Table of Contents
- GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Chapter 1 Getting Started with Switch Management
- Chapter 2 Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
- Chapter 3 Managing System Settings
- Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Settings
- Chapter 5 Configuring QoS
- Chapter 6 Managing Security
- Chapter 7 Monitoring the Switch
- Chapter 8 Maintenance
- Chapter 9 Online Help
- Appendix A Default Settings
- Index
NETGEAR GS724TP User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for GS724TP by NETGEAR which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

202-10393-01
April 2008
NETGEAR, Inc.
4500 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA
GS700TP Smart Switch
Software Administration
Manual

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
ii
v1.0, April 2008
© 2007 by NETGEAR, Inc. All Rights reserved
Trademarks
NETGEAR and the NETGEAR logo are registered trademarks of NETGEAR, Inc. in the United States and/or other
countries. Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks and Vista is a trademark of Microsoft
Corporation. Other brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to
make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or circuit
layout(s) described herein. Information is subject to change without notice.
Certificate of the Manufacturer/Importer
It is hereby certified that the GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch has been suppressed in accordance with the conditions
set out in the BMPT-AmtsblVfg 243/1991 and Vfg 46/1992. The operation of some equipment (for example, test
transmitters) in accordance with the regulations may, however, be subject to certain restrictions. Please refer to the notes
in the operating instructions.
The Federal Office for Telecommunications Approvals has been notified of the placing of this equipment on the market
and has been granted the right to test the serie s for com pliance with the regulations.
Voluntary Control Council for Interference (VCCI) Statement
This equipment is in the first category (information equipment to be used in commercial and/or industrial areas) and
conforms to the standards set by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Data Processing Equipment and
Electronic Office Machines that are aimed at preventing radio interference in commercial and/or industrial areas.
Consequently, when this equipment is used in a residential area or in an adjacent area thereto, radio interference may be
caused to equipment such as radios and TV receivers.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Compliance Notice: Radio Frequency
Notice
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired oper ation.
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC Rules. These li mit s are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a resident ia l installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accor dance with the instructio ns, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
iii
v1.0, April 2008
determined by turning the equipment of f and on, the user is encoura ged to try to correct the interference by one
or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or reloca te the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
EU Statement of Compliance
The NETGEAR GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch is compliant with the following EU Council Directives: 89/336/
EEC and LVD 73/23/EEC. Compliance is verified by testing to the following standards: EN55022 Class A, EN55024
and EN60950-1.
Canadian Department of Communications Radio Interference Regulations
This digital apparatus (NETGEAR GS700TP Smart Switch) does not exceed the Class A limits for radio-noise
emissions from digital ap paratus as set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communications.
Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique du ministère des Communications
Cet appareil numérique (NETGEAR GS700TP Smart Switch) respecte les limites de bruits radioélectriques visant les
appareils numériques de classe A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique du ministère des
Communications du Canada.
Customer Support
For assistance with installing and configuring your NETGEAR system or for questions or problems following
installation:
• Check the NETGEAR Web page at http://www.NETGEAR.com/support
• Call Technical Support in North America at 1-888-NETGEAR. If you are outside North America, please refer to
the phone numbers listed on the Support Information Card that was included with your switch.
• Email Technical Support at support@NETGEAR.com.
• Defective or damaged merchandise can be returned to your point-of-purchase representative.
Internet/World Wide Web
NETGEAR maintains a World Wide Web home page that you can access at the uniform resource locator (URL) http://
www.NETGEAR.com. A direct connection to the Internet and a Web browser such as Internet Explorer or Netscape are
required.
Warning: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference,
in which case the user may be required to take appropriate measures.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
iv
v1.0, April 2008
FCC Requirements for Operation in the United States
FCC Information to User: This product does not contain any user-serviceable components and is to be used with
approved antennas only. Any product changes or modifications will invalidate all applicable regulatory certifications and
approvals
FCC Guidelines f or Human Exp osure: This equipment compl ies with FCC ra diatio n expo sure li mits set forth fo r
an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed an d operated with a minimum distance of 20 cm
between the radiator and your body. This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
FCC Declaration Of Conformity: We, NETGEAR, Inc., 4500 Great America Parkway, Santa Clara, CA 95054,
declare under our sole responsibility that the model GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch complies with Part 15 of FCC
Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: a) This device may not cause harmful interference and b)
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.”
Product and Publication Details
Model Number: GS700TP
Publication Date: April 2008
Product Family: Smart Switch
Product Name: GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch
Home or Business Prod uct: Business
Language: English
Publication Part Number: 202-10393-01
Publication Version Number: 1.0

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
v
v1.0, April 2008

Contents vi
v1.0, April 2008
Contents
About This Manual
Who Should Use this Book ................................................................................................ x
How to Use This Book ....................................................................................................... x
Conventions, Formats, and Scope ................................................................................... xi
How to Use This Manual ..................................................................................................xii
How to Print this Manual ..................................................................................................xiii
Revision History .. ... ... ................ ... .... ... ... ................ ... .... ... ................ ... .... ... ... ................ ...xiii
Chapter 1
Getting Started with Switch Management
System Requirements ....................................................................................................1-1
Switch Management Interface ......................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ................ .... ... ... ..1-2
Network with a DHCP Server .........................................................................................1-3
Network without a DHCP Server ....................................................................................1-5
Web Access ........... ... ................ ... .... ................ ... ... ................ .... ... ................ ... ... ............1-8
Additional Utilities ............... ... ... ... .... ................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ................ .... ... ... ... ... ............1-9
Chapter 2
Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
Logging Into the NETGEAR Home Screen ....................................................................2-1
Using the NETGEAR Web Management System Options .............................................2-3
Chapter 3
Managing System Settings
Using the System Settings Utility ....................................................................................3-1
Management ................ ................ ................. ................ ................ ................ ................ ..3-1
Device View ....................................................................................................................3-7
PoE .................................................................................................................................3-7
SNMP ...........................................................................................................................3-13
LLDP ............... ................ ................. ................ ................ ................ ................ .............3-33

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
vii Contents
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 4
Configuring Switching Settings
Configuring Switching Settings .......................................................................................4-1
Ports ...............................................................................................................................4-1
LAG ................................................................................................................................4-4
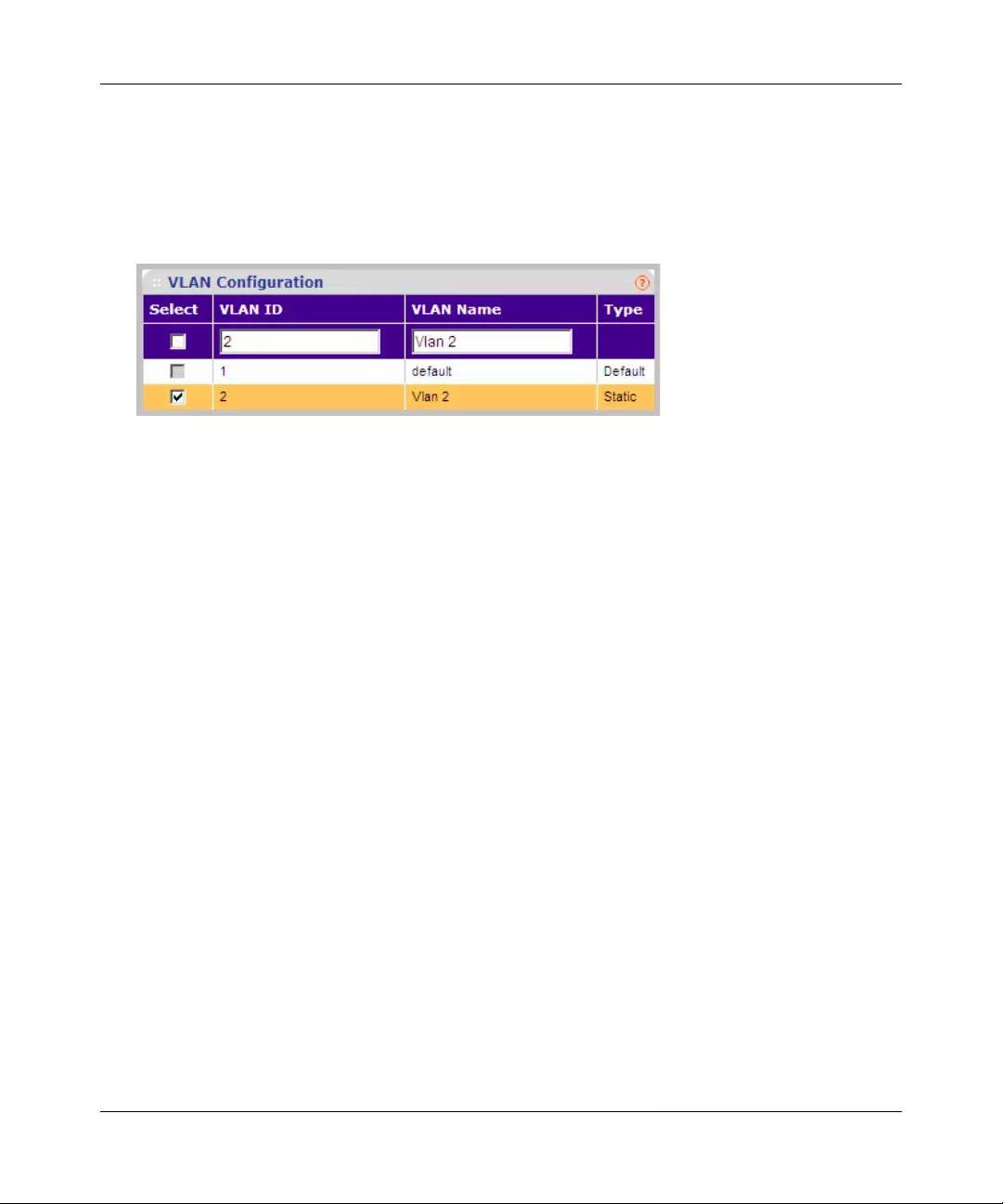
VLAN ............................................................................................................................4-14
Voic e VLAN .... .... ................ ... ................ ... ................ .... ................ ... ................ ... .... ......4-22
STP .............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ......... .............4-29
Multicast .......................................................................................................................4-39
Address Table ...............................................................................................................4-47
Chapter 5
Configuring QoS
Configuring the Basic and Advanced QoS Settings .......................................................5-1
CoS .............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ......... ...............5-1
Chapter 6
Managi ng Sec u ri ty
Setting Security Configuration Options ...........................................................................6-1
Management Security .....................................................................................................6-1
Port Authentication ............. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ................ .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ...............6-9
Traffic Control .............. ................ .... ... ... ... ................ .... ... ... ................ .... ... ... ... .............6-15
ACL .............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ......... .............6-19
Chapter 7
Monitoring the Switch
Setting Monitoring Options .......... .... ... ... ... .... ................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................ ... ..7-1
Logs ................................................................................................................................7-1
RMON ............. ................ ............. ................. ................ ................ ................ ..................7-9
Port Mirroring ............... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................ ... ... ... .... ................ ... ... .... ................ ... ...7-22
Chapter 8
Maintenance
Using the Maintenance Options ............... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..8-1
Reset ..............................................................................................................................8-1
Upload ............................................................................................................................8-3
Download ............... ................ ................ ................ ................ ................. ................ ........8-4
File Management ............................................................................................................8-5
Troubleshooting ..............................................................................................................8-6

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Contents viii
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 9
Online Help
Online Help ............... ... ... .... ... ................ ... .... ................ ... ... ................ .... ... ... ..................9-1
Support ...........................................................................................................................9-1
User Guide ............... ... ... .... ... ................ ... .... ................ ... ... ................ .... ... ................ ... ..9-2
Appendix A
Default Setting s
Index

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
ix Contents
v1.0, April 2008

x
v1.0, April 2008
About This Manual
The NETGEAR® GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual des cribes how to
install, configure, operate, and troubleshoot the GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch using its
included software. This book describes the software configuration procedures and explains the
options available within those procedures.
Who Should Use this Book
The information in this manual is intended for readers with intermediate to advanced system
management skills.
This document was created primarily for the system administrator who wishes to install and
configure the GS700TP Smart Switch in a network. This user guide assumes that the reader has a
general understanding of switch platforms and a basic knowledge of Ethernet and networking
concepts. To install this switch, it is not necessary to understand and use all of its capabilities.
Once basic configuration is performed, the switch operates using the remaining factory default
parameters. However, a greater level of configuration—anywhere from the basic up to the
maximum possible—will allow your network the full benefit of the switch’s features. The web
interface simplifies this configuration at all levels.
How to Use This Book
This document describes configuration commands for the GS700TP Smart Switch software. The
commands can all be accessed from the Web interface.
•Chapter 1, “Getting Started with Switch Management” describes how to use the SmartWizard
Discovery utility to set up your switch so that you can communicate with it.
•Chapter 2, “Introduction to the Web Browser Interface” introduces the Web browser interface.
•Chapter 3, “Managing System Settings” describes how to configure the System functions.
•Chapter 4, “Configuring Switching Settings” describe s how to configure the Switching
functions.
•Chapter 5, “Configuring QoS” describes how to configure QoS functions.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
xi About This Manual
v1.0, April 2008
•Chapter 6, “Managing Security” describes how to configure security.
•Chapter 7, “Monitoring the Switch” describes how to configure switch monitoring.
•Chapter 8, “Maintenance” describes the firmware upgrade procedure and reset functions.
•Chapter 9, “Online Help” describes how to obtain online help and support.
•Appendix A, “Default Settings” gives GS700TP Smart Switch specifications and lists default
feature values.
Conventions, Formats, and Scope
The conventions, formats, and scope of this manual are described in the following paragraphs:
•Typographical Conventions. This manual uses the following typographical conventions:
•Formats. This manual uses the following formats to highlight special messages:
Note: Refer to the product release notes for the GS700TP Smart Switch Software
application level code. The release notes detail the platform specific functionality
of the Switching, SNMP, Config, and Management packages.
Italics Emphasis, books, CDs, file and server names, extensions
Bold User input, IP addresses, GUI screen text
Fixed Command prompt, CLI text, code
italics URL links
Note: This format is used to highlight information of importance or special interest.
Tip: This format is used to highlight a procedure that will save time or resources.
Warning: Ignoring this type of note may result in a malfunction or damage to the
equipment.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
About This Manual xii
v1.0, April 2008
•Scope. This manual is written for the GS700TP Smart Switch according to these
specifications:
.
How to Use This Manual
The HTML version of this manual includes the following:
• Buttons and for browsing forwards or backwards through the manual one page
at a time.
• A button that displays the table of contents and a button. Double-click on a link
in the table of contents or index to navigate directly to where the topic is described in the
manual.
• A button to access the full NETGEAR, Inc. online knowledge base for the product
model.
• Links to PDF versions of the full manual and individual chapters.
Danger: This is a safety warning. Failure to take heed of this notice may result in
personal injury or death.
Product Ve rsion GS700TP Gigabit PoE Sma r t Switch
Manual Publication Date April 2008
Note: Product updates are available on the NETGEAR, Inc. website at
http://www.netgear.com/support.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
xiii About This Manual
v1.0, April 2008
How to Print this Manual
To print this manual, select one of the following options:
•Printing a Page from HTML. Each page in the HTML version of the manual is dedicated to
a major topic. Select File > Print from the browser menu to print the page contents.
•Printing from PDF. Your computer must have the free Adobe Acrobat reader installed in
order to view and print PDF files. The Acrobat reader is available on the Adobe Web site at
http://www.adobe.com.
– Printing a PDF Chapter.
• Click the PDF of This Chapter link at the top left of any page in the chapter you want
to print. The PDF version of the chapter you were viewing opens in a browser
window.
• Click the print icon in the upper left of your browser window.
– Printing a PDF version of the Complete Manual.
• Click the Complete PDF Manual link at the top left of any page in the manual. The
PDF version of the complete manual opens in a browser window.
• Click the print icon in the upper left of your browser window.
Revision History
Tip: If your printer supports printing two pages on a single sheet of paper, you can
save paper and printer ink by selecting this feature.
Part Number Version
Number Date Description
202-10242-02 1.0 May 2007 Product created
202-10242-02 1.0 April 2008

1-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 1
Getting Started with Switch Management
This section provides an overview of switch management, including the methods you can choose
to start managing your NETGEAR GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch . It also leads you through
the steps necessary to get started, using the SmartWizard Discovery utility. The section includes
this information under the following menu options:
•“System Requirements”
•“Switch Management Interface”
•“Network with a DHCP Server”
•“Network without a DHCP Server”
•“Web Access”
•“Additional Utilities”
System Requirements
The following hardware and software facilities are required to run the applications described in
this manual:
• Network facilities:
– Ethernet network with or without DHCP server as appropriate
– Ethernet cable to connect the switch to a PC
• For running the SmartWizard Discovery utility and local or remote Web Management:
– IBM-type PC with CD drive: RAM size and disk specification are not critical
– OS software: Microsoft Windows Vista, Windows XP, or Windows 2000
– Desktop computer running Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or later or Netscape Navigator
6.0 or later, or equivalent.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
1-2 Getting Started with Switch Management
v1.0, April 2008
Switch Management Interface
Your NETGEAR GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch contains an embedded web server and
management software for managing and monitoring switch functions. This switch operates as a
simple switch without using the management software. The management software enables you to
configure more advanced features, and consequently improve switch efficiency as well as overall
network performance.
Web-Based Management enables you to mo nitor, configure, and control your switch remotely
using a common web browser, instead of having to use expensive and complicated SNMP
software products. Simply by using your web browser, you can monitor the performance of your
switch and optimize network configuration. Using your browser, for example, you can set up
VLANs, traffic priority, and configure port trunking.
In addition, NETGEAR provides the SmartWizard Discovery utility with this product. This
program runs under Microsoft Windows XP or Windows 2000 and provides a “front end” that
discovers the switches on your network segment. When you power up your switch for the first
time, the SmartWizard Discovery utility enables you to configure its basic network parameters
without prior knowledge of IP address or subnet mask. Following such configuration, this program
leads you into the Web Management interface.
Some features of the SmartWizard Discovery utility and Web Management interface are shown in
the table below.
Note: For complete hardware installation instructions, refer to the GS700TP Smart
Switch Hardware Installation Manual included on your Resource CD, or go to
http://www.netgear.com/support.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Getting Started with Switch Management 1-3
v1.0, April 2008
For a more detailed discussion of the SmartWizard Discovery utility, continue with this section:
“Network with a DHCP Server” or “Network without a DHCP Server”. For a detailed discussion
of the Web Browser Interface, see Chapter 2, “Introduction to the Web Browser Interface”.
Network with a DHCP Server
To install the switch in a network with a DHCP server, proceed as follows:
1. Connect the GS700TP Smart Switch to a DHCP network.
2. Power on the switch by connecting its AC-DC power adapter.
3. Install the SmartWizard Discovery utility, located on the switch installation CD, on your
computer.
4. Start the SmartWizard Discovery utility.
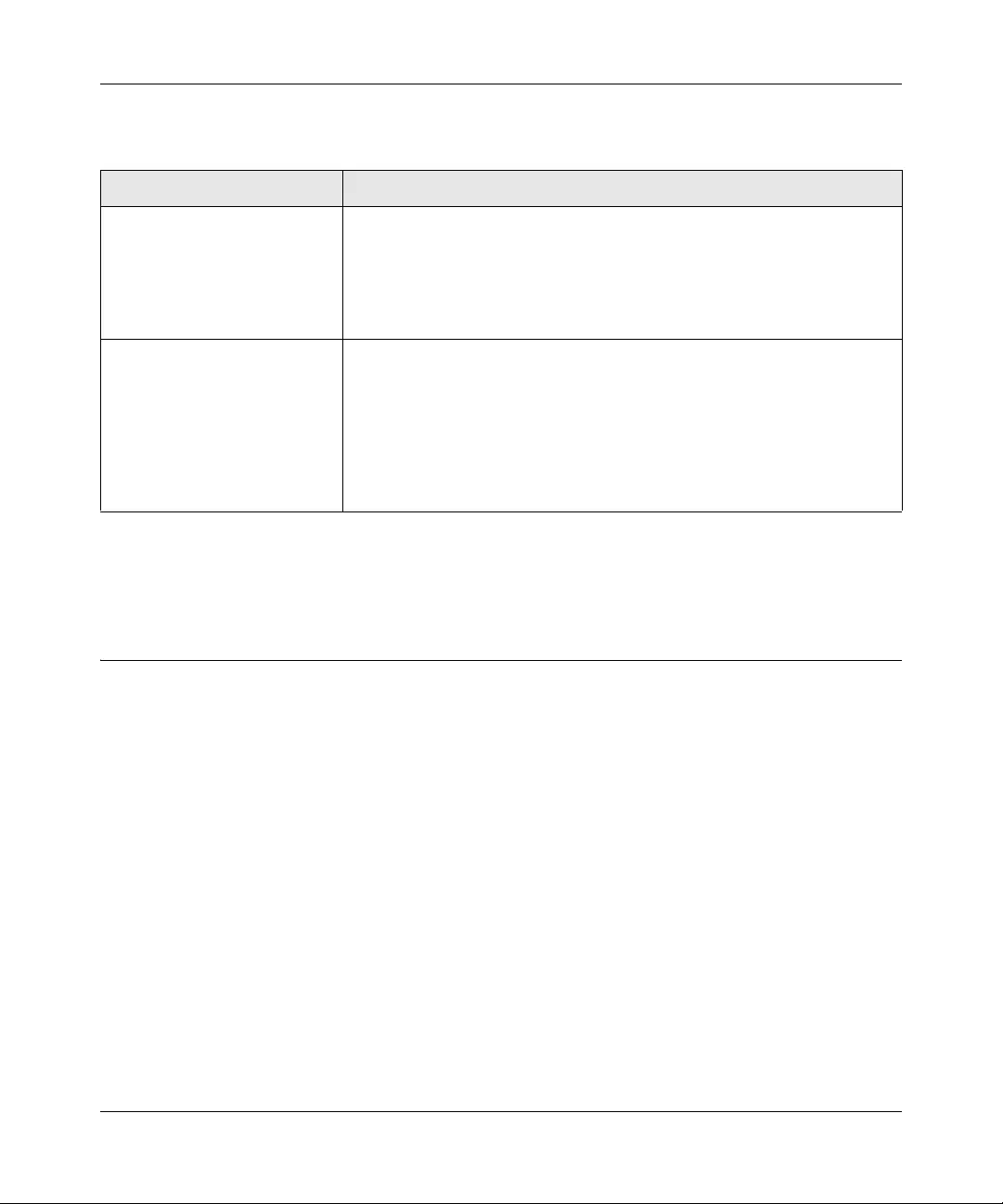
Table 1-1. Switch Management Methods
Management Method Features
SmartWizard Discovery utility No IP address or subnet mask setup needed
Discover all switches on the network
User-friendly interface under Microsoft Windows
Firmware upgrade capability
Password change feature
Provides entry to web configuration of switch
Web browser interface Password protection
Ideal for configuring the switch remotely
Compatible with Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator on any platform
Extensive switch configuration possible
Configuration backup and restore
Can be accessed from any location via the switch’s IP address
Intuitive browser interface
Most visually appealing
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
1-4 Getting Started with Switch Management
v1.0, April 2008
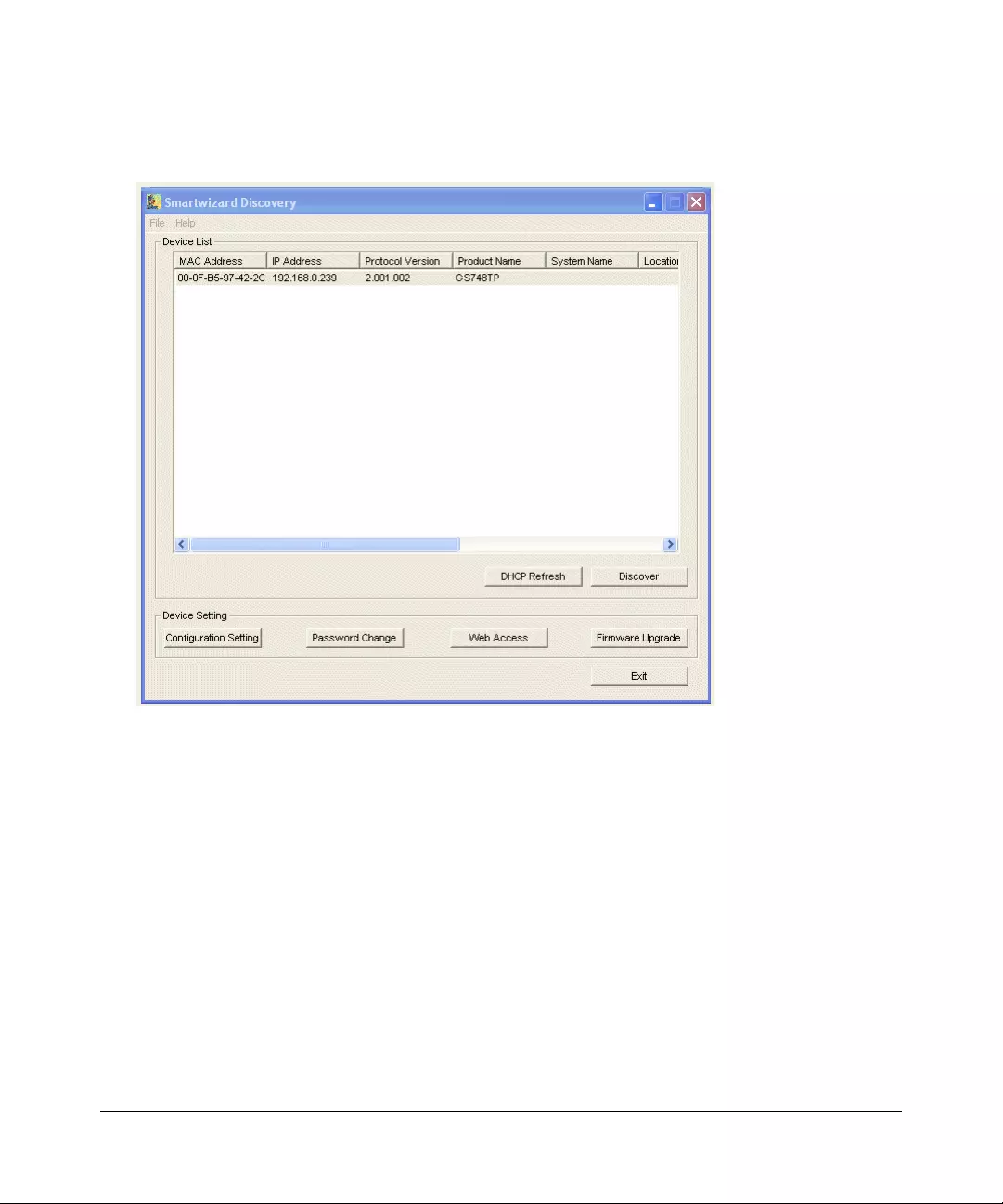
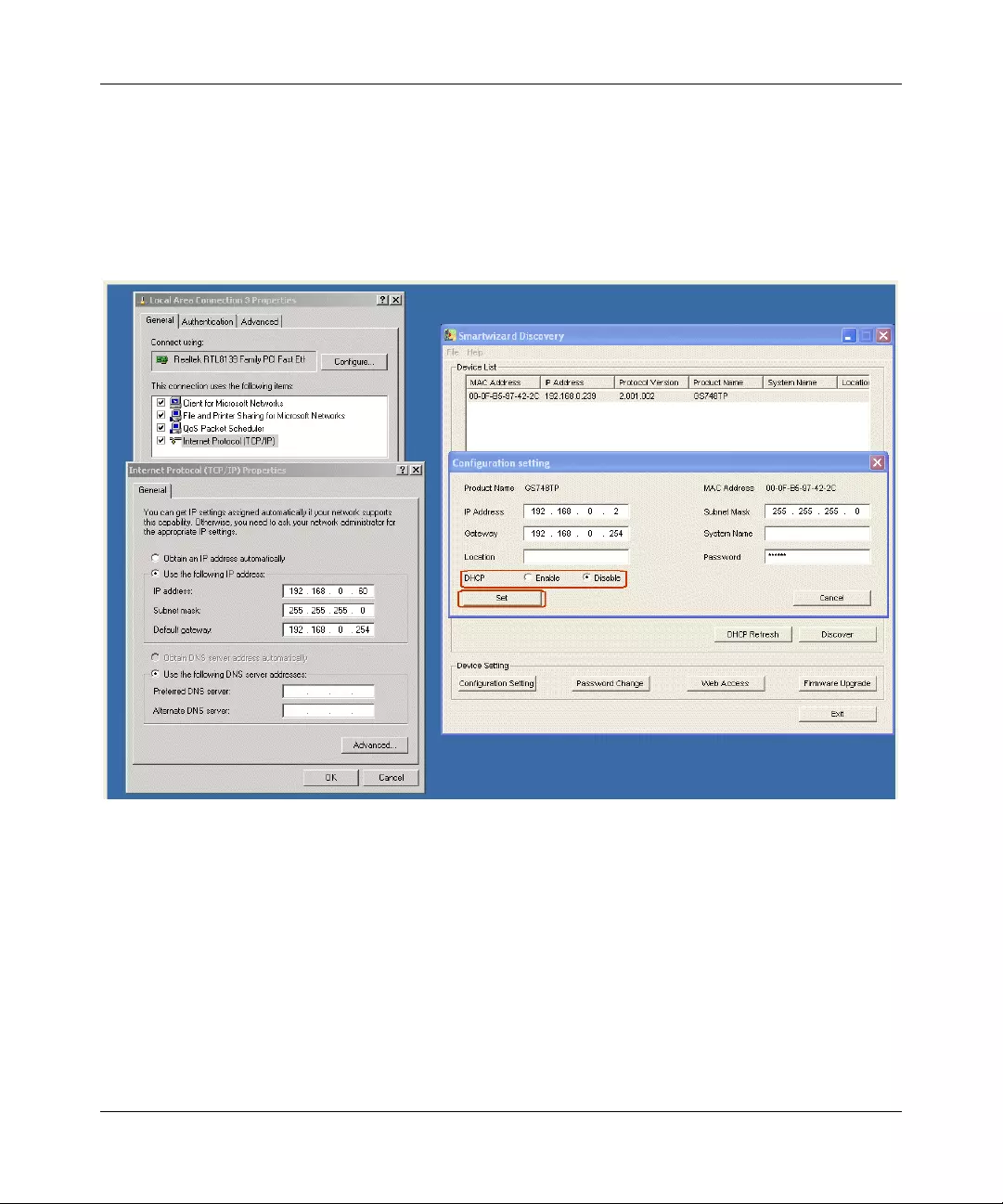
5. Click Discover for the SmartWizard Discovery utility to find your GS700TP Gigabit PoE
Smart Switch. You should see a screen similar to that shown below.
6. Note the displayed IP address assigned by the DHCP server . You will need this value to access
the switch directly from a web browser (without using the SmartWizard Discovery utility).
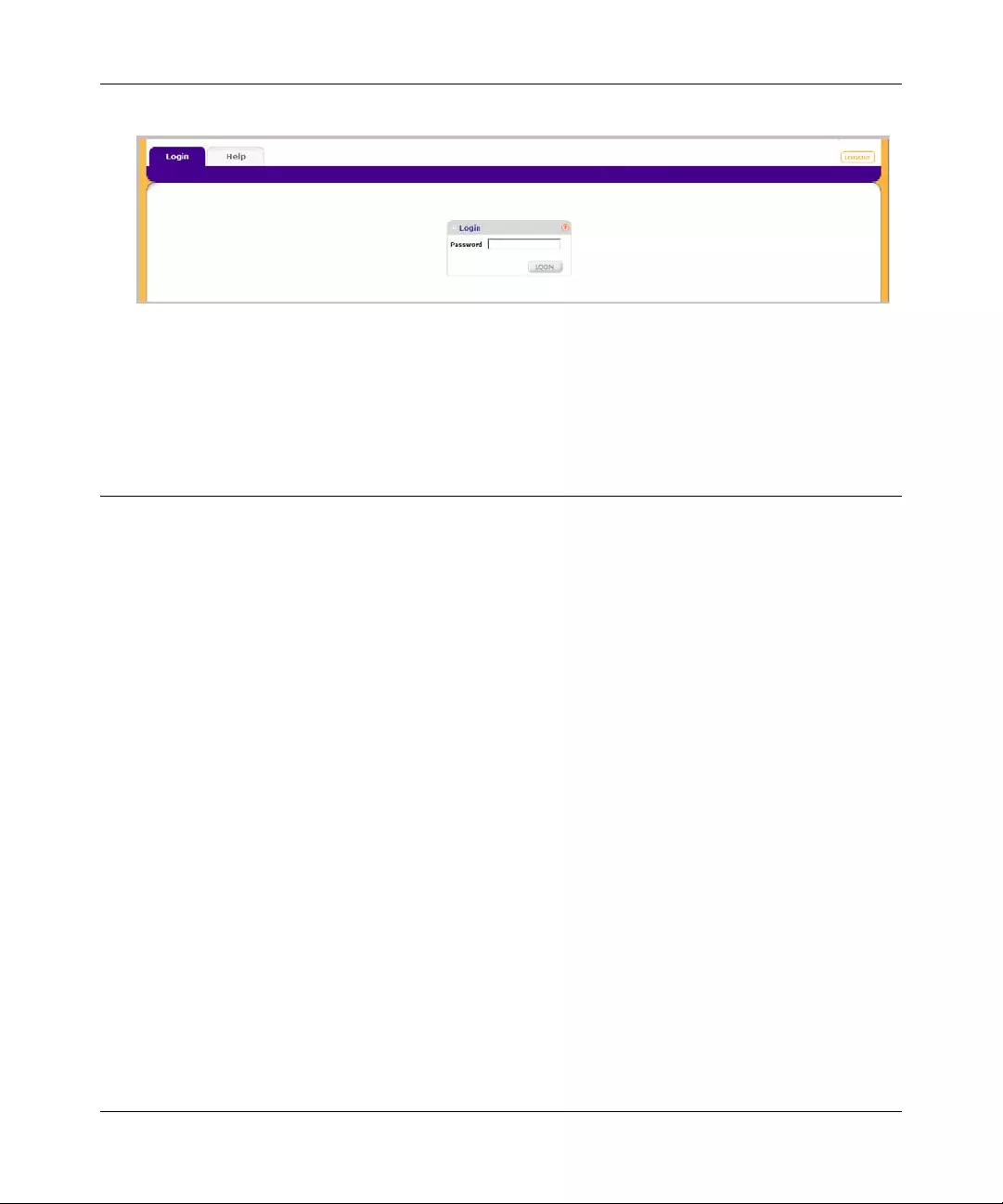
7. Select your switch by highlighting the name of the switch. Then click Web Access. The
discovery utility displays a login window similar to the following:
Figure 1-1
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Getting Started with Switch Management 1-5
v1.0, April 2008
8. Use your web browser to manage your switch. The default password is password. Then use
this screen to proceed to management of the switch covered in Chapter 2, “Introduction to the
Web Browser Interface”.
Network without a DHCP Server
This section describes how to set up your switch in a network without a DHCP server, and is
divided into the following tasks:
• M anually assign network parameters for your switch
• Configure the NIC settings on the host PC
• Log in to the web-based switch management utility
Manually Assigning Network Parameters
If your network has no DHCP service, you must assign a static IP address to your switch. You can
also assign the switch a static IP address even if your network has DHCP service. Proceed as
follows:
1. Connect the GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch to your existing network.
2. Power on the switch by plugging in the AC-DC power adapter. The default IP is
192.168.0.239.
3. Install the SmartWizard Discovery utility on your computer. The SmartWizard Discovery
utility is located on the switch installation CD.
4. Start the SmartWizard Discovery utility.
5. Click Discover for the SmartWizard Discovery utility to find your GS700TP Gigabit PoE
Smart Switch. You should see a screen similar to that shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-2
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
1-6 Getting Started with Switch Management
v1.0, April 2008
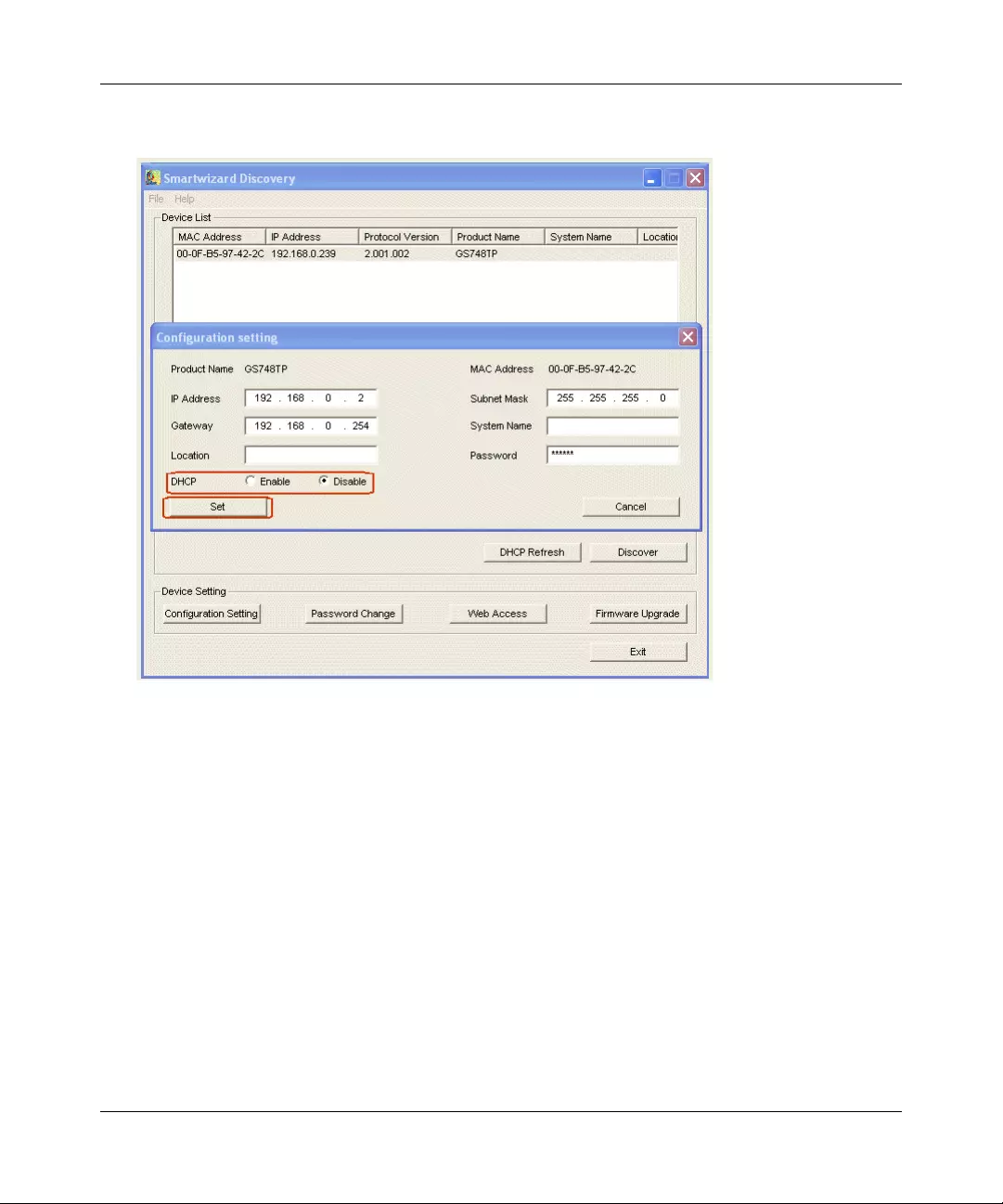
6. Click Configuration Setting. A screen similar to that shown below appears.
7. Select Disable to disable DHCP.
8. The default IP address is 192.168.0.239 and the default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. If you
want different values, enter the switch IP address, gateway IP address and subnet mask.
9. Type your password and click Set. Please ensure that your PC and the GS700TP Gigabit PoE
Smart Switch are in the same subnet. Note the settings for later use.
Figure 1-3
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Getting Started with Switch Management 1-7
v1.0, April 2008
NIC Setting on the Host that Accesses the GS700TP Gigabit PoE
Smart Switch
The settings of your Network Interface Card (NIC) under MS Windows OS are made with entries
into W indows screens similar to the ones shown below. For comparison, the settings screens of the
switch are also shown although they do not appear in the Windows view.
You need Windows Administrator privileges to change these settings.
1. On your PC, access the MS Windows operating system TCP/IP Properties.
2. Set IP address and subnet mask appropriately. The subnet mask value is identical to that set in
the switch. The PC IP address must be different from that of the switch but lie in the same
subnet.
3. Click Web Access in the SmartWizard Discovery utility to enable the management screens as
described in the following section.
Figure 1-4

