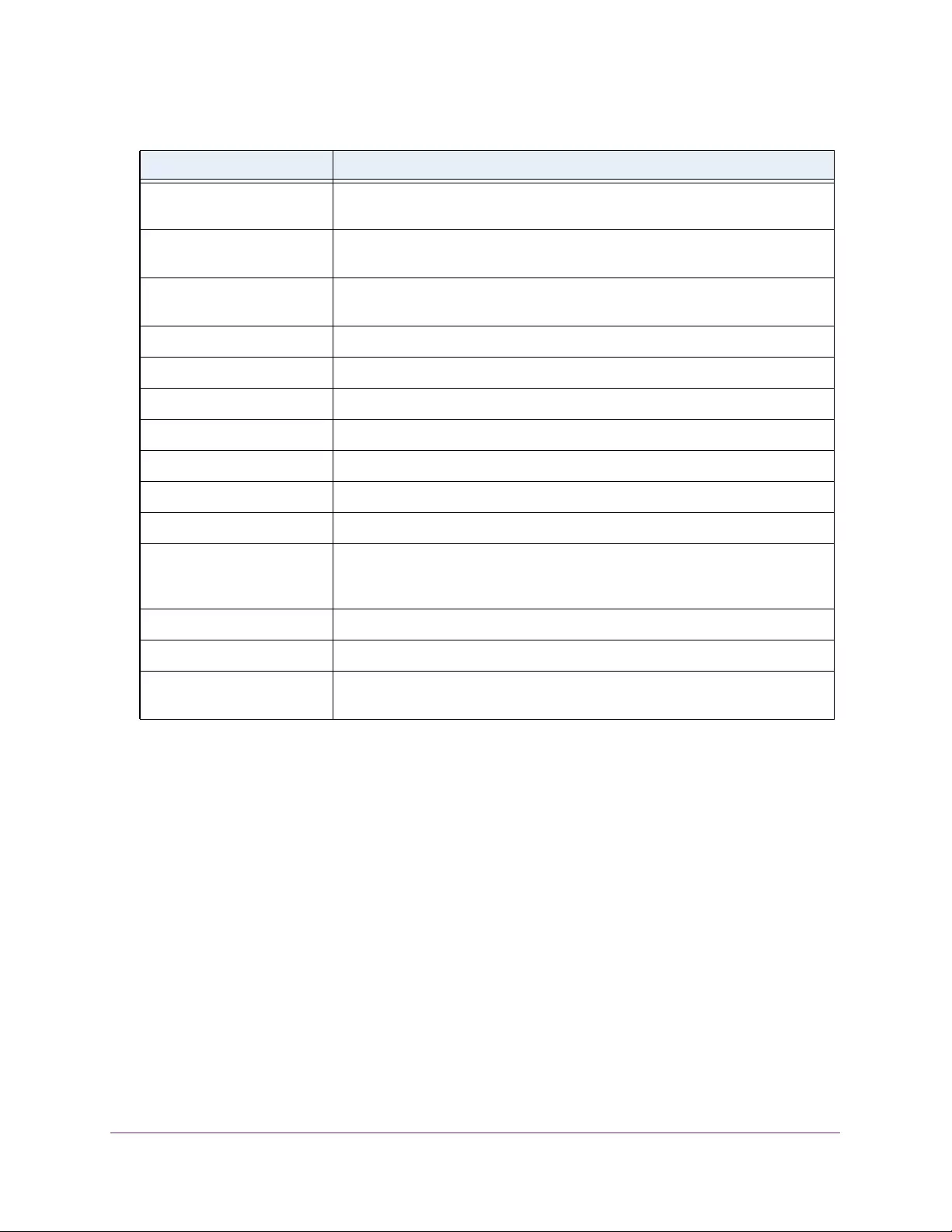
Monitor the System
389
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View or Clear EAP Statistics
You can view information about Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) packets that are
received on a specific port.
To view EAP statistics or clear the statistics:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
Single Collision Frames The number of successfully transmitted frames for which transmission was
inhibited by exactly one collision.
Multiple Collision Frames The number of successfully transmitted frames for which transmission was
inhibited by more than one collision.
Excessive Collision Frames The number of frames for which transmission failed because of excessive
collisions.
Dropped Transmit Frames The number of transmit frames discarded.
STP BPDUs Received The number of STP BPDUs received.
STP BPDUs Transmitted The number of STP BPDUs transmitted.
RSTP BPDUs Received The number of RSTP BPDUs received.
RSTP BPDUs Transmitted The number of RSTP BPDUs transmitted.
MSTP BPDUs Received The number of MSTP BPDUs received.
MSTP BPDUs Transmitted The number of MSTP BPDUs transmitted.
802.3x Pause Frames
Transmitted The number of MAC control frames transmitted with an opcode indicating the
PAUSE operation. This counter does not increment when the interface is
operating in half-duplex mode.
EAPOL Frames Received The number of valid EAPoL frames of any type that were received.
EAPOL Frames Transmitted The number of EAPoL frames of any type that were transmitted.
Time Since Counters Last
Cleared The elapsed time in days, hours, minutes, and seconds since the statistics were
cleared.
Table 88. Detailed port statistics (continued)
Field Description
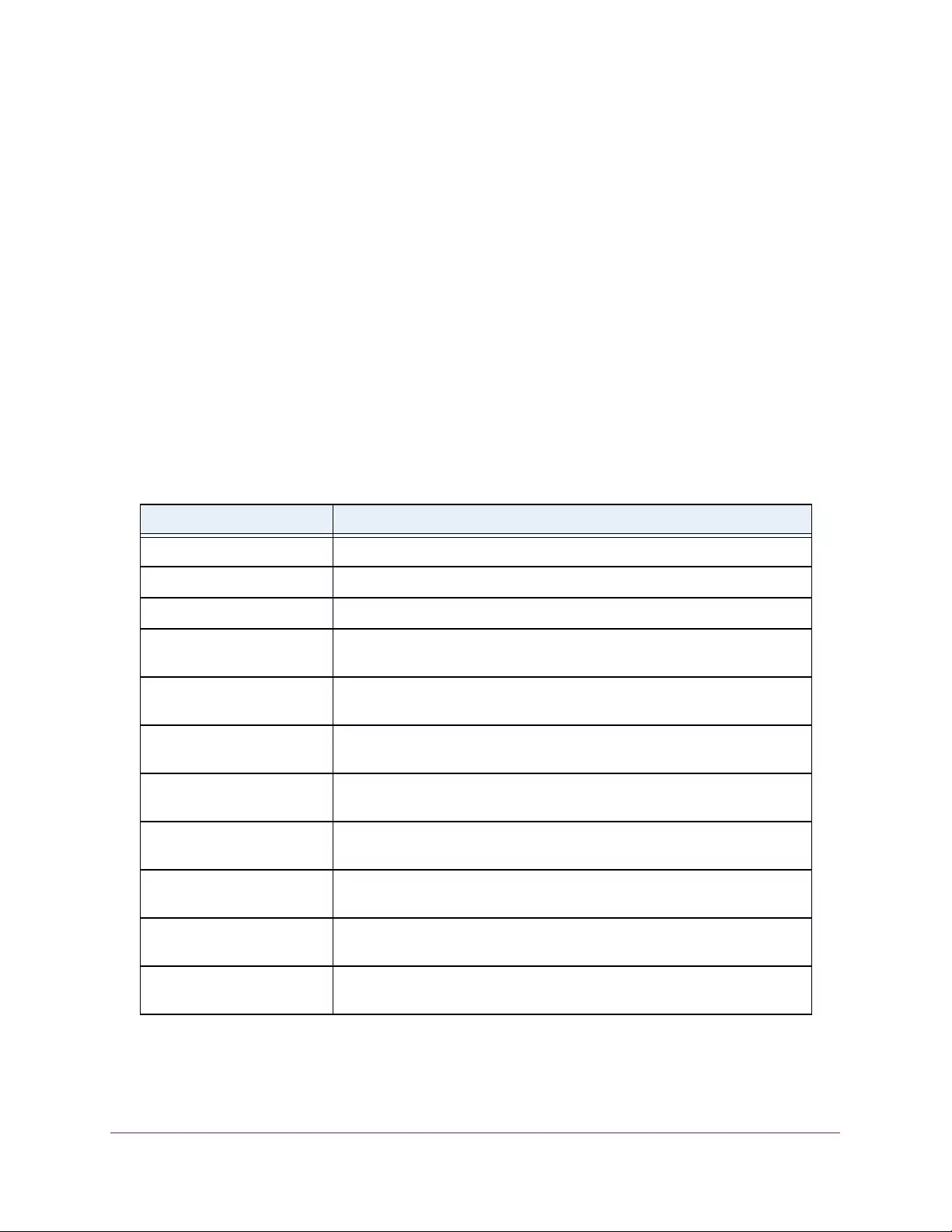
Monitor the System
390
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Ports > EAP Statistics.
The EAP Statistics page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
7. To clear the counters for a specific port, select the check box associated with the port and
click the Clear button.
8. To clear all the EAP counters for all ports on the switch, select the check box in the row
heading and click the Clear button.
Clicking the button resets all statistics for all ports to default values.
The following table describes the EAP statistics displayed on the page.
Table 89. EAP statistics
Field Description
Ports The port number for which the EAP statistics are displayed.
EAPOL Frames Received The number of received valid EAPoL frames of any type.
EAPOL Frames Transmitted The number of transmitted EAPoL frames of any type.
EAPOL Start Frames
Received The number of received EAPoL start frames.
EAPOL Logoff Frames
Received The number of received EAPoL logoff frames.
EAPOL Last Frame Version The protocol version number carried in the most recently received EAPoL
frame.
EAPOL Last Frame Source The source MAC address carried in the most recently received EAPoL
frame.
EAPOL Invalid Frames
Received The number of received EAPoL frames in which the frame type was not
recognized.
EAPOL Length Error Frames
Received The number of received EAPoL frames in which the frame type was not
recognized.
EAP Response/ID Frames
Received The number of received EAP response/identity frames.
EAP Response Frames
Received The number of received valid EAP response frames (other than resp/ID
frames).

Monitor the System
391
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Perform a Cable Test
You can test and view information about the cables that are connected to switch ports.
To perform a cable test:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Ports > Cable Test.
The Cable Test page displays.
6. Select the check boxes that are associated with the physical ports for which you want to test
the cables.
7. Click the Apply button.
A cable test is performed on all selected ports. The cable test might take up to two
seconds to complete. If the port forms an active link with a device, the cable status is
always Normal. The test returns a cable length estimate if this feature is supported by the
PHY for the current link speed. Note that if the link is down and a cable is attached to a
10/100 Ethernet adapter then the cable status might be Open or Short because some
Ethernet adapters leave unused wire pairs unterminated or grounded.
EAP Request/ID Frames
Transmitted The number of transmitted EAP request/identity frames.
EAP Request Frames
Transmitted The number of transmitted EAP request frames (other than request/identity
frames).
Table 89. EAP statistics
Field Description

Monitor the System
392
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The following table describes the nonconfigurable information displayed on the page.
Configure and View Logs
The switch generates messages in response to events, faults, or errors occurring on the
platform as well as changes in configuration or other occurrences. These messages are
stored locally and can be forwarded to one or more centralized points of collection for
monitoring purposes or long-term archival storage. Local and remote configuration of the
logging capability includes filtering of messages logged or forwarded based on severity and
generating component.
Manage the Memory Logs
The memory log stores messages in memory based upon the settings for message
component and severity. You can set the administrative status and behavior of logs in the
system buffer. These log messages are cleared when the switch reboots.
For the message log, only the latest 200 entries are displayed on the page.
To configure the memory log settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
Table 90. Cable Test information
Field Description
Cable Status Indicates the cable status:
• Normal. The cable is working correctly.
• Open. The cable is disconnected or a faulty connector exists.
• Short. An electrical short exists in the cable.
• Cable Test Failed. The cable status could not be determined. The cable
might in fact be working.
• Untested. The cable is not yet tested.
• Invalid cable type. The cable type is unsupported.
• No cable. The cable is not present.
Cable Length The estimated length of the cable in meters. The length is displayed as a range
between the shortest estimated length and the longest estimated length.
Unknown is displayed if the cable length could not be determined. The cable
length is displayed only if the cable status is Normal.
Failure Location The estimated distance in meters from the end of the cable to the failure
location. The failure location is displayed only if the cable status is Open or
Short.