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
1-8 Getting Started with Switch Management
v1.0, April 2008
Web Access
For Web access, you can either:
• Select Web Access using the SmartWizard Discovery utility (see “Network with a DHCP
Server” or “Network without a DHCP Server”).
• Access the switch directly, without using the SmartWizard Discovery utility.
You must work from the same network segment that contains the switch (i.e., the subnet mask
values of switch and PC host must be the same) and you must point your browser using the switch
IP address. If you used the SmartWizard Discovery utility to set up IP address and subnet mask,
either with or without DHCP server, use that IP address in your browser window.
If you are starting with an “out of the box” switch and are not using the SmartWizard Discovery
utility, you must initially configure your host PC to be on a network segment to match the default
parameters of the switch, which are:
• IP address: 192.168.0.239
• Subnet Mask: 25 5.255.255.0
You can change the network parameters to match those of your network (this procedure is
described in Chapter 3, “Managing System Settings”). Your host PC network parameters must
then be set to match your network.
Clicking Web Access on the SmartWizard Discovery utility or accessing the switch directly
displays the screen shown below.
.
Use this screen to proceed to management of th e switch covered in Chapter 2, “Introduction to the
Web Browser Interface”.
Figure 1-5

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Getting Started with Switch Management 1-9
v1.0, April 2008
Additional Utilities
Alternatively, from the main screen shown on Figure 1-1 you can access these additional
functions:
•“Password Change”
•“Firmware Upgrade”
Password Change
You can set a new password of up to 20 ASCII characters.
1. Click Password Change from the Switch Setting section. The Password Change screen
appears. You can set a new password. You must enter the old and new passwords and confirm
the new one.
2. Click Set to enable the new password.
Firmware Upgrade
The GS700TP Smart Switch soft ware is upgradeable, and enables your switch to take advantage of
improvements and additional features as they become available. The upgrade procedure assumes
that you have downloaded or otherwise obtained the firmware upgrade and that you have it
available as a binary file on your computer. This procedure uses the TFTP protocol to implement
the transfer from computer to switch.
.
Note: You can also upgrade the firmware using the Download menu of the switch (see
“Download”).
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
1-10 Getting Started with Switch Management
v1.0, April 2008
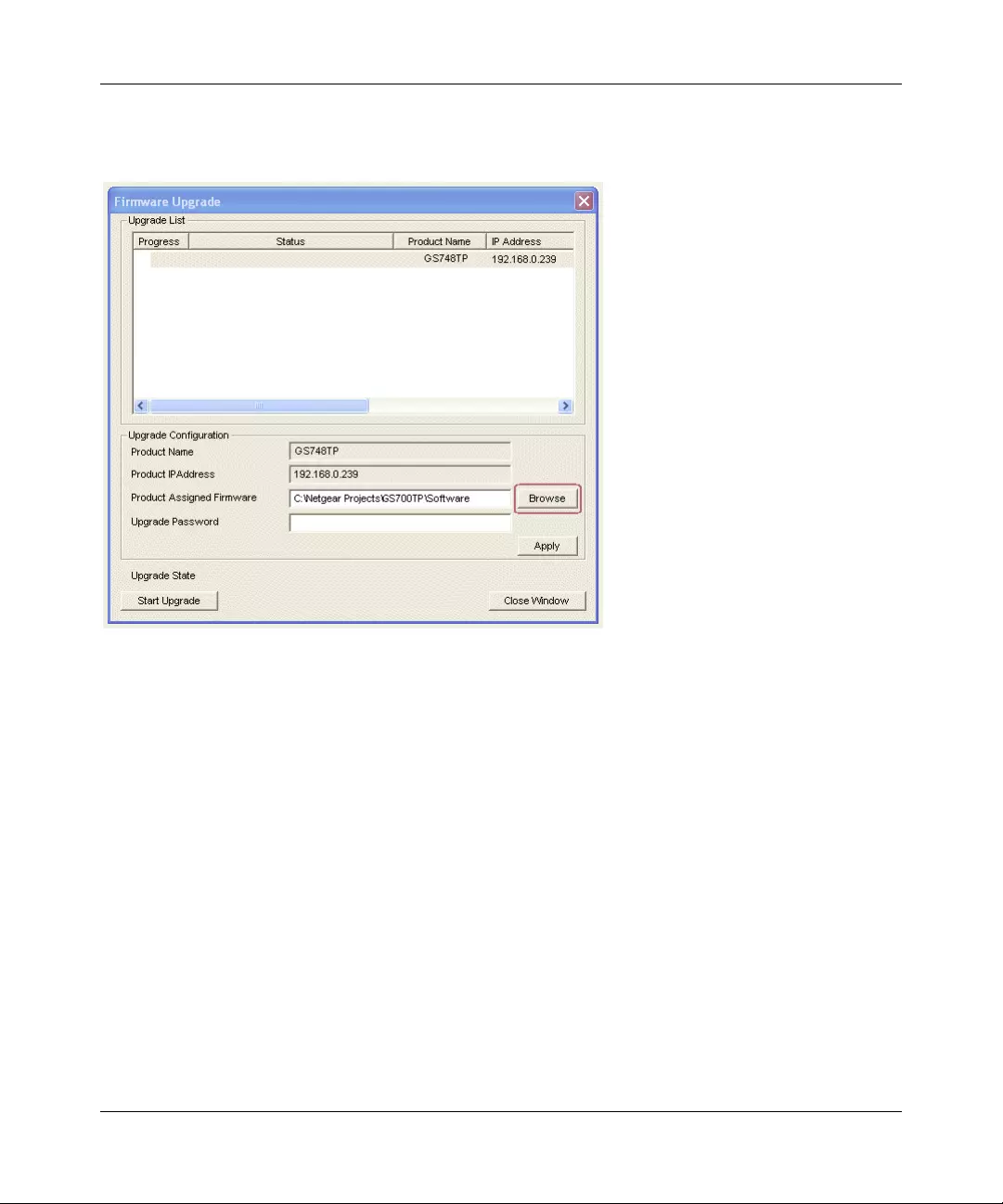
If you click Firmware Upgrade from the main screen (see Figure 1-1), after you have selected the
switch to upgrade, the following screen appears:
1. Enter the following values into the appropriate places in the form:
•Product Assigned Firmware: The location of the new firmware. If you do not know the
location, click Browse to locate the file.
•Upgrade Password: Enter your password; the default password is password.
2. Click Apply to apply the settings to the Upgrade Configuration.
3. Click Start Upgrade to begin loading the upgrade. The system software is automatically
loaded. The Upgrade State field shows upgrading in progress.When the process is complete,
the switch automatically reboots.
Exit
Click Exit from the SmartWizard Discovery screen to close the SmartWizard Discovery utility.
Figure 1-6

2-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 2
Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
This section introduces the web browser interface that enables you to configure and manage your
NETGEAR GS700TP Gigabit PoE Smart Switch. Your GS700TP Smart Swi tch provides a built-in
browser interface that enables you to configure and manage it remotely using a standard Web
browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator. Online Help is also provided
for many of the basic functions and features of the switch.
This section introduces the areas of the browser interface and includes the following topics:
•“Logging Into the NETGEAR Home Screen”
•“Using the NETGEAR Web Management System Options”
Logging Into the NETGEAR Home Screen
Begin your overview of the GS700TP Smart Switch browser interface by logging in:
1. Start the application by one of the following methods, as described in Chapter 1, “Getting
Started with Switch Management”:
a. In the SmartWizard Discovery utility click Web Access.
or
b. In the web browser enter the switch’s IP address and press Enter.
The Login screen appears.
Figure 2-1
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
2-2 Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
v1.0, April 2008
2. Enter the password (the factory default is password) and click Login. The home screen of the
GS700TP Smart Switch browser interface displays.
The Navigation Menu
As shown below, logging in brings you to the view o f the web browser interface.
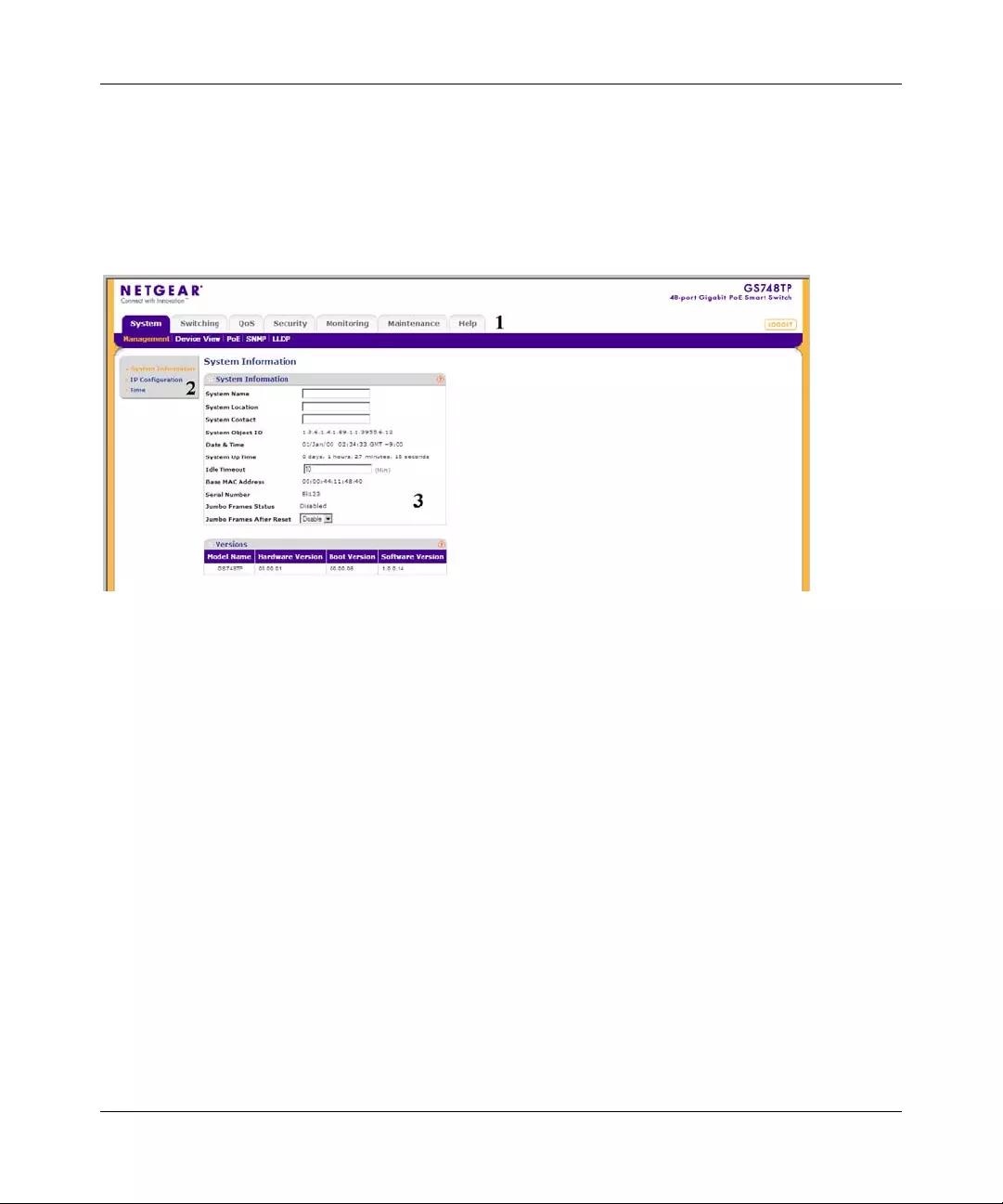
The NETGEAR GS700TP web browser interface contains the following views:
Main Navigation Area – Located on the top of the NETGEAR GS700TP web browser interface
and marked as 1 in Figure 2-2. The Main Navigation Area includes Primary and Secondary
Navigation Bars. The Primary Navigation Bar contains a list of the different features that can be
configured including System, Switching, QoS, Security, Monitoring, Maintenance and Help. Each
feature expands to a subset of features that can be configured as part of the Secondary Navigation
Bar.
Left Navigation Tree – Located on the left side of the NETGEAR GS700TP web browser
interface and marked as 2 in Figure 2-2. For each Secondary Navigation Feature the Left
Navigation Tree contains a subset of features that can be expanded to display all the components.
Work Area – Located on the right side of the NETGEAR GS700TP web browser interface and
marked as 3 in Figure 2-2. The Work Area contains device tables, general device informati on, and
configurable device parameters.
For further description of the functions, refer to the appropriate section of this manual:
•Chapter 3, “Managing System Settings” describes how to configure the System functions.
Figure 2-2

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Introduction to the Web Browser Interface 2-3
v1.0, April 2008
•Chapter 4, “Configuring Switching Settings” describes how to configure the Switch functions.
•Chapter 5, “Configuring QoS” describes how to configure QoS functions.
•Chapter 6, “Managing Security” describes how to configure security.
•Chapter 7, “Monitoring the Switch” describes how to configure monitoring functions.
•Chapter 8, “Maintenance” describes maintenance functions, such as firmware upgrade.
•Chapter 9, “Online Help” describes how to obtain online help and support.
Using the NETGEAR Web Management System Options
The GS700TP web browser interface provides the following options:
•Device Management Buttons – Provides an explanation of the management buttons in the
NETGEAR GS700TP Smart Switch.
•Informational Services – Provides access to informational services including technical
support, online help and device information.
• Using Screen and Table Options – Provides an explanation of specific GUI characteristics
and tables for configuring the device.
Device Management Buttons
The NETGEAR GS700TP Smart Switch web browser GUI management buttons allow network
managers to easily configure the device from remote locations. The management buttons are
shown below:
Table 2-1. Device Management Buttons
Button Name Description
ADD Adds information to tables or information windows.
APPLY Applies configured changes to the device.
CANCEL Cancels modifications to tables or information windows.
CLEAR ALL Refreshes device information.
CLEAR ALL COUNTERS Resets statistics counters.
CLEAR LOGS Clears logs.
CURRENT MEMBERS Displays current members of a LAG.
DELETE Deletes informatio n from tables or information windo ws.
GO Selects the specified interface.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
2-4 Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
v1.0, April 2008
Informational Services
Informational services provide access to technical support, online help and device information and
are displayed in the following topics:
•“Help Naviga tion Tab”
•“Accessing Device Information”
Help Navigation Tab
The Help Navigation Tab provides access to informational services including NETGEAR online
support and an online user guide in PDF format. For a detailed description of how to access and
use these functions, see Chapter 9, “Online Help”.
Accessing Device Information
Each screen of the web browser interface contains a help file with configuration information
relating to the selected screen.
To access the help file for a screen:
1. Click the encircled red Question Mark icon, shown in the example below.
REFRESH Refreshes the screen with current data.
TAGGED PORT MEMBERS Displays tagged port members of a VLAN.
TEST Tests copper cables.
UNTAGGED PORT MEMBERS Displays untagged port members of a VLAN.
Figure 2-3
Table 2-1. Device Management Buttons (continued)
Button Name Description

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Introduction to the Web Browser Interface 2-5
v1.0, April 2008
A help window for the screen opens.
Using Screen and Table Options
The NETGEAR GS700TP web browser interface contain s screens and tables for configurin g
devices. This section describes the table options:
•“Selecting an Entry”
•“Adding an Entry”
•“Modifying an Entry”
•“Deleting an Entry”
•“Special Table Options”
Selecting an Entry
To select an entry:
1. Check the entry’s Select box. The selected entry is highlighted and the information appears in
the first row, which contains the editable fields.
Figure 2-4
Figure 2-5
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
2-6 Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
v1.0, April 2008
To select all entries:
1. Check the Select box in the first row to select all entries in the table. Fields that are unique are
grayed out and displayed as read-only fields.
Adding an Entry
An entry may be added to the table by creating a new entry or by duplicating an existing entry.
To add an entry by creating a new entry in the table:
1. Enter the fields for the new entry in the provided fields in the first row.
2. Click ADD to update the device. The new entry is displayed.
Figure 2-6
Figure 2-7
Figure 2-8
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Introduction to the Web Browser Interface 2-7
v1.0, April 2008
Modifying an Entry
An entry may be modified by editing its values in the first row.
To modify an entry:
1. Select the entry to be modified. Its contents are displayed in the first row.
2. Modify the fields in the first row.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
Deleting an Entry
To delete entries from a table:
1. Select the entries to be deleted.
2. Click DELETE to update the device.
Special Table Options
The NETGEAR web browser interface tables have a unique GUI design which includes the
following options:
• Gold Buttons
•Quick Boxes
• Interface Vie w and Selection
Figure 2-9

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
2-8 Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
v1.0, April 2008
Gold Buttons
Gold Buttons provide flexibility in viewing and configuring VLANs/LAGs on a port level. The
following example displays gold button basic usage options.
To view the LAG configuration of the ports:
1. Click anywhere on the ports gold button. The ports panel is displayed:
2. Select the ports to be added as LAG members within the selected LAG by clicking on their
respective boxes.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
Quick Boxes
Quick Boxes provide users with flexibility in configuring VLANs for all ports or LAGs. Clicking
on the quick box toggles between the various options that exist for this field. A quick box appears
to the right of the arrow on the left-hand side of the gold button. The following example displays
quick box basic usage options.
To mark or unmark all ports:
1. Click on the quick box that appears to the left of the Port gold button. A T appears in the
quick box. This sets all ports as Tagged.
Figure 2-10
Figure 2-11

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Introduction to the Web Browser Interface 2-9
v1.0, April 2008
2. Click on the Port gold button to display the ports, which are now all Tagged.
3. Click again on the Port quick box, and a U appears in the quick box and in all the port boxes,
marking the ports as untagged.
4. Click again on the quick box, and the quick box and all the port boxes appear blank, marking
the ports as neither tagged nor untagged.
5. You may click on individual port boxes to toggle their tagged/untagged status.
Figure 2-12
Figure 2-13
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
2-10 Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
v1.0, April 2008
Interface View and Selection
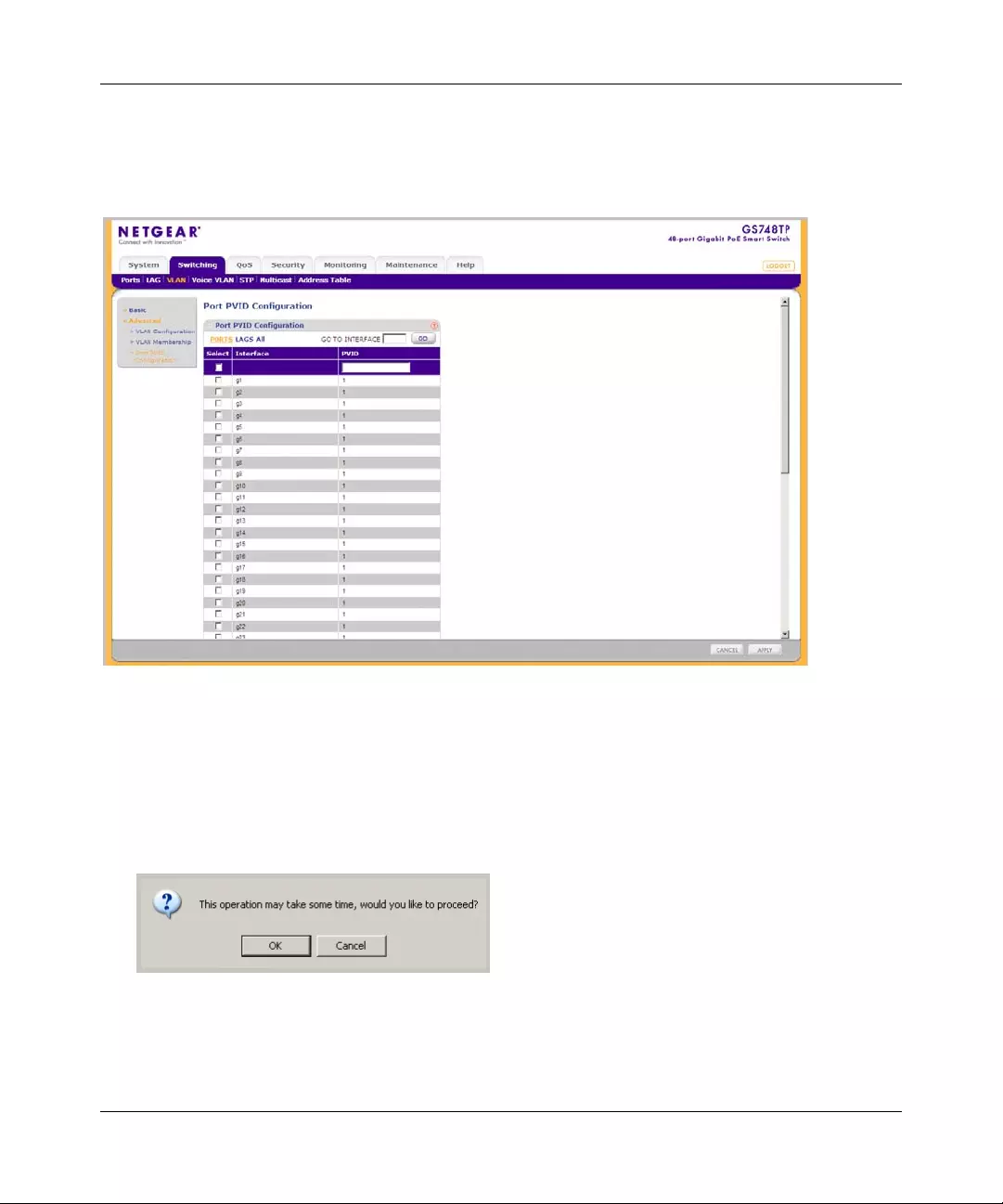
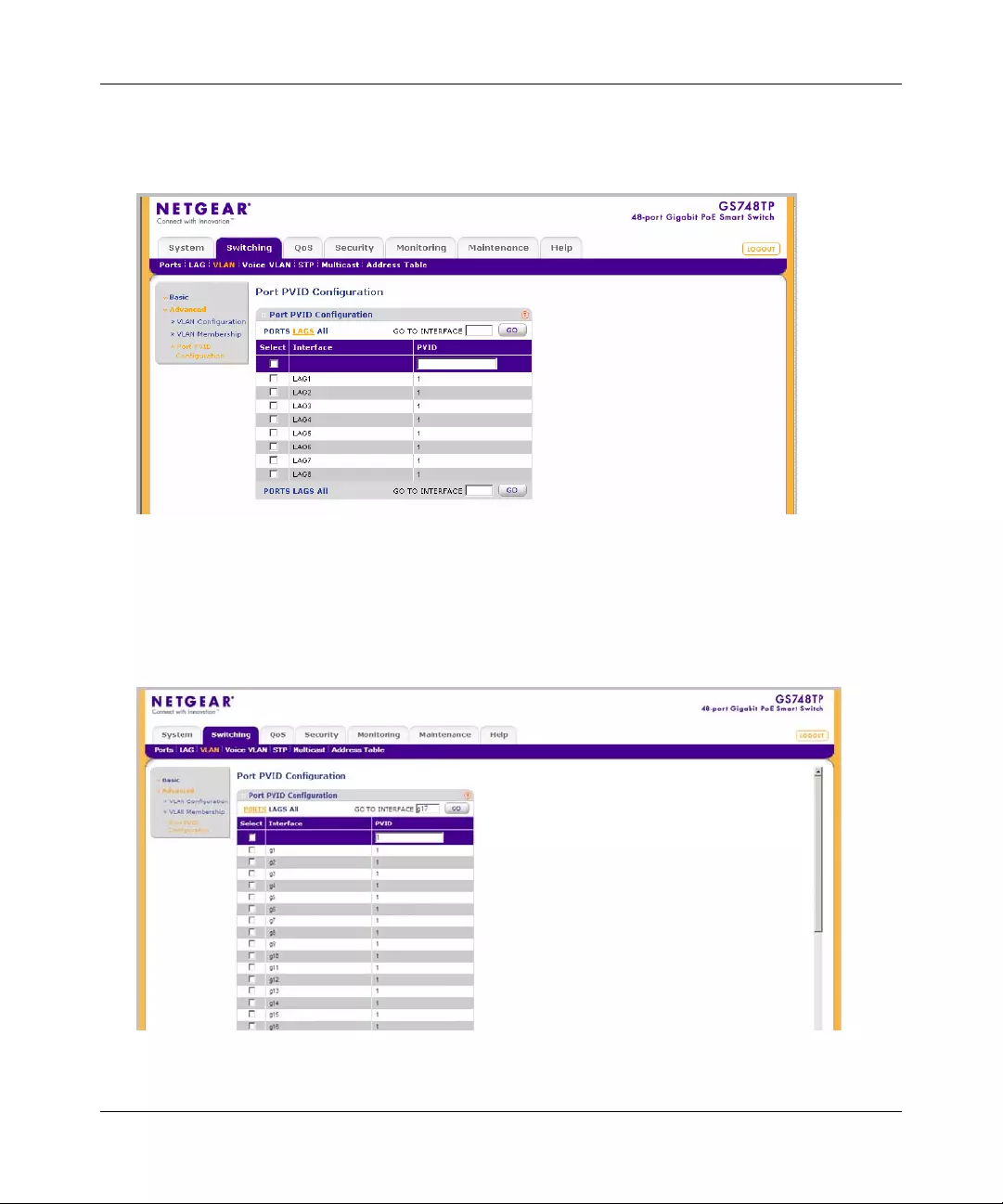
A port or LAG interface may be selected from a table by using the interface selection row, located
above the row of column headers. Clicking on Ports or LAGS displays the ports or the LAGs:
To display all ports:
1. Click Ports in the interface selection row. The screen displays a table of all ports.
To display all interfaces:
1. Click All in the interface selection row. A confirmation window opens.
2. Click OK. The screen displays a table of all interfaces.
Figure 2-14
Figure 2-15
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Introduction to the Web Browser Interface 2-11
v1.0, April 2008
To display the LAG table:
1. Click LAGS in the interface selection row. The screen displays a table of all LAGs.
To select an interface:
1. Enter the number of the interface in the GO TO INTERFACE field.
2. Click GO to select the interface, as in the following example.
Figure 2-16
Figure 2-17

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
2-12 Introduction to the Web Browser Interface
v1.0, April 2008

3-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 3
Managing System Settings
Using the System Settings Utility
The navigation pane at the top of the web browser interface contains a System tab that enables you
to manage your GS700TP Smart Switch with features under the following main menu options:
•“Management”
•“Device View”
•“PoE”
•“SNMP”
•“LLDP”
The description that follows in th is chapter describes configuring and managing system settings in
the GS700TP Smart Switch.
Management
The Management menu en ab les co nfig uration of so me sy stem parameters, the switch IP Address
and the system time, and contains the following options:
•“System Information”
•“IP Configuration”
•“Time”
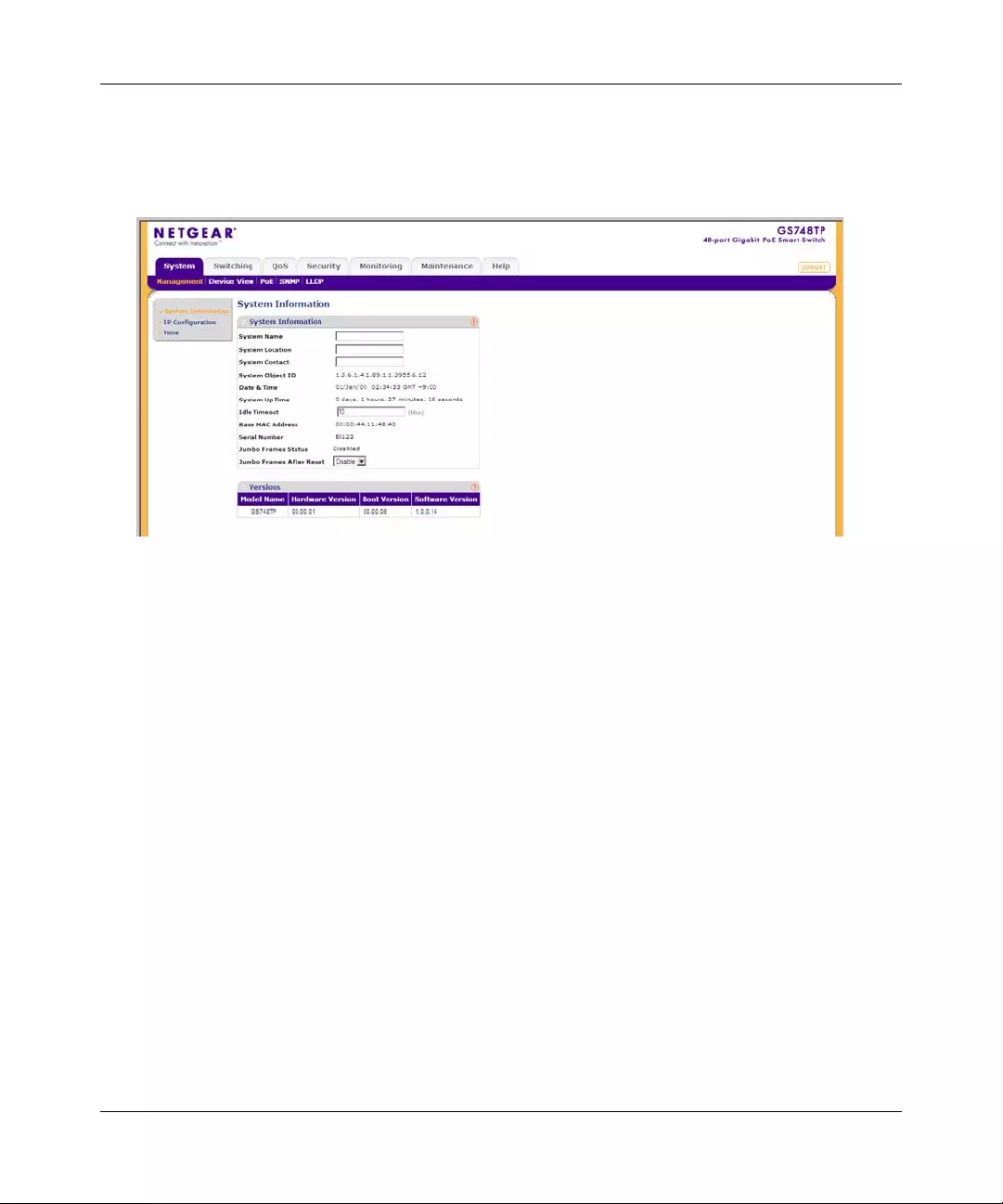
System Information
The System Information screen contains parameters for configuring general device information
including the system name, system location, system contact, and idle timeout.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-2 Managing Syst em Sett ing s
v1.0, April 2008
To configure system parameters:
1. Click System > Management > System Information. The System Information screen
displays:
The System Information screen contains the following fields:
•System Name – Enter the user-defined device name. The field may contain 0-160
characters.
•System Location – Enter the location where the system is currently running. The field
may contain 0-160 characters.
•System Contact – Enter the name of the contact person. The field may contain 0-160
characters.
•System Object ID – Displays the vendor’s authoritative identification.
•Date & Time – Displays the current date and local time.
•System Up Time – Displays the amount of time since the most recent device reset. The
system time is displayed in the following format: da ys, hours, minutes, seconds. For
example, 41 days, 2 hou r s, 22 minutes, 15 seconds .
•Idle Timeout – Enter the amount of time (minutes) that elapses before an idle station is
timed out. Idle stations that are timed out must login to the system. The field range is 5 -
30 minutes. The field default value is 10 minutes.
•Base MAC Address – Displays the MAC address of the device.
Figure 3-1