Monitor the System
393
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Logs > Memory Log.
The Memory Log Configuration page displays.
6. Select one of the following Admin Status radio buttons:
•Enable. Enable system logging.
•Disable. Prevent the system from logging messages.
7. From the Behavior menu, specify the behavior of the log when it is full.
•Wrap. When the buf fer is full, the oldest log messages are deleted as the system logs
new messages.
•Stop on Full. When the buffer is full, the system stops logging new messages and
preserves all existing log messages.
8. From the Severity Filter menu, select one of the following severity levels:
•Emergency (0). System is unusable.
•Alert (1). Action must be taken immediately.
•Critical (2). Critical conditions.
•Error (3). Error conditions.
•Warning (4). Warning conditions.
•Notice (5). Normal but significant conditions.
•Informational (6). Informational messages.
•Debug (7). Debug-level messages.
Note: A log records messages equal to or above a configured severity
threshold.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The Memory Log table displays on the Memory Log Configuration page.
The Total number of Messages field displays the number of messages the system logged
in memory. Only the 200 most recent entries are displayed on the page.
The rest of the page displays the Memory Log messages. The format of the log message
is the same for messages that are displayed for the message log, persistent log, or

Monitor the System
394
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
console log. Messages logged to a collector or relay through syslog support the same
format as well.
The following example shows the standard format for a log message:
<14>2017-09-02 16:35:40 10.131.12.183-1 UNKN[2176789276]:
main_login.c(179) 3855 %% HTTP Session 19 initiated for user admin
connected from 10.27.64.122
The number contained in the angle brackets represents the message priority, which is
derived from the following values:
Priority = (facility value × 8) + severity level.
The facility value is usually 1, which means it is a user-level message. Therefore, to
determine the severity level of the message, subtract 8 from the number in the angle
brackets. The sample log message shows a severity level of 6 (informational). For more
information about the severity of a log message, see Manage the Server Log on
page 396.
The message was generated on September 2, 2017, at 5:35:40 p.m. by the switch with
an IP address of 10.131.12.183. The component that generated the message is
unknown, but it came from line 179 of the main_login.c file. This is the 3,855th
message logged since the switch was last booted. The message indicates that the
administrator logged on to the HTTP management interface from a host with an IP
address of 10.27.64.122.
10. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
11. To clear the messages from the buffered log in the memory, click the Clear button.
Message Log Format
This topic applies to the format of all logged messages that are displayed for the message
log, persistent log, or console log.
Messages logged to a collector or relay through syslog use an identical format:
•<15>2017-09-02 05:34:05 0.0.0.0-1 MSTP[2110]: mspt_api.c(318)
237%% Interface 12 transitioned to root state on message age timer
expiry.
This example indicates a message with severity 7 (15 mod 8) (debug) on a switch and
generated by component MSTP running in thread ID 2110 on September 2, 2017, at
05:34:05 a.m. by line 318 of file mstp_api.c. This is the 237th message logged with
system IP 0.0.0.0 and task-ID 1.
•<15>2017-09-02 06:24:15 STK0 MSTP[2110]: mspt_api.c(318) 237%%
Interface 12 transitioned to root state on message age timer
expiry.
This example indicates a user-level message (1) with severity 7 (debug) on a system that
is not a chassis and generated by component MSTP running in thread ID 2110 on
September 2, 2017, at 06:24:15 a.m. by line 318 of file mstp_api.c. This is the 237th

Monitor the System
395
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
message logged. Messages logged to a collector or relay through syslog use a format
identical to the previous message.
Manage the Flash Log
The flash log is a persistent log, that is, is a log that is stored in persistent storage. Persistent
storage survives across platform reboots. The first log type is the system startup log. The
system startup log stores the first 32 messages received after system reboot. The second log
type is the system operation log. The system operation log stores messages received during
system operation.
To configure flash log settings:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Logs > FLASH Log.
The FLASH Log Configuration page displays.
6. Select one of the following Admin Status radio buttons:
•Enable. A log that is enabled logs messages.
•Disable. A log that is disabled does not log messages.
7. From the Severity Filter menu, select the logging level for messages that must be sent to
the logging host.
Log messages with the selected severity level and all log messages of greater severity
are sent to the host. For example, if you select Error, the logged messages include Error,
Critical, Alert, and Emergency. The default severity level is Alert (1). The severity can be
one of the following levels:
-Emergency (0). The highest warning level. If the device is down, or not
functioning properly, an emergency log message is saved to the device.
-Alert (1). The second-highest warning level. An alert log message is saved if a
serious device malfunction occurs, such as all device features being down. Action
must be taken immediately.

Monitor the System
396
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
-Critical (2). The third-highest warning level. A critical log message is saved if a
critical device malfunction occurs, for example, two device ports are not
functioning, while the rest of the device ports remain functional.
-Error (3). A device error occurred, such as a port being offline.
-Warning (4). The lowest level of a device warning.
-Notice (5). Normal but significant conditions. Provides the network administrators
with device information.
-Informational (6). Provides device information.
-Debug (7). Provides detailed information about the device.
8. From the Logs to be Displayed menu, select one of the following options:
•Current Logs. The log messages for the current switch sessions are displayed. This
is the default setting.
•Previous Logs. The previous log messages are displayed, that is, the log messages
that are still in the flash memory from before the switch was rebooted.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The Total Number of Messages field shows is the total number of persistent log
messages that are stored on the switch. The maximum number of persistent log
messages displayed on the switch is 64.
Description: <15>2017-09-02 07:10:44 STK0 MSTP[2110]:
mspt_api.c(318) 237 %% Interface 12 transitioned to root state on
message age timer expiry
The previous log message example indicates a user-level message (1) with severity 7
(debug) on a system that is not stacked and generated by component MSTP running in
thread ID 2110 on September 2, 2017, at 07:10:44 a.m. by line 318 of file mstp_api.c.
This is the 237th message logged. Messages logged to a collector or relay via syslog
support an identical format as the previous message.
Manage the Server Log
You can let the switch send log messages to remote logging hosts configured on the system.
Configure the Local Log Server
To configure local log server:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.

Monitor the System
397
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Logs > Server Log.
The Server Log page displays.
6. Select one of the following Admin Status radio buttons:
•Enable. Send log messages to all configured hosts (syslog collectors or relays) using
the values configured for each host.
•Disable. Stop logging to all syslog hosts. Disable means no messages are sent to
any collector or relay.
7. In the Local UDP Port field, specify the port on the switch from which syslog messages
must be sent. The Local UDP port values are 1 to 65535. The default port is 514.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The Server Log Configuration section displays the following information:
•Messages Received. The number of messages received by the log process. This
includes messages that are dropped or ignored.
•Messages Relayed. The number of messages forwarded by the syslog function to a
syslog host. Messages forwarded to multiple hosts are counted once for each host.
•Messages Ignored. The number of messages that were ignored.
Add a Remote Syslog Server
You can add a remote log server, which is the same as a remote syslog host.
To add a remote syslog server:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.

Monitor the System
398
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Logs > Server Log.
The Server Log Configuration page displays.
6. Specify the following settings:
•IP Address Type. Specify the IP address type of the host, which can be IPv4, IPv6,
or DNS.
•Host Address. Specify the IP address or host name of the syslog host.
•Port. Specify the port on the host to which syslog messages must be sent. The
default port number is 514.
•Severity Filter. Use the menu to select the severity of the logs that must be sent to
the logging host. Logs with the selected severity level and all logs of greater severity
are sent to the host. For example, if you select Error, the logged messages include
Error, Critical, Alert, and Emergency. The default severity level is Alert (1). The
severity can be one of the following levels:
-Emergency (0). The highest warning level. If the device is down or not functioning
properly, an emergency log is saved to the device.
-Alert (1). The second-highest warning level. An alert log is saved if a serious
device malfunction occurs, such as all device features being down.
-Critical (2). The third-highest warning level. A critical log is saved if a critical
device malfunction occurs, for example, two device ports are not functioning,
while the rest of the device ports remain functional.
-Error (3). A device error occurred, such as a port being offline.
-Warning (4). The lowest level of a device warning.
-Notice (5). Provides the network administrators with device information.
-Informational (6). Provides device information.
-Debug (7). Provides detailed information about the log.
7. Click the Add button.
The remote server is added.
The Status field in the Server Configuration table shows whether the remote logging host
is currently active.
Modify the Settings for a Remote Syslog Server
To modify the settings for a remote syslog server:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.