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-3
v1.0, November 2007
•Serial Number – Displays the device serial number.
•Jumbo Frames Status – Displays the Jumbo Frame status.
•Jumbo Frames After Reset – Select the Jumbo Frame status. The possible field values
are:
– Enable – Enable Jumbo Frames.
– Disable – Disable Jumbo Frames.
The Versions Table displays the following fields:
•Model Name – Displays the device model name.
•Hardware Version – Displays the installed device hardware version number.
•Boot Version – Displays the current boot version running on the device.
•Software Version – Displays the installed software version number.
2. Enter the System Name, System Location, System Contact and Idle Timeout in the
provided fields.
3. Select whether to enable or disable Jumbo Frames After Reset.
4. Click APPLY to update the system settings.
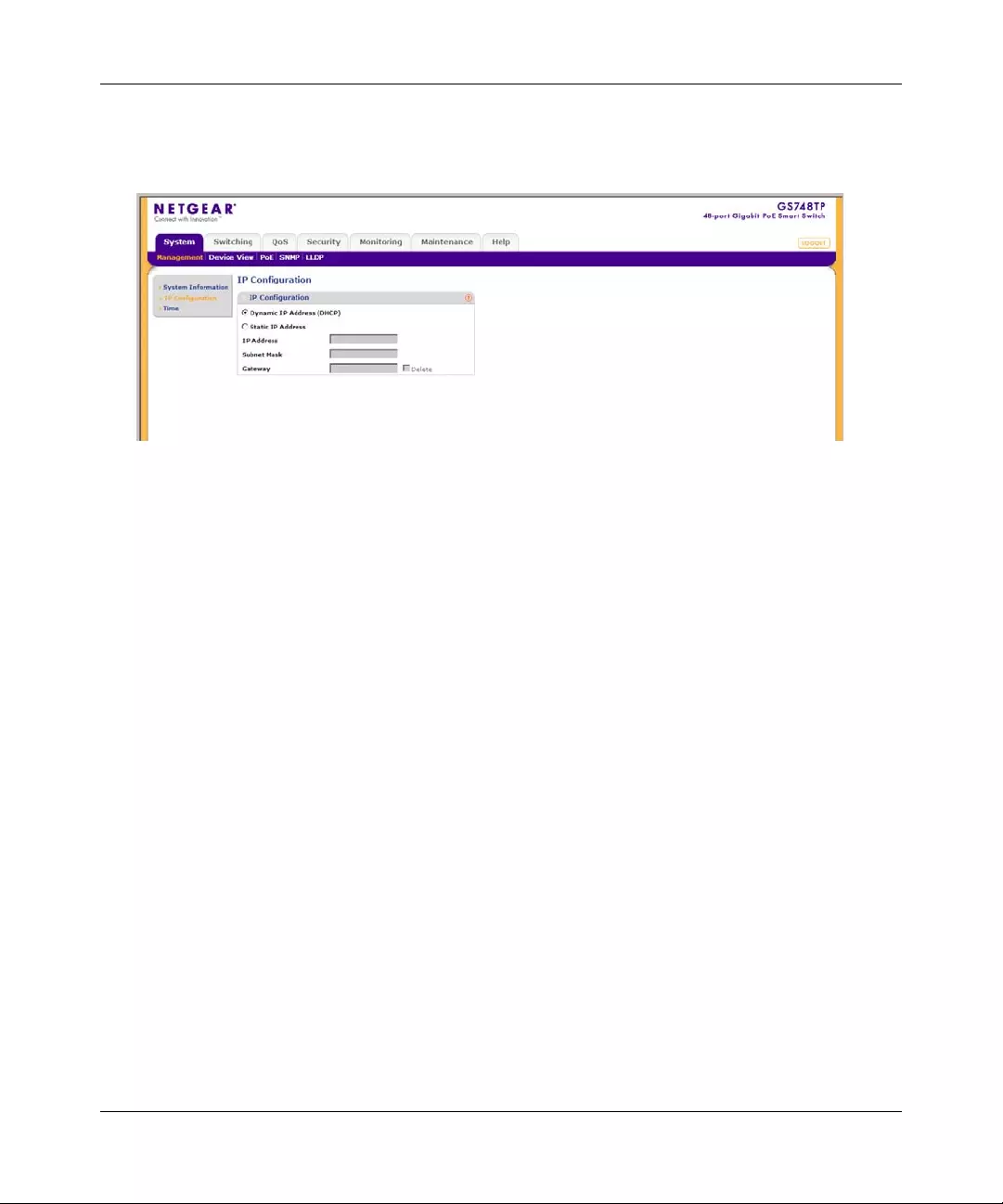
IP Configuration
The IP Configuration screen contains fields for assigning IP addresses. IP addresses are either
defined as static or are retrieved using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). The IP
Interface screen also contains information for defining default gateways. DHCP is also co nfigured
from the IP Interface screen. The DHCP assigns dynamic IP addresses to devices on a network.
DHCP ensures that network devices can have a different IP address every time the device connects
to the network.
Note the following when configuring IP Addresses:
• If the device is accessed using SmartWizard Discovery, the IP address retrieved through
DHCP is displayed.
• If the device fails to retrieve an IP address through DHCP, the default IP address is
192.168.0.239.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-4 Managing Syst em Sett ing s
v1.0, April 2008
To define an IP interface:
1. Click System > Management > IP Configuration. The IP Configuration screen displays:
The IP Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Dynamic IP Address (DHCP) – Enable the IP address to be configured automatically by
the DHCP server. Selecting this field disables the IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway
and Delete fields.
•Static IP Address – Enable the user to define a static IP address.
•IP Address – Enter the static IP address used to manage the device.
•Subnet Mask – Enter the IP address mask.
•Gateway – Enter the default gateway IP address. The following option is available:
–Delete – Delete the default gateway IP address.
2. Select the method of assigning the IP address by selecting either Dynamic IP Address or
Static IP Address.
3. If you selected Static IP Addr ess, enter the IP Ad dress , Subnet Mask and Gateway address
in the provided fields.
4. Click APPLY to update the system settings.
Time
The Time menu enables local system time or SNTP server configuration, and contains the
following options:
•“Time Configuration”
Figure 3-2
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-5
v1.0, November 2007
•“SNTP Server Configuration”
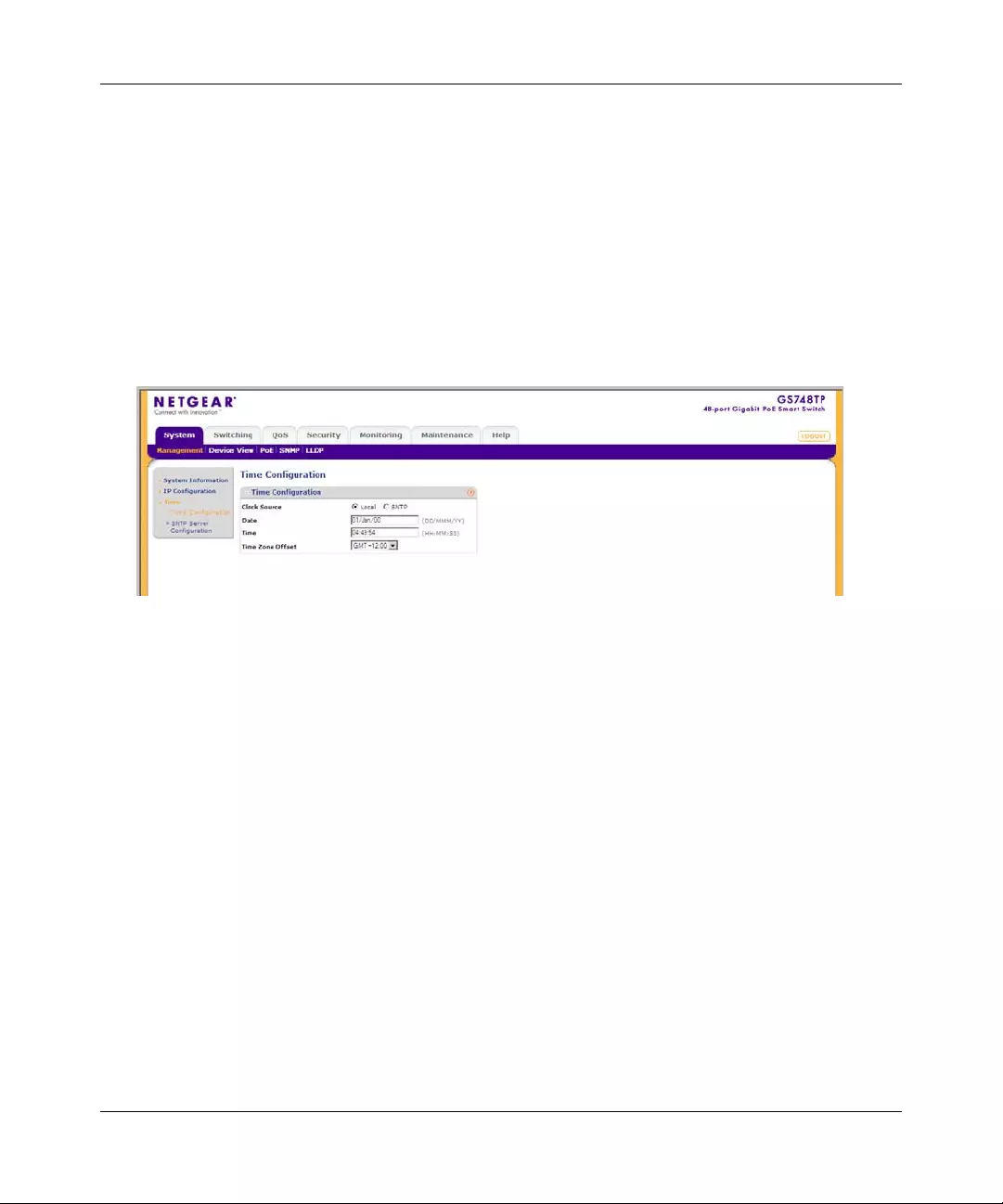
Time Configuration
The Time Configuration screen contains information for defining both the local hardware clock
and the external SNTP clock. If the system time is managed via an external SNTP clock, and the
external SNTP clock fails, the system time reverts to the local hardware clock.
To configure the local system time:
1. Click System > Management > Time > Time Configuration. The Ti me Configuration
screen displays:
The Time Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Clock Source – Select the source used to set the system clock. The possible field values
are:
– Local – The system time is set locally via the Date and Time fields.
– SNTP – The system time is set via an SNTP server. Select SNTP to disable the Date
and Time fields.
•Date – Enter the local system date. The field format is DD/MMM/YY (Day/Month/Year).
For example: 04/May/50 (May 4, 2050).
•Time – Enter the local system time. The field format is HH:MM:SS.
For example: 21:15:03.
•Time Zone Offset – Select the difference between Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and
local time. For example, the Time Zone Offset for Paris is GMT +1, while the Time Zone
Offset for New York is GMT –5.
2. Select the Clock Source by selecting either Local or SNTP.
Figure 3-3
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-6 Managing Syst em Sett ing s
v1.0, April 2008
3. If you selected Local, then enter the local Date and Time in the provided fields.
4. Select the Time Zone Offset from the list.
5. Click APPLY to update the system settings.
Note: If you selected SNTP, you must configure the SNTP servers. See “SNTP Server
Configuration” for detailed instructions on configuring the SNTP servers.
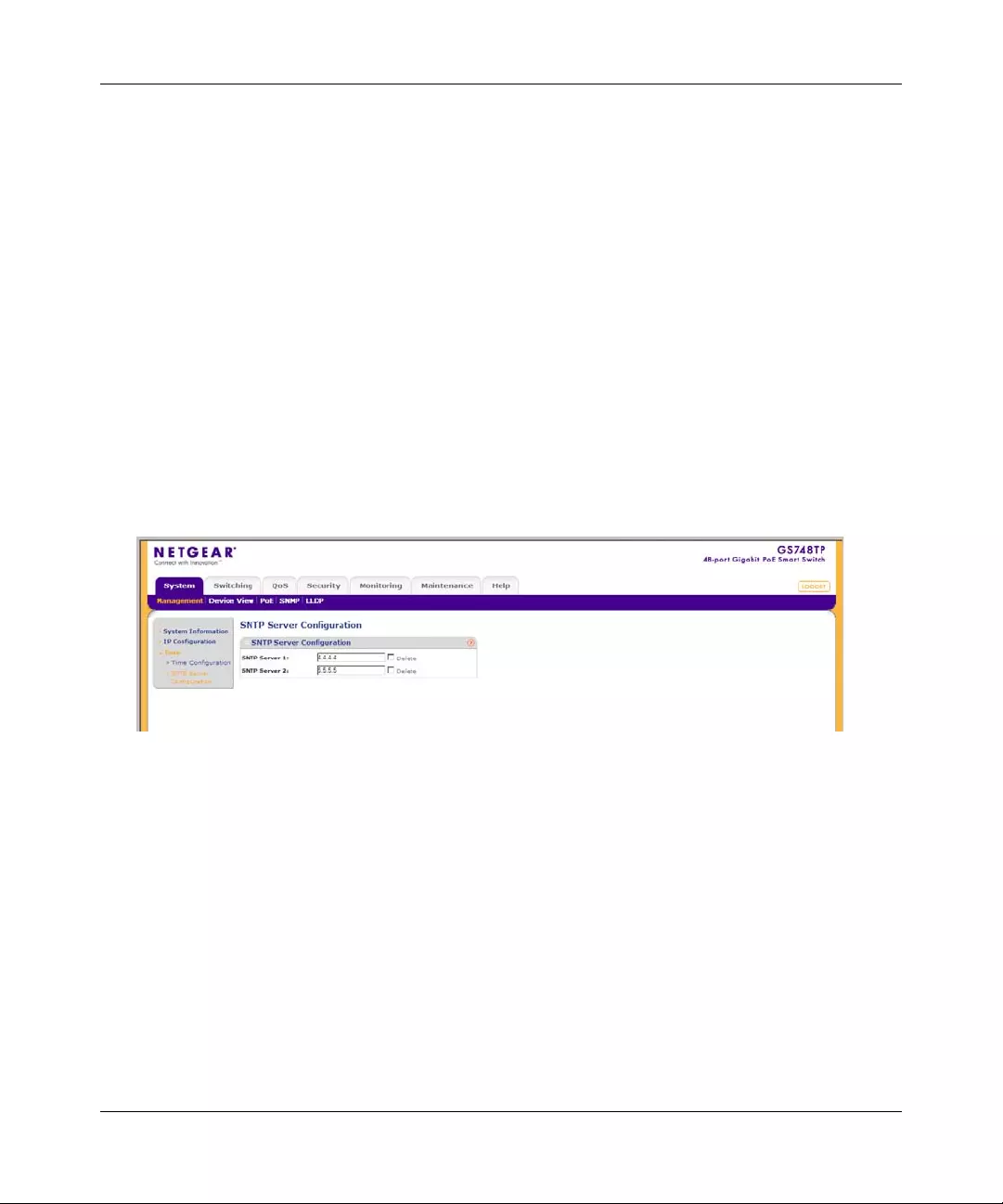
SNTP Server Configuration
The SNTP Server Configuration screen allows network administrators to define primary and
secondary SNTP servers. The system time is first retrieved through the primary SNTP server. If
the device is unable to retrieve the system time through the primary server , the device retrieves the
system time from the secondary server.
To configure SNTP servers:
1. Click System > Management > Time > SNTP Server Configuration. The SNTP Server
Configuration screen displays:
The SNTP Server Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•SNTP Server 1 – Enter the primary SNTP server IP address. The Primary SNTP server is
the first server used to retrieve the system time. The following option is available:
– Delete – Remove the currently configured SNTP Server 1.
•SNTP Server 2 – Enter the secondary SNTP server IP address. The Secondary SNTP
server retrieves the system time if the Primary SNTP server time s out. The following
option is available:
– Delete – Remove the currently configured SNTP Server 2.
2. Enter the SNTP Server 1 and SNTP Server 2 in the provided fields.
Figure 3-4
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-7
v1.0, November 2007
3. Click APPLY to update the system settings.
To remove SNTP servers:
1. Check the Delete box for each SNTP server that is to be removed.
2. Click APPLY to update the system settings.
Device View
The Device View m enu option displays the Device View screen, which provides a graphic
representation of the device, including the port and LED statuses.
To display the Device View screen:
1. Click System > Device View. The Device View screen displays:
PoE
Power over Ethernet (PoE) provides power to devices over existing LAN cabling without updating
or modifying the network infrastructure. This removes the limitation of placing network devices
close to power sources.
Power over Ethernet can be used in the following applications:
• IP Phones
• Wireless Access Points
•IP Gateways
Figure 3-5
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-8 Managing Syst em Sett ing s
v1.0, April 2008
• Audio and video remote monitoring
Powered Devices are devices that receive power from the device power supply, for example IP
phones.
The PoE menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The PoE Basic menu contains the following option:
•“PoE Configuration”
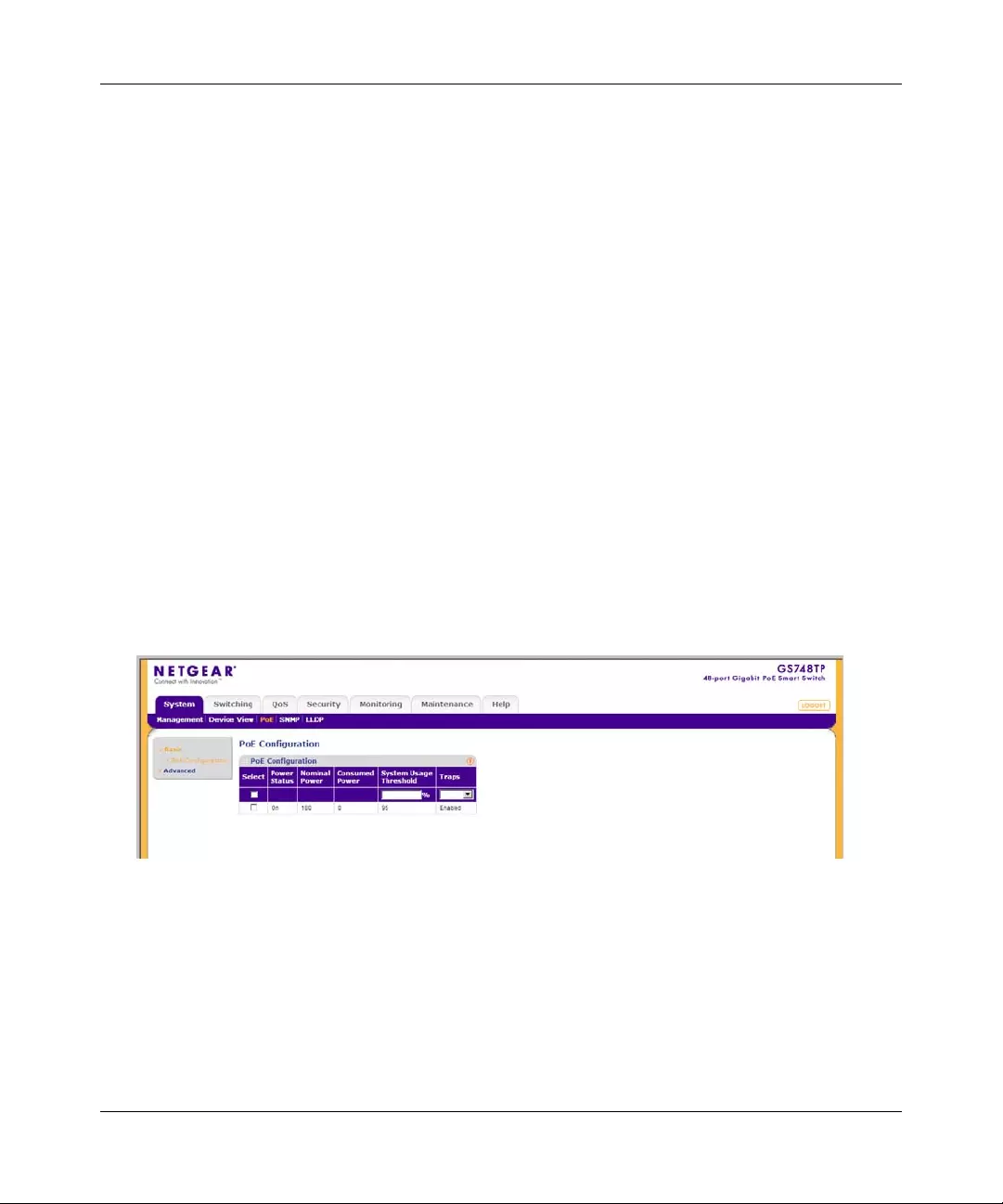
PoE Configuration
The Basic PoE Configuration screen contains system PoE information for enabling PoE on the
device, monitoring the current power usage, and enabling PoE traps.
To configure PoE on the device:
1. Click System > PoE > Basic > PoE Configuration. The Basic PoE Configuration screen
displays:
The Basic PoE Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Power Status – Displa ys the online power source status. The possible field value s are:
– On – The power supply unit is functioning.
– Off – The power supply unit is not functioning.
Figure 3-6

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-9
v1.0, November 2007
– Faulty – The power supply unit is functioning, but an error has occurred. For example,
a power overload or a short circuit.
•Nominal Power – Displays the actual amount of power the device can supply. The field
value is displayed in Watts.
•Consumed Power – Displays the amount of the power used by the device. The field value
is displayed in Watts.
•System Usage Threshold – Enter the percentage of power consumed before an alarm is
generated. The field value is 1-99 percent. The default is 95 percent.
•Traps – Select the PoE device trap state. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable PoE traps on the device.
– Disable – Disable PoE traps on the device. This is the default value.
2. Enter the System Usage Threshold in the provided field.
3. Select either Enable or Disable in the Traps field.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Advanced
The PoE Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“PoE Configuration”
•“PoE Port Configuration”
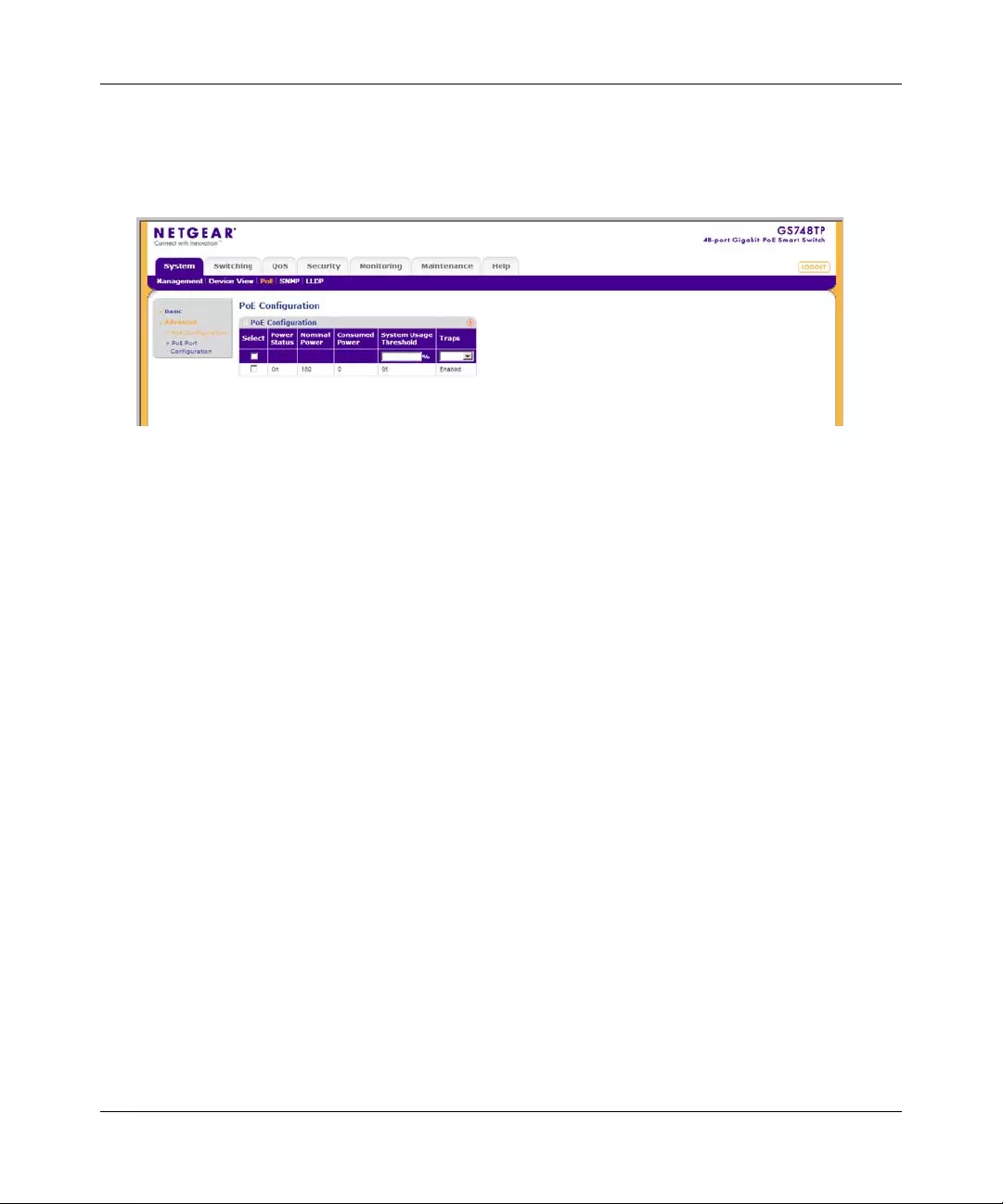
PoE Configuration
The Advanced PoE Configuratio n screen contain s system PoE information for enabling PoE on
the device, monitoring the current power usage, and enabling PoE traps.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-10 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To configure PoE on the device:
1. Click System > PoE > Advanced > PoE Configuration. The Advanced PoE Configuration
screen displays:
The Advanced PoE Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Power Status – Displa ys the online power source status. The possible field value s are:
– On – The power supply unit is functioning.
– Off – The power supply unit is not functioning.
– Faulty – The power supply unit is functioning, but an error has occurred. For example,
a power overload or a short circuit.
•Nominal Power – Displays the actual amount of power the device can supply. The field
value is displayed in Watts.
•Consumed P ower – Displays the amount of the power used by the connecting devices.
The field value is displayed in Watts.
•System Usage Threshold – Enter the percentage of power consumed before an alarm is
generated. The field value is 1-99 percent. The default is 95 percent.
•Traps – Select the PoE device trap state. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable PoE traps on the device.
– Disable – Disable PoE traps on the device. This is the default value.
2. Enter the System Usage Threshold in the provided field.
3. Select the Traps mode from the list in the provided field.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 3-7
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-11
v1.0, November 2007
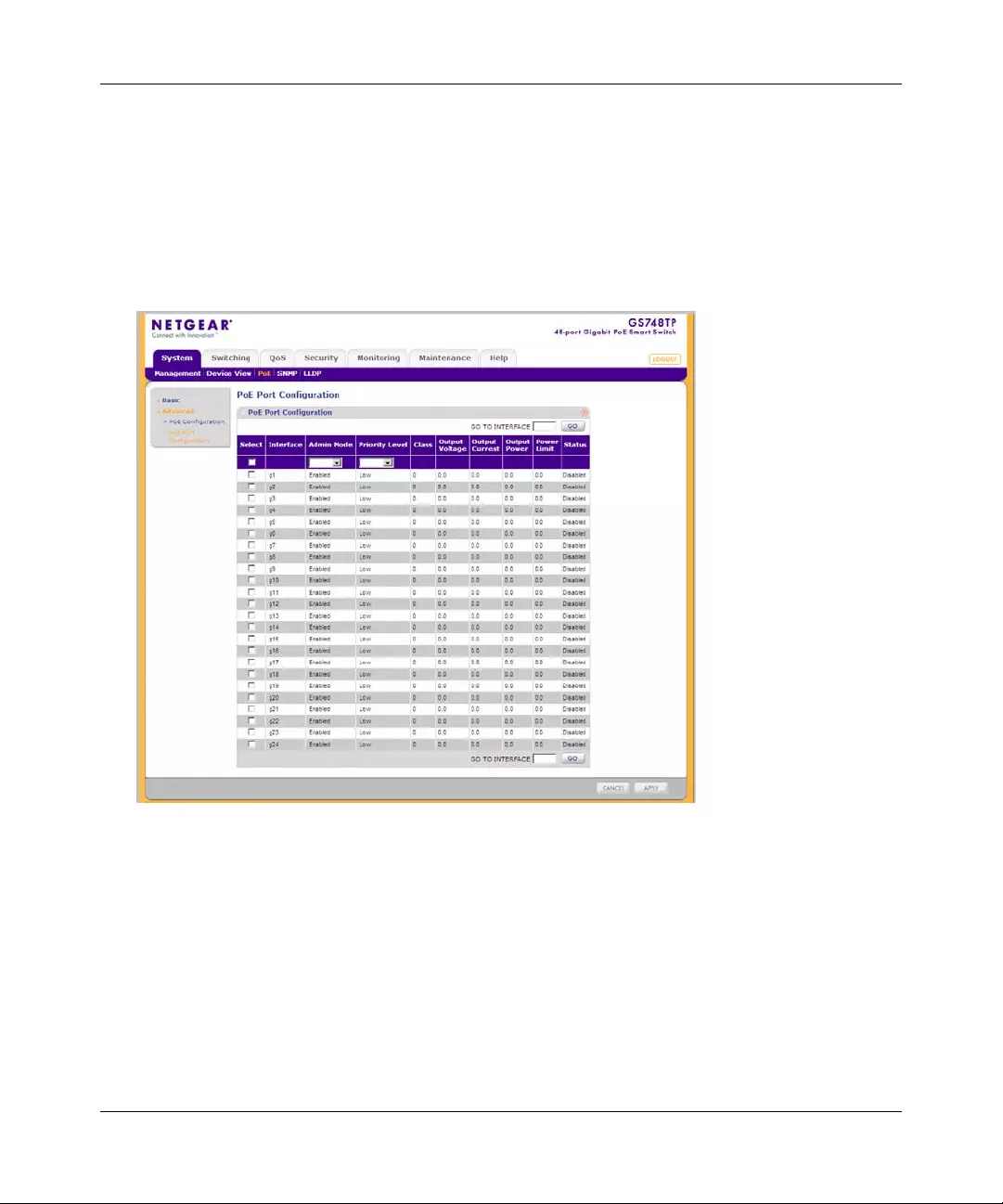
PoE Port Configuration
The PoE Port Configuration screen contains system PoE information for enabling PoE on the
device, monitoring the current power usage, and enabling PoE traps.
To enable PoE on the device:
1. Click System > PoE > Advanced > PoE Port Configuration. The PoE Port Configuration
screen displays:
The PoE Port Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the specific interface for which PoE parameters are defined. PoE
parameters are assigned to the powered device that is connected to the selected interface.
•Admin Mode – Select the device PoE mode. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable the Devic e Discovery protocol and provides power to the device
using the PoE module. The Device Discovery Protocol enables the device to discover
Powered Devices attached to the device interfaces and to learn their classific ation.
This is the default setting.
Figure 3-8

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-12 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
– Disable – Disable the Device Discovery protocol and stops the power supply to the
device using the PoE module.
•Priority Level – Select the port priority if the power supply is low. The field default is
low. For example, if the power supply is running at 99% usage, and port 1 is prioritized as
high, but port 3 is prioritized as low, port 1 is prioritized to receive power and port 3 may
be denied power. The possible field values are:
– Low – Set the PoE priority level as low. This is the default level.
– Medium – Set the PoE priority level as medium.
– High – Set the PoE priority level as high.
•Class – Displays the classification of the powered device. The class defines the maximum
power that can be provided to the powered device. The possible field values are:
– Class 0 – The maximum power level at the Power Sourcing Equipment is 15.4 Watts.
– Class 1 – The maximum power level at the Power Sourcing Equipment is 4.0 Watts.
– Class 2 – The maximum power level at the Power Sourcing Equipment is 7.0 Watts.
– Class 3 – The maximum power level at the Power Sourcing Equipment is 15.4 Watts.
– Class 4 – Treated as Class 0.
•Output Voltage – Displays the Output Voltage in Volts.
•Output Curr ent – Displays the Output current in milliamps.
•Output Power – Displays the Output power in Watts.
•Power Limit – Displays the power limit in Watts.
•Status – Displays the port’s PoE status. The possible field values are:
– Delivering Power – The device is enabled to deliver power via the interface.
– Disabled – The device is disabled for delivering power via the interface.
– Test Fail – The powered device test has failed. For example, a port could not be
enabled and cannot be used to deliver power to the powered device.
– Testing – The powered device is being tested. For example, a powered device is tested
to confirm it is receiving power from the power supply.
– Searching – The device is currently searching for a powered device. Searching is the
default PoE operational status.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-13
v1.0, November 2007
– Fault – The device has detected a fault on the powered device when the port is forced
on. For example, the power supply voltage is out of range, or there is a communication
error with PoE devices, or a sh ort occurs or unknown e rror occurs.
– Other Fault – The device has detect ed a fault on the powered device when the port is
not forced on. For example, a hardware fault occurred, or the system is initializing, or
the port is not responding, or there is an overload or underload, or the power budget is
exceeded or the maximum temperature is exceeded.
2. Select an interface.
3. Select the Admin Mode and Priority Level from the lists in the provided fields in the first
row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides a method for managing network
devices. The device supp orts the following SNMP version s:
• SNMP v1 and v2c
•SNMP version 3
The SNMP agents maintain a list of variables that are used to manage the device. The variables are
defined in the Management Information Base (MIB). The SNMP agent defines the MIB
specification format, as well as the format used to access the information over the network. Access
strings control access rights to the SNMP agents. SNMP v3 applies access control and a new traps
mechanism. In addition, User Security Model (USM) parameters are defined for SNMPv3,
including:
•Authentication – Provides data integrity and data origin authentication.
•Privacy – Protects against the disclosure of message content. Cipher Block-Chaining (CBC) is
used for encryption. Either authentication is enabled on an SNMP message, or both
authentication and privacy. However, privacy cannot be enabled without authentication.
•Timeliness – Protects against message delay or message redundancy. The SNMP agent
compares the incoming message to the message time information. Enter the amount of time
the device waits before re-sending informs.
•Key Management – Enter key generation, key updates, and key usage.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-14 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
The device supports SNMP notification filters based on Object IDs (OIDs). OIDs are used by the
system to manage device features. SNMP v3 supports the following features:
• Security
• Feature Access Control
• Traps. The device generates copy traps.
The SNMP menu contains the following options:
•“SNMPv1/v2”
•“SNMPv3”
SNMPv1/v2
The SNMPv1/v2 menu contains the following options:
•“Community Configuration”
•“Trap Configuration”
Community Configuration
Access rights are managed by defining communities in the Community Configuration screen.
When community names are changed, access rights are also modified.
To configure SNMP communities:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Community Configuration. The Community
Configuration screen displays:
The SNMPv1/v2 Community Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Management Station – Enter the management station IP address for which the Basic
SNMP community is defined.
Figure 3-9

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-15
v1.0, November 2007
•Community String – Enter the SNMP community string used to authenticate the
management station to the device.
•Access Mode – Select the access rights of the community. The possible field values are:
– Read Only – Management access is restricted to read-only. Changes cannot be made
to the device configuration and to the community.
– Read Write – Management access is read-write. Changes can be made to the device
configuration but not to the community.
– SNMP Admin – User has access to all device configuration options, as well as
permissions to mo di fy the community.
2. Select the community entry.
3. Enter the Management Station and Community String in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Select the Access Mode from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new SNMP community:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Community Configuration. The Community
Configuration screen displays.
2. Enter the Management Station and Community String in the provided fields in the first row.
3. Select the Access Mode from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove an SNMP community:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Community Configuration. The Community
Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the entry to be removed.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
Trap Configuration
The SNMPv1/v2 Trap Configuration screen contains information for defining filters that
determine whether traps are sent to specific users, and the trap type sent. SNMP notification filters
provide the following services:
• Identifying Management Trap Targets
• Defining Trap Filtering

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-16 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
• Defining Trap Generation Parameters
• Providing Access Control Checks
To configure SNMPv1/v2 trap station management:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Trap Configuration. The SNMPv1/v2 Trap
Configuration screen displays:
The SNMPv1/v2 Trap Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Recipien ts IP – Enter the IP address to which the traps are sent.
•Notification Type – (Configurable only if the Notification Version is SNMPv2.) Select
the type of notification sent. The possible field values are:
– Traps – Traps are sent.
– Informs – Informs are sent only when SNMPv2 is enabled.
•Community String – Enter the community string of the trap manager.
•Notification Version – Select the trap type. The possible field values are:
– SNMPv1 – SNMP Version 1 traps are sent.
– SNMPv2 – SNMP Version 2c traps are sent.
•UDP Port – Enter the UDP port used to send notifications. The default UDP port is 162.
•Timeout – Enter the amount of time (in seconds) the device waits before re-sending
informs. The default is 15 seconds.
•Retries – Enter the amount of times the device re-sends an inform request. The default is 3
seconds.
2. Select the trap entry.
Figure 3-10