Monitor the System
399
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Logs > Server Log.
The Server Log Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box that is associated with the server.
7. Change the information as needed.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete the Settings for a Remote Syslog Server
To delete the settings for a remote syslog server:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Logs > Server Log.
The Server Log Configuration page displays.
6. Select the check box that is associated with the server.
7. Click the Delete button.
The server is removed.
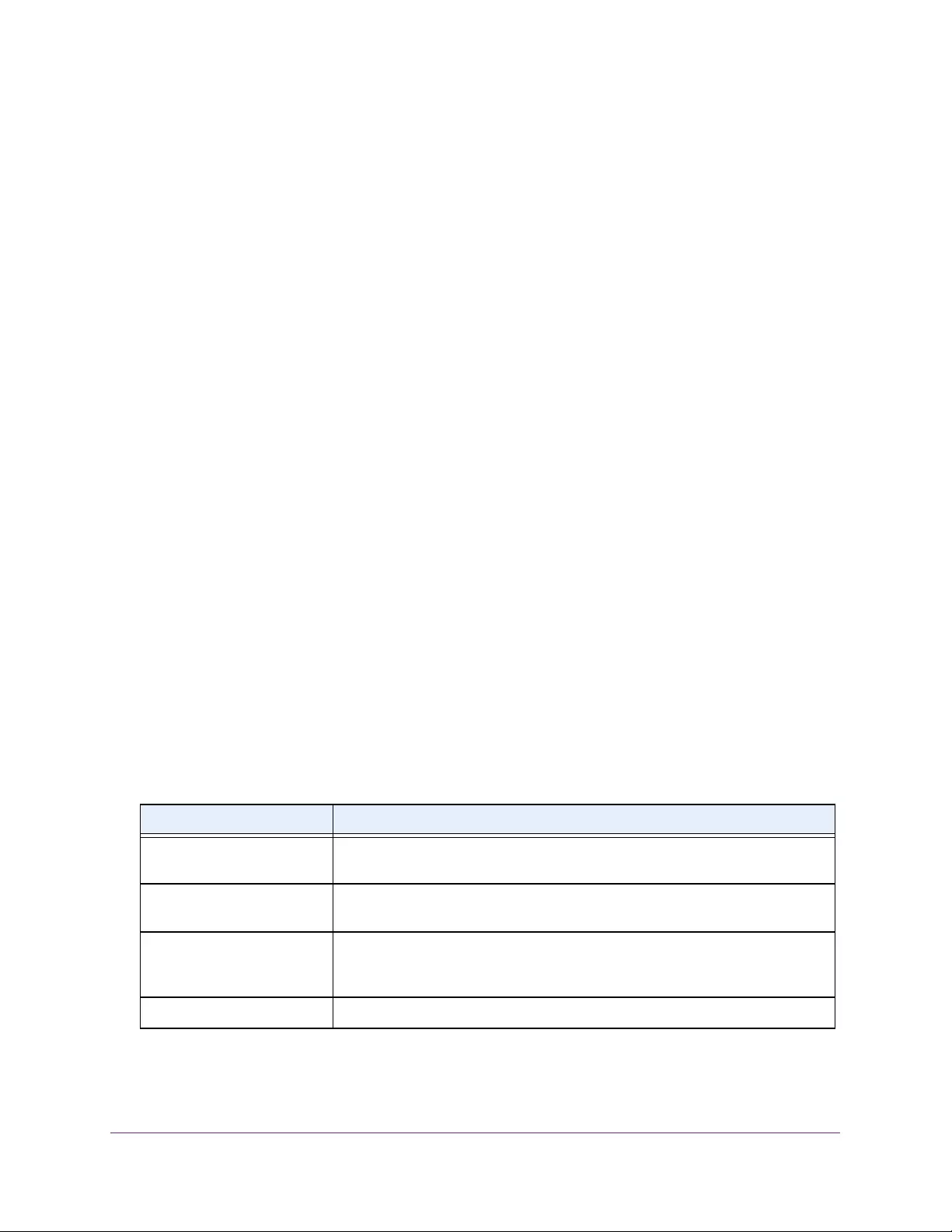
Monitor the System
400
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View or Clear the Trap Logs
You can view information about the SNMP traps generated on the switch. The information
can be retrieved as a file.
You can also display information about the traps that were sent.
View the trap logs or clear the counters:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Logs > Trap Logs.
The Trap Logs page displays.
6. To clear all counters, click the Clear button.
All statistics for the trap logs are reset to their default values.
The following table describes the trap logs information that is displayed on the page.
Table 91. Trap Logs information
Field Description
Number of Traps Since Last
Reset The number of traps that occurred since the switch last rebooted.
T rap Log Capacity The maximum number of traps stored in the log. If the number of traps exceeds
the capacity, the entries overwrite the oldest entries.
Number of Traps since log
last viewed The number of traps that occurred since the traps were last displayed.
Displaying the traps by any method (terminal interface display, web display,
upload file from switch, and so on) causes this counter to be cleared to 0.
Log The sequence number of the trap.
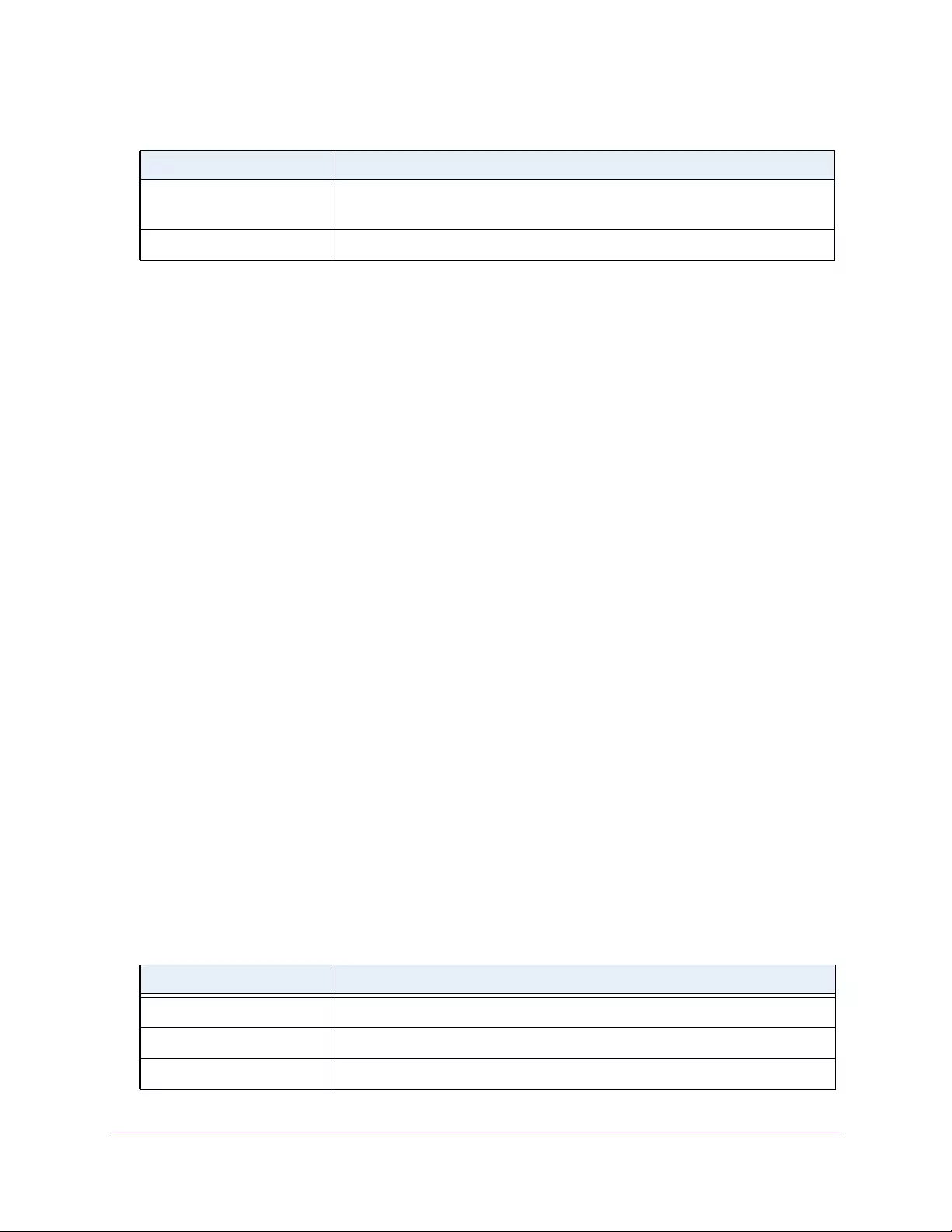
Monitor the System
401
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
View or Clear the Event Log
You can display the event log, which is used to hold error messages for catastrophic events.
After the event is logged and the updated log is saved in flash memory, the switch is reset.
The log can hold at least 2,000 entries and is erased when an attempt is made to add an
entry after it is full. The event log is preserved across system resets.
To view the event log or clear the log:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Logs > Event Logs.
The Event Logs page displays.
6. To refresh the page with the latest information about the switch, click the Refresh button.
7. To clear the messages from the event log, click the Clear button.
The following table describes the event log information that is displayed on the page.
System Up Time The time when the trap occurred, expressed in days, hours, minutes, and
seconds, since the last reboot of the switch.
Trap Information identifying the trap.
Table 92. Event Logs information
Field Description
Entry The sequence number of the event.
Type The type of the event.
File Name The file in which the event originated.
Table 91. Trap Logs information (continued)
Field Description
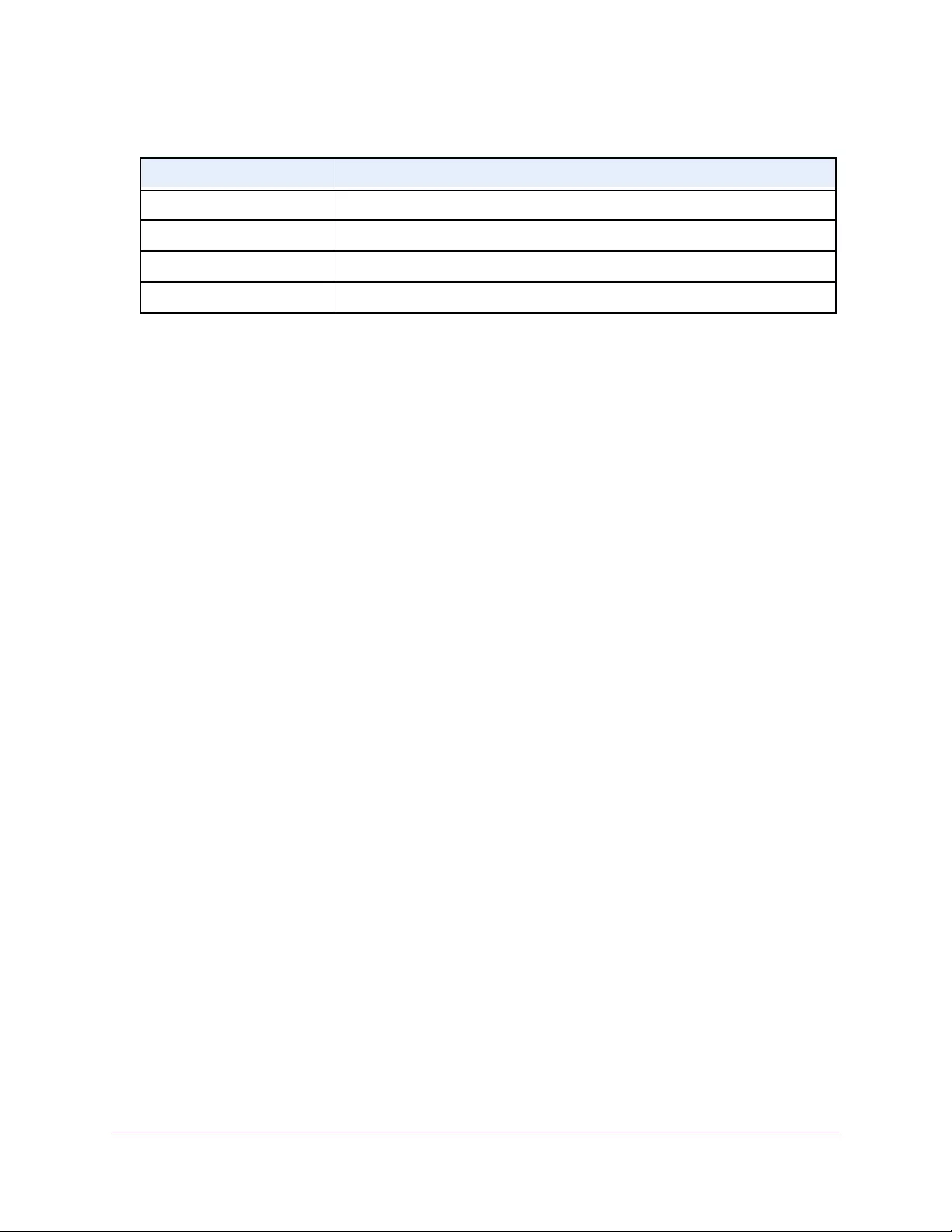
Monitor the System
402
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Configure Port Mirroring
Port mirroring selects the network traffic for analysis by a network analyzer. This is done for
specific ports of the switch. As such, many switch ports are configured as source ports and
one switch port is configured as a destination port. You can configure how traffic is mirrored
on a source port. Packets that are received on the source port, that are transmitted on a port,
or are both received and transmitted can be mirrored to the destination port.
The packet that is copied to the destination port is in the same format as the original packet
on the wire. This means that if the mirror is copying a received packet, the copied packet is
VLAN tagged or untagged as it was received on the source port. If the mirror is copying a
transmitted packet, the copied packet is VLAN tagged or untagged as it is being transmitted
on the source port.
To globally enable port mirroring, specify the destination port, and specify one or
more source ports:
1. Connect your computer to the same network as the switch.
You can use a WiFi or wired network connection, or connect directly to a switch that is
off-network using an Ethernet cable.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. In the address field of your web browser, enter the IP address of the switch.
If you do not know the IP address of the switch, see Access the Switch on page 13.
The login window opens.
4. Enter the switch’s password in the password field.
The default password is password. If you added the switch to a network on the Insight
app before and you did not yet change the password through the local browser interface,
enter your Insight network password.
The System Information page displays.
5. Select Monitoring > Mirroring > Port Mirroring.
The Global Configuration page displays.
Line The line number of the event.
Task Id The task ID of the event.
Code The event code.
Time The time the event occurred.
Table 92. Event Logs information (continued)
Field Description

Monitor the System
403
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. Select an Admin Mode radio button:
•True. Port mirroring is enabled.
•False. Port mirroring is enabled.
7. From the Destination Port menu, select the destination port to which port traffic must be
copied.
You can configure only one destination port on the system. The port functions as a probe
port and receives traffic from all configured source ports. If no port is configured, None is
displayed. The default is None.
Perform the following steps in the Source Interface Configuration section.
8. Use one of the following methods to narrow down the ports that are displayed:
•Select 1 to display the physical ports of the selected unit.
•Select LAG to display a list of LAGs only.
•Select CPU to display a list of CPUs only.
•Select All to display a list of all physical ports, LAGs, CPUs, and VLANs.
9. Use one of the following methods to select one or more source ports:
•Select a specific interface by specifying the interface number using the respective
naming convention (for example, g1 or l1) in the Go To Interface field and clicking the
Go button. See Interface Naming Conventions on page 12 for more information. The
entry corresponding to the specified interface is selected.
•Select one or more check boxes in the Interface column.
10. From the Direction menu, specify the direction of the traffic that must be mirrored from the
selected source ports:
•None. The value is not configured. This is the default setting.
•Tx and Rx. Monitors transmitted and received packets.
•Rx. Monitors received (ingress) packets only.
•Tx. Monitors transmitted (egress) packets only.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved. Traffic from the selected ports is sent to the probe port.
The Status field indicates the interface status.

404
A
A. Configuration Examples
This appendix contains information about how to configure the following features.
The appendix covers the following topics:
•Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)
•Access Control Lists (ACLs)
•Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
•802.1X
•Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)

Configuration Examples
405
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)
A local area network (LAN) can generally be defined as a broadcast domain. Hubs, bridges,
or switches in the same physical segment or segments connect all end node devices. End
nodes can communicate with each other without the need for a router . Routers connect LANs
together, routing the traffic to the appropriate port.
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a local area network with a definition that maps workstations on
some basis other than geographic location (for example, by department, type of user, or
primary application). To enable traffic to flow between VLANs, traffic must go through a
router, just as if the VLANs were on two separate LANs.
A VLAN is a group of computers, servers, and other network resources that behave as if they
were connected to a single network segment—even though they might not be. For example,
all marketing personnel might be spread throughout a building. Yet if they are all assigned to
a single VLAN, they can share resources and bandwidth as if they were connected to the
same segment. The resources of other departments can be invisible to the marketing VLAN
members, accessible to all, or accessible only to specified individuals, depending on how the
IT manager sets up the VLANs.
VLANs present a number of advantages:
•It is easy to do network segmentation. Users who communicate most frequently with each
other can be grouped into common VLANs, regardless of physical location. Each group’s
traffic is contained largely within the VLAN, reducing extraneous traf fic and improving the
efficiency of the whole network.
•They are easy to manage. The addition of nodes, as well as moves and other changes,
can be dealt with quickly and conveniently from a management interface rather than from
the wiring closet.
•They provide increased performance. VLANs free up bandwidth by limiting node-to-node
and broadcast traffic throughout the network.
•They ensure enhanced network security. VLANs create virtual boundaries that can be
crossed only through a router. So standard, router-based security measures can be used
to restrict access to each VLAN.
Packets received by the switch are treated in the following way:
•When an untagged packet enters a port, it is automatically tagged with the port’s default
VLAN ID tag number. Each port supports a default VLAN ID setting that is user
configurable (the default setting is 1). The default VLAN ID setting for each port can be
changed on the Port PVID Configuration page. See Configure Port PVID Settings on
page 120.
•When a tagged packet enters a port, the tag for that packet is unaffected by the default
VLAN ID setting. The packet proceeds to the VLAN specified by its VLAN ID tag number.
•If the port through which the packet entered is not a member of the VLAN as specified by
the VLAN ID tag, the packet is dropped.
•If the port is a member of the VLAN specified by the packet’s VLAN ID, the packet can be
sent to other ports with the same VLAN ID.

Configuration Examples
406
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Packets leaving the switch are either tagged or untagged, depending on the setting for
that port’s VLAN membership properties. A U for a given port means that packets leaving
the switch from that port are untagged. Inversely, a T for a given port means that packets
leaving the switch from that port are tagged with the VLAN ID that is associated with the
port.
The example given in this section comprises numerous steps to illustrate a wide range of
configurations to help provide an understanding of tagged VLANs.
VLAN Configuration Examples
This example demonstrates several scenarios of VLAN use and describes how the switch
handles tagged and untagged traffic.
In this example, you create two new VLANs, change the port membership for default VLAN 1,
and assign port members to the two new VLANs:
1. On the VLAN Configuration page (see Add a VLAN on page 113), create the following
VLANs:
•A VLAN with VLAN ID 10.
•A VLAN with VLAN ID 20.
2. On the VLAN Membership page (see Configure VLAN Membership on page 117) specify the
VLAN membership as follows:
•For the default VLAN with VLAN ID 1, specify the following members: port 7 (U) and
port 8 (U).
•For the VLAN with VLAN ID 10, specify the following members: port 1 (U), port 2 (U),
and port 3 (T).
•For the VLAN with VLAN ID 20, specify the following members: port 4 (U), port 5 (T),
and port 6 (U).
3. On the Port PVID Configuration page (see Configure Port PVID Settings on page 120),
specify the PVID for ports g1 and g4 so that packets entering these ports are tagged with the
port VLAN ID:
•Port g1: PVID 10
•Port g4: PVID 20
4. With the VLAN configuration that you set up, the following situations produce results as
described:
•If an untagged packet enters port 1, the switch tags it with VLAN ID 10. The packet
can access port 2 and port 3. The outgoing packet is stripped of its tag to leave port 2
as an untagged packet. For port 3, the outgoing packet leaves as a tagged packet
with VLAN ID 10.
•If a tagged packet with VLAN ID 10 enters port 3, the packet can access port 1 and
port 2. If the packet leaves port 1 or port 2, it is stripped of its tag to leave the switch
as an untagged packet.
•If an untagged packet enters port 4, the switch tags it with VLAN ID 20. The packet
can access port 5 and port 6. The outgoing packet is stripped of its tag to become an

Configuration Examples
407
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
untagged packet as it leaves port 6. For port 5, the outgoing packet leaves as a
tagged packet with VLAN ID 20.
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
ACLs ensure that only authorized users can access specific resources while blocking off any
unwarranted attempts to reach network resources.
ACLs are used to provide traffic flow control, restrict contents of routing updates, decide
which types of traffic are forwarded or blocked, and provide security for the network. ACLs
are normally used in firewall routers that are positioned between the internal network and an
external network, such as the Internet. They can also be used on a router positioned between
two parts of the network to control the traffic entering or exiting a specific part of the internal
network. The added packet processing required by the ACL feature does not affect switch
performance. That is, ACL processing occurs at wire speed.
Access lists are sequential collections of permit and deny conditions. This collection of
conditions, known as the filtering criteria, is applied to each packet that is processed by the
switch or the router. The forwarding or dropping of a packet is based on whether or not the
packet matches the specified criteria.
Traffic filtering requires the following two basic steps:
1. Create an access list definition.
The access list definition includes rules that specify whether traffic matching the criteria is
forwarded normally or discarded. Additionally, you can assign traffic that matches the
criteria to a particular queue or redirect the traffic to a particular port. A default deny all
rule is the last rule of every list.
2. Apply the access list to an interface in the inbound direction.
The switch allow ACLs to be bound to physical ports and LAGs. The switch software supports
MAC ACLs and IP ACLs.
MAC ACL Sample Configuration
The following example shows how to create a MAC-based ACL that permits Ethernet traffic
from the Sales department on specified ports and denies all other traffic on those ports.
1. On the MAC ACL page (see Configure a Basic MAC ACL on page 301), create an ACL
with the name Sales_ACL for the Sales department of your network.
By default, this ACL is bound on the inbound direction, which means that the switch
examines traffic as it enters the port.
2. On the MAC Rules page (see Configure MAC ACL Rules on page 304) , create a rule for
the Sales_ACL with the following settings:
•Sequence Number. 1
•Action. Permit
•Assign Queue ID. 0

Configuration Examples
408
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
•Match Every. False
•CoS. 0
•Destination MAC. 01:02:1A:BC:DE:EF
•Destination MAC Mask. 00:00:00:00:FF:FF
•EtherType. User Value.
•Source MAC. 02:02:1A:BC:DE:EF
•Source MAC Mask. 00:00:00:00:FF:FF
•VLAN ID. 2
3. On the MAC Binding Configuration page (see Configure MAC Bindings on page 308) ,
assign the Sales_ACL to ports 6, 7, and 8, and then click the Apply button.
You can assign an optional sequence number to indicate the order of this access list
relative to other access lists if any are already assigned to this interface and direction.
4. The MAC Binding Table (see View or Delete MAC ACL Bindings in the MAC Binding
Table on page 310) displays the interface and MAC ACL binding information.
The ACL named Sales_ACL looks for Ethernet frames with destination and source MAC
addresses and MAC masks defined in the rule. Also, the frame must be tagged with VLAN
ID 2, which is the Sales department VLAN. The CoS value of the frame must be 0, which is
the default value for Ethernet frames. Frames that match this criteria are permitted on
interfaces 6, 7, and 8 and are assigned to the hardware egress queue 0, which is the default
queue. All other traffic is explicitly denied on these interfaces. To allow additional traffic to
enter these ports, you must add a new Permit rule with the desired match criteria and bind
the rule to interfaces 6, 7, and 8.
Standard IP ACL Sample Configuration
The following example shows how to create an IP-based ACL that prevents any IP traffic
from the Finance department from being allowed on the ports that are associated with other
departments. Traffic from the Finance department is identified by each packet’s network IP
address.
1. On the IP ACL page (see Configure an IP ACL on page 311), create a new IP ACL with
an IP ACL ID of 1.
2. On the IP Rules page (see Configure Rules for a Basic IP ACL on page 313), create a rule
for IP ACL 1 with the following settings:
•Sequence Number. 1
•Action. Deny
•Assign Queue ID. 0 (optional: 0 is the default value)
•Match Every. False
•Source IP Address. 192.168.187.0
•Source IP Mask. 255.255.0
3. Click the Add button.

Configuration Examples
409
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
4. On the IP Rules page (see Configure Rules for a Basic IP ACL on page 313), create a
second rule for IP ACL 1 with the following settings:
•Sequence Number. 2
•Action. Permit
•Match Every. T rue
5. Click the Add button.
6. On the IP Binding Configuration page (see Configure IP ACL Interface Bindings on
page 333), assign ACL ID 1 to the interface Gigabit ports 2, 3, and 4, and assign a
sequence number of 1.
By default, this IP ACL is bound on the inbound direction, so it examines traffic as it
enters the switch.
7. Click the Apply button.
8. Use the IP Binding Table page to view the interfaces and IP ACL binding information. (See
View or Delete IP ACL Bindings in the IP ACL Binding Table on page 335)
The IP ACL in this example matches all packets with the source IP address and subnet mask
of the Finance department’s network and deny it on the Ethernet interfaces 2, 3, and 4 of the
switch. The second rule permits all non-Finance traffic on the ports. The second rule is
required because an explicit deny all rule exists as the lowest priority rule.
Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
Standard IP-based networks are designed to provide best effort data delivery service. Best
effort service implies that the network delivers the data in a timely fashion, although there is
no guarantee that it does. During times of congestion, packets might be delayed, sent
sporadically, or dropped. For typical Internet applications, such as email and file transfer, a
slight degradation in service is acceptable and in many cases unnoticeable. However, any
degradation of service can negatively affect applications with strict timing requirements, such
as voice or multimedia.
Quality of Service (QoS) can provide consistent, predictable data delivery by distinguishing
between packets with strict timing requirements from those that are more tolerant of delay.
Packets with strict timing requirements are given special treatment in a QoS-capable
network. With this in mind, all elements of the network must be QoS capable. If one node
cannot meet the necessary timing requirements, this creates a deficiency in the network path
and the performance of the entire packet flow is compromised.
Two basic types of QoS are supported:
•Integrated Services. Network resources are apportioned based on request and are
reserved (resource reservation) according to network management policy (RSVP, for
example).
•Differentiated Services. Network resources are apportioned based on traffic
classification and priority, giving preferential treatment to data with strict timing
requirements.
The switch supports DiffServ.

Configuration Examples
410
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
The DiffServ feature contains a number of conceptual QoS building blocks that you can use
to construct a differentiated service network. Use these same blocks in dif ferent ways to build
other types of QoS architectures.
You must configure three key QoS building blocks for DiffServ:
•Class
•Policy
•Service (the assignment of a policy to a directional interface)
Class
You can classify incoming packets at Layers 2, 3, and 4 by letting the switch inspect the
following information for a packet:
•Source/destination MAC address
•EtherType
•Class of Service (802.1p priority) value (first/only VLAN tag)
•VLAN ID range (first/only VLAN tag)
•IP Service Type octet (also known as: ToS bits, Precedence value, DSCP value)
•Layer 4 protocol (such as TCP or UDP)
•Layer 4 source/destination ports
•Source/destination IP address
From a DiffServ point of view, two types of classes exist:
•DiffServ traffic classes
•DiffServ service levels/forwarding classes
DiffServ Traffic Classes
With DiffServ, you define which traffic classes to track on an ingress interface. You can define
simple BA classifiers (DSCP) and a wide variety of multifield (MF) classifiers:
•Layer 2; Layers 3, 4 (IP only)
•Protocol-based
•Address-based
You can combine these classifiers with logical AND or OR operations to build complex
MF-classifiers (by specifying a class type of all or any, respectively). That is, within a single
class, multiple match criteria are grouped together as an AND expression or a sequential OR
expression, depending on the defined class type. Only classes of the same type can be
nested; class nesting does not allow for the negation (exclude option) of the referenced class.
To configure DiffServ, you must define service levels, namely the forwarding classes/PHBs
identified by a given DSCP value, on the egress interface. You define these service levels by
configuring BA classes for each.