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-17
v1.0, November 2007
3. Enter the fields in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new SNMP trap:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Trap Configuration. The SNMPv1/v2 Trap
Configuration screen displays.
2. Enter the fields in the first row.
3. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove an SNMP trap:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv1/v2 > Trap Configuration. The SNMPv1/v2 Trap
Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the entry to be removed.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
SNMPv3
The SNMPv3 menu contains the following options:
•“Engine ID”
•“View Name”
•“View Content”
•“Community Configuration”
•“Group Configuration”
•“User Configuration”
•“Global Trap Configuration”
•“Trap Configuration”
•“Trap Filter Name”
•“Trap Filter Content”
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-18 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
Engine ID
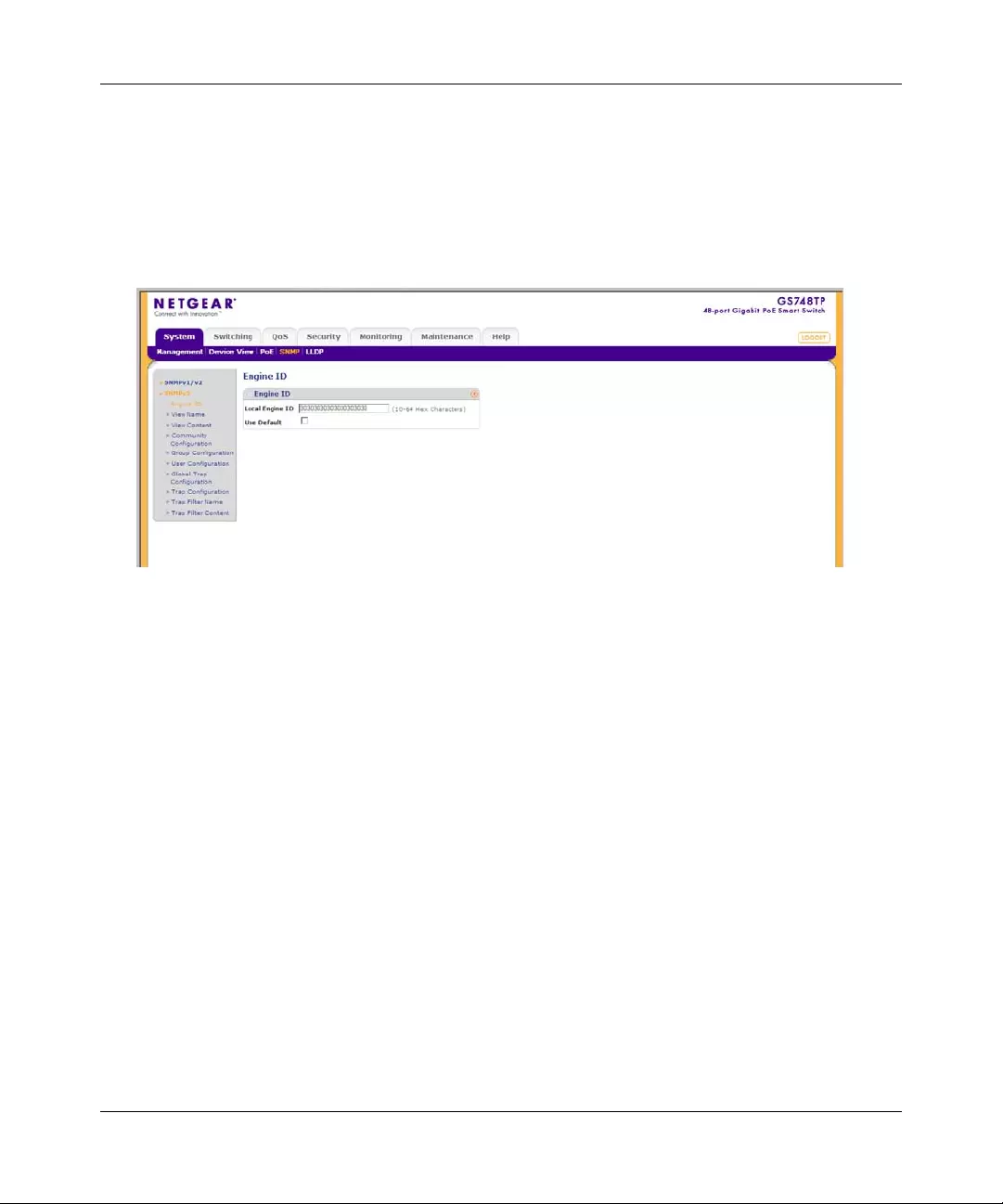
The SNMPv3 Engine ID screen allows network managers to define the SNMP Engine ID and to
assign the default parameters to SNMP.
To define the Local Engine ID:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Engine ID. The SNMPv3 Engine ID screen displays:
The SNMPv3 Engine ID screen contains the following fields:
•Local Engine ID (10-64 Characters) – Enter the local device Eng ine ID. The field value
is a hexadecimal string. Each byte in hexadecimal character strings is two hexadecimal
digits. Each byte digit can be separated by a period or a colon. The Engine ID must be
defined before SNMPv3 is enabled.
•Use Default – Check the box to use the device-generated Engine ID. The default Engine
ID is based on the device MAC address and is defined per standard as:
– First 4 octets – First bit = 1, the rest is the IANA Enterprise number.
– Fifth octet – Set to 3 to indicate the MAC address that follows.
– Last 6 octets – MAC address of the device.
2. Specify the Local Engine ID field or check Use Default to use the device-generated Engine
ID (Checking Use Default will override any entry in the Local Engine ID field).
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 3-11
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-19
v1.0, November 2007
View Name
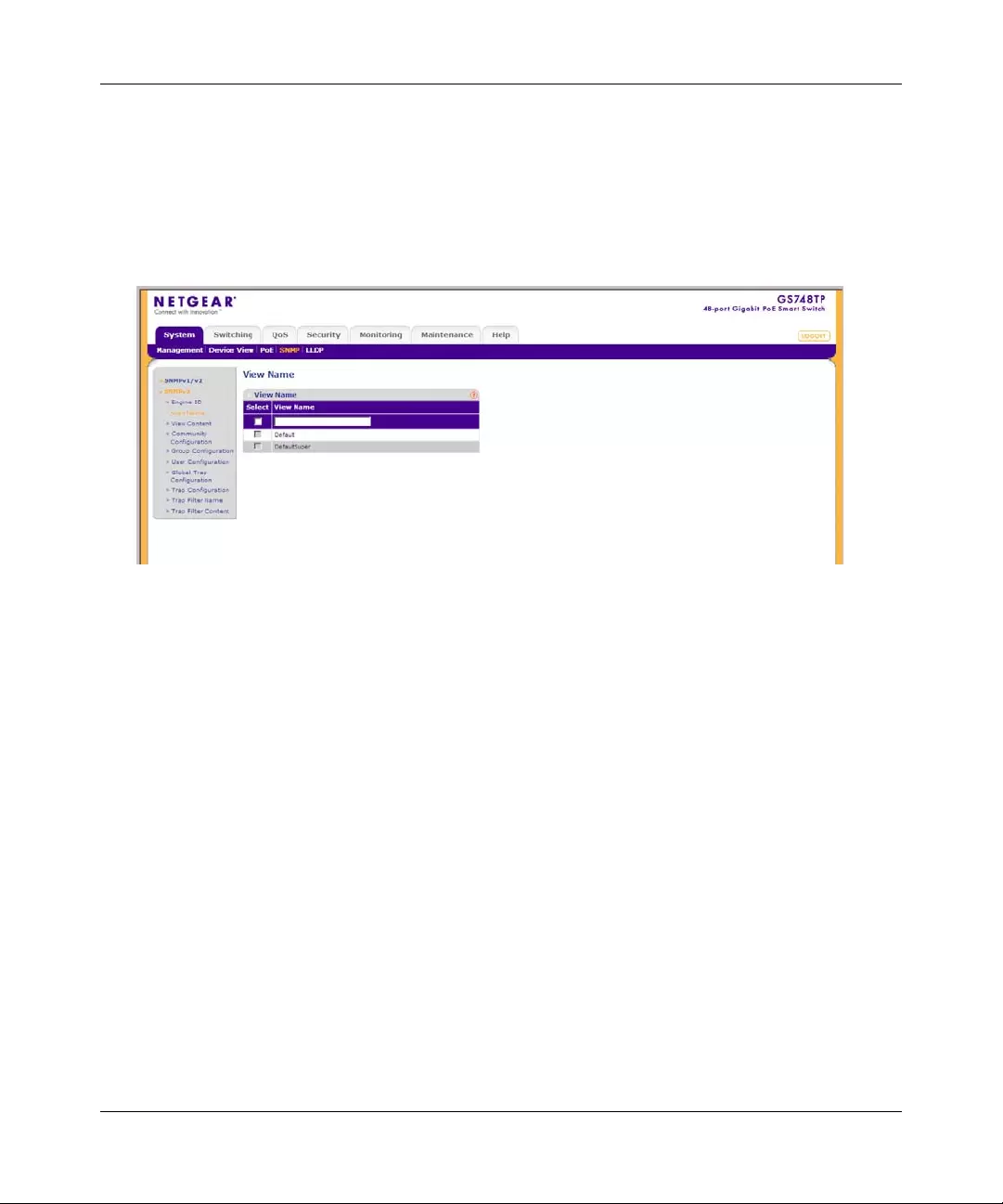
The SNMPv3 View Name screen allows the network managers to define SNMPv3 View Names.
SNMPv3 views provide or block access to device features or portions of features.
To define SNMPv3 view names:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > V iew Name. The SNMPv3 View Name screen displays:
The SNMPv3 View Name screen contains the following field:
•View Name – Enter the user-defined view name. The view name can contain a maximum
of 30 alphanumeric characters.
2. Select the entry.
3. Enter the View Name field in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new SNMP View Name:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > View Name. The SNMPv3 View Name screen displays.
2. Enter the View Name field in the first row.
3. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove an SNMP View Name:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > View Name. The SNMPv3 View Name screen displays.
2. Select the entry to be removed.
Figure 3-12
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-20 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
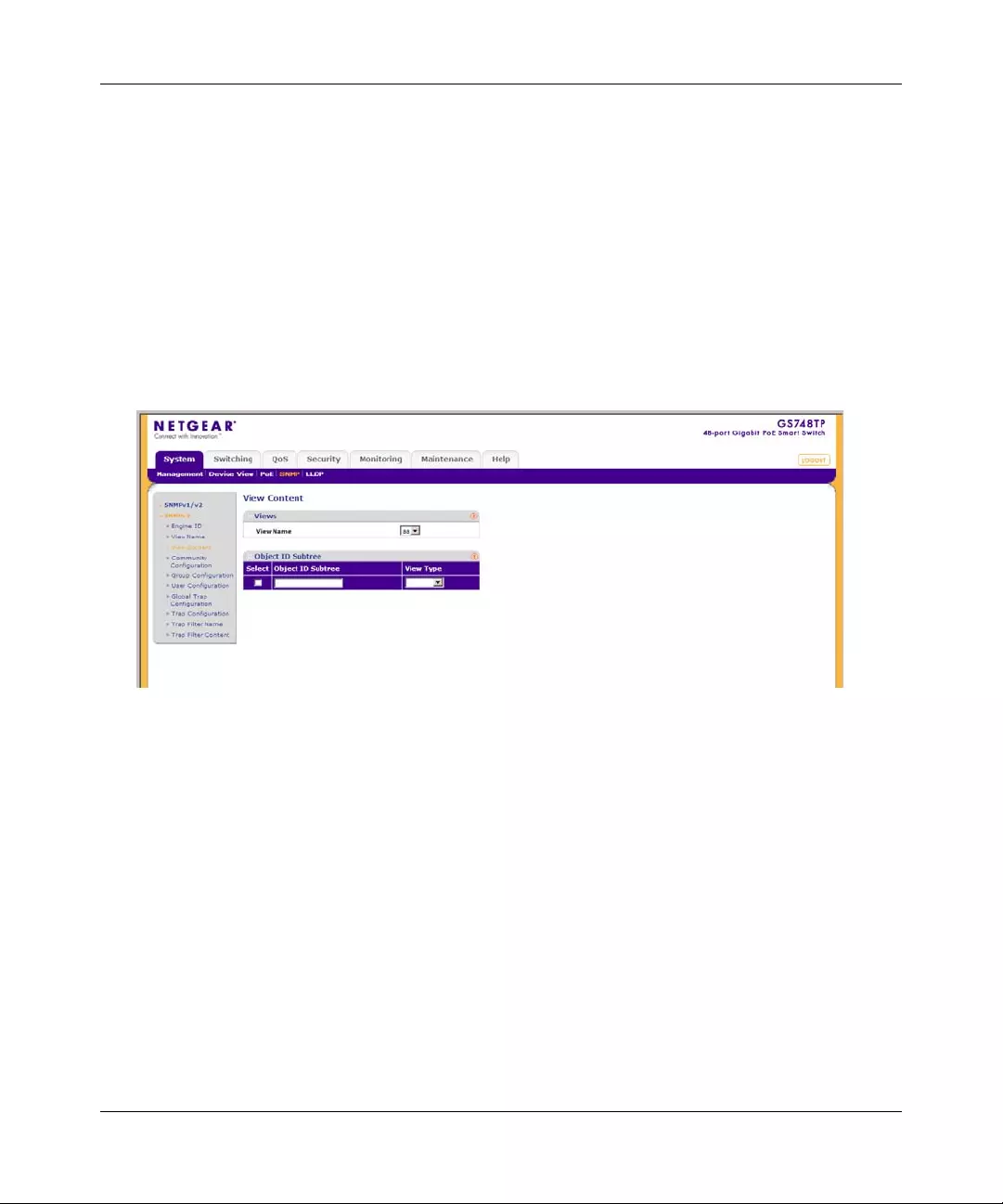
View Content
SNMP views provide or block access to device features or portions of features. For example, a
view can be defined to provide a view that SNMP group A has Read Only (R/O) access to
Multicast groups, while SNMP group B has Read-Write (R/W) access to Multicast groups. Feature
access is granted via the MIB name or MIB Object ID.
To define the SNMP View Content:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > View Content. The SNMPv3 View Content screen
displays:
The SNMPv3 View Content screen contains the following fields:
Views
•View Name – Select the user-defined view name. The view name can contain a maximum
of 30 alphanumeric characters.
•Object ID Subtree – Enter the device feature OID.
•View T ype – Select whether the defined OID branch will be included in or excluded from
the selected SNMP vie w. The possible field valu es ar e:
– Included – The OID is included in the SNMP view.
– Excluded – The OID is excluded from the SNMP view.
2. Select the View Name from the list in the provided field in the Views table.
Figure 3-13

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-21
v1.0, November 2007
3. Enter the Object ID Subtree in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select either Included or Excluded from the View Type provided field in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new SNMP OID entry:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > View Content. The SNMPv3 View Content screen
displays.
2. Select the View Name from the list in the provided field in the Views table.
3. Enter the Object ID Subtree in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select either Included or Excluded from the View Type provided field in the first row.
5. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove an SNMP OID entry:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > View Content. The SNMPv3 View Content screen
displays.
2. Select the View Name from the list in the provided field in the Views table.
3. Select the OID entry to be removed.
4. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
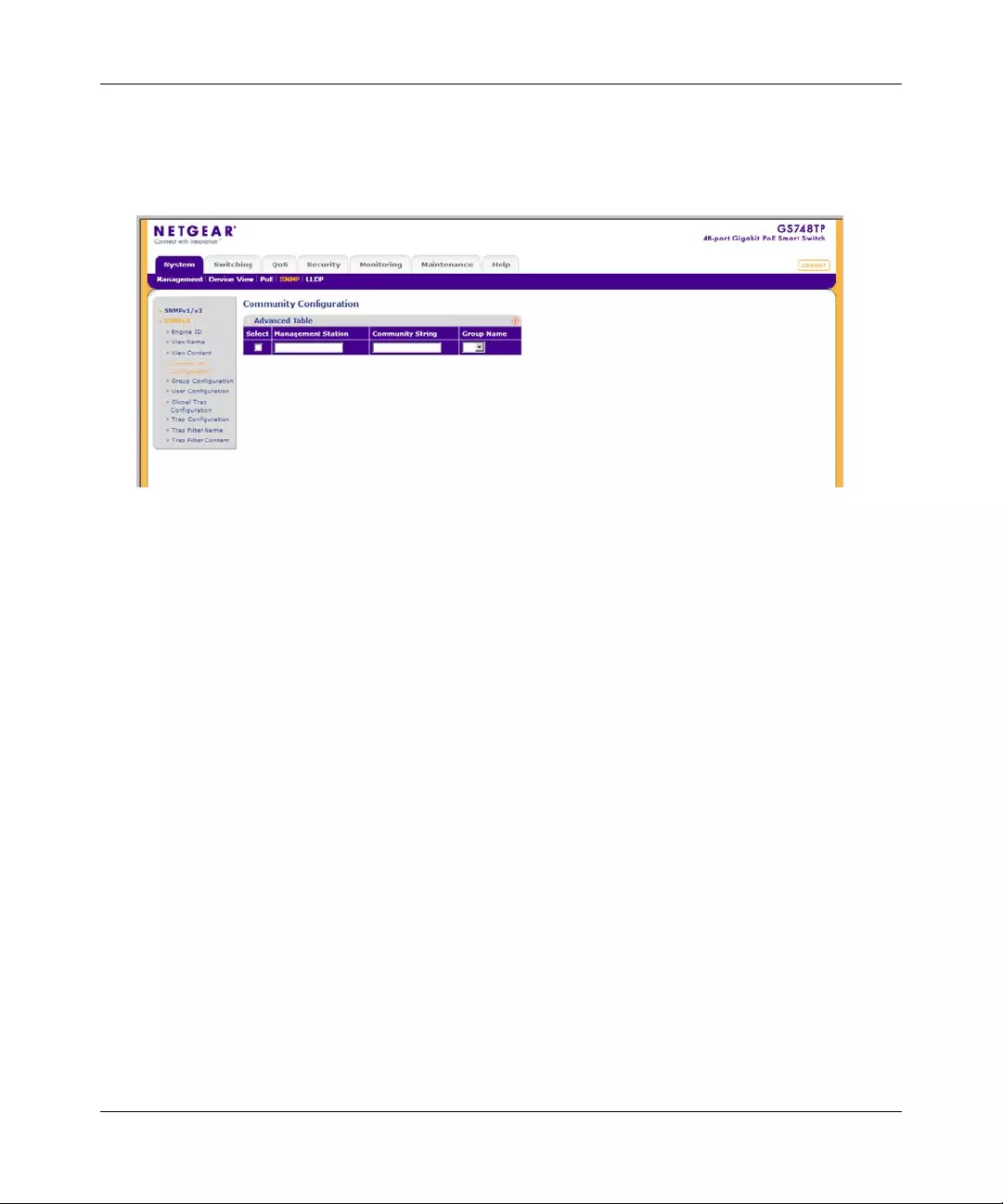
Community Configuration
Access rights are managed by defining communities in the Community Configuration screen.
When community names are changed, access rights are also changed.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-22 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To define SNMPv3 communities:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Community Configuration. The SNMPv3 Community
Configuration screen displays:
The SNMPv3 Community Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Management Station – Enter the management station IP address for which the SNMP
community is defined.
•Community String – Enter the password used to authenticate the management station to
the device.
•Group Name – Select the SNMP gro up from a list of SNMP groups defined in the SNMP
Group Configuration screen.
2. Select the SNMP community entry.
3. Enter the Management Station and Community String in the provided fields.
4. Select the Group Name from the list.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new SNMPv3 community:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Community Configuration. The SNMPv3 Community
Configuration screen displays.
2. Enter the Management Station and Community String in the provided fields in the first row.
3. Select the Group Name from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click ADD to update the device.
Figure 3-14
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-23
v1.0, November 2007
To remove an SNMPv3 community:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Community Configuration. The SNMPv3 Community
Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the community entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
Group Configuration
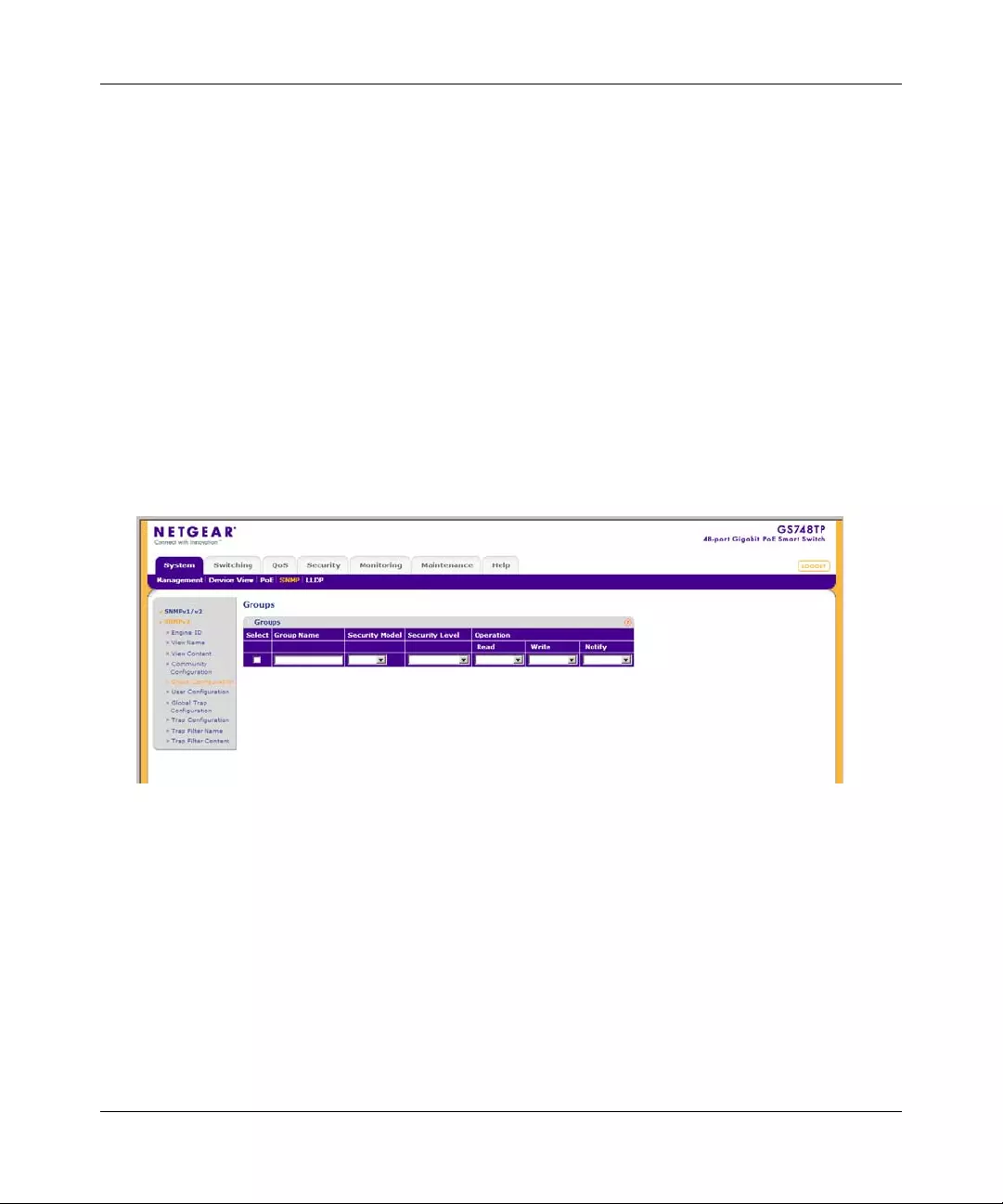
The SNMPv3 Groups screen provides information for creating SNMP groups and assigning
SNMP access control privileges to SNMP groups. Groups allow network managers to assign
access rights to specific device features or fea ture as pects.
To define an SNMP group:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Group Configuration. The SNMPv3 Groups screen
displays:
The SNMPv3 Groups screen contains the following fields:
•Group Name – Enter the user-defined group to which access control rules are applied.
The field range is up to 30 characters.
•Security Model – Select the SNMP version associated with the group. The possible field
values are:
– SNMPv1 – SNMPv1 is defined for the group.
– SNMPv2 – SNMPv2c is defined for the group.
– SNMPv3 – SNMPv3 is defined for the group.
Figure 3-15

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-24 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•Security Level – Select the security level attached to the group. Security levels apply to
SNMPv3 only. The possible field values are:
– No Authentication – Neither the Authentication nor the Privacy security levels are
assigned to the group.
– Authentication – Authenticates SNMP messages and ensures that the SNMP
message’s origin is authenticated.
– Privacy – Encrypts SNMP messages.
•Operation – Select the group access rights. The possible field values are:
– Read – Management access is restricted to read-only. Changes are made to the
assigned SNMP view.
– Write – Management access is read-write. Changes are made to the assigned SNMP
view.
– Notify – Sends traps for the assigned SNMP view.
2. Select the SNMP group entry.
3. Select the Security Model and Security Level from the lists in the provided fields in the first
row.
4. Specify the group access rights for the selected SNMP views in the Operation provided fields
in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new SNMPv3 group:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Group Configuration. The SNMPv3 Groups screen
displays.
2. Select the Security Model and Security Level from the lists in the provided fields in the first
row.
3. Specify the group access rights for the selected SNMP views in the Operation provided fields
in the first row.
4. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove an SNMPv3 group:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Group Configuration. The SNMPv3 Groups screen
displays.
2. Select the group entry.
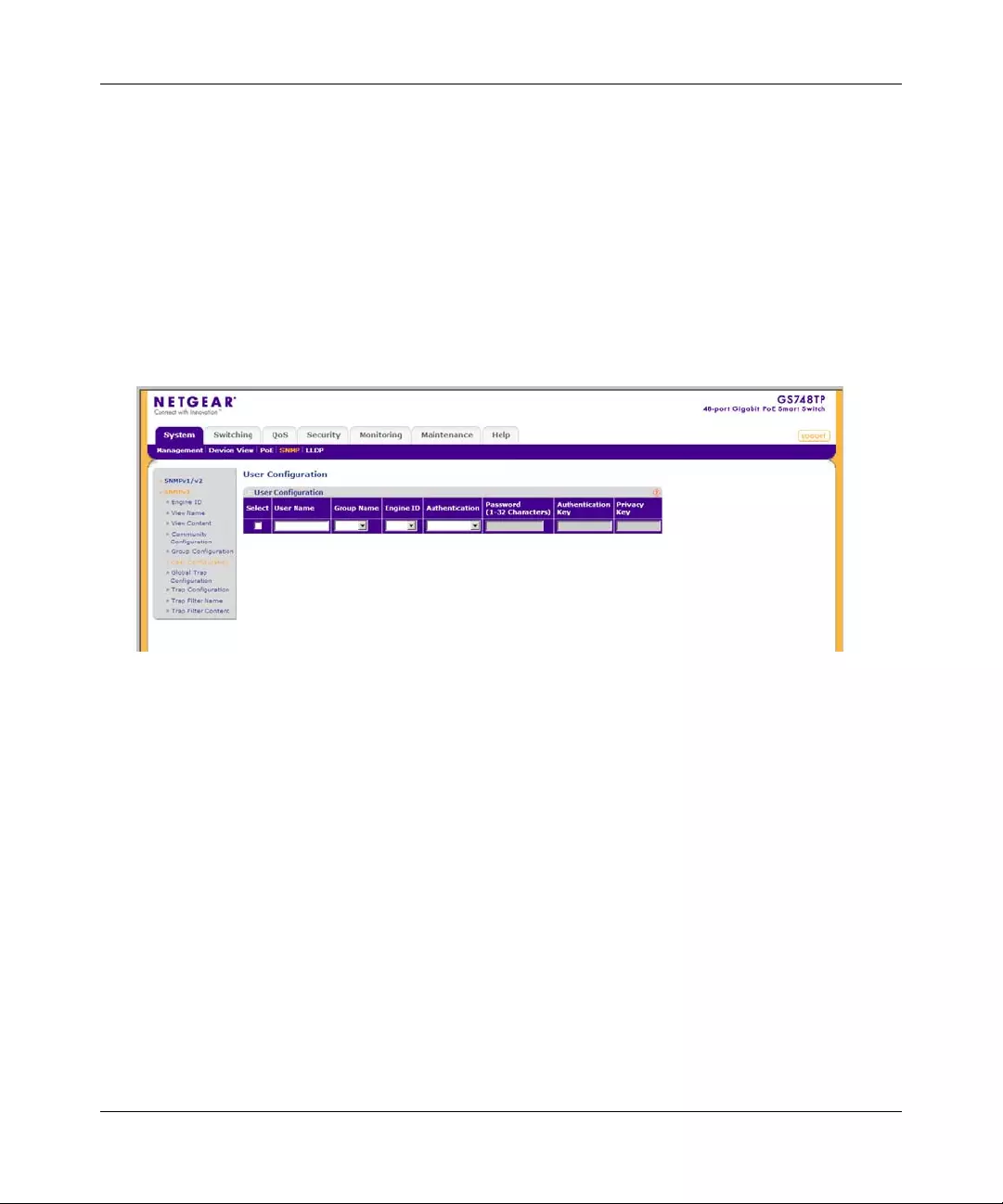
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-25
v1.0, November 2007
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
User Configuration
The SNMPv3 User Configuration screen provides information for creating SNMP groups and
assigning SNMP access control privileges to SNMP groups. Groups allow network managers to
assign access rights to specific device features or feature aspects.
To define SNMP users:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > User Configuration. The SNMPv3 User Configuration
screen displays:
The SNMPv3 User Configuration screen contains the follo wing fields:
•User Name – Enter the user name. The field range is up to 30 alphanumeric characters.
•Group Name – Enter the group name from a list of user-defined SNMP groups. SNMP
groups are defined in the Groups screen.
•Engine ID – Select either the local or remote SNMP entity to which the user is connected.
Changing or removing the local SNMP Engine ID deletes the SNMPv3 user database.
•Authentication – Select the method used to authenticate users. The possible field values
are:
– MD5 Key – Users are authenticated using the HMAC-MD5 algorithm.
– SHA Key – Users are authenticated using the HMAC-SHA-96 authentication level.
– MD5 Password – The HMAC-MD5-96 password is used for authentication. The user
must enter a password.
Figure 3-16

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-26 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
– SHA Password – Users are authenticated using the HMAC-SHA-96 authentication
level. The user must enter a password.
– None – No user authentication is used.
•Password (1-32 Characters) – Enter the password for the group member.
•Authentication Key – Enter the HMAC-MD5-96 or HMAC-SHA-96 authentication
level. The authentication and privacy keys are entered to define the authentication key. If
only authentication is required, 16 bytes are defined. If both privacy and authentication are
required, 32 bytes are defined. Each byte in hexadecimal character strings is two
hexadecimal digits. Each byte can be separated by a period or a colon.
•Privacy Key – Enter the privacy key (LSB). If only authentication is required, 20 bytes
are defined. If both privacy an d authentication are required, 36 bytes are defined. Each
byte in hexadecimal character strings is two hexadecimal digits. Each byte can be
separated by a period or colon.
2. Select the user entry.
3. Enter the User Name in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select the Group Name and Engine ID from the lists in the provided fields in the first row.
5. Select the Authentication method from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. If you selected a password method of Authentication, enter the Password in the provided
field in the first row. If you selected a key method of Authentication, enter the
Authentication Key and Privacy Key in the provided fields in the first row.
7. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new SNMPv3 user:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Users Configuration. The SNMPv3 User
Configuration screen displays.
2. Enter the User Name in the provided field in the first row.
3. Select the Group Name and Engine ID from the lists in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Select the Authentication method from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. If you selected a password method of Authentication, enter the Password in the provided
field in the first row. If you selected a key method of Authentication, enter the
Authentication Key and Privacy Key in the provided fields in the first row.
6. Click ADD to update the device.
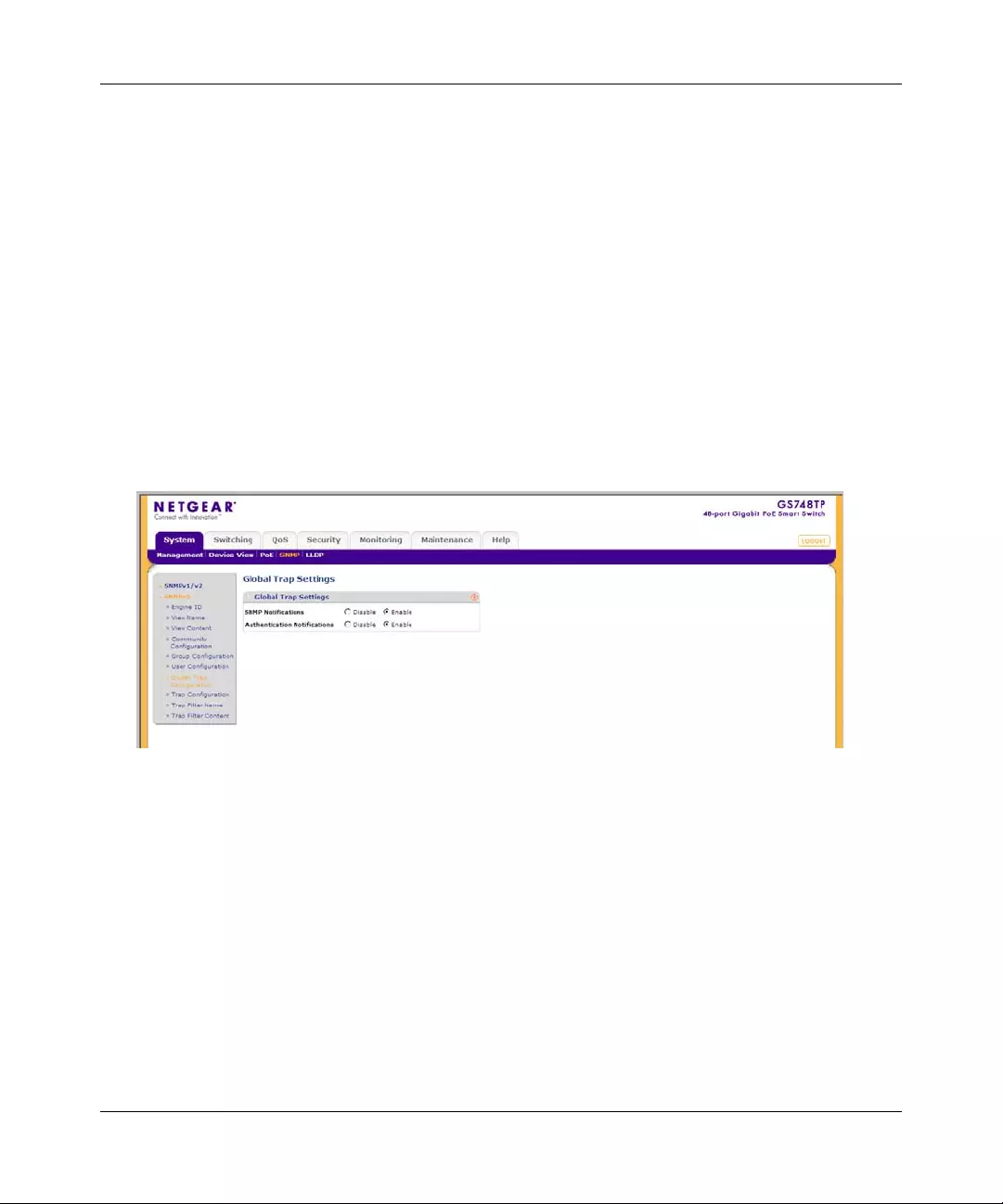
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-27
v1.0, November 2007
To remove an SNMPv3 user:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Users Configuration. The SNMPv3 User
Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the user entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
Global Trap Configuration
The SNMPv3 Global Trap Settings screen contains parameters for defining SNMP notification
parameters.
To configure SNMP notification global parameters:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Global Trap Configuration. The SNMPv3 Global T rap
Settings screen displays:
The SNMPv3 Global Trap Settings screen contains the following fields:
•SNMP Notifications – Select whether or not the device can send SNMP notifications.
The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable SNMP notifications.
– Disable – Disable SNMP notifications.
•Authentication Notifications – Select the SNMP authentication failure notification status
on the device. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable the device to send authentication failure notifications.
– Disable – Disable the device from sending authentication failure notifications.
Figure 3-17
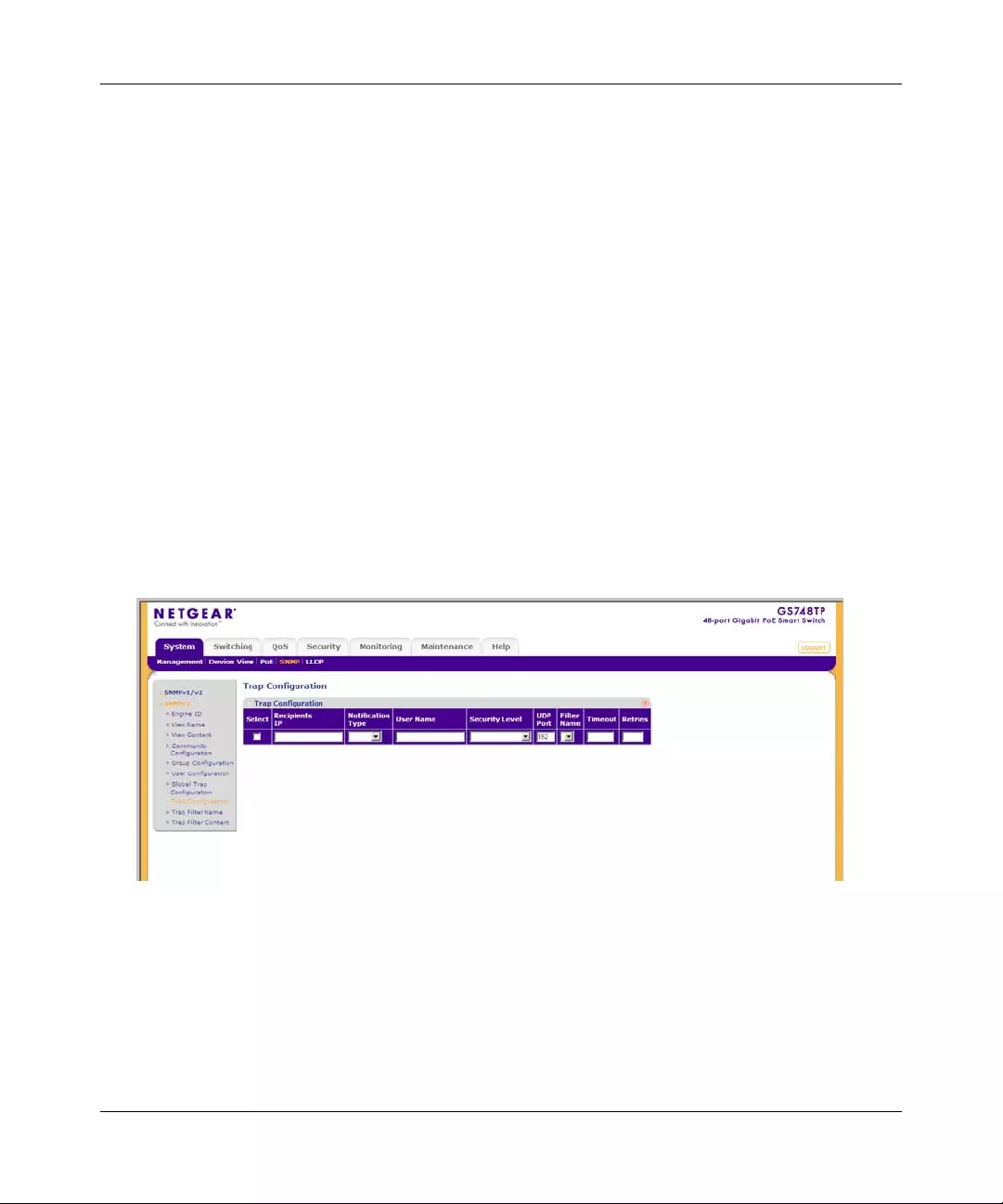
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-28 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
2. Select either Enable or Disable in the SNMP Notifications provided field.
3. Select either Enable or Disable in the Authentication Notifications provided field.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Trap Configuration
The SNMPv3 Trap Configuration screen contains information for defining filters that determine
whether traps are sent to specific users, and the trap type sent. SNMP notification filters provide
the following services:
• Identifying Management Trap Targets
• Defining Trap Filtering
• Selecting Trap Generation Parameters
• Providing Access Control Checks
To define trap station management:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Configuration. The SNMPv3 Trap Configuration
screen displays:
The SNMPv3 Trap Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Recipien ts IP – Enter the IP address to which the traps are sent.
•Notification Type – Select the type of notification sent. The possible field values are:
– Traps – Traps are sent.
Figure 3-18

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-29
v1.0, November 2007
– Informs – Informs are sent.
•User Name – Enter the user name. The field range is up to 30 alphanumeric characters.
•Security Level – Select the security level attached to the group. Security levels apply to
SNMPv3 only. The possible field values are:
– No Authentication – Neither the Authentication nor the Privacy security levels are
assigned to the group.
– Authentication – Authenticates SNMP messages and ensures that the SNMP
message’s origin is authenticated.
– Privacy – Encrypts SNMP messages.
•UDP Port – Enter the UDP port used to send notifications. The default is 162.
•Filter Name – Select the SNMP filter name from the list of SNMP Notification filters.
•Timeout – Enter the amount of time (in seconds) the device waits before re-sending
informs. The default is 15 seconds.
•Retries – Enter the amount of times the device re-sends an inform request. The default is 3
seconds.
2. Enter the Recipients IP address in the provided field in the first row.
3. Select either Traps or Informs in the Notification Type provided field in the first row.
4. Enter the User Name in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the Security Level from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. Enter the UDP Port in the provided field in the first row.
7. Select the Filter Name from the list in the provided field in the first row.
8. Enter the Timeout and Retries in the provided fields in the first row.
9. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new trap:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Configuration. The SNMPv3 Trap Configuration
screen displays.
2. Enter the Recipients IP address in the provided field in the first row.
3. Select either Traps or Informs in the Notification Type provided field in the first row.
4. Enter the User Name in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the Security Level from the list in the provided field in the first row.
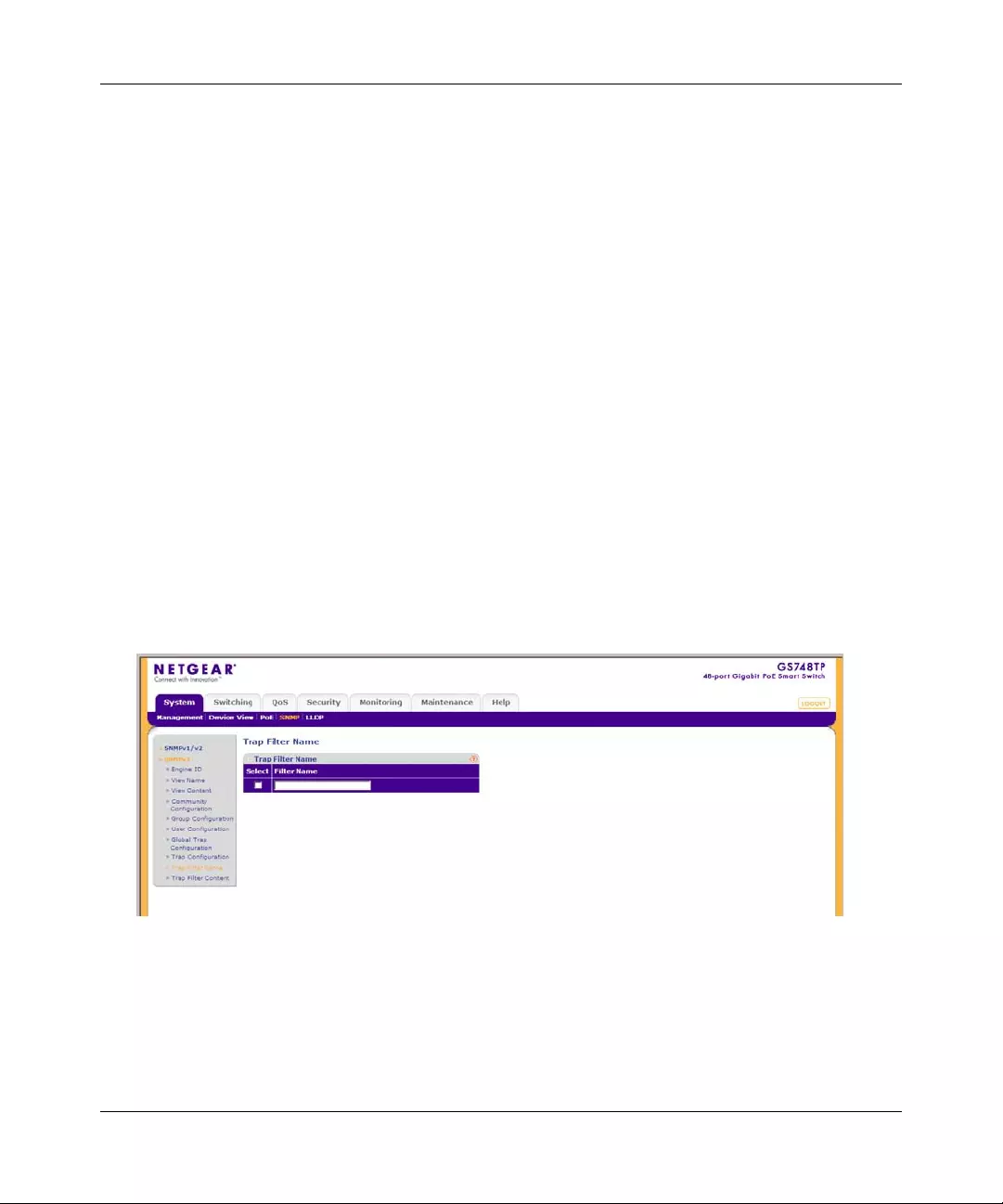
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-30 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
6. Enter the UDP Port in the provided field in the first row.
7. Select the Filter Name from the list in the provided field in the first row.
8. Enter the Timeout and Retries in the provided fields in the first row.
9. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a trap:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Configuration. The SNMPv3 Trap Configuration
screen displays.
2. Select the trap entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
Trap Filter Name
The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Name screen permits filtering traps based on OIDs. Each OID is linked
to a device feature or a portion of a feature. The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Name screen also allows
network managers to filter notifications.
To define the SNMPv3 Trap Filter Name:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Filter Name. The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Name
screen displays:
The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Name screen contains th e following field:
•Filter Name – Enter the user-defined notification filter name.
2. Select the trap filter entry.
Figure 3-19

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-31
v1.0, November 2007
3. Enter the trap Filter Name in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new trap filter name:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Filter Name. The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Name
screen displays.
2. Enter the trap Filter Name in the provided field in the first row.
3. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a trap filter name:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Filter Name. The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Name
screen displays.
2. Select the trap filter name entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
Trap Filter Content
The SNMPv3 T rap Filter Content screen permits filt ering traps based on OIDs. Each OID is linked
to a device feature or a portion of a feature. The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Content screen also allows
network managers to filter notifications.
To define SNMPv3 Trap Filter settings:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Filter Content. The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Content
screen displays:
Figure 3-20

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-32 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Content screen contains the following fields:
Trap Filter Settings
•Filter Name – Select the user-defined notification filter from the list.
Trap Filter Settings
•Object ID Subtree – Enter the OID for which notifications are sent or blocked. If a filter
is attached to an OID, traps or informs are generated and sent to the trap recipients. OIDs
are selected from either the Select field or the Object ID field.
•Filter Type – Select whether to send traps or informs relating to the selected OID. The
possible field values are:
– Excluded – Do not send traps or informs.
– Included – Send traps or informs.
2. Select the Filter Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the trap filter content entry from the OID table.
4. Enter the Object ID Subtree in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the Filter Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new trap filter content entry:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Filter Content. The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Content
screen displays.
2. Select the Filter Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Enter the Object ID Subtree in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select the Filter Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a trap filter content entry:
1. Click System > SNMP > SNMPv3 > Trap Filter Content. The SNMPv3 Trap Filter Content
screen displays.
2. Select the Filter Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the trap filter content entry.
4. Click DELETE to remove the entry.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-33
v1.0, November 2007
LLDP
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) allows network managers to troubleshoot and
enhance network management by disc overing and maintaining network topologies over multi-
vendor environments. LLDP discovers network neighbors by standardizing methods for network
devices to advertise themselves to other system, and to store discovered information. Device
discovery info rmation includes:
• Device Identification
• Device Capabilities
• Device Configuration
The advertising device transmits multiple adverti sement message sets in a single LAN packet. The
multiple advertisement sets are sent in the packet Type Length Value (TLV) field. LLDP devices
must support chassis and port ID advertisement, as well as system name, system ID, system
description, and system capability advertisements.
The LLDP menu enables configuration of LLDP parameters and contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The LLDP Basic menu contains the following option:
•“LLDP Configuration”
LLDP Configuration
The Basic LLDP Configuration screen allows network managers to assign global LLDP and
LLDP-MED (LLDP – Media Endpoint Discovery) parameters.
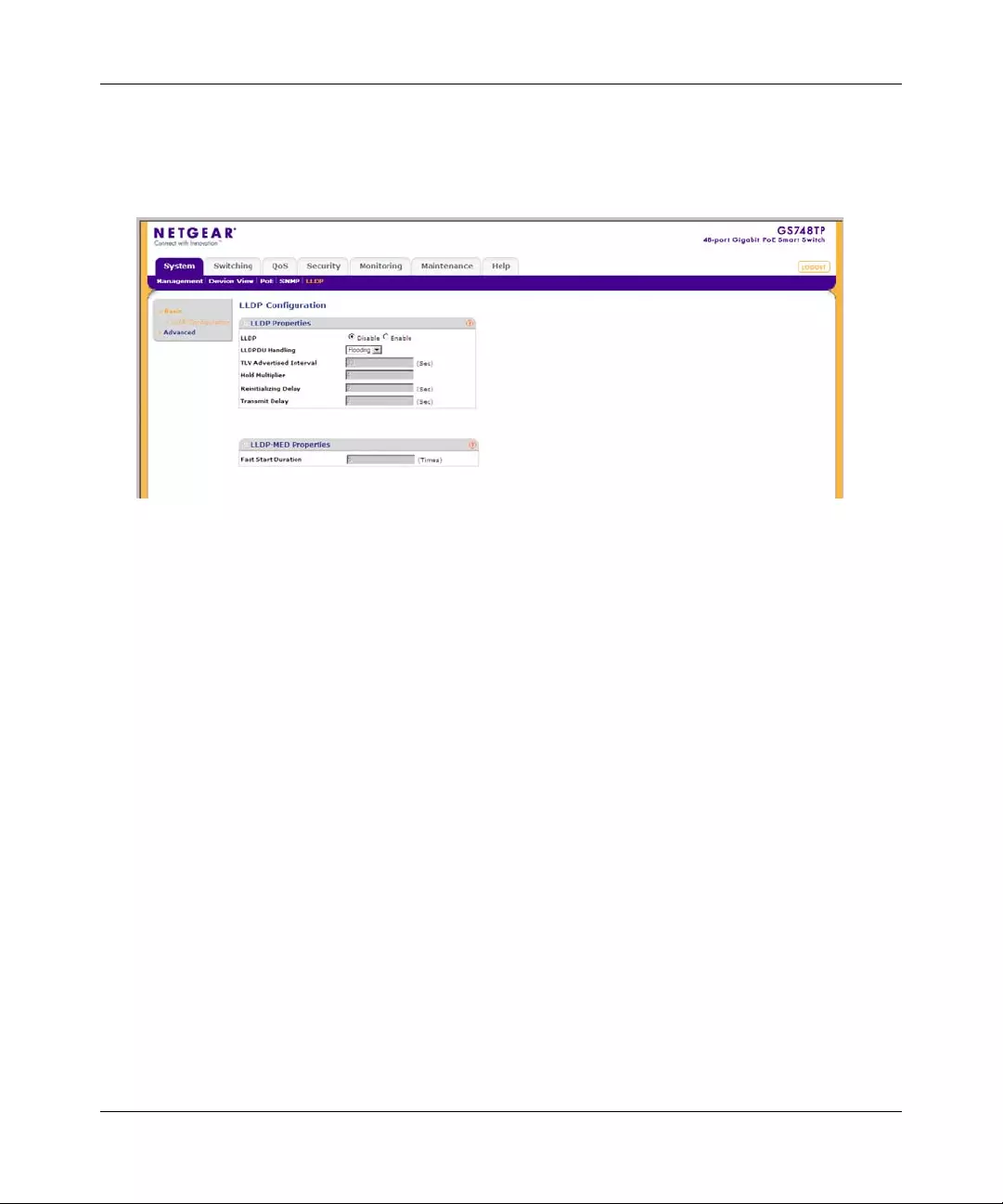
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-34 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To configure LLDP settings:
1. Click System > LLDP > Basic > LLDP Configuration. The Basic LLDP Configuration
screen displays:
The Basic LLDP Configuration screen contains the following fields:
LLDP Properties
•LLDP – Select the LLDP global status on the device. The possible field values are:
– Disable – Disable LLDP on the device. This is the default value.
– Enable – Enable LLDP on the device.
•LLDPDU Handling – Select LLDPDU (LLDP Data Unit) packet handling when LLDP is
disabled. The possible field values are:
– Flooding – LLDPDU packets are flooded to all ports in the system.
– Filtering – LLDPDU packets are filtered. This is the default.
•TLV Advertised Interval – Enter the rate in seconds at which LLDP advertisement
updates are sent. The possible field range is 5 - 32768 seconds . The default value is 30
seconds.
•Hold Multiplier – Enter the amount of time that LLDP packets are held before the
packets are discarded, measured in multiples of the TLV Advertised Interval. The possible
field range is 2 - 10. The field default is 4. For example, if the TLV Advertised Interval is
30 seconds and the Hold Multiplier is 4, then the LLDP packets are discarded after 120
seconds.
Figure 3-21

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-35
v1.0, November 2007
•Reinitializing Delay – Enter the amount of time in seconds that passes between disabling
and reinitializing LLDP. The possible field range is 1 - 10 seconds. The field default is 2
seconds.
•Transmit Delay – Enter the amount of time in seconds that passes betw een successive
LLDP frame transmissions due to changes in the LLDP local systems MIB. The possible
field value is 1 - 8192 seconds. The fiel d default is 2 seconds.
LLDP-MED Properties
•Fast Start Duration – Enter the number of times LLDP packets are sent when the LLDP-
MED Fast Start mechanism is initialized, which occurs when a new Endpoint device links
with the LLDP-MED Network Connectivity Device.
2. Select the LLDP global status on the device by selecting Enable or Disable in the LLDP field.
3. If you selected Disable in the LLDP field, select the type of LLDPDU Handling from the list
in the provided field.
4. If you selected Enable in the LLDP field, enter the TLV Advertised Interval, Hold
Multiplier, Reinitializing Delay, Transmit Delay and Fast Start Duration in the provided
fields.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Advanced
The LLDP Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“LLDP Configuration”
•“LLDP Port Settings”
•“LLDP-MED Network Policy”
•“LLDP-MED Port Settings”
•“Local Information”
•“Neighbors Information”
LLDP Configuration
The Advanced LLDP Configuration sc reen allows network managers to as sign global LLDP and
LLDP-MED (LLDP – Media Endpoint Discovery) parameters.
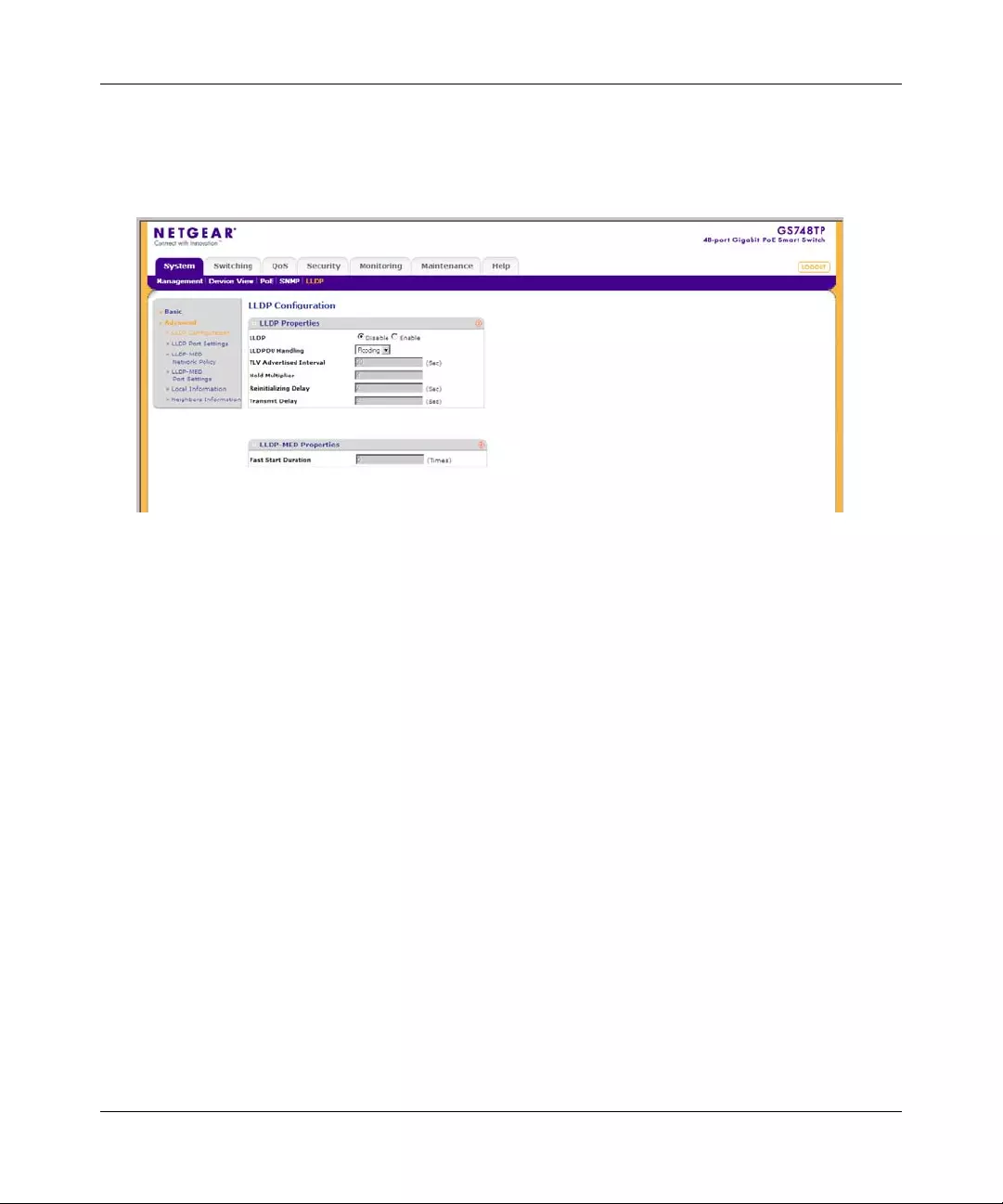
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-36 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To configure LLDP settings:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP Configuration. The Advanced LLDP
Configuration screen displays:
The Advanced LLDP Configuration screen contains the following fields:
LLDP Properties
•LLDP – Select the LLDP global status on the device. The possible field values are:
– Disable – Disable LLDP on the device. This is the default value.
– Enable – Enable LLDP on the device.
•LLDPDU Handling – Select LLDPDU (LLDP Data Unit) packet handling when LLDP is
disabled. The possible field values are:
– Flooding – LLDPDU packets are flooded to all ports in the system.
– Filtering – LLDPDU packets are filtered. This is the default.
•TLV Advertised Interval – Enter the rate in seconds at which LLDP advertisement
updates are sent. The possible field range is 5 - 32768 seconds . The default value is 30
seconds.
•Hold Multiplier – Enter the amount of time that LLDP packets are held before the
packets are discarded, measured in multiples of the TLV Advertised Interval. The possible
field range is 2 - 10. The field default is 4. For example, if the TLV Advertised Interval is
30 seconds and the Hold Multiplier is 4, then the LLDP packets are discarded after 120
seconds.
Figure 3-22

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-37
v1.0, November 2007
•Reinitializing Delay – Enter the amount of time in seconds that passes between disabling
and reinitializing LLDP. The possible field range is 1 - 10 seconds. The field default is 2
seconds.
•Transmit Delay – Enter the amount of time in seconds that passes betw een successive
LLDP frame transmissions due to changes in the LLDP local systems MIB. The possible
field value is 1 - 8192 seconds. The fiel d default is 2 seconds.
LLDP-MED Properties
•Fast S tart Duration – Enter the number of LLDP packets sent when the LLDP-MED Fast
Start mechanism is initialized, which occurs when a new Endpoint device links with the
LLDP-MED Network Connectivity Device.
2. Select the LLDP global status on the device by selecting Enable or Disable in the LLDP field.
3. If you selected Disable in the LLDP field, select the type of LLDPDU Handling from the list
in the provided field.
4. If you selected Enable in the LLDP field, enter the TLV Advertised Interval, Hold
Multiplier, Reinitializing Delay, Transmit Delay and Fast Start Duration in the provided
fields.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
LLDP Port Settings
The LLDP Port Settings screen allows network administrators to define LLDP port settings,
including the port type, the LLDP port state, and the type of port information advertised.
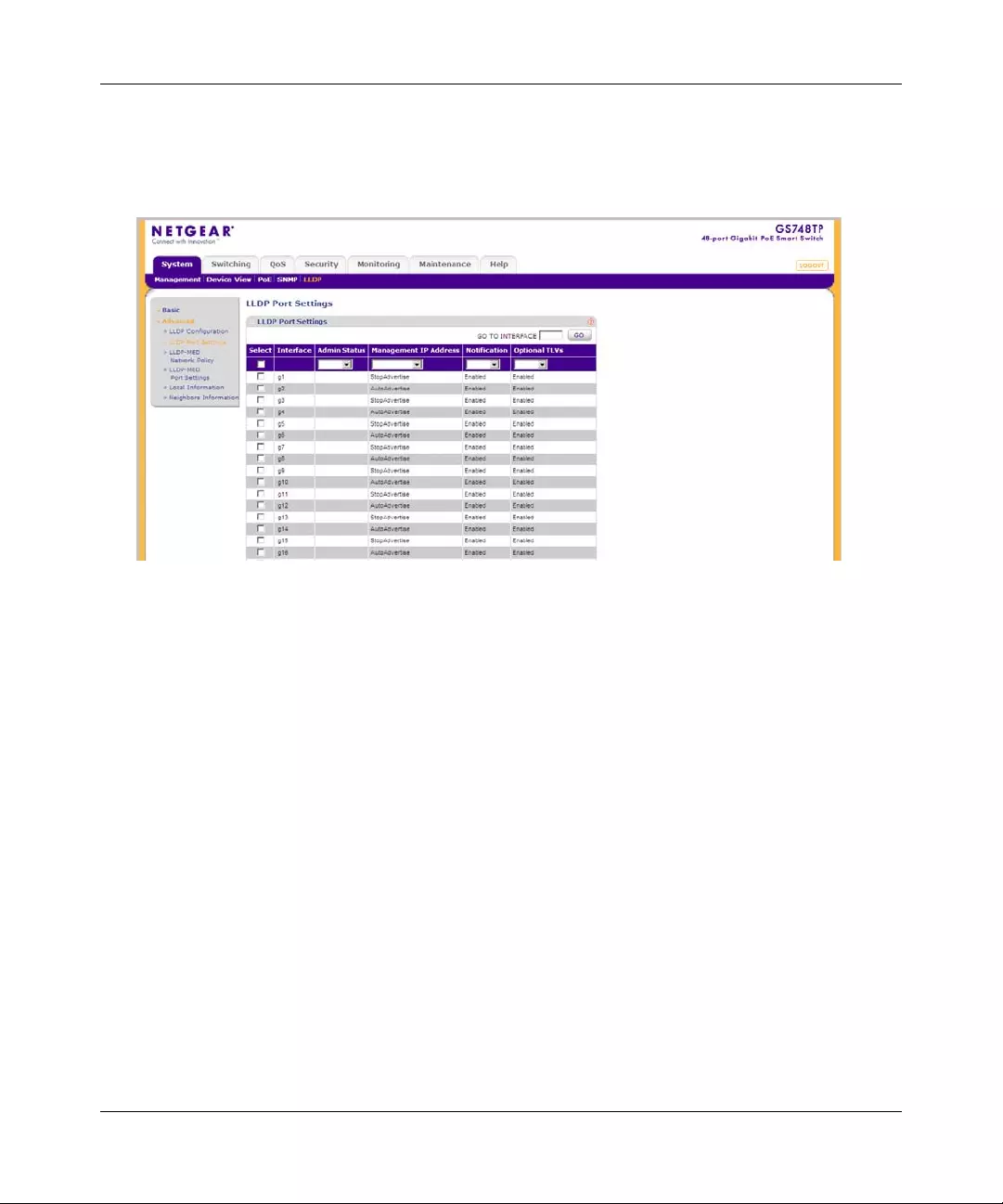
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-38 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To define LLDP Port Properties:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP Port Settings. The LLDP Port Settings screen
displays:
The LLDP Port Settings screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the specific interface for which LLDP parameters are defined.
•Admin Status – Select the LLDP packet transmitting and receiving status of the interface.
The possible field values are:
– Tx Only – Enable transmitting LLDP packets only.
– Rx Only – Enable receiving LLDP packets only.
– Tx & Rx – Enable transmitting and receiving LLDP packets.
– Disable – Disable LLDP on the interface.
•Management IP Address – Select the management IP address that is advertised from the
interface. The possible field values are:
– StopAdvertise – Stop advertising the management IP address from the interface.
– AutoAdvertise – Advertise the device’s current IP address as the management IP
address.
•Notification – Select the topology change notification status on the interface.
Figure 3-23

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-39
v1.0, November 2007
– Enable – Enable topology change notification on the interface. This is the default
value.
– Disable – Disable topology change notification on the interface.
•Optional TLVs – Select whether optional TLVs are advertised from the interface.
– Enable – Enable optional TLVs on the interface. This is the default value.
– Disable – Disable optional TLVs on the interface.
2. Select the Interface to configure.
3. Select the Admin Status from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select the Management IP Address from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the Notification status from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. Select the Optional TLVs status from the list in the provided field in the first row.
7. Click APPLY to update the device.
LLDP-MED Network Policy
LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) increases network flexibility by allowing
different IP systems to coexist on a single network.
LLDP:
• Provides detailed network topology information, including what devices are located on the
network, and where the devices are located. For example, what IP phone is connected to what
port, what software is running on what switch, and what port is connected to what PC.
• Automatically deploys policies over networks for:
–QoS Policies
– Voice VLANs
• Provides Emergency Call Service (E-911) via IP Phone location information.
• Provides troubleshooting information. LLDP-MED sends network managers alerts for:
– Port speed and duplex mode conflicts
– QoS policy misconfigurations
The LLDP-MED Network Policy screen allows network administrators to define LLDP-MED
network policies, which include the application, VLAN ID, VLAN type, user priority and DSCP
value.
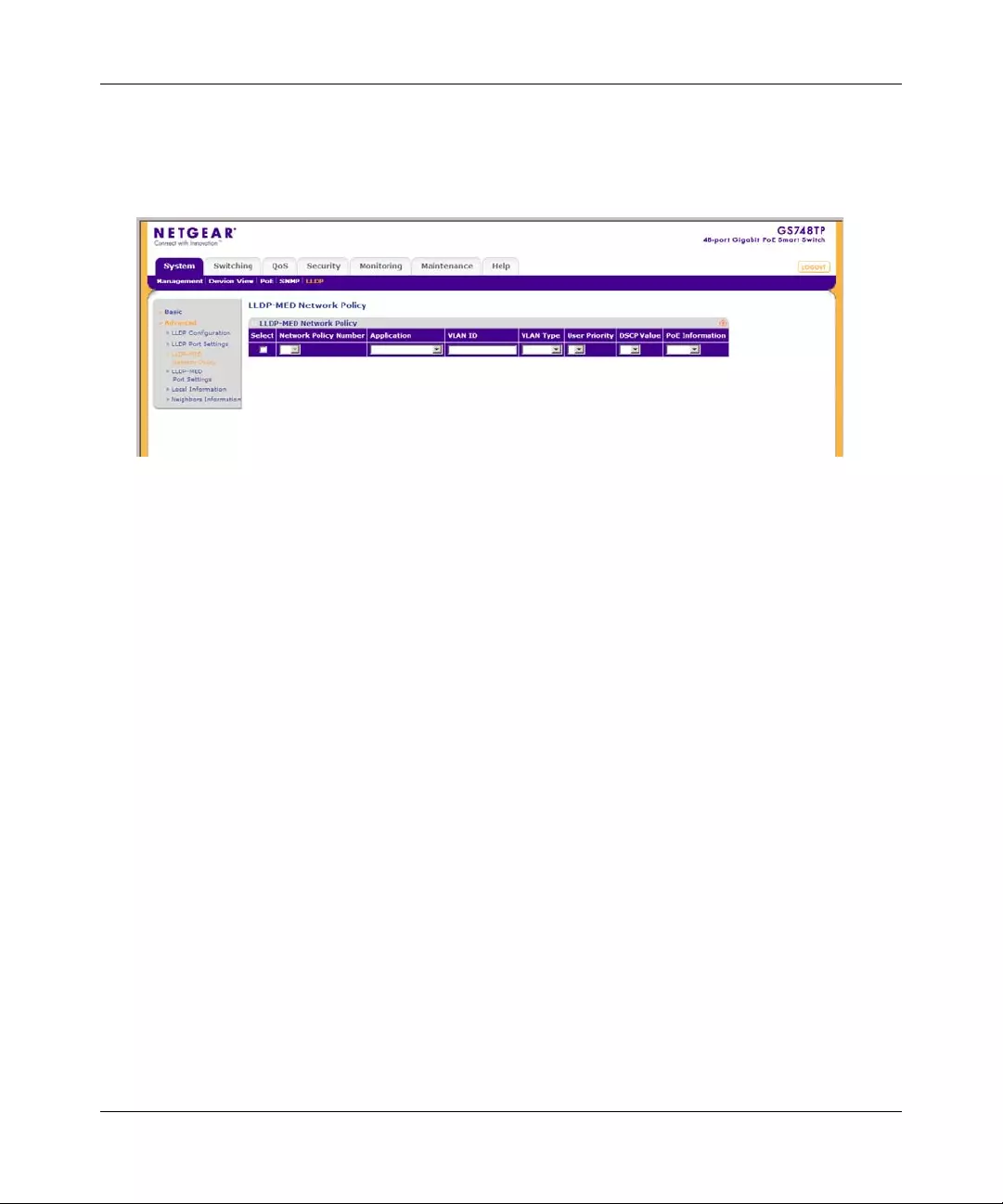
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-40 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To configure LLDP-MED Network Policy:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP-MED Network Policy. The LLDP-MED
Network Policy screen displays:
The LLDP-MED Network Policy screen contains the following fields:
•Network Policy Number – Select the network policy number. The field range is 1 - 32.
•Application – Select the application for which the network policy is defined. The possible
field values are:
– Voice – The network policy is defined for a Voice application.
– Voice Signaling – The network policy is defined for a Voice Signaling application.
– Guest Voice – The network policy is defined for a Guest Voice application.
– Guest Voice Signaling – The network policy is defined for a Guest Voice Signaling
application.
– Softphone Voice – The netw ork policy is defined for a Softphone Voice application.
– Video Conferencing – The network policy is defined for a Video Conferencing
application.
– Streaming Video – The network policy is defined for a Streaming Video application.
– Video Signaling – The network policy is defined for a Video Signaling application.
•VLAN ID – Enter the VLAN ID for which the network policy is defined.
•VLAN Type – Select the VLAN type for which the network policy is defined. The
possible field values are:
Figure 3-24

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-41
v1.0, November 2007
– Tagged – The network policy is defined for tagged VLANs.
– Untagged – The network policy is defined for untagged VLANs.
•User Priority – Select the priority assigned to the network application. The field range is
0 – 7.
•DSCP Value – Select the DSCP value assigned to the network policy. The possible field
value is 0 – 63.
2. Select the Network Policy entry to configure.
3. Select the Network Policy Number from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. Enter the VLAN ID in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the VLAN Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. Select the User Priority from the list in the provided field in the first row.
7. Select the DSCP Value from the list in the provided field in the first row.
8. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new network policy entry:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP-MED Network Policy. The LLDP-MED
Network Policy screen displays.
2. Select the Network Policy Number from the list in the provided field in the first row.
3. Enter the VLAN ID in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select the VLAN Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the User Priority from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. Select the DSCP Value from the list in the provided field in the first row.
7. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a network policy entry:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP-MED Network Policy. The LLDP-MED
Network Policy screen displays.
2. Select the Network Policy entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
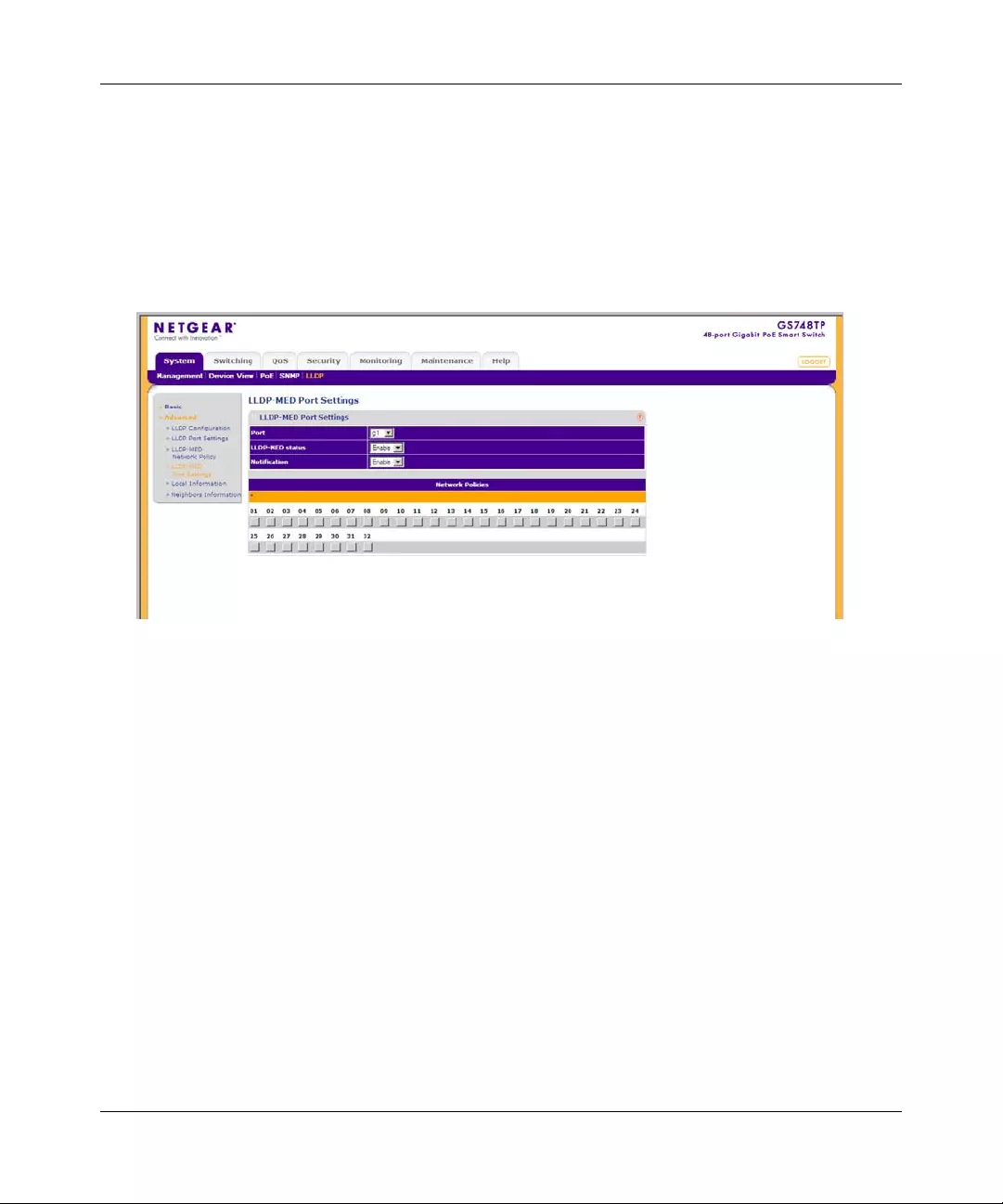
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-42 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
LLDP-MED Port Settings
The LLDP-MED Port Settings screen contains parameters for assigning LLDP-MED network
policies to specific ports.
To configure LLDP-MED port settings:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > LLDP-MED Port Settings. The LLDP-MED Port
Settings screen displays:
The LLDP-MED Port Settings screen contains the following fields:
•Port – Select the port to configure.
•LLDP-MED Status – Select the LLDP-MED status for the selected port. The possible
field values are:
– Enable – Enable LLDP-MED on the selected port.
– Disable – Disable LLDP-MED on the selected port.
•Notification – Select the notification status for the selected port. The possible field values
are:
– Enable – Enable notification on the selected port.
– Disable – Disable notification on the selected port.
•Network Policies – Click on the gold button to select the network poli cy numbers to apply
to the selected port.
2. Select the Port from the list in the provided field.
Figure 3-25
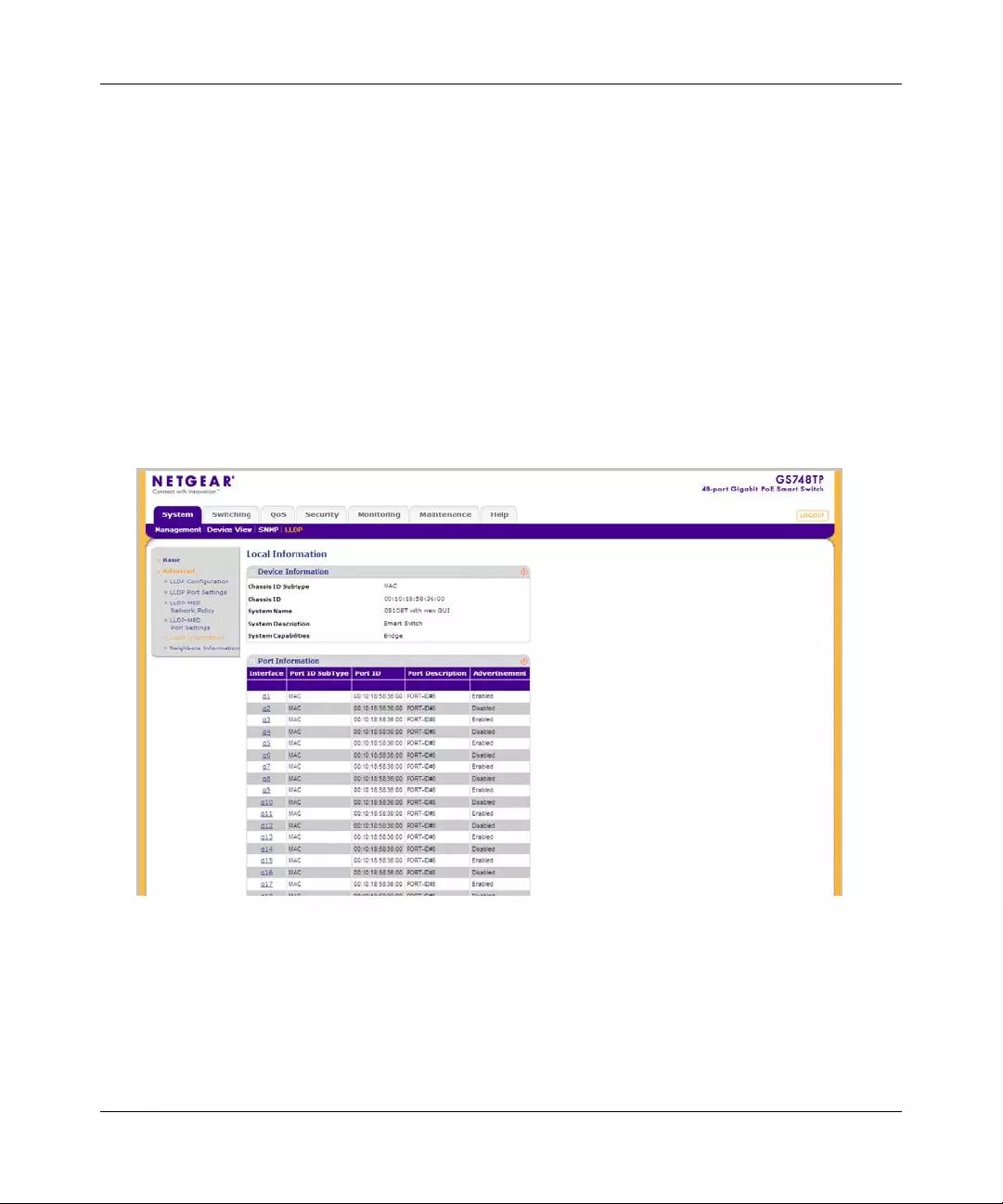
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-43
v1.0, November 2007
3. Select the LLDP-MED Status of the selected port from the list in the provided field.
4. Select the Notification Status of the selected port from the list in the provided field.
5. Click on the Network Policies gold bar and select the network policy numbers to apply to the
port.
6. Click APPLY to update the device.
Local Information
The LLDP Local Information screen enables viewing detailed port LLDP-MED information.
To view LLDP-MED port information:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > Local Information. The LLDP-MED Local
Information screen displays:
The LLDP-MED Local Information screen contains the following fields:
Device Information
•Chassis ID Subtype – Displays the chassis ID type. For example, MAC address.
Figure 3-26