Configuration Examples
411
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Creating Policies
Use DiffServ policies to associate a collection of classes that you configure with one or more
QoS policy statements. The result of this association is referred to as a policy.
From a DiffServ perspective, two types of policies exist:
•Traffic Conditioning Policy. A policy that is applied to a DiffServ traffic class.
•Service Provisioning Policy. A policy that is applied to a DiffServ service level.
You must manually configure the various statements and rules used in the traffic conditioning
and service provisioning policies to achieve the desired Traffic Conditioning Specification
(TCS) and the Service Level Specification (SLS) operation, respectively.
Traffic Conditioning Policy
Traffic conditioning pertains to actions performed on incoming traffic. Several distinct QoS
actions are associated with traffic conditioning:
•Dropping. Drop a packet upon arrival. This is useful for emulating access control list
operation using DiffServ, especially when DiffServ and ACL cannot coexist on the same
interface.
•Marking IP DSCP or IP Precedence. Marking/re-marking the DiffServ code point in a
packet with the DSCP value representing the service level associated with a particular
DiffServ traffic class. Alternatively, the IP precedence value of the packet can be
marked/re-marked.
•Marking CoS (802.1p). Sets the 3-bit priority field in the first/only 802.1p header to a
specified value when packets are transmitted for the traffic class. An 802.1p header is
inserted if it does not already exist. This is useful for assigning a Layer 2 priority level
based on a DiffServ forwarding class (such as the DSCP or IP precedence value)
definition to convey some QoS characteristics to downstream switches that do not
routinely look at the DSCP value in the IP header.
•Policing. A method of constraining incoming traffic associated with a particular class so
that it conforms to the terms of the TCS. Special treatment can be applied to out-of-profile
packets that are either in excess of the conformance specification or are nonconformant.
The DiffServ feature supports the following types of traffic policing treatments (actions):
•drop. The packet is dropped.
•mark cos. The 802.1p user priority bits are (re)marked and forwarded.
•mark dscp. The packet DSCP is (re)marked and forwarded.
•mark prec. The packet IP Precedence is (re)marked and forwarded.
•send. The packet is forwarded without DiffServ modification.
•Policing with color mode awareness. Policing in the DiffServ feature uses either color
blind or color aware mode. Color blind mode ignores the coloration (marking) of the
incoming packet. Color aware mode takes into consideration the current packet marking
when the switch determines the policing outcome. An auxiliary traffic class is used in
conjunction with the policing definition to specify a value for one of the 802.1p, secondary
802.1p, IP DSCP, or IP precedence fields designating the incoming color value to be

Configuration Examples
412
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
used as the conforming color. You can also specify the color of traffic that exceeds the
threshold.
•Counting. Updating octet and packet statistics to keep track of data handling along traffic
paths within DiffServ. In this DiffServ feature, counters are not explicitly configured by the
user, but are designed into the system based on the DiffServ policy being created. For
more information, see View DiffServ Service Statistics on page 247.
•Assigning QoS queue. Directs a traffic stream to the specified QoS queue. This allows a
traffic classifier to specify which one of the supported hardware queues are used for
handling packets belonging to the class.
•Redirecting. Forces a classified traffic stream to a specified egress port (physical or
LAG). This can occur in addition to any marking or policing action. It can also be specified
along with a QoS queue assignment.
DiffServ Example Configuration
To create a DiffServ class and policy and attach them to a switch interface, follow these
steps:
1. On the Class Configuration page (see Create and Configure a DiffServ Class on
page 228), create a new class with the following settings:
•Class Name. Class1
•Class Type. All
2. Click the Class1 hyperlink to view the DiffServ Class Configuration page for this class.
3. Configure the following settings for Class1:
•Protocol Type. UDP
•Source IP Address. 192.12.1.0.
•Source Mask. 255.255.255.0.
•Source L4 Port. Other, and enter 4567 as the source port value.
•Destination IP Address. 192.12.2.0.
•Destination Mask. 255.255.255.0.
•Destination L4 Port. Other, and enter 4568 as the destination port value.
For more information about this page, see Create and Configure a DiffServ Class on
page 228.
4. Click the Apply button.
5. On the Policy Configuration page (see Create and Configure a DiffServ Policy on
page 239), create a new policy with the following settings:
•Policy Selector. Policy1
•Member Class. Class1
6. Click the Add button.
The policy is added.

Configuration Examples
413
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
7. Click the Policy1 hyperlink to view the Policy Class Configuration page for this policy.
8. Configure the Policy attributes as follows:
•Assign Queue. 3
•Policy Attribute. Simple Policy
•Color Mode. Color Blind
•Committed Rate. 1000000 Kbps
•Committed Burst Size. 128 KB
•Confirm Action. Send
•Violate Action. Drop
For more information about this page, see Create and Configure a DiffServ Policy on
page 239.
9. On the Service Interface Configuration page (see Attach a DiffServ Policy to an Interface
on page 245), select the check box next to interfaces g7 and g8 to attach the policy to these
interfaces, and then click the Apply button.
All UDP packet flows destined to the 192.12.2.0 network with an IP source address from the
192.12.1.0 network that include a Layer 4 Source port of 4567 and Destination port of 4568
from this switch on ports 7 and 8 are assigned to hardware queue 3.
On this network, traffic from streaming applications uses UDP port 4567 as the source and
4568 as the destination. This real-time traffic is time sensitive, so it is assigned to a
high-priority hardware queue. By default, data traffic uses hardware queue 0, which is
designated as a best-effort queue.
Also the confirmed action on this flow is to send the packets with a committed rate of
1000000 Kbps and burst size of 128 KB. Packets that violate the committed rate and burst
size are dropped.
802.1X
Local area networks (LANs) are often deployed in environments that permit unauthorized
devices to be physically attached to the LAN infrastructure, or permit unauthorized users to
attempt to access the LAN through equipment already attached. In such environments you
might want to restrict access to the services offered by the LAN to those users and devices
that are permitted to use those services.
Port-based network access control makes use of the physical characteristics of LAN
infrastructures to provide a means of authenticating and authorizing devices attached to a
LAN port with point-to-point connection characteristics. If the authentication and authorization
process fails, access control prevents access to that port. In this context, a port is a single
point of attachment to the LAN, such as a port of a MAC bridge and an association between
stations or access points in IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs.
The IEEE 802.11 standard describes an architectural framework within which authentication
and consequent actions take place. It also establishes the requirements for a protocol
between the authenticator (the system that passes an authentication request to the

Configuration Examples
414
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
authentication server) and the supplicant (the system that requests authentication), as well as
between the authenticator and the authentication server.
The switch can support a guest VLAN, which allows unauthenticated users limited access to
the network resources.
Note: You can use QoS features to provide rate limiting on the guest VLAN
to limit the network resources that the guest VLAN provides.
Another 802.1X feature is the ability to configure a port to enable or disable EAPoL packet
forwarding support. You can disable or enable the forwarding of EAPoL when 802.1X is
disabled on the device.
The ports of an 802.1X authenticator switch provide the means by which it can offer services
to other systems reachable through the LAN. Port-based network access control allows the
operation of a switch’s ports to be controlled to ensure that access to its services is permitted
only by systems that are authorized to do so.
Port access control provides a means of preventing unauthorized access by supplicants to
the services offered by a system. Control over the access to a switch and the LAN to which it
is connected can be desirable when you restrict access to publicly accessible bridge ports or
to restrict access to departmental LANs.
Access control is achieved by enforcing authentication of supplicants that are attached to an
authenticator's controlled ports. The result of the authentication process determines whether
the supplicant is authorized to access services on that controlled port.
A port access entity (PAE) is able to adopt one of two distinct roles within an access control
interaction:
1. Authenticator. A port that enforces authentication before allowing access to services
available through that port.
2. Supplicant. A port that attempts to access services offered by the authenticator.
Additionally, a third role exists:
3. Authentication server. A server that performs the authentication function necessary to
check the credentials of the supplicant on behalf of the authenticator.
All three roles are required for an authentication exchange.
The switch supports the authenticator role only, in which the PAE is responsible for
communicating with the supplicant. The authenticator PAE is also responsible for submitting
the information received from the supplicant to the authentication server for the credentials to
be checked, which determines the authorization state of the port. The authenticator PAE
controls the authorized/unauthorized state of the controlled port depending on the outcome of
the RADIUS-based authentication process.
Configuration Examples
415
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Figure 1. 802.1X authentication roles
802.1X Example Configuration
This example shows how to configure the switch so that 802.1X-based authentication is
required on the ports in a corporate conference room (1/0/5–1/0/8). These ports are available
to visitors and must be authenticated before access is granted to the network. The
authentication is handled by an external RADIUS server. When the visitor is successfully
authenticated, traffic is automatically assigned to the guest VLAN. This example assumes
that a VLAN was configured with a VLAN ID of 150 and VLAN name of Guest.
1. On the Port Authentication page (see Configure 802.1X Settings for a Port on
page 275), select ports 1/0/5, 1/0/6, 1/0/7, and 1/0/8.
2. From the Port Control menu, select Unauthorized.
The selection from the Port Control menu for all other ports on which authentication is
not needed must be Authorized. When the selection from the Port Control menu is
Authorized, the port is unconditionally put in a force-authorized state and does not
require any authentication. When the selection from the Port Control menu is Auto, the
authenticator PAE sets the controlled port mode.
3. In the Guest VLAN ID field for ports 1/0/5–1/0/8, enter 150 to assign these ports to the
guest VLAN.
You can configure additional settings to control access to the network through the ports.
See Configure 802.1X Settings for a Port on page 275 for information about the settings.
4. Click the Apply button.
5. On the 802.1X Configuration page (see Configure Global 802.1X Settings on page 274) ,
set the port based authentication state to Enable, and click the Apply button.
This example uses the default values for the port authentication settings, but you can
configure several additional settings. For example, the EAPOL Flood Mode field allows
you to enable the forwarding of EAPoL frames when 802.1X is disabled on the device.

Configuration Examples
416
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
6. On the Server Configuration page (see Configure a RADIUS Authentication Server on the
Switch on page 254), configure a RADIUS server with the following settings:
•Server Address. 192.168.10.23
•Secret Configured. Yes
•Secret. secret123
•Active. Primary
7. Click the Add button.
8. On the Dot1x Authentication List page (see Configure the Dot1x Authentication List on
page 265), configure the default list to use RADIUS as the first authentication method.
This example enables 802.1X-based port security on the switch and prompts the hosts
connected on ports g5-g8 for an 802.1X-based authentication. The switch passes the
authentication information to the configured RADIUS server.
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) runs on bridged networks to help eliminate loops. If a bridge
loop occurs, the network can become flooded with traffic. IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning
Tree Protocol (MSTP) supports multiple instances of spanning tree to efficiently channel
VLAN traffic over different interfaces. Each instance of the spanning tree behaves in the
manner specified in IEEE 802.1w, Rapid Spanning Tree, with slight modifications in the
working but not the end effect (chief among the effects is the rapid transitioning of the port to
the forwarding state).
The difference between the RSTP and the traditional STP (IEEE 802.1D) is the ability to
configure and recognize full-duplex connectivity and ports that are connected to end stations,
resulting in rapid transitioning of the port to the Forwarding state and the suppression of
Topology Change Notification. These features are represented by the parameters
pointtopoint and edgeport. MSTP is compatible to both RSTP and STP. It behaves in a way
that is appropriate for STP and RSTP bridges.
An MSTP bridge can be configured to behave entirely as a RSTP bridge or an STP bridge.
So, an IEEE 802.1s bridge inherently also supports IEEE 802.1w and IEEE 802.1D.
The MSTP algorithm and protocol provide simple and full connectivity for frames assigned to
any given VLAN throughout a bridged LAN comprising arbitrarily interconnected networking
devices, each operating MSTP, STP, or RSTP. MSTP allows frames assigned to different
VLANs to follow separate paths, each based on an independent Multiple Spanning Tree
Instance (MSTI), within Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) regions composed of LANs and or
MSTP bridges. These regions and the other bridges and LANs are connected into a single
Common Spanning Tree (CST). (IEEE DRAFT P802.1s/D13)
MSTP connects all bridges and LANs with a single Common and Internal Spanning Tree
(CIST). The CIST supports the automatic determination of each MST region, choosing its
maximum possible extent. The connectivity calculated for the CIST provides the CST for
interconnecting these regions, and an Internal Spanning T ree (IST) within each region. MSTP
ensures that frames with a given VLAN ID are assigned to one and only one of the MSTIs or