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-44 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•Chassis ID – Displays the chassis identification of the device transmitting the LLDP
frame.
•System Name – Displays the administratively assigned device name.
•System Description – Describes the device. For example, syste m hardware type and
version, operating system and network software.
•System Capabilities – Describes the primary device function. For example: Bridge,
Router.
Port Information
•Interface – Displays the port number.
•Port ID Subtype – Displays the port ID type. For example, MAC address.
•Port ID – Displays the port identification of the port transmitting the LLDP frame.
•Port Description – Displays information about the port, including manufacturer, product
name and hardware/software version.
•Advertisement – Displays the advertisement status of the port. The possible field values
are:
– Enabled – Adve rtisement is enable d on the port.
– Disabled – Advertisement is disabled on the port.
2. Click REFRESH to refresh the Local Information screen.
To view LLDP-MED detailed port information:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > Local Information. The LLDP-MED Local
Information screen displays.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-45
v1.0, November 2007
2. Click the Interface to view its detailed information. The Port Information window opens:
The Port Information window contains the following fields:
Managed Address
•Address Subtype – Displays the managed address subtype. For example, IPv4.
•Address – Displays the managed address.
•Interface Subtype – Displays the port subtype.
•Interface Number – Displays the port number.
MAC/PHY Details
•Auto-Negotiation Supported – Displays the port speed auto-negotiation support status.
The possible values are:
– True – Auto-negotiation is supported on the port.
– False – Auto-negotiation is not supported on the port.
•Auto-Negotiation Enabled – Displays the port speed auto-negotiation active status. The
possible values are:
Figure 3-27

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-46 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
– Enabled – Auto-neg otiation is enabled on the port.
– Disabled – Auto-negotiation is not enabled on the port.
•Auto-Negotiation Advertised Capabilities – Displays the port speed auto-negotiation
capabilities. For example, 1000BASE-T half duplex mode, 100BASE-TX full duplex
mode.
•Operational MAU Type – Displays the Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) type. The
MAU performs physical layer functions, including digital data conversion from the
Ethernet interfaces’ collision detection and bit injection into the network. For example,
100BASE-TX full duplex mode.
MED Details
•Capabilities Supported – Displays the MED capabilities enabled on the port.
•Current Capabilities – Capabilities indicates the TLV is advertised by the port.
•Device Class – Network Connectivity indicates the device is a network connectivity
device
Network Policies
•Application Type – Displays the network policy application type. For example, Voice.
•VLAN ID – Displays the network policy VLAN ID.
•VLAN Type – Displays the VLAN type for which the network policy is defined. The
possible field values are:
– Tagged – The network policy is defined for tagged VLANs.
– Untagged – The network policy is defined for untagged VLANs.
•User Priority – Displays the network policy user priority.
•DSCP – Displays the network policy DSCP.
3. Click the Network Policies gold bar to display the network policies applied to the port.
Neighbors Information
The LLDP Neighbors Information screen contains information received from neighboring device
LLDP advertisements.
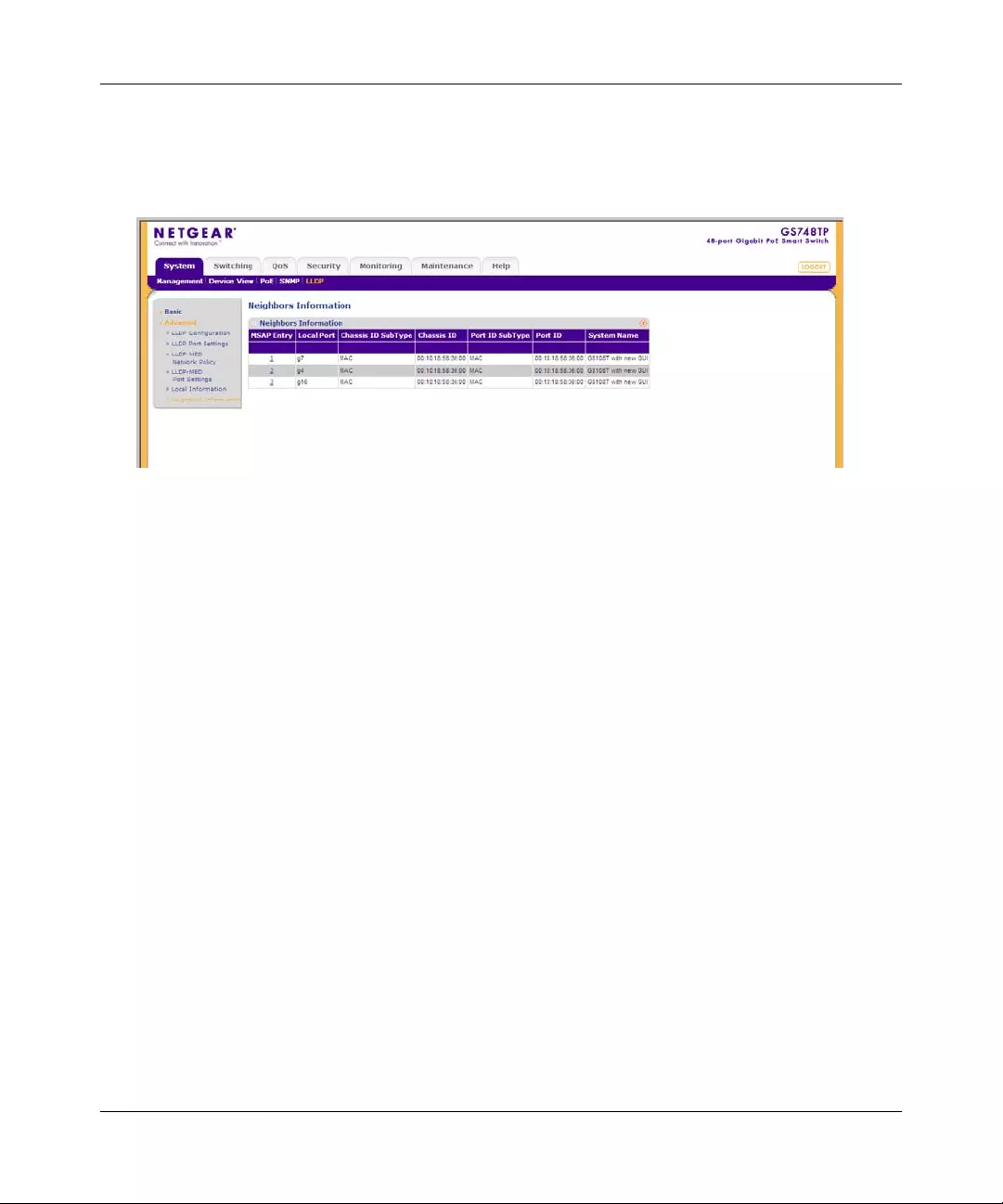
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-47
v1.0, November 2007
To view LLDP neighbors information:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > Neighbors Information. The LLDP Neighbors
Information screen displays:
The LLDP Neighbors Information screen contains the following fields:
•MSAP Entry – Displays the device’s Media Service Access Point (MSAP) entry number.
•Local Port – Displays the port number.
•Chassis ID Subtype – Displays the chassis ID subtype. For example, MAC address.
•Chassis ID – Displays the chassis identification of the device transmitting the LLDP
frame.
•Port ID Subtype – Displays the port ID subtype. For example, MAC address.
•Port ID – Displays the port identification of the port transmitting the LLDP frame.
•System Name – Displays the administratively assigned device name.
2. Click REFRESH to refresh the Neighbors Information screen.
To view LLDP Neighbors detailed information:
1. Click System > LLDP > Advanced > Neighbors Information. The LLDP Neighbors
Information screen displays.
Figure 3-28
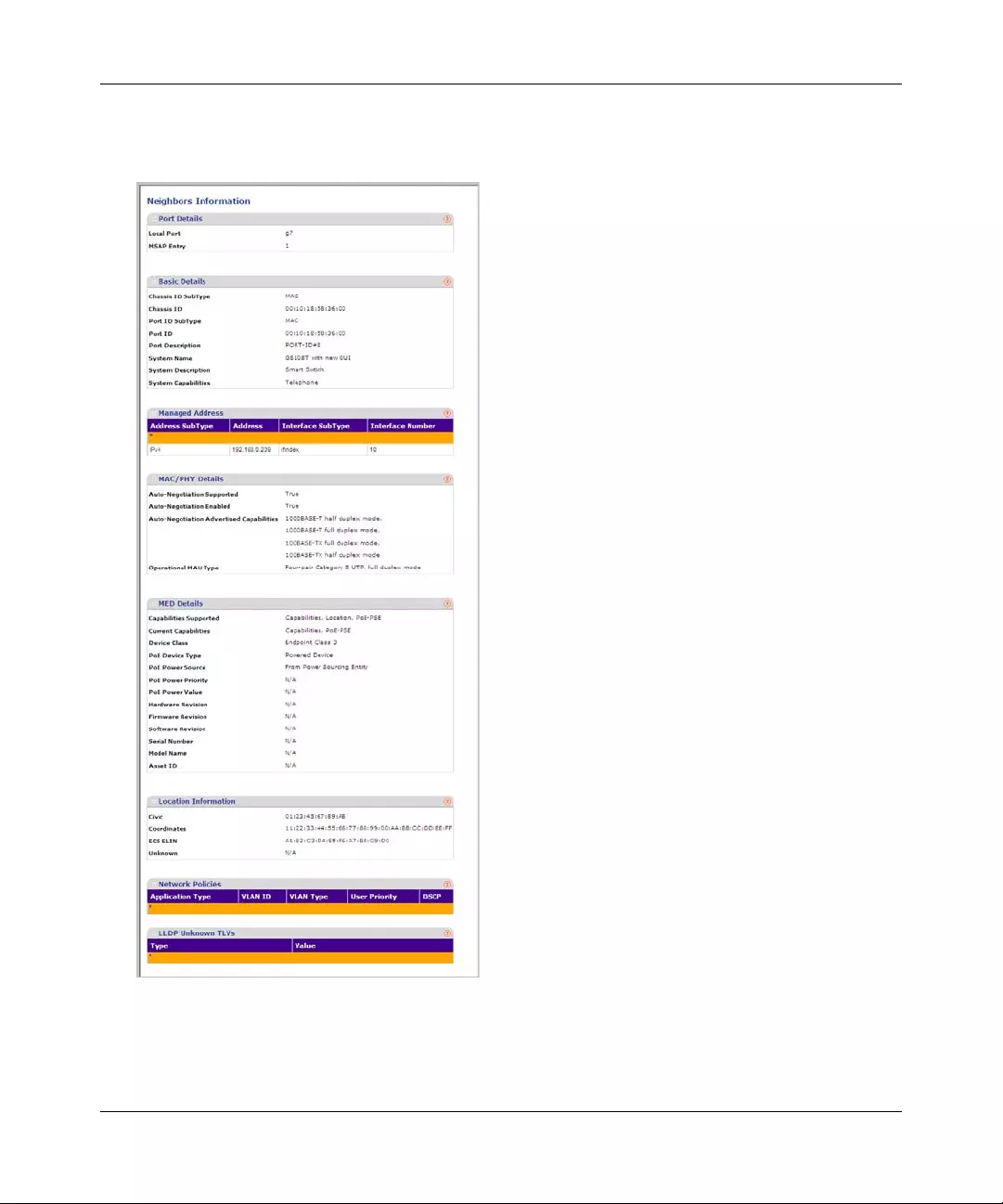
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-48 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
2. Click the MSAP Entry to view its detailed information. The Neighbors Information window
opens:
Figure 3-29

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-49
v1.0, November 2007
The Neighbors Information window contains the following fields:
Port Details
•Local Port – Displays the port number.
•MSAP Entry – Displays the device’s Media Service Access Point (MSAP) entry number.
Basic Details
•Chassis ID Subtype – Displays the chassis ID subtype. For example, MAC address.
•Chassis ID – Displays the chassis identification of the device transmitting the LLDP
frame.
•Port ID Subtype – Displays the port ID subtype. For example, IPv4 address.
•Port ID – Displays the port identification of the port transmitting the LLDP frame.
•Port Description – Displays information about the port, including manufacturer, product
name and hardware/software version.
•System Name – Displays the administratively assigned device name.
•System Description – Describes the device. For example, syste m hardware type and
version, operating system and network software.
•System Capabilities – Describes the primary device function. For example: Bridge,
Router.
Managed Address
•Address Subtype – Displays the managed address subtype. For example, MAC or IPv4.
•Address – Displays the managed address.
•Interface Subtype – Displays the port subtype.
•Interface Number – Displays the port number.
MAC/PHY Details
•Auto-Negotiation Supported – Displays the port speed auto-negotiation support status.
The possible values are:
– True – Auto-negotiation is supported on the port.
– False – Auto-negotiation is not supported on the port.
•Auto-Negotiation Enabled – Displays the port speed auto-negotiation active status. The
possible values are:
– Enabled – Auto-neg otiation is enabled on the port.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-50 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008
– Disabled – Auto-negotiation is not enabled on the port.
•Auto-Negotiation Advertised Capabilities – Displays the port speed auto-negotiation
capabilities. For example, 1000BASE-T half duplex mode, 100BASE-TX full duplex
mode.
•Operational MAU Type – Displays the Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) type. The
MAU performs physical layer functions, including digital data conversion from the
Ethernet interfaces’ collision detection and bit injection into the network. For example,
100BASE-TX full duplex mode.
MED Details
•Capabilities Supported – Displays the MED capabilities enabled on the port.
•Current Capabilities – Displays the MED TLVs advertised by the port.
•Device Class – Displays the LLDP-MED endpoint device class. The possible device
classes are:
– Endpoint Class 1 – Indicates a generic endpoint class, offering basic LLDP services.
– Endpoint Class 2 – Indicates a media endpoint class, offering media streaming
capabilities as well as all Class 1 features.
– Endpoint Class 3 – Indicates a communications device class, offering all Class 1 and
Class 2 features plus location, 911, Layer 2 switch support and device information
management capabilities.
•PoE Device Type – Displays the port PoE type. For example, Powered.
•PoE Power Source – Displays the port’s power source.
•PoE Power Priority – Displays the port’s power priority.
•PoE Power Value – Displays the port’s power value.
•Hardware Revision – Displays the hardware version.
•Firmware Revision – Displays the firmware version.
•Software Revision – Displays the software version.
•Serial Number – Displays the device serial number.
•Model Name – Displays the devic e model name.
•Asset ID – Displays the asset ID.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing System Settings 3-51
v1.0, November 2007
Location Information
•Civic – Displays the device’s civic or street address location. For example, 123 45th St E.
The field value length range is 6 - 160 characters.
•Coordinates – Displays the device’s location map coordinates - latitude, longitude and
altitude.
•ECS ELIN – Displays the device’s Emergency Call Service (ECS) Emergency Location
Identification Number (ELIN). The field range is 10 - 25.
•Unknown – Displays unknown location information.
Network Policies
•Application Type – Displays the network policy application type. For example, Voice.
•VLAN ID – Displays the VLAN ID for which the network policy is defined.
•VLAN Type – Displays the VLAN type for which the network policy is defined. The
possible field values are:
– Tagged – The network policy is defined for tagged VLANs.
– Untagged – The network policy is defined for untagged VLANs.
•User Priority – Displays the network policy user priority.
•DSCP – Displays the network policy DSCP.
LLDP Unknown TLVs
•Type – Displays the unknown TLV type field.
•Value – Displays the unknown TLV value field.
3. Click the Network Policies gold bar to display the network policies applied to the MSAP
entry.
4. Click the LLDP Unknown TLVs gold bar to display the MSAP entry’s unknown TLVs.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
3-52 Managing System Settings
v1.0, April 2008

4-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 4
Configuring Switching Settings
Configuring Switching Settings
The navigation pane at the top of the web browser interface contains a Switching tab that enables
you to manage your GS700TP Smart Switch with features under the following main heading s:
•“Ports”
•“LAG”
•“VLAN”
•“Voice VLAN”
•“STP”
•“Multicast”
•“Address Table”
The description that follows in this chapter describes configuring and managing switching settings
in the GS700TP Smart Switch.
Ports
The Ports menu contains the following option:
•“Port Configuration”
Port Configuration
The Port Configuration screen contains fields for defining port parameters enabled on the ports.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-2 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To configure port parameters:
1. Click Switching > Ports > Port Configuration. The Port Configuration screen displays:
The Port Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Port – Displays the port number.
•Port Description – Enter a user-defined port description.
•Status – Select the port’s operational status. The possible field values are:
– Up – The port is operational.
– Down – The port is not operational.
•Reactivate Suspended – Select the reactivation status for a port disabled through the
locked port security option. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable reactivation.
– Disable – Disable reactivation.
Figure 4-1

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-3
v1.0, April 2008
•Port Speed – Select the data transmission rate for the port. The port type determines
which speed setting options are available. Port speeds can only be configured when auto
negotiation is disabled. The possible field values are:
– 10M – The port is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
– 100M – The port is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
– 1000M – The port is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
•Duplex Mode – Select the port duplex mode. This field is configurable only when auto
negotiation is disabled and the port speed is set to 10M or 100M. The possible field values
are:
– Half – The interface supports transmission between the device and the client in only
one direction at a time.
– Full – The interface supports transmission between the device and its link partner in
both directions simultaneously.
– Auto – The interface supports transmission between the device and the link partner
based on the transmission mode of the link partner.
•Auto Negotiation – Select the port auto negotiation status. Auto negotiation is a protocol
between two link partners that enables a port to advertise its transmission rate, duplex
mode, and flow control abilities to its partner. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable auto negotiation.
– Disable – Disable auto negotiation.
•Back Pressure – Select the back pressure mode of the Port. Back Pressure mode is used
with half duplex mode to disable ports from receiving messages. Back Pressure mode is
disabled by default. The pos sible field values are:
– Enable – Enable back pressure mode.
– Disable – Disable back pressure mode.
•Flow Control – Select the flow contro l status of the port. Operates when the port is in full
duplex mode. Flow control is disabled by default. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable flow control.
– Disable – Disable Flow control.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-4 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•MDI/MDIX – Select the MDI/MDIX status of the port. Hubs and switches are
deliberately wired opposite the way end stations are wired, so that when a hub or switch is
connected to an end station, a straight through Ethernet cable can be used and the pairs
will match up properly. When two hubs or switches are connected to each other or two end
stations are connected to each other, a crossover cable is used to ensure that the correct
pairs are connected. The possible field values are:
– Auto – Provide automatic cable type detection.
– MDI (Media Dependent Interface) – Connect en d stations.
– MDIX (Media Dependent Interface with Crossover) – Connect HUBs and switches.
•LAG ID – Select the LAG ID to which the selected port is assigned.
2. Select the interface.
3. Enter or modify the fields in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
LAG
A Link Aggregated Group (LAG) optimizes port usage by linking a group of ports together to
form a single LAG. Aggregating ports multiplies the bandwidth between the devices, increases
port flexibility, and provides link redundancy. Ports added to a LAG lose their individual port
configuration. When ports are removed from the LAG, the original port configuration is applied to
the ports. Ensure the following, when configuring LAGs:
• All ports within a LAG must be of the same media type.
• A VLAN is not configured on the port.
• The port is not assigned to a different LAG.
• Auto-negotiation mode is not configured on the port.
• The port is in full-duplex mode.
• All ports in the LAG have the same ingress filtering and tagged modes.
• All ports in the LAG have the same back pressure and flow control modes.
• All ports in the LAG have the same priority.
• All ports in the LAG have the same transceiver type.
• The device supports up to eight LAGs with eight ports in each LAG.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-5
v1.0, April 2008
• LACP LAGs support up to 16 ports, with eight ports active at any given time.
The LAG menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The LAG Basic menu contains the following options:
•“LAG Configuration”
•“LAG Membership”
LAG Configuration
The Basic LAG Configuration screen contains fields for configuring LAG parameters. The system
supports 8 LAGs, and each LAG can contain up to 8 ports.
To define LAG parameters:
1. Click Switching > LAG > Basic > LAG Configuration. The Basic LAG Configuration
screen displays:
The Basic LAG Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the LAG number.
•Description – Enter a user-defined LAG description.
Figure 4-2

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-6 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•Status – Select the current link operation. The possible field values are:
– Up – The LAG is currently linked and forwarding traffic.
– Down – The LAG is currently not linked.
•Reactivate Suspended – Select the action to apply to a suspended LAG. The possible
field values are:
– Enable – Reactivate the suspended LAG.
– Disable – Do not reactivate the suspended LAG.
•Type – Displays the LAG type. The possible field values are:
– S tatic – The LAG is configured manu ally.
– LACP – The LAG is configured automatically.
•Speed – Select the data transmission rate for the LAG. The LAG type determines what
speed setting options are available. The possible field values are:
– 10M – The LAG is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
– 100M – The LAG is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
– 1000M – The LAG is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
•Duplex Mode – Displays the duplex mode of the LAG. The possible field value is:
– Full – The interface supports transmission between the device and its link partner in
both directions simultaneously.
•Auto Negotiation – Select the auto negotiation status of the LAG. Auto Negotiation is a
protocol between two lin k partners that enables a port to adve rtise its transmission rate,
duplex mode, and flow control abilities to its partner. Auto Negotiation is enabled by
default. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable auto negotiation.
– Disable – Disable auto negotiation.
•Flow Control – Select the flow control status of the LAG. Operates when the LAG is in
full duplex mode. Flow Control is disabled by default. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable flow control.
– Disable – Disable flow control.
2. Select the interface.
3. Enter or modify the fields in the first row.
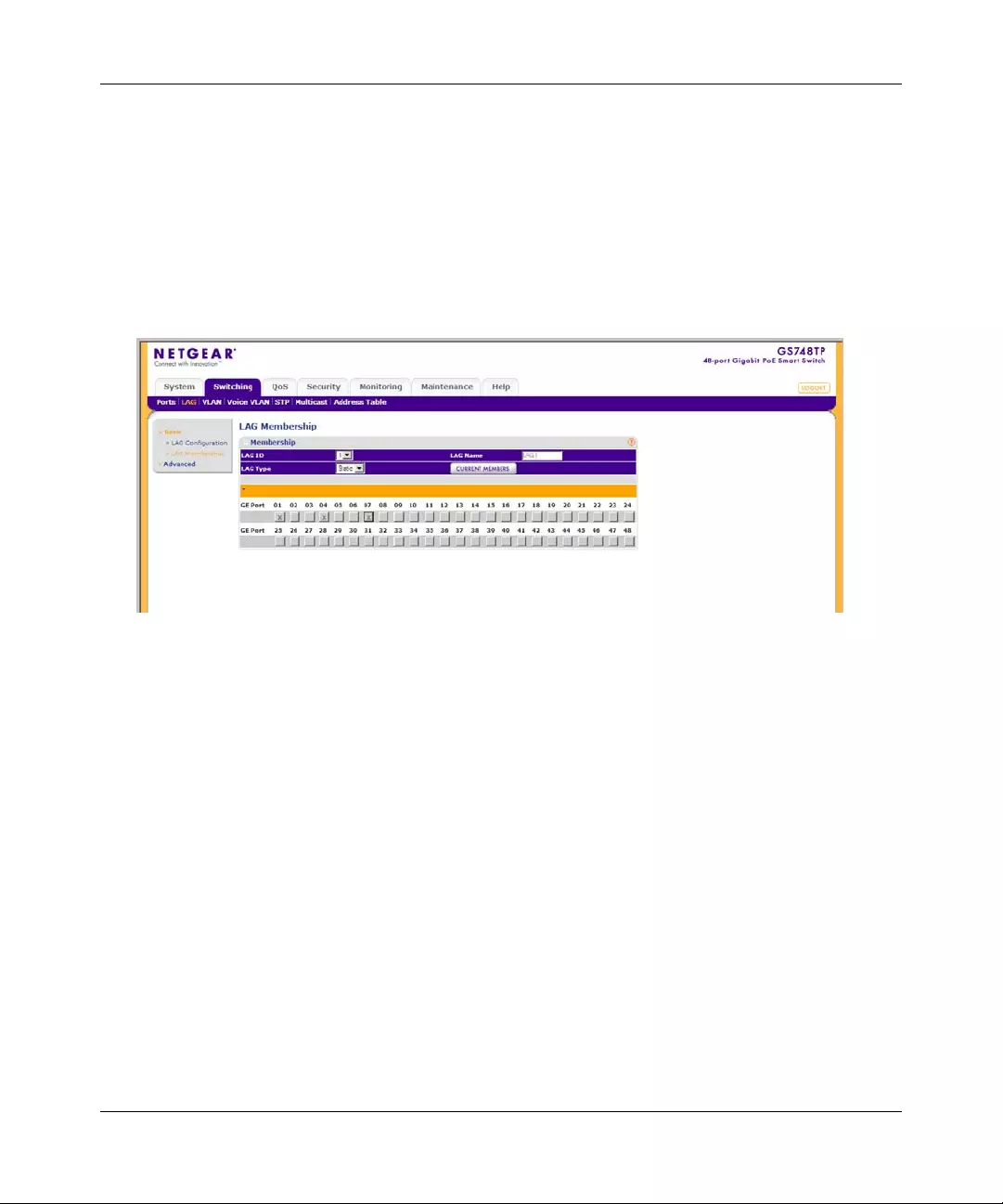
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-7
v1.0, April 2008
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
LAG Membership
The Basic LAG Membership screen allows network managers to assign ports to LAGs.
To assign ports to LAGs:
1. Click Switching > LAG > Basic > LAG Membership. The Basic LAG Membership screen
displays:
The Basic LAG Membership screen contains the following fields:
•LAG ID – Select the LAG ID.
•LAG Name – Displays the user-defined LAG name.
•LAG Type – Select the LAG type. The possible field values are:
– S tatic – The LAG is configured manu ally.
– LACP – The LAG is configured dynamically.
2. Select the LAG ID and LAG Type.
3. Click on the gold button. The port panel displays.
4. Select the ports to be members of the LAG.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 4-3
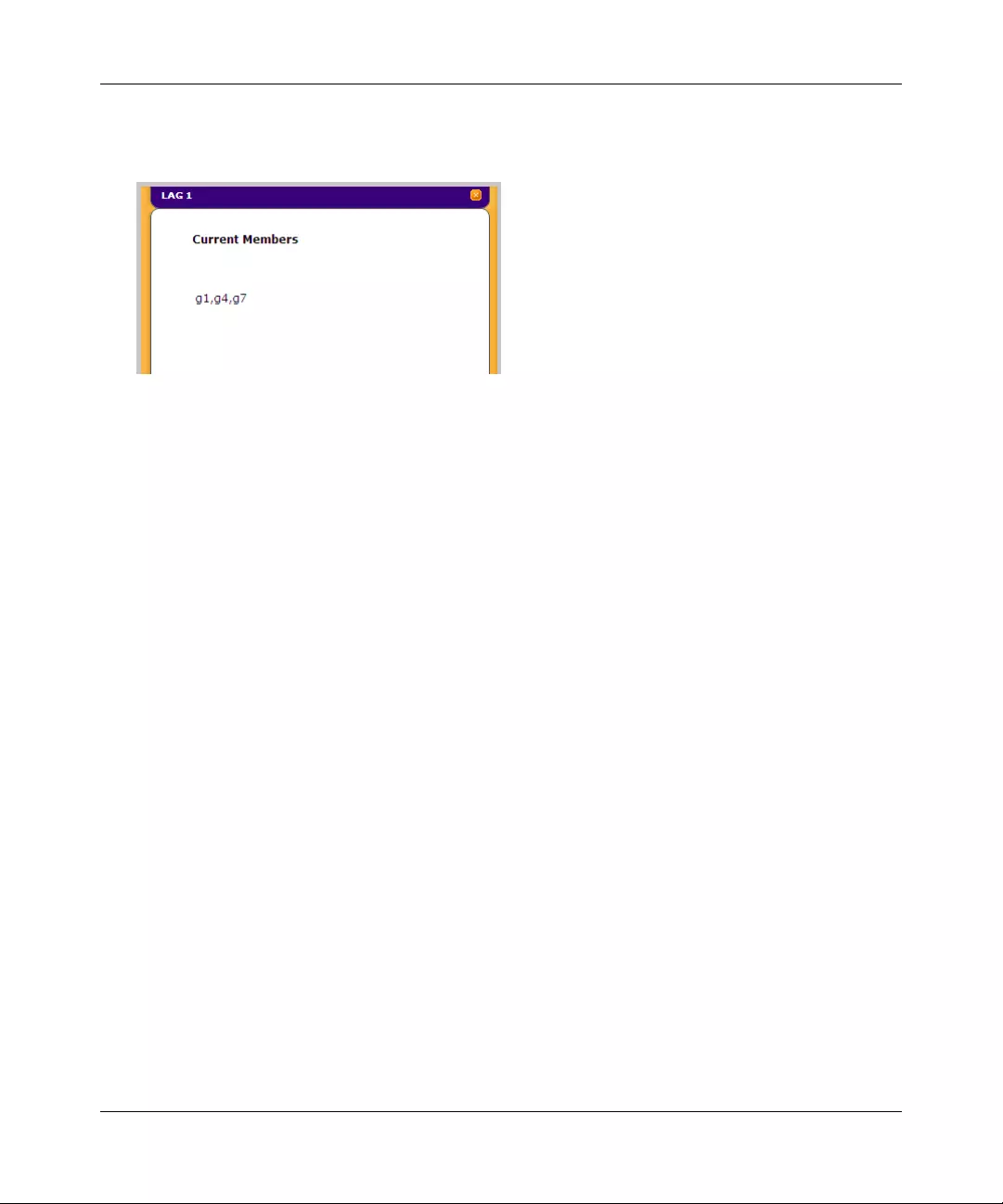
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-8 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
6. Click CURRENT MEMBERS. The Current Members window opens and displa ys the
member ports included in the LAG:
Advanced
The LAG Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“LAG Configuration”
•“LAG Membership”
•“LACP Configuration”
•“LACP Port Configuration”
LAG Configuration
The Advanced LAG Configuratio n screen contain s fields for configuring LAG parameters. The
system supports 8 LAGs, and each LAG can contain up to 8 ports.
Figure 4-4

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-9
v1.0, April 2008
To define LAG parameters:
1. Click Switching > LAG > Advanced > LAG Configuration. The Advanced LAG
Configuration screen displays:
The Advanced LAG Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the LAG number.
•Description – Enter a user-defined LAG description.
•Status – Select the current link operation. The possible field values are:
– Up – The LAG is currently linked and forwarding traffic.
– Down – The LAG is currently not linked.
•Reactivate Suspended – Select the action to apply to a suspended LAG. The possible
field values are:
– Enable – Reactivate the suspended LAG.
– Disable – Do not reactivate the suspended LAG.
•Type – Displays the LAG Type. The possible field values are:
– S tatic – The LAG is configured manu ally.
– LACP – The LAG is configured automatically.
•Speed – Select the data transmission rate for the LAG. The LAG type determines what
speed setting options are available. LAG speeds can only be configured when auto
negotiation is disabled. The possible field values are:
Figure 4-5