Configuration Examples
417
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
the IST within the region, that the assignment is consistent among all the networking devices
in the region, and that the stable connectivity of each MSTI and IST at the boundary of the
region matches that of the CST. The stable active topology of the bridged LAN with respect to
frames consistently classified as belonging to any given VLAN thus simply and fully connects
all LANs and networking devices throughout the network, though frames belonging to
different VLANs can take different paths within any region, per IEEE DRAFT P802.1s/D13.
All bridges, whether they use STP, RSTP, or MSTP, send information in configuration
messages through Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) to assign port roles that determine
each port’s participation in a fully and simply connected active topology based on one or
more spanning trees. The information communicated is known as the spanning tree priority
vector. The BPDU structure for each of these different protocols is different. An MSTP bridge
transmits the appropriate BPDU depending on the received type of BPDU from a particular
port.
An MST region comprises of one or more MSTP bridges with the same MST configuration
identifier, using the same MSTIs, and without any bridges attached that cannot receive and
transmit MSTP BPDUs. The MST configuration identifier includes the following components:
1. Configuration identifier format selector
2. Configuration name
3. Configuration revision level
4. Configuration digest: 16-byte signature of type HMAC-MD5 created from the MST
Configuration Table (a VLAN ID to MSTID mapping)
Because multiple instances of spanning tree exist, an MSTP state is maintained on a
per-port, per-instance basis (or on a per-port, per-VLAN basis, as any VLAN can be in one
and only one MSTI or CIST). For example, port A can be forwarding for instance 1 while
discarding for instance 2. The port states changed since IEEE 802.1D specification.
To support multiple spanning trees, configure an MSTP bridge with an unambiguous
assignment of VLAN IDs (VIDs) to spanning trees. For such a configuration, ensure the
following:
1. The allocation of VIDs to FIDs is unambiguous.
2. Each FID that is supported by the bridge is allocated to exactly one spanning tree instance.
The combination of VID to FID and then FID to MSTI allocation defines a mapping of VIDs to
spanning tree instances, represented by the MST Configuration Table.
With this allocation we ensure that every VLAN is assigned to one and only one MSTI. The
CIST is also an instance of spanning tree with an MSTID of 0.
VIDs might be not be allocated to an instance, but every VLAN must be allocated to one of
the other instances of spanning tree.
The portion of the active topology of the network that connects any two bridges in the same
MST region traverses only MST bridges and LANs in that region, and never bridges of any
kind outside the region. In other words, connectivity within the region is independent of
external connectivity.
Configuration Examples
418
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
MSTP Example Configuration
This example shows how to create an MSTP instance from the switch. The example network
includes three different switches that serve dif ferent locations in the network. In this example,
ports 1/0/1–1/0/5 are connected to host stations, so those links are not subject to network
loops. Ports 1/0/6–1/0/8 are connected across switches 1, 2, and 3.
Figure 2. MSTP sample configuration
Perform the following procedures on each switch to configure MSTP:
1. On the VLAN Configuration page for each switch, create VLANs 300 and 500 (see Add
a VLAN on page 113).
2. On the VLAN Membership page for each switch, include ports 1/0/1–1/0/8 as tagged (T) or
untagged (U) members of VLAN 300 and VLAN 500 (see Configure VLAN Membership on
page 117).
3. On the Global Settings page (for STP) for each switch, enable the Spanning Tree State
option (see Configure STP Settings on page 134).
Use the default values for the rest of the STP configuration settings. By default, the STP
operation mode is MSTP and the configuration name is the switch MAC address.
4. On the CST Configuration page for each switch (see Configure CST Settings on
page 136), set the bridge priority value for each of the three switches to force Switch 1 to be
the root bridge:
•Switch 1. 4096
•Switch 2. 12288
•Switch 3. 20480
Note: Bridge priority values are multiples of 4096.

Configuration Examples
419
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
If you do not specify a root bridge and all switches are assigned the same bridge priority
value, the switch with the lowest MAC address is elected as the root bridge.
5. On the Port Configuration page (fro CST) for each switch, select ports 1/0/1–1/0/8 and select
Enable from the STP Status menu (see Configure CST Port Settings on page 137).
6. Click the Apply button.
7. Select ports 1/0/1–1/0/5 (edge ports), and select Enable from the Fast Link menu.
Since the edge ports are not at risk for network loops, ports with Fast Link enabled
transition directly to the forwarding state.
8. Click the Apply button.
You can use the CST Port Status page for each switch (see View CST Port Status on
page 139) to view spanning tree information about each port.
9. On the MST Configuration page for each switch (see Manage MST Settings on page 142),
create a MST instances with the following settings:
•MST ID. 1
•Priority. Use the default (32768)
•VLAN ID. 300
10. Click the Add button.
11. Create a second MST instance with the following settings
•MST ID. 2
•Priority. 49152
•VLAN ID. 500
12. Click the Add button.
In this example, assume that Switch 1 became the root bridge for the MST instance 1, and
Switch 2 became the root bridge for MST instance 2. Switch 3 supports hosts in the sales
department (ports 1/0/1, 1/0/2, and 1/0/3) and in the HR department (ports 1/0/4 and 1/0/5).
Switches 1 and 2 also include hosts in the sales and HR departments. The hosts connected
from Switch 2 use VLAN 500, MST instance 2 to communicate with the hosts on Switch 3
directly. Likewise, hosts of Switch 1 use VLAN 300, MST instance 1 to communicate with the
hosts on Switch 3 directly.
The hosts use different instances of MSTP to effectively use the links across the switch. The
same concept can be extended to other switches and more instances of MSTP.
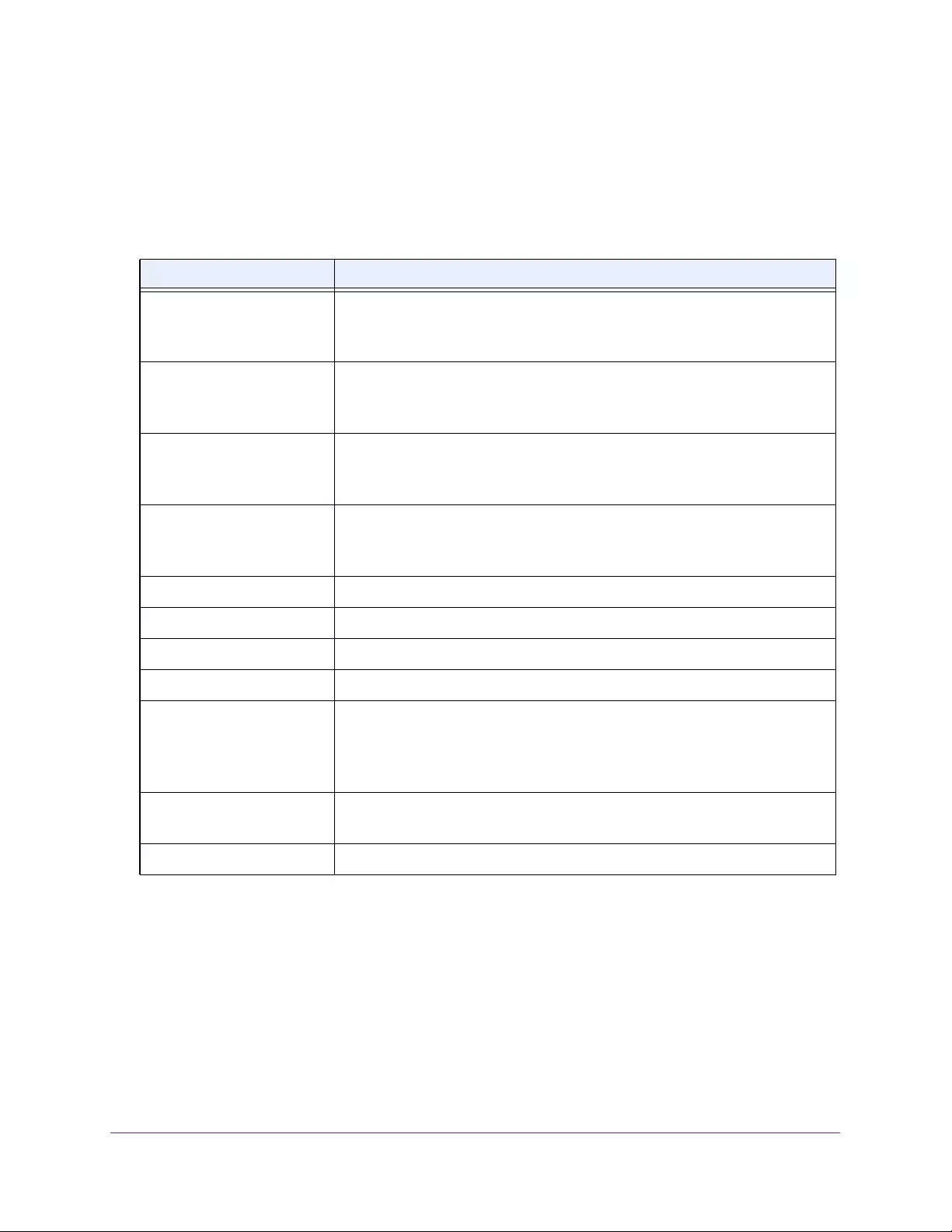
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
421
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Switch Specifications
The switch conforms to the TCP/IP, UDP, HTTP, ICMP, TFTP, DHCP, IEEE 802.1D, IEEE
802.1p, and IEEE 802.1Q standards.
Table 93. Switch Specifications and Performance
Feature Details
GC728X 10/100/1000Mbps ports: 24
1G SFP ports: 2
10G/1G SFP+ ports: 2
GC728XP PoE+ 10/100/1000Mbps ports: 24
1G SFP ports: 2
10G/1G SFP+ ports: 2
GC752X 10/100/1000Mbps ports: 48
1G SFP ports: 2
10G/1G SFP+ ports: 2
GC752XP PoE+ 10/100/1000Mbps ports: 48
1G SFP ports: 2
10G/1G SFP+ ports: 2
Flash memory size 8 MB SPI, 256 MB NAND
SRAM size and type 512 MB DDR3 SDRAM
Switching capacity Non-Blocking Full WireSpeed on all packet sizes
Forwarding method Store and Forward
Packet forwarding rate
(per port)
10M:14,880 pps
100M:148,800 pps
1G:1,488,000 pps
10G: 14,880,000 pps
Total packet forwarding rate 68.5 Mpps (GC728X and GC728XP)
104.2 Mpps (GC752X and GC752XP)
MAC addresses 16K
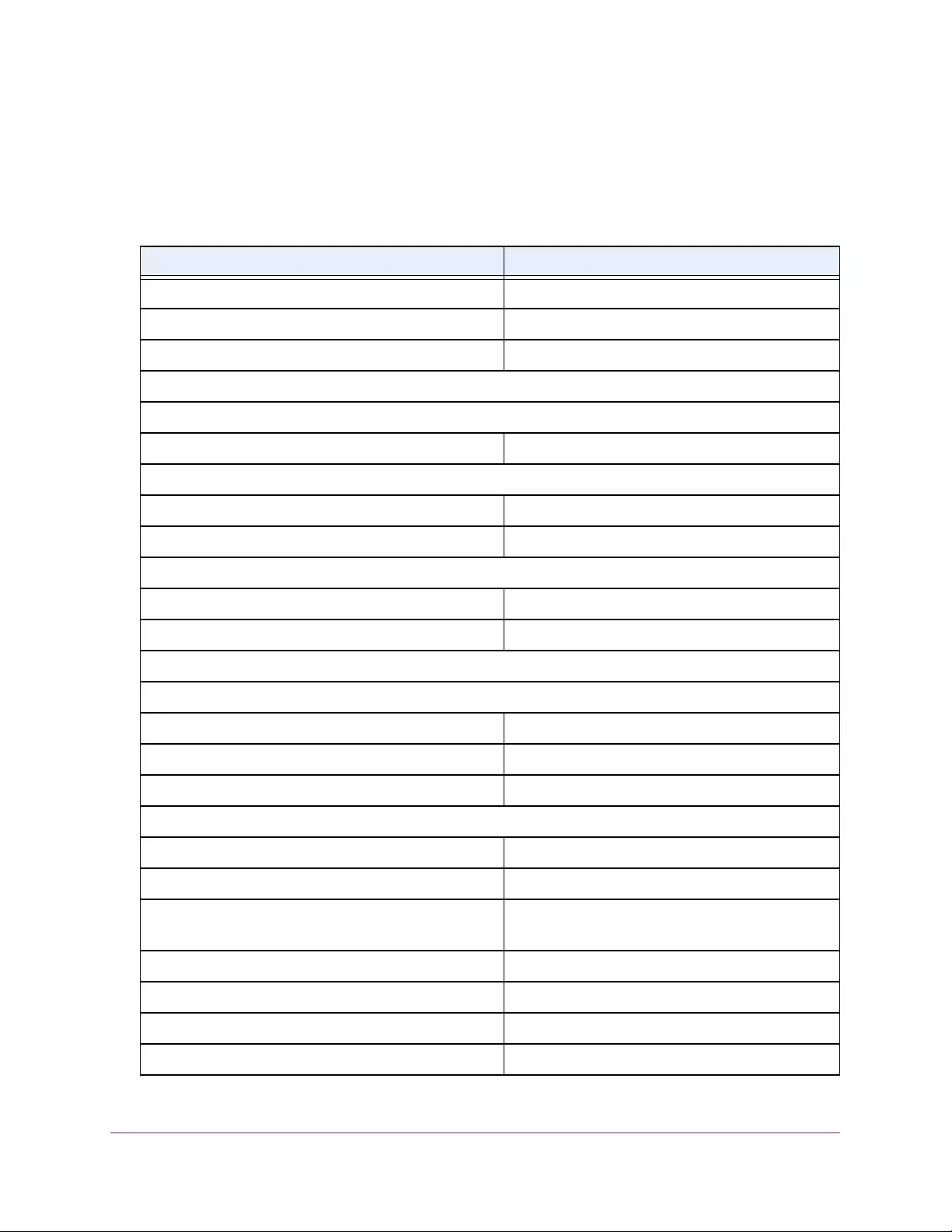
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
422
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Switch Features and Defaults
The tables in this section provide information about the switch features and default values.
Table 94. Feature Default Values and Default State
Feature Name/Parameter Default
Bonjour Enabled
SNMP Disabled
Routing Mode Disabled
DHCP L2 Relay
Global
Admin Mode Disabled
VLAN
Admin Mode Disabled
Circuit ID Mode Disabled
Interface
Admin Mode Disabled
82 Option Trust Mode Disabled
PoE
Global
System Usage Threshold 95%
Power Management Mode Dynamic
Traps Enabled
Interface
Admin Mode Enabled
Port Priority Low
Power Mode Models GC728X and GC752X: None
Models GC728XP and GC752XP: 802.3at
Power Limit Type User
Power Limit (mW) 30000 (mW)
Detection Type IEEE 802
Timer Schedule None
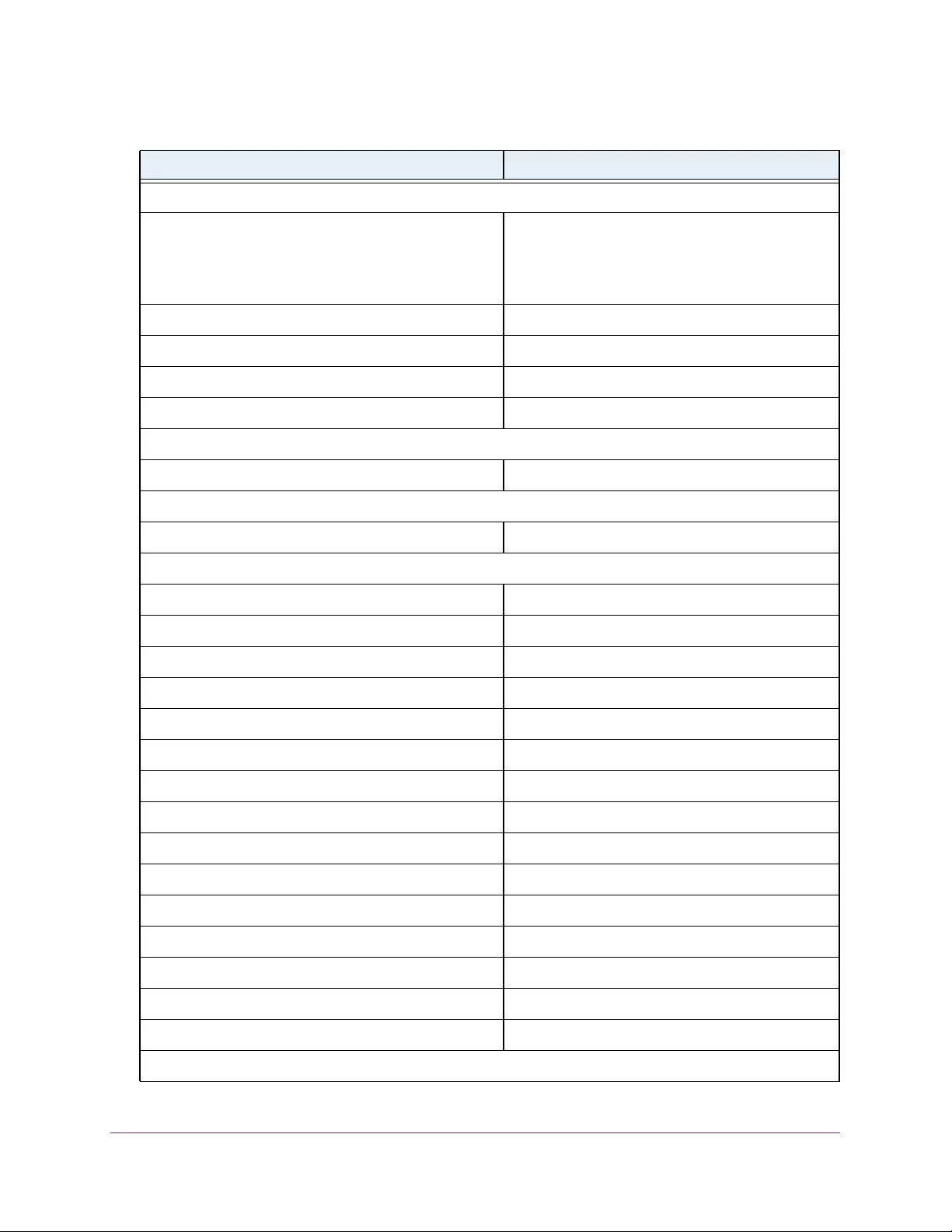
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
423
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Virtual LAN (IEEE 802.1Q)
Default VLANs 1 (Default)
All ports are members of the default VLAN.
4089 (Auto-Video)
No ports are members of the Auto-Video VLAN.
PVID 1
Acceptable Frame Types Admit All
Ingress Filtering Disabled
Port Priority 0
Jumbo Frames
Maximum Frame Size 1518
Flow Control
Admin Mode Disabled
802.1X
Port Based Authentication State Disabled
VLAN Assignment Mode Disabled
Dynamic VLAN Creation Mode Disabled
EAPOL Flood Mode Disabled
Port Control Auto
Guest VLAN ID 0
Guest VLAN Period 90
Unauthenticated VLAN ID 0
Periodic Reauthentication Disabled
Reauthentication Period 3600
Quiet Period 60
Resending EAP 30
Max EAP Requests 2
Supplicant T imeout 30
Server T imeout 30
STP/RSTP/MSTP
Table 94. Feature Default Values and Default State (continued)
Feature Name/Parameter Default
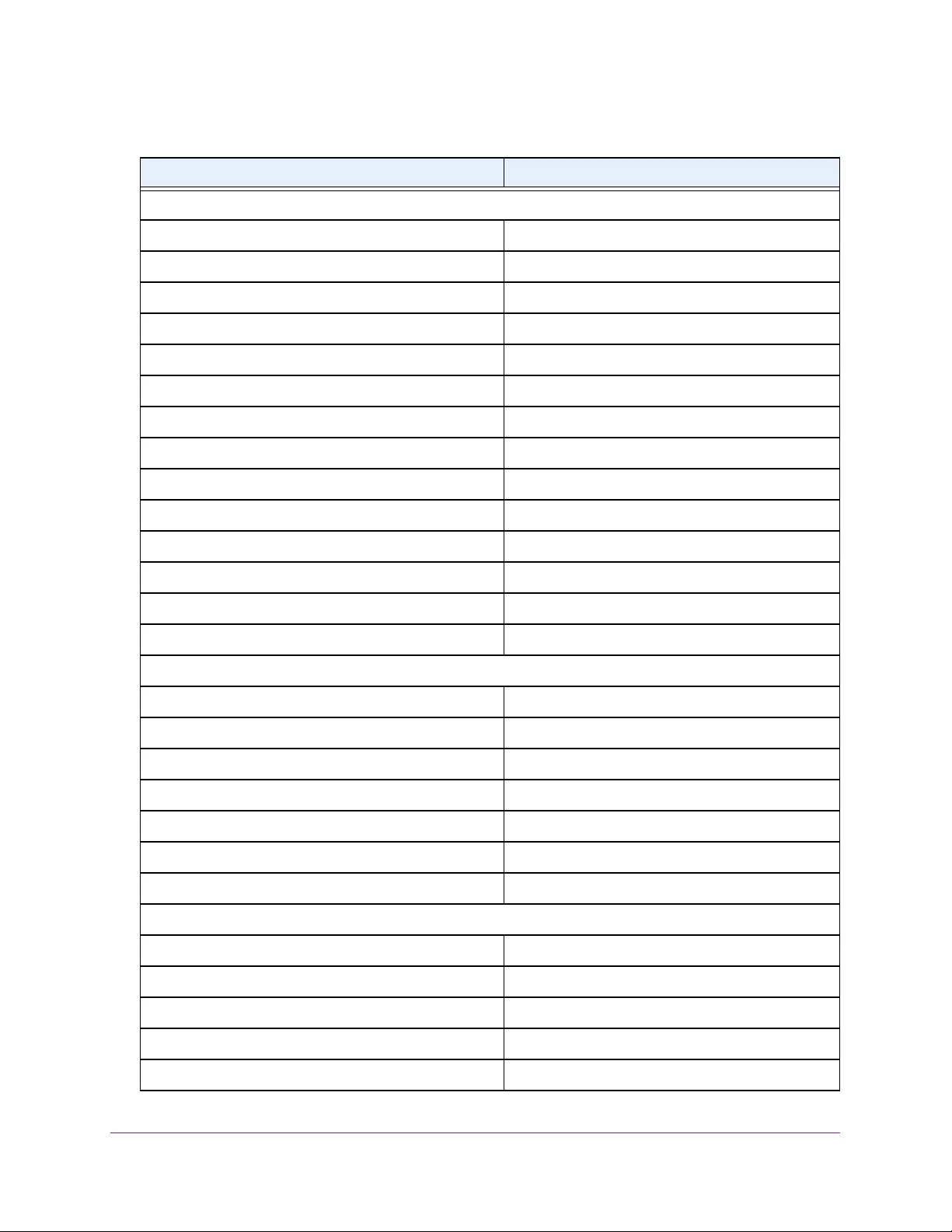
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
424
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Global
Spanning T ree State Disabled
STP Operation Mode RSTP
Configuration Name <MAC address>
Configuration Revision Level 0
Forward BPDU while STP Disabled Disabled
CST Bridge Priority 32768
CST Bridge Max Age 20
CST Bridge Hello Time 2
CST Bridge Forward Delay 15
CST Spanning Tree Max Hops 20
MST Default Instance ID 0
MST Instance 0 Priority 32768
MST Instance 0 VLAN IDs 1,2,3
PV(R)STP UplinkFast Rate 150
Interface
CST STP Status Enabled
CST Auto Edge Enabled
CST Fast Link Disabled
CST BDPU Forwarding Disabled
CST Path Cost 0
CST Priority 128
CST External Path Cost 0
Link Aggregation
Lag Name ch<n> where n is 1 to 24
Admin Mode Enabled
STP Mode Enabled
Link T rap Enabled
LAG Type Static
Table 94. Feature Default Values and Default State (continued)
Feature Name/Parameter Default
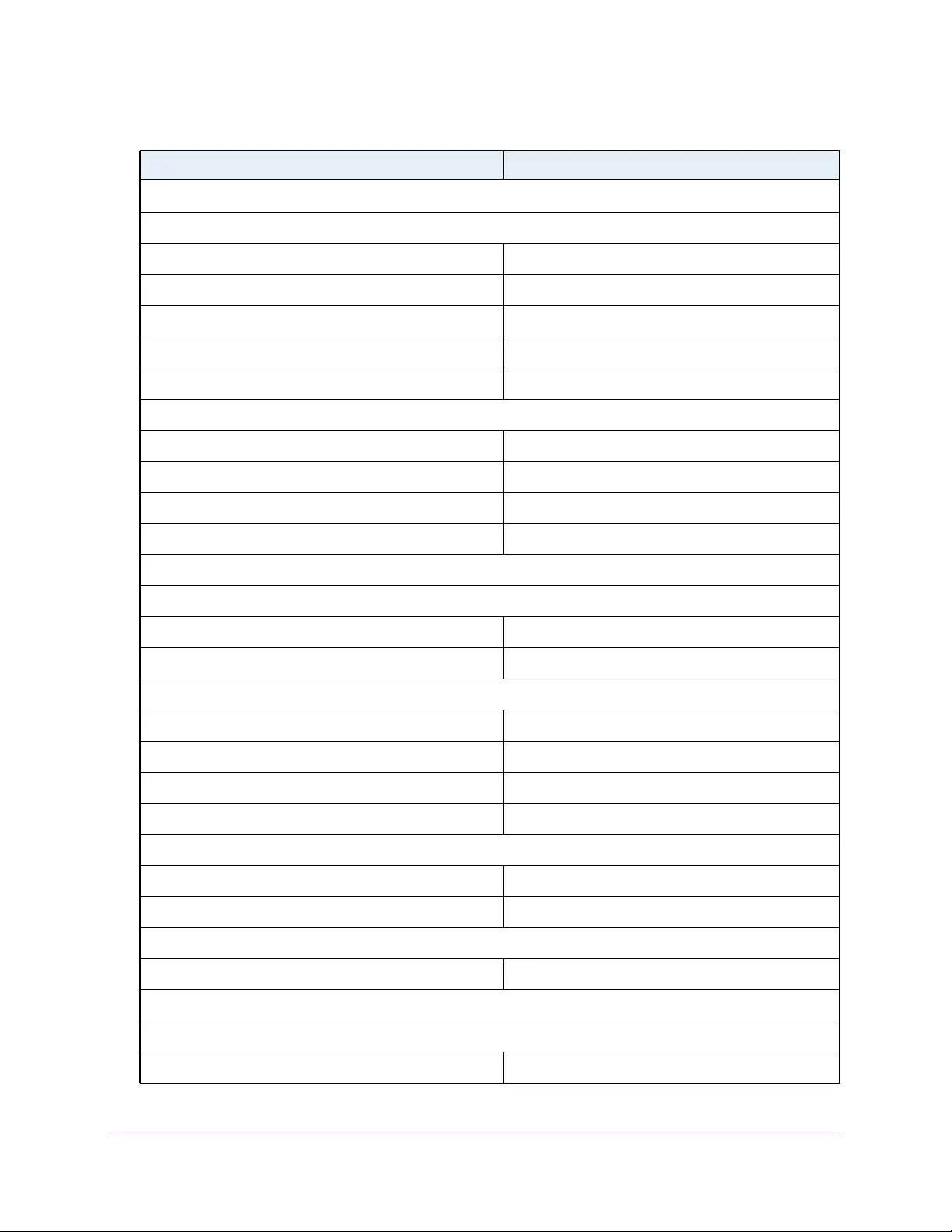
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
425
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Local Link Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
Global
TL V Advertised Interval 30
Hold Multiplier 4