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-10 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
– 10M – The LAG is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
– 100M – The LAG is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
– 1000M – The LAG is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
•Duplex Mode – Displays the duplex mode of the LAG. The possible field value is:
– Full – The interface supports transmission between the device and its link partner in
both directions simultaneously.
•Auto Negotiation – Select the auto negotiation status of the LAG. Auto Negotiation is a
protocol between two lin k partners that enables a port to adve rtise its transmission rate,
duplex mode, and flow control abilities to its partner. Auto Negotiation is enabled by
default. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable auto negotiation.
– Disable – Disable auto negotiation.
•Flow Control – Select the flow control status of the LAG. Operates when the port is in full
duplex mode. Flow Control is disabled by default. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable flow control.
– Disable – Disable flow control.
2. Select the interface.
3. Enter or modify the fields in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
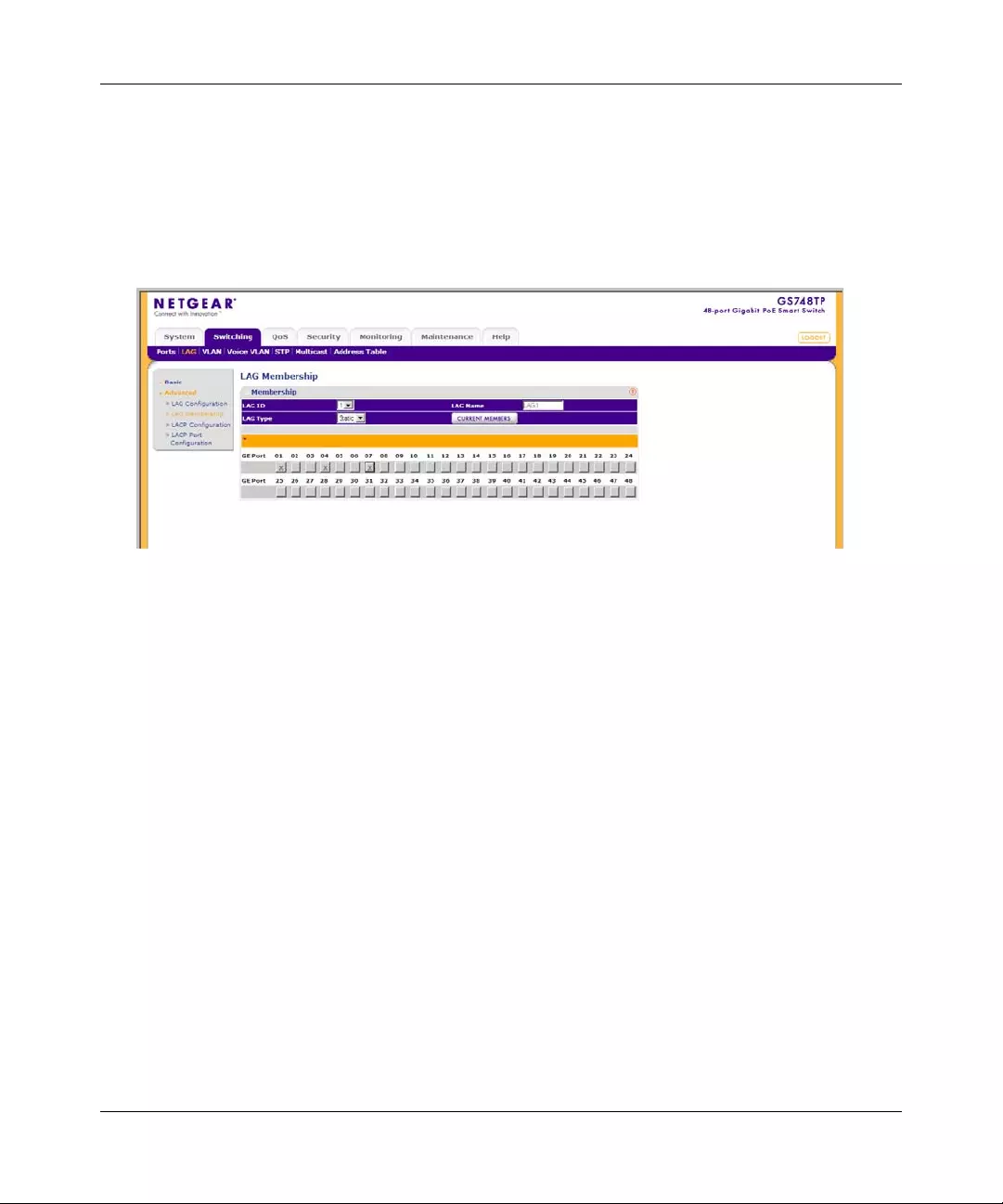
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-11
v1.0, April 2008
LAG Membership
The Advanced LAG Membership screen allows network managers to assign ports to LAGs.
To assign ports to LAGs:
1. Click Switching > LAG > Advanced > LAG Membership. The Advanced LAG
Membership screen displays:
The Advanced LAG Membership screen contains the following fields:
•LAG ID – Select the LAG ID.
•LAG Name – Displays the user-defined LAG name.
•LAG Type – Select the LAG type. The possible field values are:
– S tatic – The LAG is configured manu ally.
– LACP – The LAG is configured automatically.
2. Select the LAG ID and LAG Type.
3. Click on the gold button. The port panel displays.
4. Select the ports to be members of the LAG.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 4-6
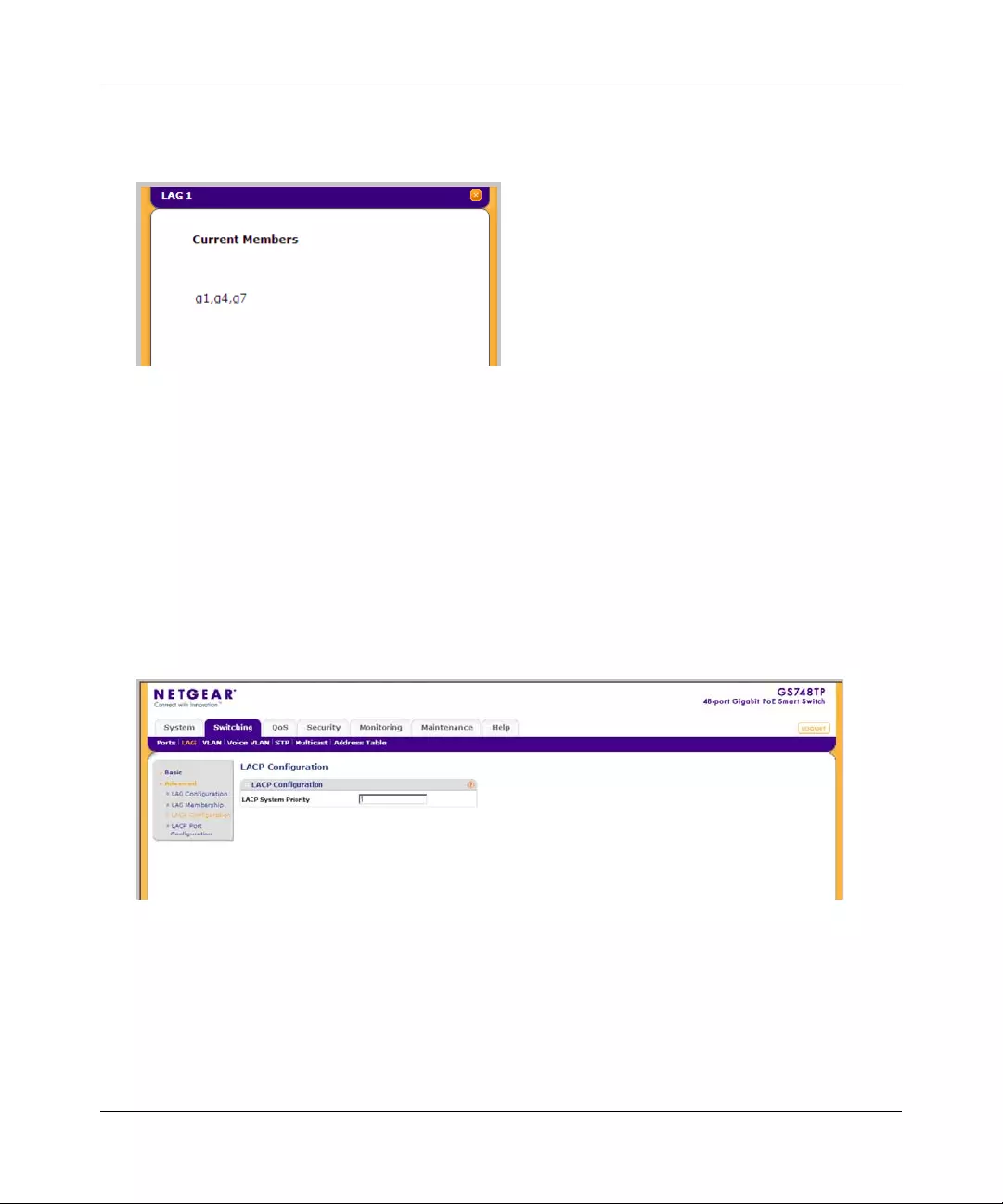
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-12 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
6. Click CURRENT MEMBERS. The Current Members window opens and displa ys the
member ports included in the LAG:
LACP Configuration
Aggregated links can be set up manually or automatically established by enabling LACP on the
relevant links. Aggregated ports can be linked into link-aggregation port-groups. Each group is
comprised of ports with the same speed. The LACP Configuration screen contains fields for
configuring LACP.
To configure LACP:
1. Click Switching > LAG > Advanced > LACP Configuration. The LACP Configuration
screen displays:
The LACP Configurati on screen contains the follo wi ng field:
•LACP System Priority – Enter the system priority value. The field range is 1-65535. Th e
field default is 1.
2. Enter the LACP System Priority in the provided field.
Figure 4-7
Figure 4-8
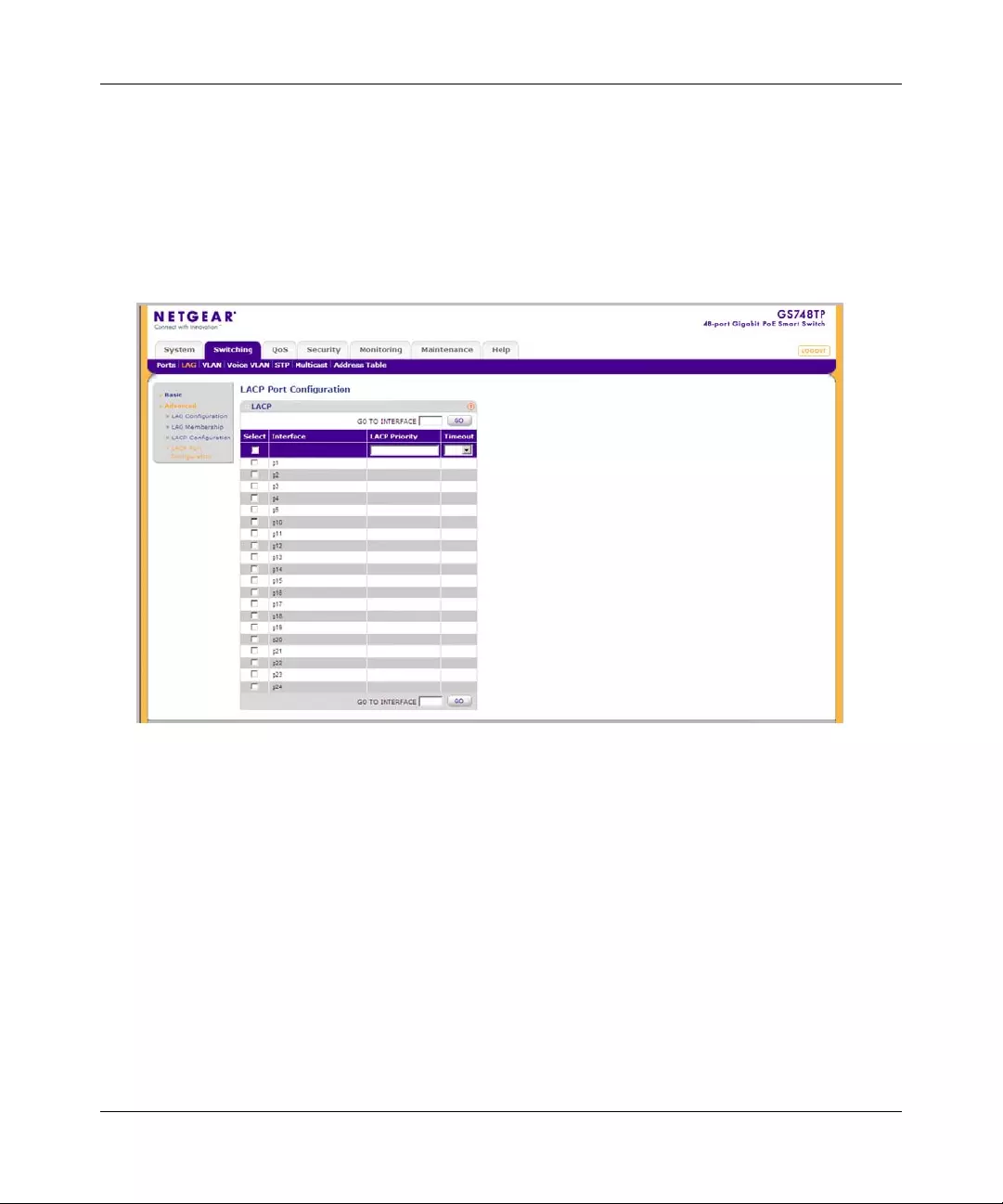
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-13
v1.0, April 2008
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
LACP Port Configuration
To configure LACP port priority:
1. Click Switching > LAG > Advanced > LACP Port Configuration. The LACP Port
Configuration screen displays:
The LACP Port Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the interface number to which timeout and priority values are
assigned.
•LACP Priority – Enter the port priority value. The field range is 1-65535.
•Timeout – Select the administrative LACP timeout. The possible field value s are:
– Long – A long timeout value (90 seconds). This is the default.
– Short – A short timeout value (3 seconds).
2. Select the interface.
3. Enter the LACP Priority and select the Timeout in the provided fields in the first row.
Figure 4-9

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-14 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
VLAN
VLANs are logical subgroups with a Local Area Network (LAN) which combine user stations and
network devices into a single unit, regardless of the physical LAN segment to which they are
attached. VLANs allow network traffic to flow more efficiently within subgroups. VLANs use
software to reduce the amount of time it takes for network changes, additions, and moves to be
implemented.
VLANs have no minimum numb er of ports, and can be created per unit, per device, or through an y
other logical connection combination, since they are software-based and not defined by physical
attributes.
VLANs function at Layer 2. Since VLANs isolate traffic within the LAN, a Layer 3 router
working at a protocol level is required to allow traffic flow between VLANs. Layer 3 routers
identify segments and coordinate with VLANs. VLANs are Broa dcast and Multicast domains.
Broadcast and Multicast traffic is transmitted only in the VLAN in which the traffic is generated.
VLAN tagging provides a method of transferring VLAN information between VLAN groups.
VLAN tagging attaches a 4-byte tag to packet headers. The VLAN tag indicates to which VLAN
the packets belong. VLAN tags are attached to the VLAN by either the end station or the network
device. VLAN tags also contain VLAN network priority information.
The VLAN menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The VLAN Basic menu contains the following options:
•“VLAN Configuration”
VLAN Configuration
The Basic VLAN Configuration screen provides information and parameters for configuring and
working with VLANs. The maximum number of activ e VLANs is 128.
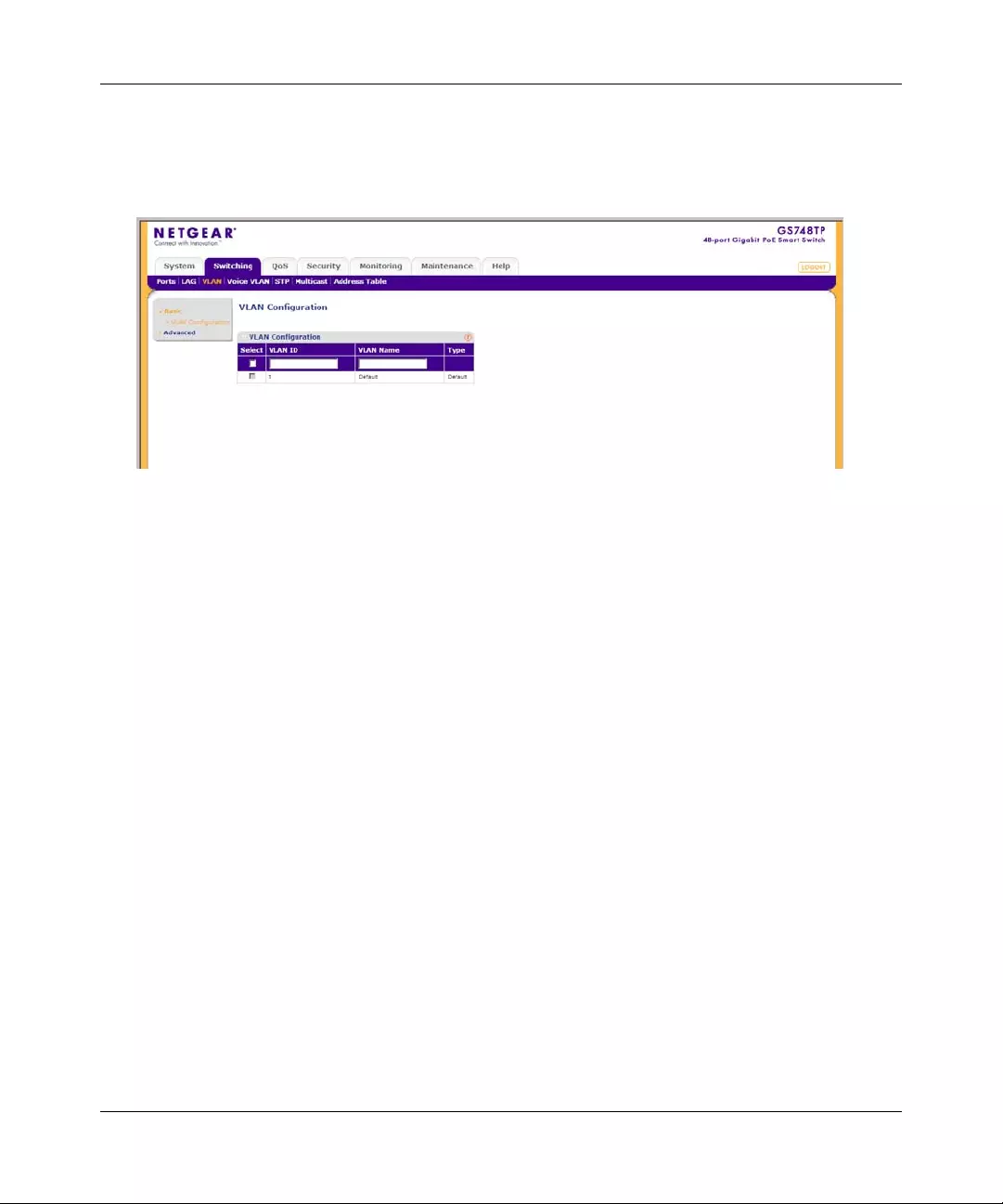
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-15
v1.0, April 2008
To define VLAN properties:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Basic > VLAN Configuration. The Basic VLAN Configuration
screen displays:
The Basic VLAN Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•VLAN ID – Enter the VLAN ID. The field range is 2-4093.
•VLAN Name – Enter the user-defined VLAN name.
•Type – Displays the VLAN type. The possible field values are:
– S tatic – The VLAN is user-d efin e d.
– Default – The default VLAN ID is 1. It cannot be modified by the user.
2. Select the VLAN entry.
3. Enter the VLAN ID and VLAN Name in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new VL AN :
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Basic > VLAN Configuration. The Basic VLAN Configuration
screen displays.
2. Enter the VLAN ID and VLAN Name in the provided fields in the first row.
3. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a VLAN:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Basic > VLAN Configuration. The Basic VLAN Configuration
screen displays.
Figure 4-10
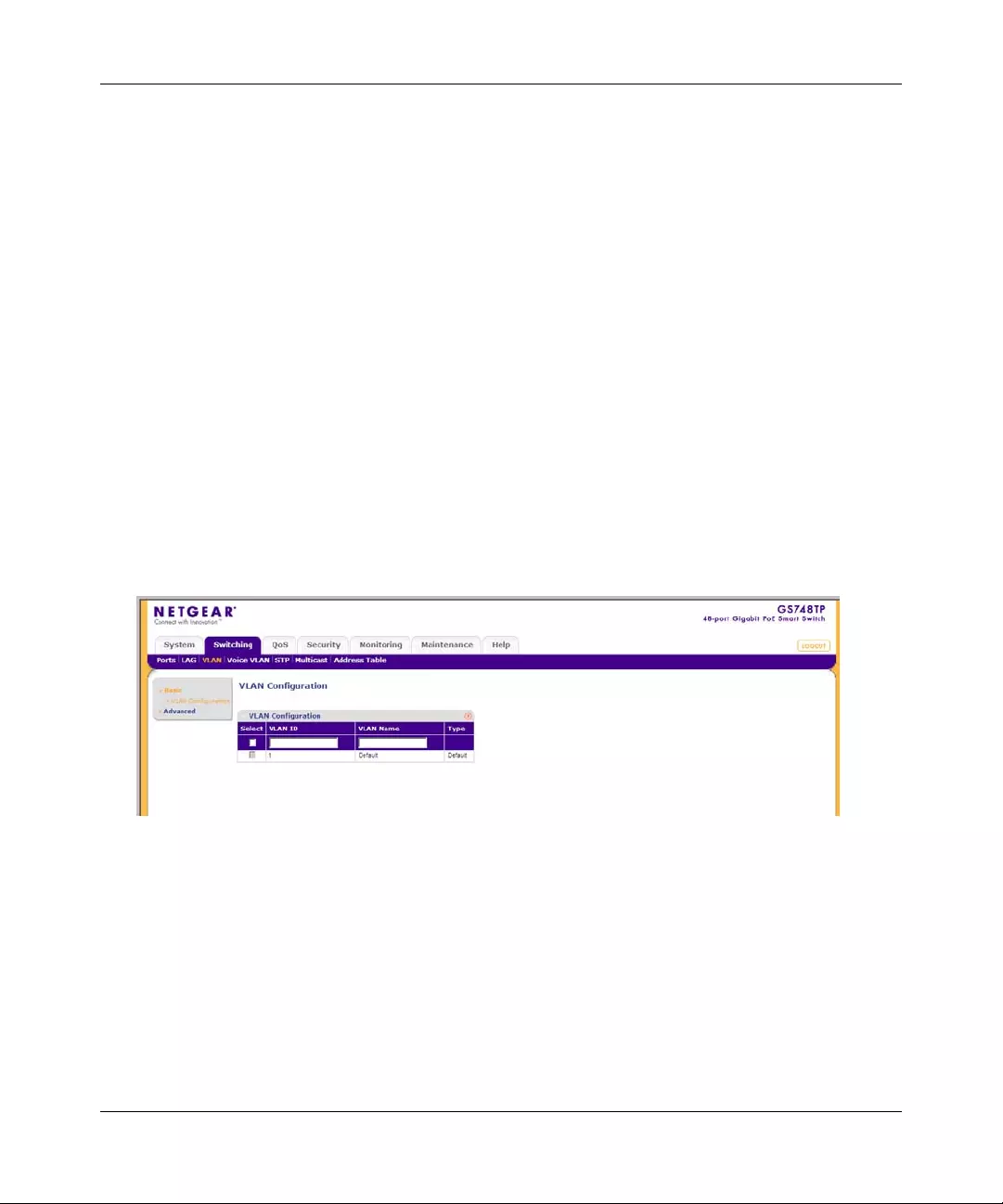
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-16 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
2. Select the VLAN entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
Advanced
The VLAN Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“VLAN Configuration”
•“VLAN Membership”
•“Port PVID Configuration”
VLAN Configuration
The Advanced VLAN Configuration screen provides information and parameters for configuring
and working with VLANs. The maximum number of active VLANs is 128.
To define VLAN properties:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Configuration. The Advanced VLA N
Configuration screen displays:
The Advanced VLAN Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•VLAN ID – Enter the VLAN ID. The field range is 2-4093.
•VLAN Name – Enter the user-defined VLAN name.
•Type – Displays the VLAN type. The possible field values are:
– S tatic – The VLAN is user-d efin e d.
– Default – The VLAN is the default VLAN. The default VLAN is enabled by default.
Figure 4-11
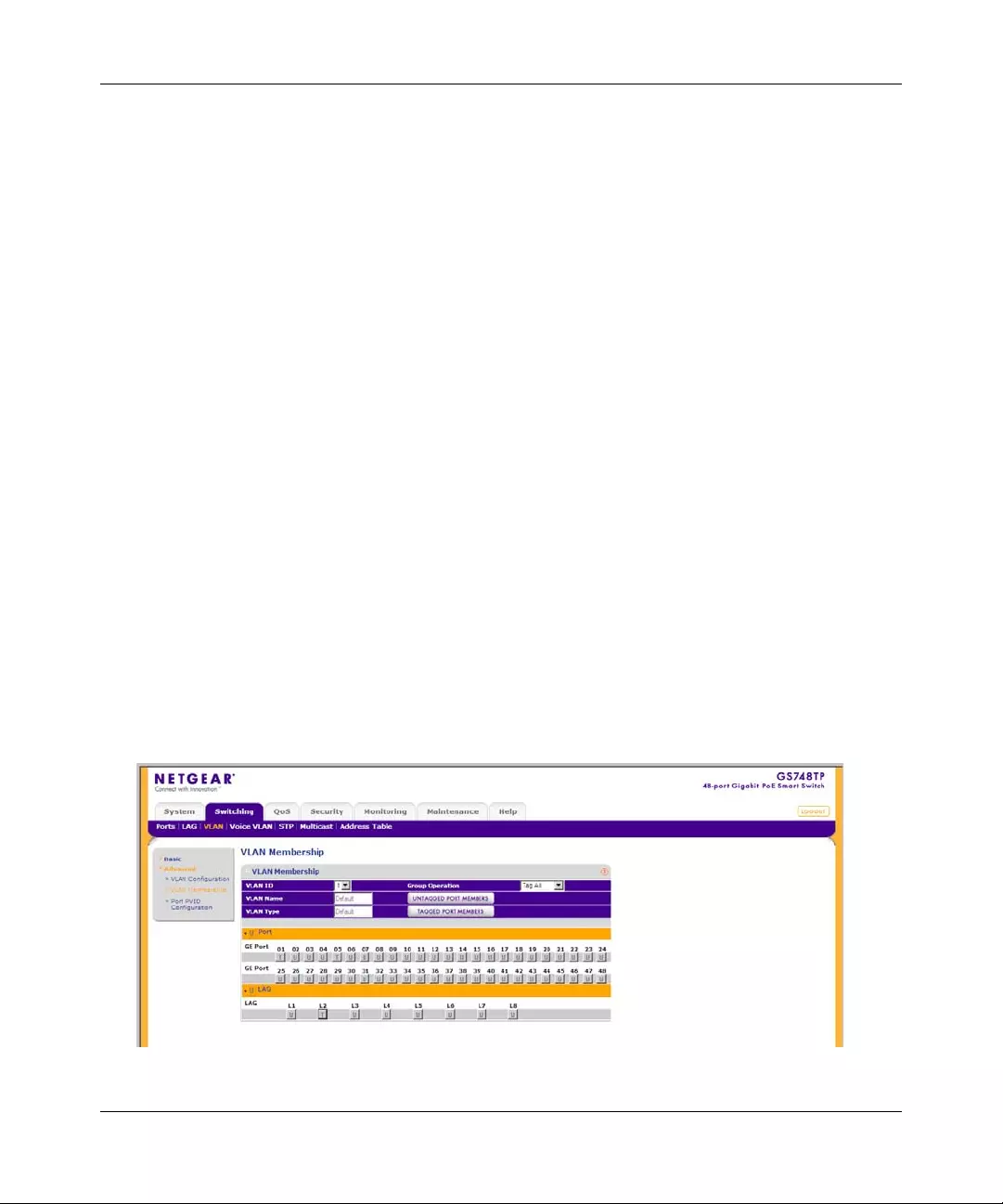
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-17
v1.0, April 2008
2. Select the VLAN entry.
3. Enter the VLAN ID and VLAN Name in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new VL AN :
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Configuration. The Advanced VLA N
Configuration screen displays.
2. Enter the VLAN ID and VLAN Name in the provided fields in the first row.
3. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a VLAN:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Configuration. The Advanced VLA N
Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the VLAN entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
VLAN Membership
The VLAN Membership screen contains a table that maps ports to VLANs. Ports are assigned
VLAN membership by toggling through the Port Control settings.
To define VLAN group membership:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Membership. The VLAN Membership
screen displays:
Figure 4-12

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-18 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
The VLAN Membership screen contains the following fields:
•VLAN ID – Select the VLAN ID to be displayed and configured. VLAN ID = 1 cannot be
modified.
•VLAN Name – Displays the name of the VLAN.
•VLAN Type – Displays the VLAN type. The possible field values are:
– S tatic – The VLAN is user-d efin e d.
– Default – The VLAN is the default VLAN. The default VLAN is enabled.
•Group Operation – Select the VLAN membership for all ports and LAGs. The possible
field values are:
– Tag All – Defines all selected interfaces as tagged VLAN members. Packets
belonging to the respective VLAN are tagged. The packets contain VLAN
information.
– Untag All – Defines all selected interfaces as untagged VLAN members. Packets
belonging to the respective VLAN are untagged.
– Remove All – Remove all the interfaces participating in the VLAN.
2. Select the VLAN ID from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the Group Operation from the list in the provided field.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To tag or untag selected ports or LAGs:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Membership. The VLAN Membership
screen displays.
2. Click a gold button to display the ports or LAGs.
3. Click the boxes below the selected ports or LAGs to mark them as tagged (T) or untagged (U).
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To tag or untag all the ports or all the LAGs:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Membership. The VLAN Membership
screen displays.
2. Click the ports quick box or the LAG quick box, repeatedly if necessary, until a T or U
appears in the quick box, marking all the ports or LAGs as tagged or untagged, respectively.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-19
v1.0, April 2008
To view VLAN tagged port members:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Membership. The VLAN Membership
screen displays.
2. Click TAGGED PORT MEMBERS. The VLAN Tagged Ports window opens:
Figure 4-13
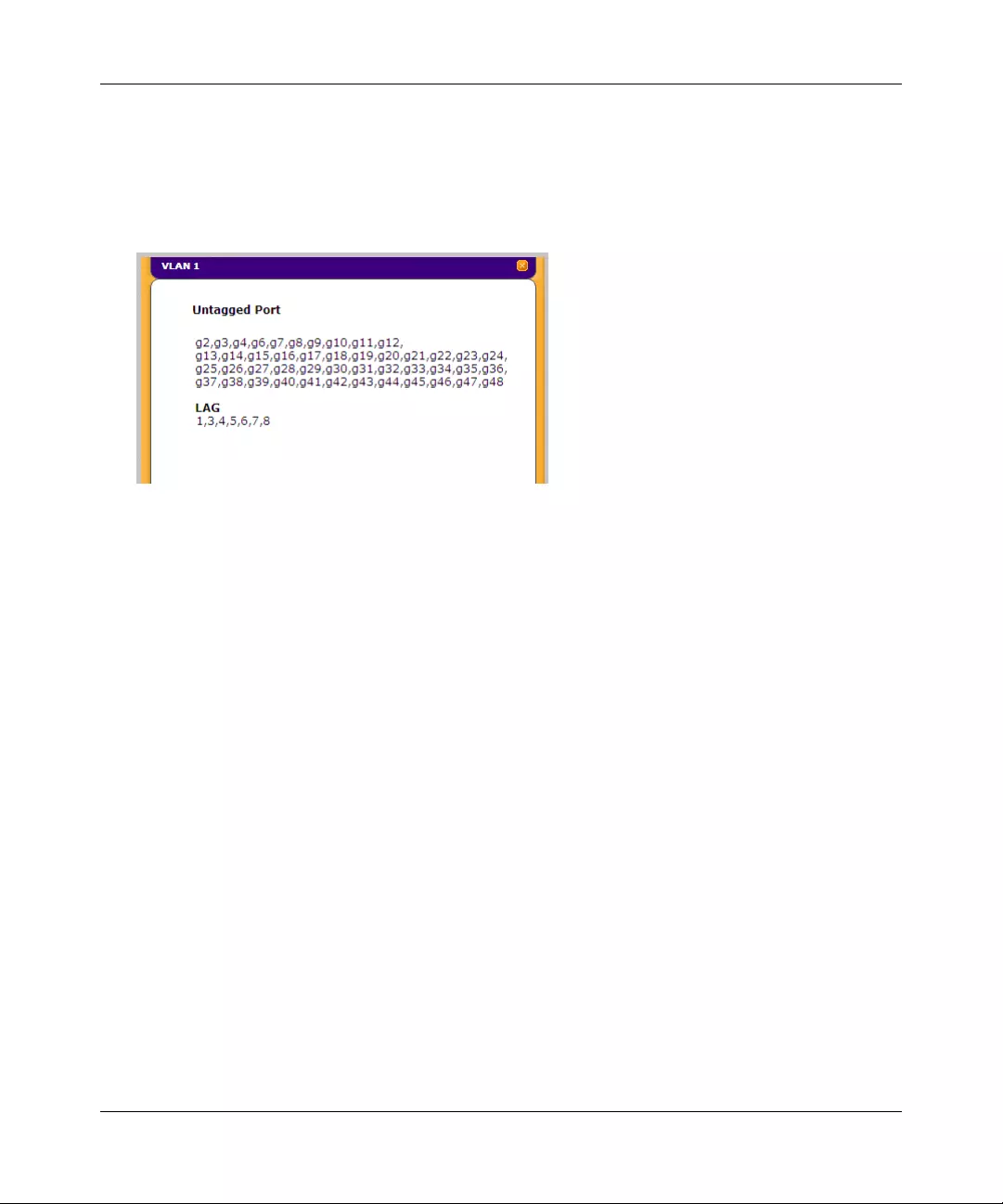
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-20 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To view VLAN untagged port members:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > VLAN Membership. The VLAN Membership
screen displays.
2. Click UNTAGGED PORT MEMBERS. The VLAN Untagged Ports screen opens:
Port PVID Configuration
The Port PVID Configuration screen contains parameters for assigning Port VLAN ID (PVID)
values to interfaces. All ports must have a defined PVID. If no other value is configured the default
VLAN PVID is used. VLAN ID 1 belongs to the default VLAN which cannot be deleted from the
system. Once the PVID is changed from 1 to another VLAN ID on an interface, the default VLAN
on that interface is automatically removed.
Figure 4-14
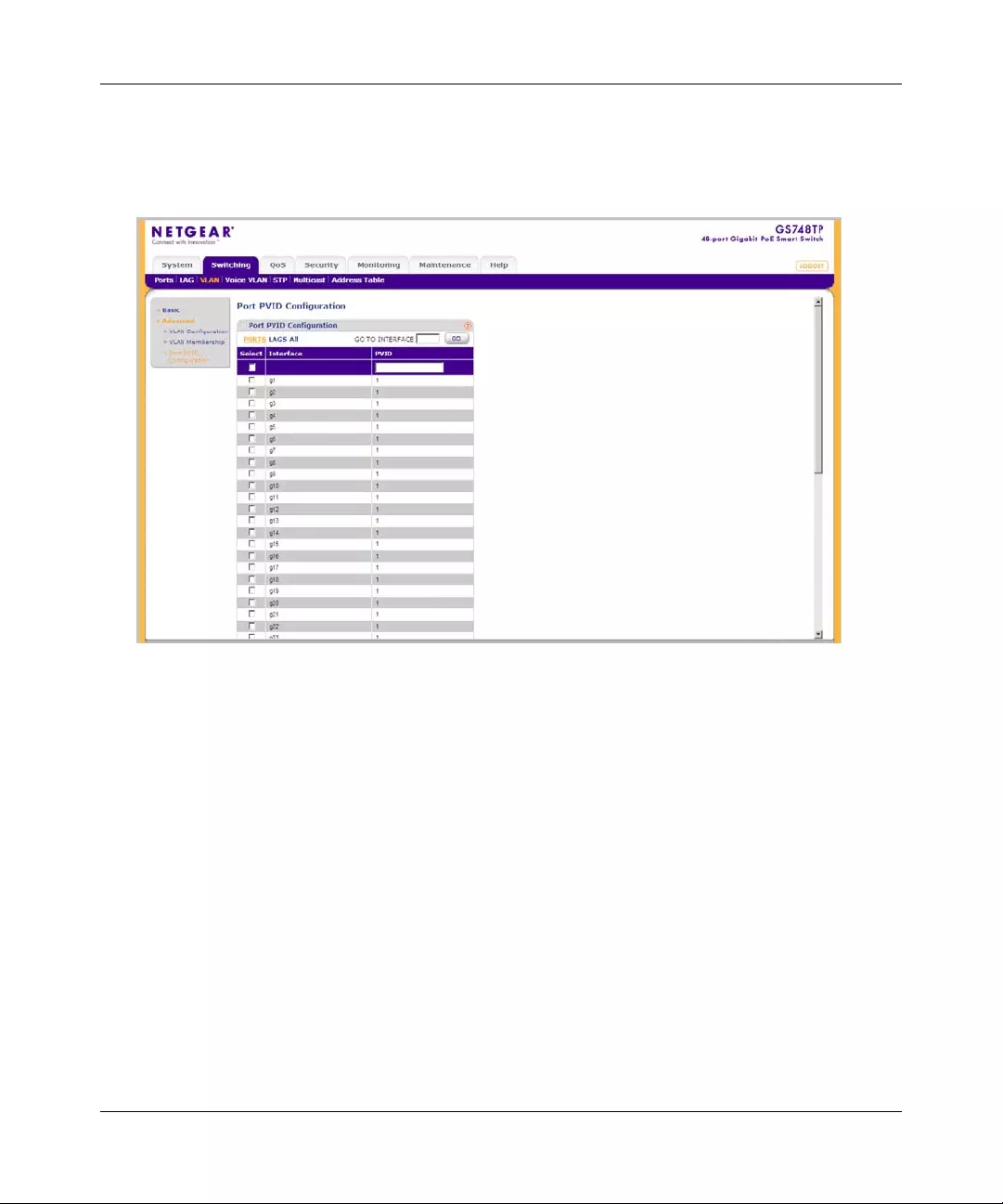
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-21
v1.0, April 2008
To configure Port PVID parameters:
1. Click Switching > VLAN > Advanced > Port PVID Configuration. The Port PVID
Configuration screen displays:
The Port PVID Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the interface id (port number or LAG number) to which the PVID tag
is assigned.
•PVID – Enter the PVID value. The possible field range is 1-4093.
2. Select an interface.
3. Enter the PVID in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 4-15

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-22 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN allows you to enhance VoIP service by co nfiguring ports to carry IP voice traffic
from IP phones on a specific VLAN. VoIP traffic has a preconfigured OUI prefix in the source
MAC address.
You can configure VLANs on which voice IP traffic is forwarded. Non-VoIP traffic is dropped
from the Voice VLAN in auto Voice VLAN secure mode. Voice VLAN also provides QoS to VoIP,
ensuring that the quality of voice does not deteriorate if the IP traffic is received unevenly. The
system supports one Voice VLAN.
There are two operational modes for IP Phones:
• IP phones are configured with VLAN-mode as enabled, ensuring that tagged packets are used
for all communications.
• If the IP phone’s VLAN-mode is disabled, the phone uses untagged packets. The phone uses
untagged packets while retrieving the initial IP address through DHCP. The phone eventually
uses the Voice VLAN and starts sending tagge d packets.
The Voice VLAN menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The Voice VLAN Basic menu contains the following options:
•“Properties”
Properties
The Voice VLAN Basic Properties screen contains information about Voice VLAN on the device,
including the ports enabled and included in the Voice VLAN.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-23
v1.0, April 2008
To define Voice VLAN settings:
1. Click Switching > Voice VLAN > Basic > Properties. The Voice VLAN Basic Properties
screen displays:
The Voice VLAN Basic Properties screen contains the following fields:
•Voice VLAN Status – Select the Voice VLAN status on the device. The possible field
values are:
– Enable – Enable Voice VLAN on the device.
– Disable – Disable Voice VLAN on the device. This is the default value.
•VoiceVL AN ID – Select the Voice VLAN ID number.
•Class of Service – Select the CoS tag to add to untagged packets received on the voice
VLAN. The possible field values are 0-7, where zero is the lowest priority, and seven is
the highest priority.
•Remark CoS – Enable or disable reassigning the CoS tag value to packets received on the
voice VLAN. The possible field values are:
– Disable – Disable remarking the packet CoS tag value. This is the default value.
– Enable – Enable remarking the packet CoS tag value.
Figure 4-16