Reinitializing Delay 2
Transmit Delay 5
Fast Start Duration 3
Interface
Admin Status Tx and Rx
Management IP Address Auto Advertise
Notification Disabled
Optional TLVs Enabled
DHCP Snooping
Global
Admin Mode Disabled
MAC Address V alidation Enabled
Interface
Trust Mode Disabled
Logging Invalid Packets Disabled
Rate Limit N/A
Burst Interval N/A
Persistent Configuration
Store Local
Write Delay 300
Differentiated Services
Admin Mode Disabled
Class of Service (CoS)
Global
Trust Mode 802.1p
Table 94. Feature Default Values and Default State (continued)
Feature Name/Parameter Default
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
426
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
802.1p to Queue Mapping (802.1p -> Queue) 0 -> 1
1 -> 0
2 -> 0
3 -> 1
4 -> 2
5 -> 2
6 -> 3
7 -> 3
Class Selector:
(CS 0) 000000 -> 1
(CS 1) 001000 -> 0
(CS 2) 010000 -> 0
(CS 3) 011000 -> 1
(CS 4) 100000 -> 2
(CS 5) 101000 -> 2
(CS 6) 110000 -> 3
(CS 7) 111000 -> 3
Assured Forwarding:
(AF 11) 001010 -> 0
(AF 12) 001100 -> 0
(AF 13) 001110 -> 0
(AF 21) 010010 -> 0
(AF 22) 010100 -> 0
(AF 23) 010110 -> 0
(AF 31) 011010 -> 1
(AF 32) 011100 -> 1
(AF 33) 011110 -> 1
(AF 41) 100010 -> 1
(AF 42) 100100 -> 1
(AF 43) 100110 -> 1
Expedited Forwarding:
(EF) 101110 -> 2
Table 94. Feature Default Values and Default State (continued)
Feature Name/Parameter Default
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
427
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
DSCP to Queue Mapping (DSCP -> Queue)
(continued) Other:
(1) 000001 -> 1
(2) 000010 -> 1
(3) 000011 -> 1
(4) 000100 -> 1
(5) 000101 -> 1
(6) 000110 -> 1
(7) 000111 -> 1
(9) 001001 -> 0
(11) 001011 -> 0
(13) 001101 -> 0
(15) 001111 -> 0
(17) 010001 -> 0
(19) 010011 -> 0
(21) 010101 -> 0
(23) 010111 -> 0
(25) 011001 -> 1
(27) 011011 -> 1
(29) 011101 -> 1
(31) 011111 -> 1
(33) 100001 -> 2
(35) 100011 -> 2
(37) 100101 -> 2
(39) 100111 -> 2
(41) 101001 -> 2
(43) 101011 -> 2
(45) 101101 -> 2
(47) 101111 -> 2
(49) 110001 -> 3
(50) 110010 -> 3
(51) 110011 -> 3
(52) 110100 -> 3
(53) 110101 -> 3
(54) 110110 -> 3
(55) 110111 -> 3
(57) 111011 -> 3
(58) 111010 -> 3
(59) 111011 -> 3
(60) 111100 -> 3
(61) 111101 -> 3
(62) 111110 -> 3
(63) 111111 -> 3
Interface
Trust Mode 802.1p
Table 94. Feature Default Values and Default State (continued)
Feature Name/Parameter Default
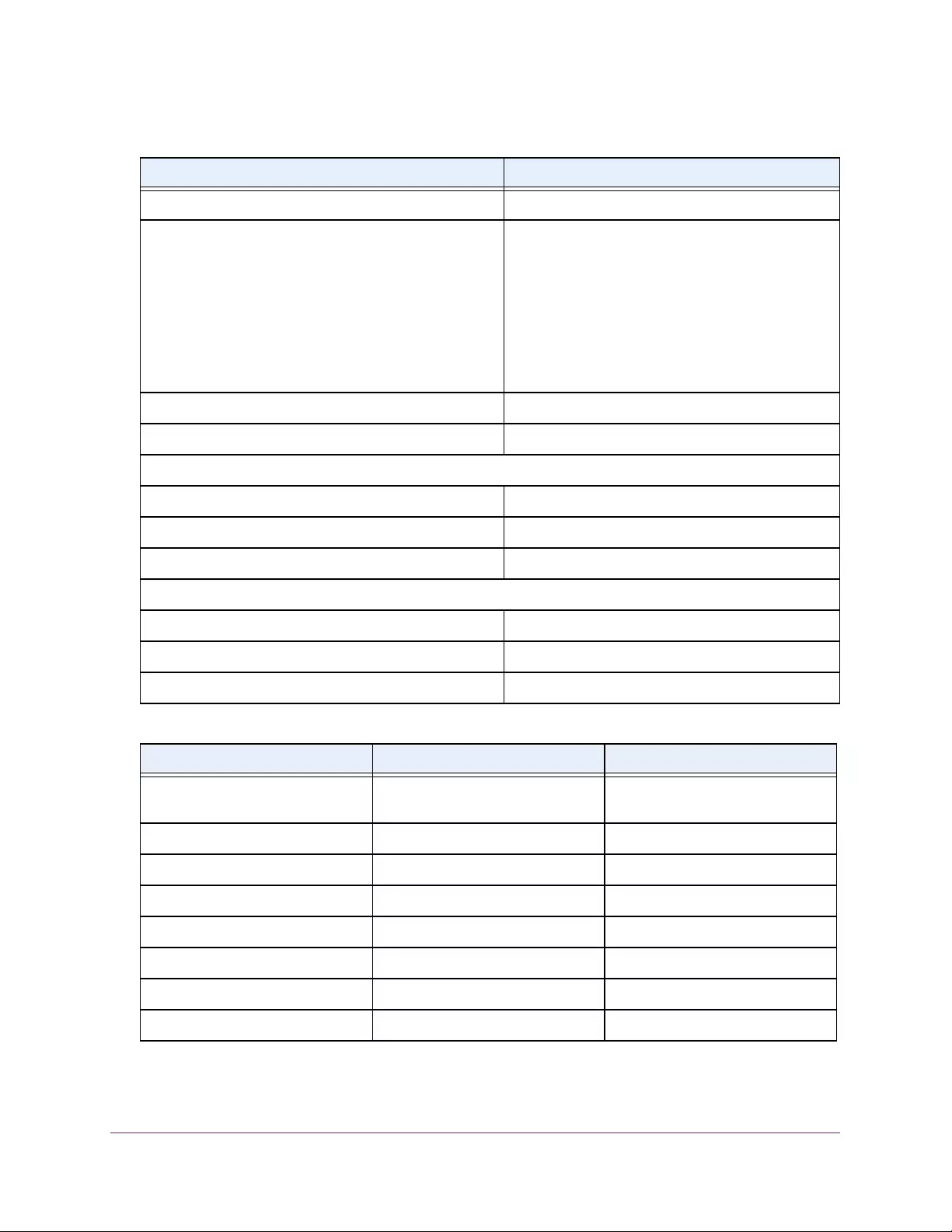
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
428
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Interface Shaping Rate 0
802.1p to Queue Mapping (802.1p –> Queue) 0 -> 1
1 -> 0
2 -> 0
3 -> 1
4 -> 2
5 -> 2
6 -> 3
7 -> 3
Queue Minimum Band Width 0
Queue Scheduler Type Weighted
Auto-VoIP Protocol-based
Admin Mode Disabled
Prioritization Type T raf fic Class
Traffic Class 3
Auto-VoIP OUI-based
Admin Mode Disabled
Auto-VoIP VLAN 2
OUI-based priority 7
Table 95. Port characteristics
Feature Sets Supported Default
Auto negotiating speed and full/half
duplex All ports Auto negotiation
Auto MDI/MDIX for cross over cables on all ports Enabled
802.3x flow control/back pressure 1 (per system) Disabled
Port mirroring: TX, RX, Both 4 Disabled
Port trunking (aggregation) 24 Pre-configured
802.1D spanning tree 1 Disabled
802.1w RSTP 1 Enabled
802.1s spanning tree 24 and 8 MST instances Disabled
Table 94. Feature Default Values and Default State (continued)
Feature Name/Parameter Default
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
429
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Static 802.1Q tagging 256 VID = 1
Max member ports are equal to the
number of ports on the switch.
Learning process Supports static and dynamic MAC
entries Dynamic learning is enabled by
default
Table 96. Traffic control
Feature Sets Supported Default
Storm control All ports Disabled
Jumbo frame All ports Disabled
Max = 9216 bytes
Table 97. Quality of service
Feature Sets Supported Default
Number of queues 7 N/A
802.1p 1 Enabled
DSCP 1 Disabled
Rate limiting All ports Disabled
Table 98. Security
Feature Sets Supported Default
802.1X All ports Disabled
MAC ACL 100 (shared with IP and IPv6 ACLs) All MAC addresses allowed
IP ACL 100 (shared with MAC and IPv6
ACLs) All IP addresses allowed
IPv6 ACL 100 (shared with IP ACL and MAC
ACL) All IP addresses allowed
Password control access 1 Idle timeout = 5 mins.
Password = “password”
Management security 1 profile with 20 rules for
HTTP/HTTPS access to allow/deny
an IP address/subnet
All IP addresses allowed
Port MAC lock down All ports Disabled
Table 95. Port characteristics
Feature Sets Supported Default
Hardware Specifications and Default Values
430
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Table 99. System setup and maintenance
Feature Sets Supported Default
Boot code update 1 N/A
DHCP/manual IP 1 DHCP enabled/192.168.0.239
Default gateway 1 192.168.0.254
System name configuration 1 NULL
Configuration save/restore 1 N/A
Firmware upgrade 1 N/A
Restore defaults 1 (web and front-panel button) N/A
Dual image support 1 Enabled
Factory reset 1 N/A
Table 100. System management
Feature Sets Supported Default
Multi-session web connections 4 Enabled
Time control 1 (Local or SNTP) Local Time enabled
LLDP/LLDP-MED All ports Enabled
Logging 3 (Memory/Flash/Server) Memory Log enabled
MIB support 1 Disabled
Statistics N/A N/A
Table 101. Other features
Feature Sets Supported Default
Timer Schedules 100 Type — Absolute
IGMP snooping v1/v2/v3 All ports Enabled on VLAN 1
Configurations upload/download 1 N/A
EAPoL flooding All ports Disabled
BPDU flooding All ports Disabled
Static multicast groups 20 Disabled
Filter multicast control 1 Disabled

Hardware Specifications and Default Values
431
Insight Managed 28-Port and 52-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Cloud Switches
Number of DHCP snooping
bindings 8K N/A
Number of DHCP static entries 1024 N/A
MLD Snooping All ports Enabled on VLAN 1
Protocol and MAC-based VLAN N/A N/A
Table 101. Other features (continued)
Feature Sets Supported Default