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-24 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•Voice VLAN Aging Time – Enter the Voice VLAN aging time. The Voice VLAN aging
time sets the maximum inactivity time for a Voice VLAN port member after its MAC
address is aged out. If the time since the last MAC address with telephony MAC address
was aged out exceeds the Voice VLAN aging time, the port is dropped from the voice
VLAN. The default time is one day . The field format is Day, Hour, Minute. The aging time
starts after the MAC Address is aged out from the Dynamic MAC Address table. The
default time is 300 sec. For more information on defining MAC address age out time, see
“Dynamic Addresses”.
2. Select the device VoiceVLAN Status in the provided field.
3. If you selected Enable in the VoiceVLAN Status field, select the VoiceVLAN ID, Class of
Service, Remark CoS and enter the Voice VLAN Aging Time in the provided fields.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Advanced
The Voice VLAN Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“Properties”
•“Port Setting”
•“OUI”
Properties
The Voice VLAN Advanced Properties scree n contains information about Voice VLAN on the
device, including the ports enabled and included in the Voice VLAN.
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-25
v1.0, April 2008
To define Voice VLAN settings:
1. Click Switching > Voice VLAN > Advanced > Properties. The Voice VLAN Advanced
Properties screen displays:
The Voice VLAN Advanced Properties screen contains the following fields:
•VoiceVL AN Status – Select the Voice VLAN status on the device. The possible field
values are:
– Enable – Enable Voice VLAN on the device.
– Disable – Disable Voice VLAN on the device. This is the default value.
•VoiceVL AN ID – Select the Voice VLAN ID number.
•Class of Service – Select a CoS tag to add to untagged packets received on the voice
VLAN. The possible field values are 0-7, where zero is the lowest priority, and seven is
the highest priority.
•Remark CoS – Enable or disable reassigning the CoS tag value to packets received on the
voice VLAN. The possible field values are:
– Disable – Disable remarking the packet CoS tag value. This is the default value.
– Enable – Enable remarking the packet CoS tag value.
Figure 4-17

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-26 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•Voice VLAN Aging Time – Enter the Voice VLAN aging time. The Voice VLAN aging
time sets the maximum inactivity time for a Voice VLAN port member after its MAC
address is aged out. If the time since the last MAC address with telephony MAC address
was aged out exceeds the Voice VLAN aging time, the port is dropped from the voice
VLAN. The default time is one day . The field format is Day, Hour, Minute. The aging time
starts after the MAC Address is aged out from the Dynamic MAC Address table. The
default time is 300 sec. For more information on defining MAC address age out time, see
“Dynamic Addresses”.
2. Select the device VoiceVLAN Status in the provided field.
3. If you selected Enable in the VoiceVLAN Status field, select the VoiceVLAN ID, Class of
Service, Remark CoS and enter the Voice VLAN Aging Time in the provided fields.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Port Setting
The Voice VLAN Port Setting screen allows network managers to add ports or LAGs to the voice
VLAN.
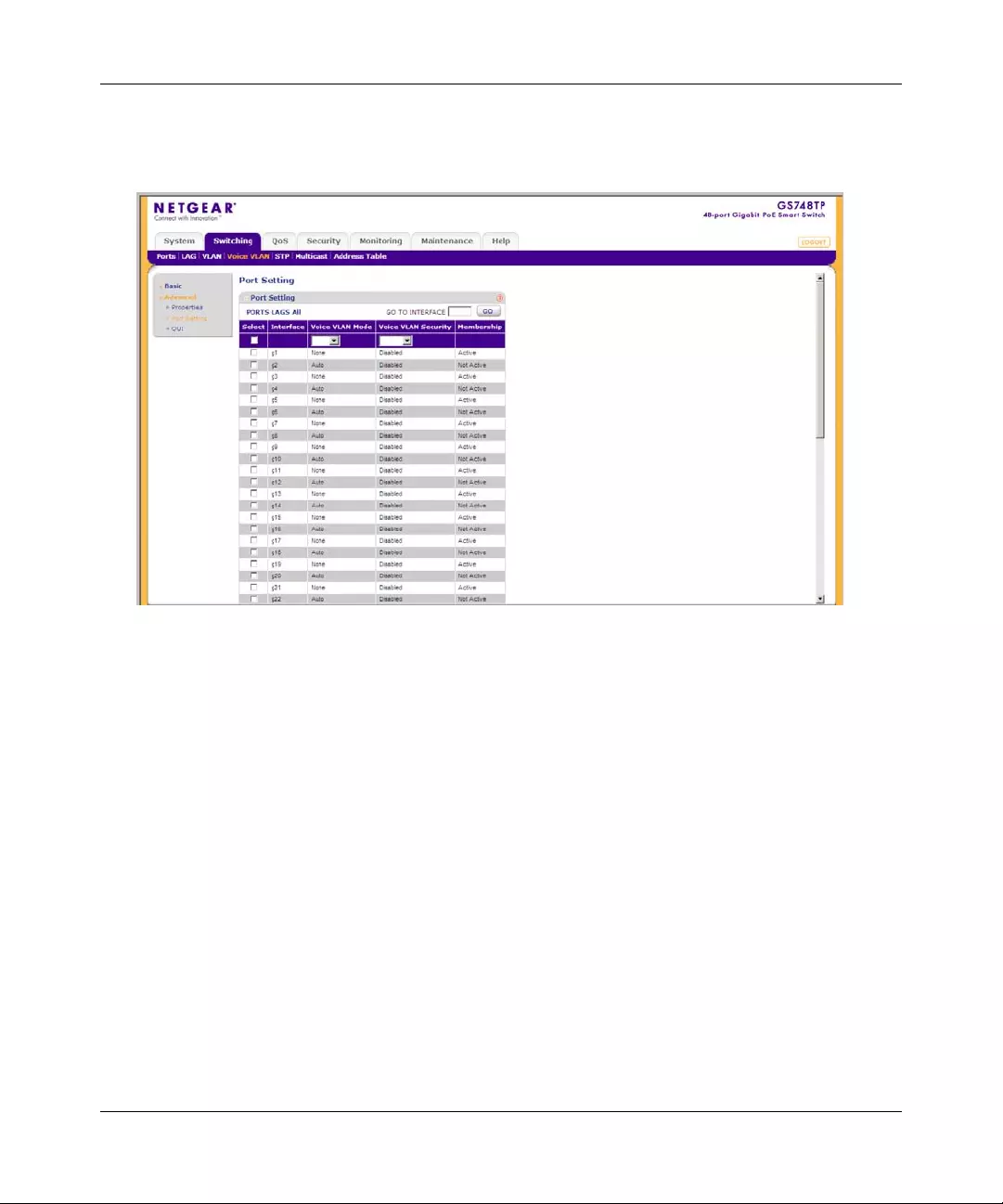
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-27
v1.0, April 2008
To add ports or LAGs to the Voice VLAN:
1. Click Switching > Voice VLAN > Advanced > Port Setting. The Port Setting screen opens:
The Voice VLAN Port Setting screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the interface for which the Voice VLAN settings are applied.
•Voice VLAN Mode – Select the Voice VLAN mode. The possible field values are:
–None – Maintain the current Voice VLAN port/LAG set tings. This is the default value.
–Auto – Enable the port/LAG to join the Voice VLAN if traffic with an IP Phone MAC
Address is transmitted on the port/LAG. The port/LAG is aged out of the voice VLAN
if the IP phone’s MAC address (with an OUI prefix) is aged out and exceeds the
defined aging time. If the MAC Address of the IP phones OUI was added manually to
a port/LAG in the Voice VLAN, the user cannot add it to the Voice VLAN in Auto
mode, only in Manual mode.
•Voice VLAN Security – Select the port/LAG security mode on the Voice VLAN. Port
Security ensures that packets arriving with an unrecognized OUI are dropped.
– Enable – Enable port/LAG security on the Voice VLAN.
– Disable – Disable port/LAG security on the Voice VLAN. This is the default value.
Figure 4-18

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-28 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•Membership – Displays the Voice VLAN member status. The possible field values are:
– Active – Indicates the Voice VLAN membership is active for the interface.
– Not Active – Indicates the Voice VLAN membership is not active for the interface.
2. Select the interface.
3. Select the Voice VLAN Mode, Voice VLAN Security and Membership in the provided
fields in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
OUI
The OUI screen lists the Organizationally Unique Identifiers (OUIs) associated with the Voice
VLAN. The first three bytes of the MAC Address contain a manufacturer identifier , while the last
three bytes contain a unique station ID. Using the OUI, you can add specific manufacturer’s MAC
addresses to the OUI table. Once the OUIs are added, all traffic received on the Voice VLAN ports
from the specific IP phone with a listed OUI is forwarded on the voice VLAN.
To define OUIs:
1. Click Switching > Voice VLAN > Advanced > OUI. The Voice VLAN OUI screen displays:
The Voice VLAN OUI screen contains the following fields:
•Telephony OUI(s) – Enter the OUI to enable on the Voice VLAN. The following OUIs
are enabled by default.
– 00-01-E3 – Assigned to Siemens IP Phones.
–00-03-6B – Assigned to Cisco IP Phones.
Figure 4-19

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-29
v1.0, April 2008
– 00-0F-E2 – Assigned to H3C IP Phones.
– 00-60-B9 – Assigned to NEC/Philips IP Phones.
– 00-D0-1E – Assigned to Pingtel IP Phones.
– 00-E0-75 – Assigned to Polycom/Veritel IP Phones.
– 00-E0-BB – Assigned to 3COM IP Phones.
•Description – Enter an OUI description up to 32 characters.
2. Select the OUI entry.
3. Enter the Telephony OUI(s) and Description in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new Voice VLAN OUI:
1. Click Switching > Voice VLAN > Advanced > OUI. The Voice VLAN OUI screen displays.
2. Enter the Telephony OUI(s) and Description in the provided fields in the first row.
3. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a Voice VLAN OUI:
1. Click Switching > Voice VLAN > Advanced > OUI. The Voice VLAN OUI screen displays.
2. Select the OUI entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
To restore Voice VLAN OUI factory defaults:
1. Click Switching > Voice VLAN > Advanced > OUI. The Voice VLAN OUI screen displays.
2. Click RESTORE DEFAULTS to restore the factory defaults.
STP
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides network topology for any arrangement of bridges. STP
also provides a single path between end stations on a network, eliminatin g loop s. Loop s occu r
when alternate routes exist between hosts. Loops in an extended network can cause bridges to
forward traffic indefinitely, resulting in increased traffic and reducing network efficiency.
The STP menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
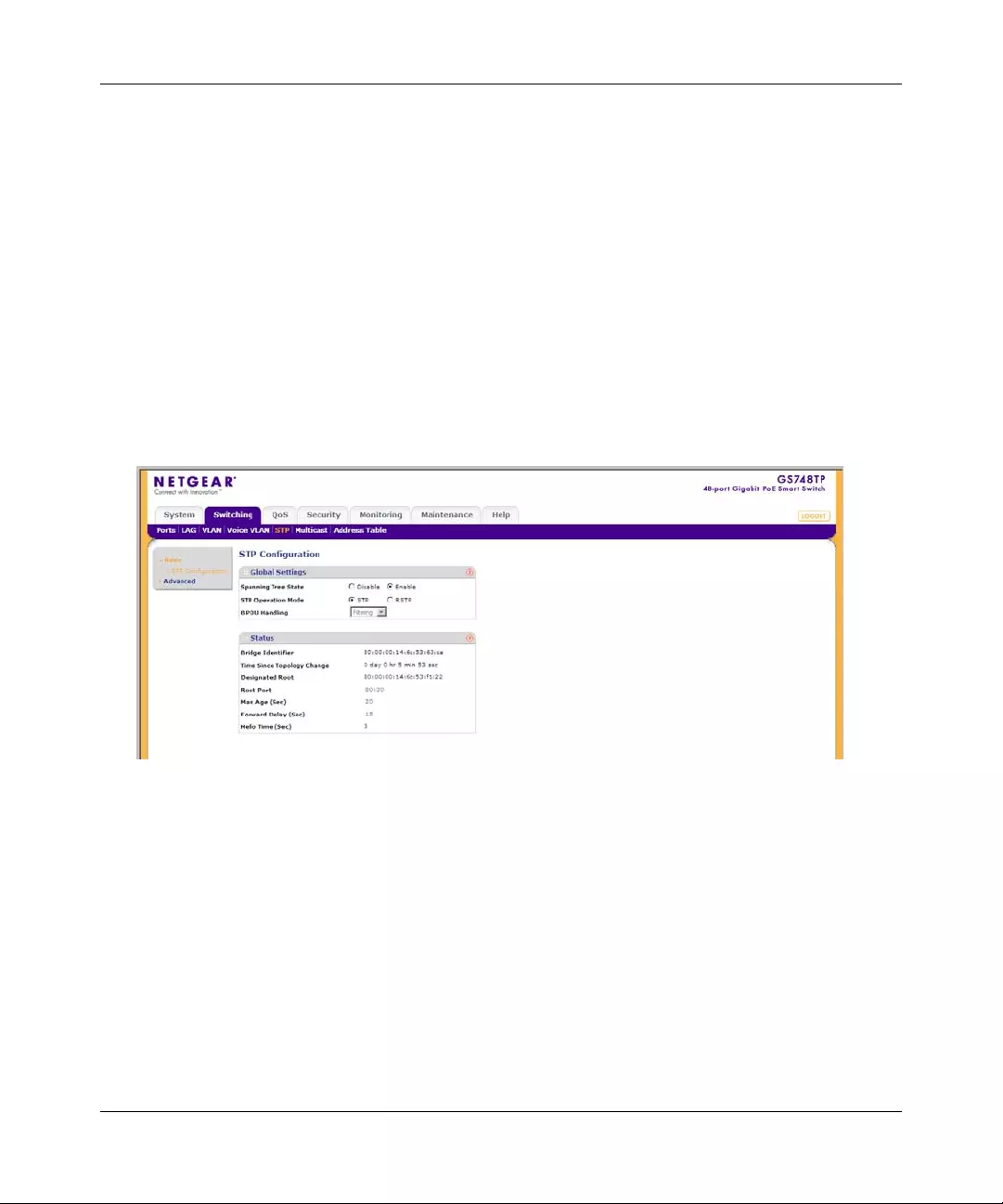
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-30 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•“Advanced”
Basic
The STP Basic menu contains the following options:
•“STP Configuration”
STP Configuration
The Basic STP Configuration screen contains parameters for configuring STP on the device.
To configure STP on the device:
1. Click Switching > STP > Basic > STP Configuration. The Basic STP Configuration screen
displays:
The Basic STP Configuration screen contains the following fields:
Global Settings
•Spanning Tree State – Select the STP state on the device. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable STP on the device.
– Disable – Disable STP on the device.
•STP Operation Mode – Select the STP mode on the device. The possible field values are:
– STP – Enable classic STP on the device.
– RSTP – Enable Rapid Spa nn i ng Tree Protocol (RSTP) on the device .
Figure 4-20

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-31
v1.0, April 2008
•BPDU Handling – Select the method of handlin g STP BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data
Units) when STP is disabled on the device or interface. The possible field values are:
– Filtering – BPDUs are filtered. This the default.
– Flooding – BPDUs are flooded to all ports in the system.
– Bridging – BPDUs are bridged to all ports in the VLAN.
Status
•Bridge Identifier – Displays the Bridge priority and MAC address.
•Time Since Topology Change – Displays the amount of time that has elapsed since the
bridge was initialized or reset or the last topology change that occurred. The time is
displayed in a day-hour-minute-second fo rmat, such as 2 days 5 hours 10 minutes and 4
seconds.
•Designated Root – Displays the Root Bridge priority and MAC address.
•Root Port – Displays the port number that offers the lowest cost path from this bridge to
the Root Bridge. This field is significant when the bridge is not the Root Bridge.
•Max Age (Sec) – Displays the device Maximum Age Time. The Maximum Age Time is
the amount of time in seconds a bridge waits before sending configuration messages. The
default Maximum Age Time is 20 seconds.
•Forward Delay (Sec) – Displays the device Forward Delay Time. The Forward Delay
Time is the amount of time in seconds a bridge remains in a listening and learning state
before forwarding pac kets. The default is 15 seconds.
•Hello Time (Sec) – Displays the device Hello T ime. The Hello Time indicates the amount
of time in seconds a Root Bridge waits between configuration messages. The default is 2
seconds.
2. Select Enable or Disable in the Spanning Tree State provided field.
3. Select the STP Operation Mode in the provided field.
4. If you selected Disable in the Spanning Tree State field, select the BPDU Handling mode
from the list in the provided field.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Advanced
The STP Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“STP Configuration”
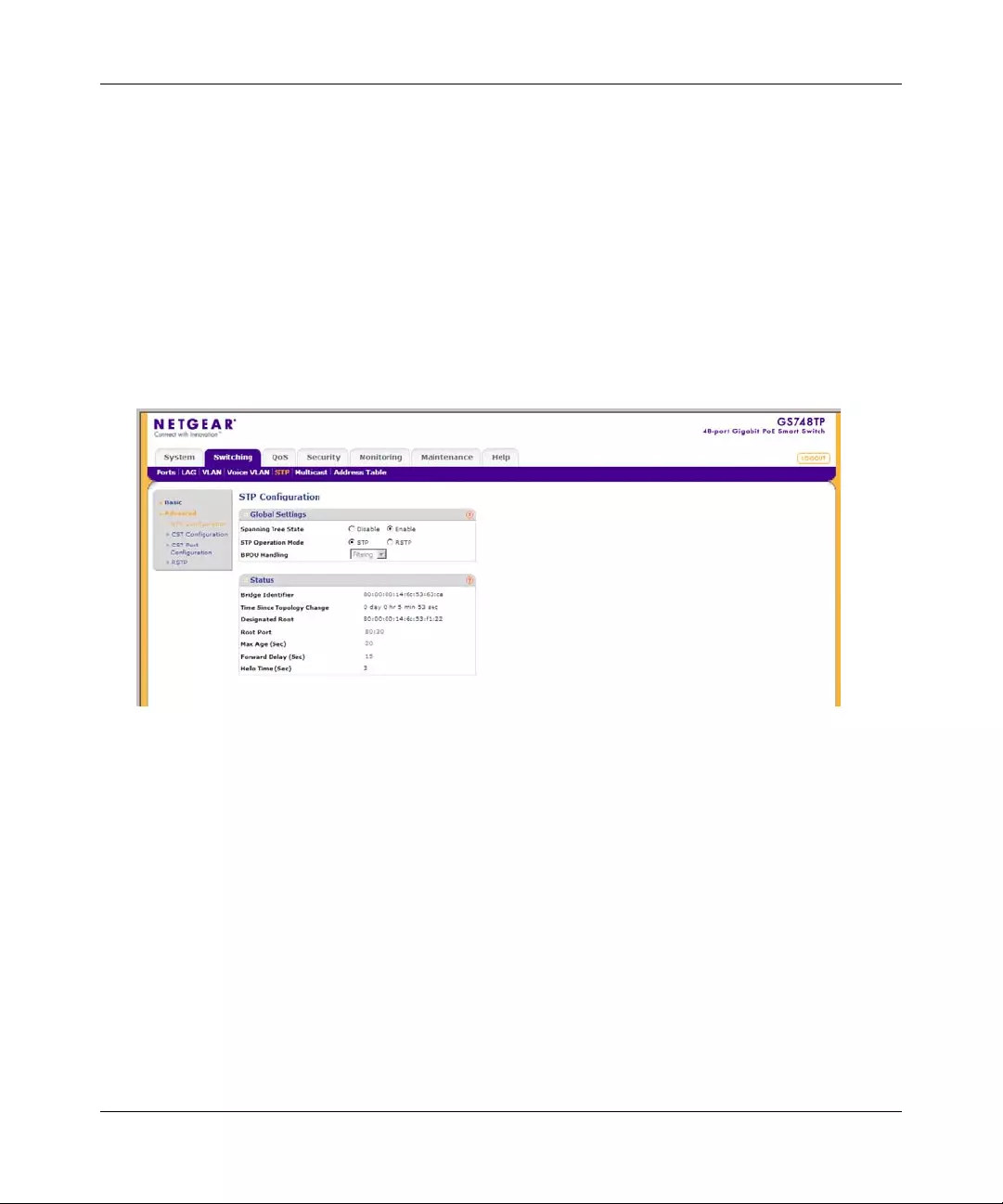
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-32 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•“CST Configuration”
•“CST Port Configuration”
•“Rapid STP”
STP Configuration
The Advanced STP Configuration screen contains parameters for enabling STP on the device.
To configure STP on the device:
1. Click Switching > STP > Advanced > STP Configuration. The Advanced STP
Configuration screen displays:
The Advanced STP Configuration screen contains the following fields:
Global Settings
•Spanning Tree State – Select the STP state on the device. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable STP on the device.
– Disable – Disable STP on the device.
•STP Operation Mode – Select the STP mode on the device. The possible field values are:
– STP – Enable classic STP on the device.
– RSTP – Enable Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) on the device.
Figure 4-21

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-33
v1.0, April 2008
•BPDU Handling – Select the method of handlin g STP BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data
Units) when STP is disabled on the device or interface. The possible field values are:
– Filtering – BPDUs are filtered. This the default.
– Flooding – BPDUs are flooded to all ports in the system.
– Bridging – BPDUs are bridged to all ports in the VLAN.
Status
•Bridge Identifier – Displays the Bridge priority and MAC address.
•Time Since Topology Change – Displays the amount of time that has elapsed since the
bridge was initialized or reset, and the last topographic change that occurred. The time is
displayed in a day-hour-minute-second fo rmat, such as 2 days 5 hours 10 minutes and 4
seconds.
•Designated Root – Displays the Root Bridge priority and MAC address.
•Root Port – Indicates the port number that offers the lowest cost path from this bridge to
the Root Bridge. This field is significant when the bridge is not the Root Bridge. The
default is zero.
•Max Age (Sec) – Displays the device Maximum Age Time. The Maximum Age Time is
the amount of time in seconds a bridge waits before sending configuration messages. The
default Maximum Age Time is 20 seconds.
•Forward Delay (Sec) – Displays the device Forward Delay Time. The Forward Delay
Time is the amount of time in seconds a bridge remains in a listening and learning state
before forwarding pac kets. The default is 15 seconds.
•Hello Time (Sec) – Displays the device Hello T ime. The Hello Time indicates the amount
of time in seconds a Root Bridge waits between configuration messages. The default is 2
seconds.
2. Select Enable or Disable in the Spanning Tree State provided field.
3. Select the STP Operation Mode in the provided field.
4. If you selected Disable in the Spanning Tree State field, select the BPDU Handling mode
from the list in the provided field.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
CST Configuration
The Common Spanning Tree (CST) describes the topology connecting STP/RSTP Bridges and
MSTP regions.
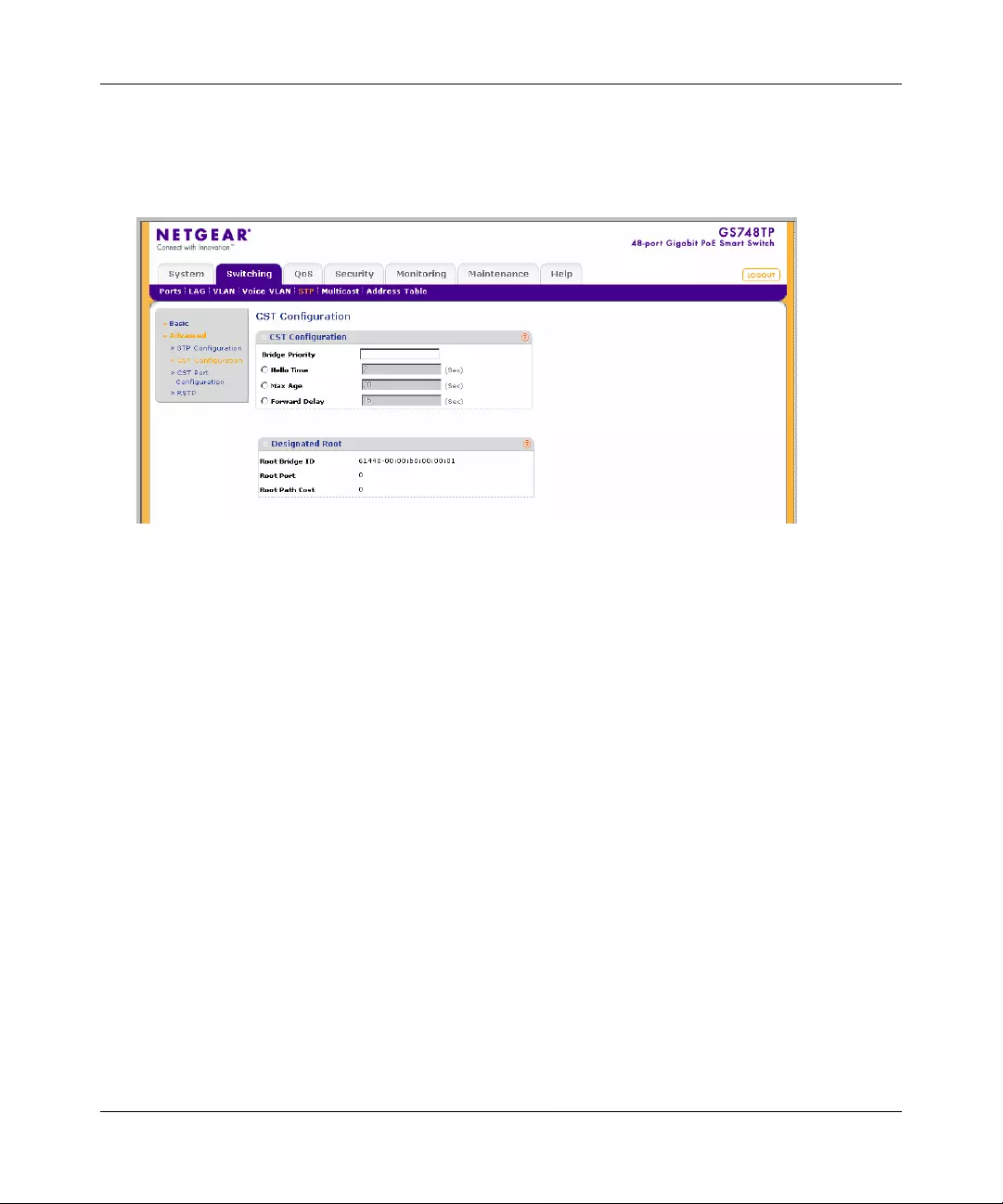
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-34 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To configure CST on the device:
1. Click Switching > STP > Advanced > CST Configuration. The CST Configuration screen
displays:
The CST Configuration screen contains the following fields:
CST Configuration
•Bridge Priority – Enter the bridge priority value. When switches or bridges are running
STP, each is assigne d a priority. After exchanging BPDUs, the device with the lowest
priority value becomes the Root Bridge. The default value is 32768. The bridge priority
value is provided in increments of 4096.
•Hello Time – Enter the device Hello Time. The Hello Time indicates the amount of time
in seconds a Root Bridge waits between configuration messages. The default is 2 seconds.
•Max Age – Enter the device Maximum Age T ime. The Maximum Age T ime is the amount
of time in seconds a bridge waits before sending configuration messages. The default
Maximum Age Time is 20 seconds.
•Forward Delay – Enter the device Forward Delay Time. The Forward Delay Time is the
amount of time in seconds a bridge remains in a listening and learning state before
forwarding packets. The default is 15 seconds.
Designated Root
•Root Bridge ID – Displays the priority and MAC Address of the root bridge.
Figure 4-22
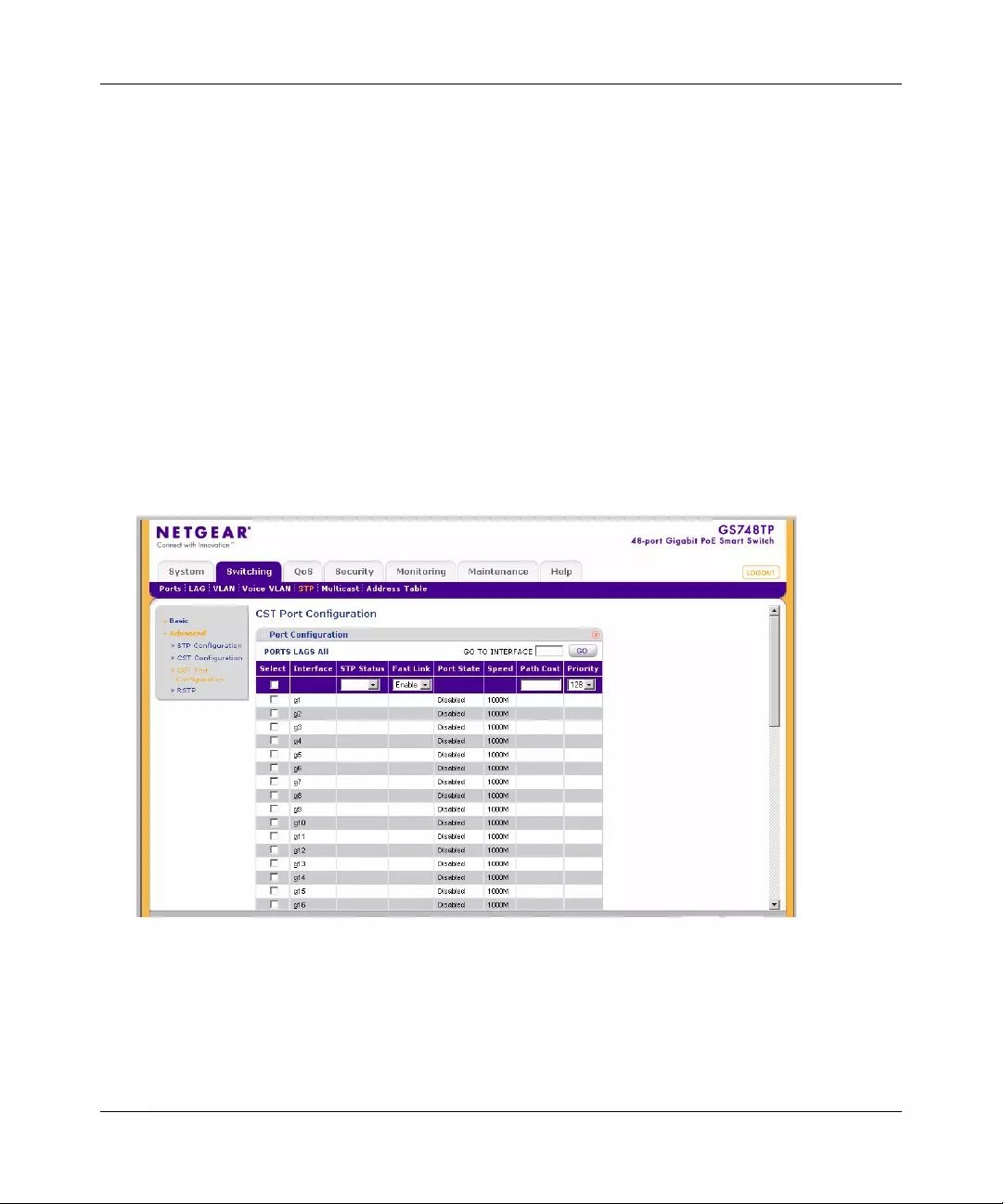
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-35
v1.0, April 2008
•Root Port – Displays the port number that offers the lowest cost path from this bridge to
the Root Bridge. This field is significant when the bridge is not the Root Bridge. The
current root port is zero when the device is not connected to the network.
•Root Path Cost – Displays the cost of the path from this bridge to the Root Bridge. The
current root path cost is zero when the device is not connected to the network.
2. Enter the Bridge Priority in the provided field.
3. Select Hello Time, Max Age or Forward Delay and enter the value in the provided field.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
CST Port Configuration
To configure CST ports on the device:
1. Click Switching > STP > Advanced > CST Port Configuration. The CST Port
Configuration screen displays:
The CST Port Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the port or LAG for which the STP information is displayed.
•STP Status – Select the STP status on the interface. The possible field values are:
Figure 4-23

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-36 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
– Enable – Enable STP on the interface.
– Disable – Disable STP on the interface.
•Fast Link – Select the Fast Link state on the interface. If Fast Link mode is enabled for a
interface, the Port Stat e is automatically placed in the Forwarding state when th e po rt link
is up. Fast Link optimizes the STP protocol convergence. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable Fast Link on the interface.
– Disable – Disable Fast Link on the interface.
•Port State – Displays the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines
what forwarding action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are:
– Forwarding – STP is enabled on the port, and the port is forwarding packets based on
the STP topology.
– Disabled – STP is currently disabled on the port. The port forwards traffic while
learning MAC addresses.
– Blocking – The port is currently blocked and cannot forward traffic or learn MAC
addresses.
– Listening – The port is in Listening mode. The port cannot forward traffic nor can it
learn MAC addresses.
– Learning – The port is in Learning mode. The port cannot forward traffic, however it
can learn new MAC addresses.
•Speed – Displays the speed at which the port is operating.
•Path Cost – Enter the method used to assign default path cost to STP ports. The possible
field range is 1 - 2000000 00 . The default path cost assigned to an interface varies
according to the selected CST configuration method (Hello Time, Max Age or Forward
Delay).
•Priority – Select the port priority value. When switches or ports are running STP, each is
assigned a priority. After exch anging BPDUs, the device with the lowest priority value
becomes the Root Port. The port priority has a range of 0-240 in increments of 16. The
default value is 128.
2. Select the STP Status and Fast Link status in the provided fields.
3. Enter the Path Cost in the provided field.
4. Select the Priority from the list in the provided field.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
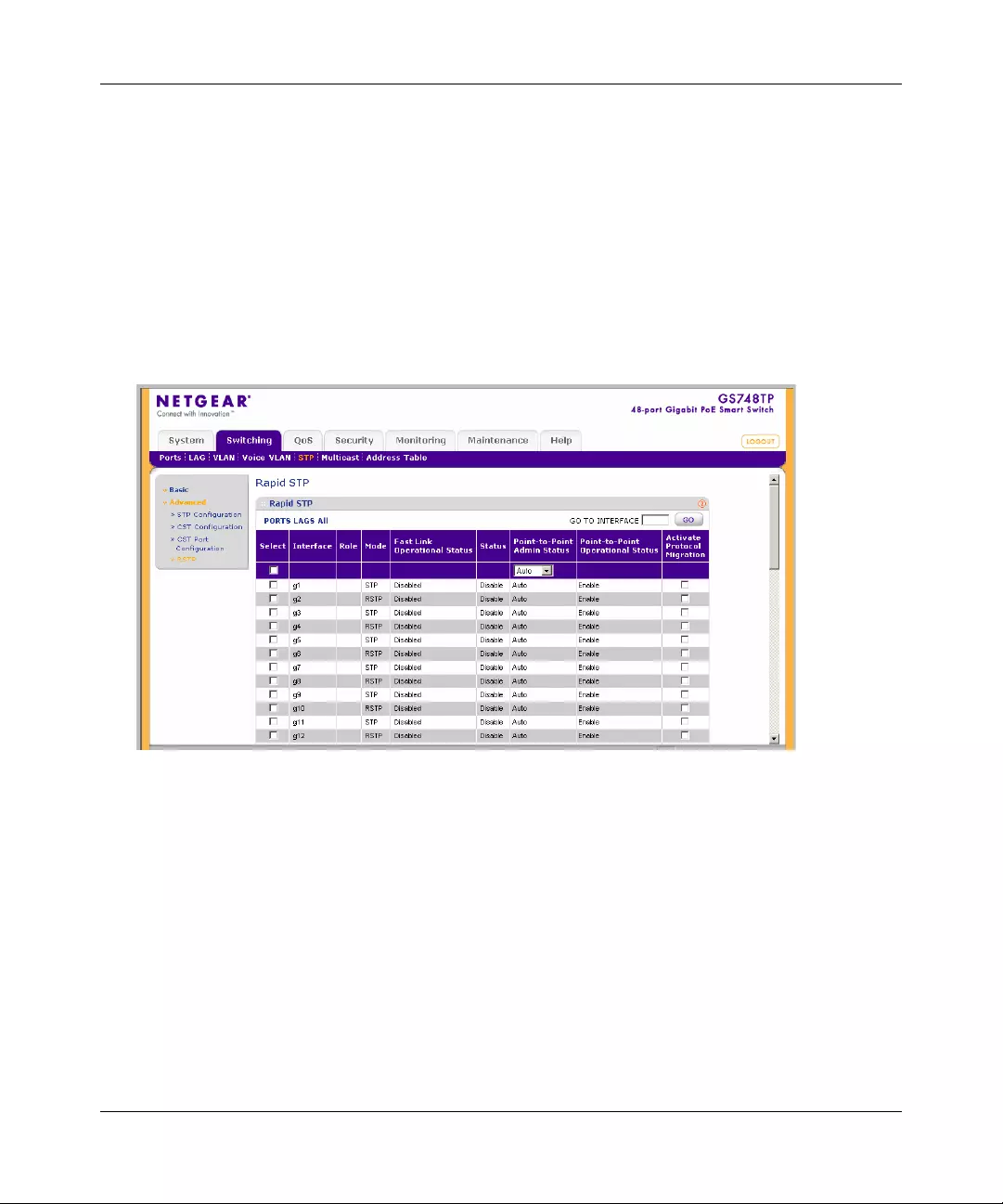
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-37
v1.0, April 2008
Rapid STP
While Classic STP prevents forwarding loops in a general network topology , conver gence can take
between 30-60 seconds. This time may delay detecting possible loops and propagating status
topology changes. Rapid Spanning T ree Protocol (RSTP) detects and uses network topologies that
allow a faster STP convergence without creating forwarding loops. The Global System LAG
information displays the same field information as the ports, but represents the LAG RSTP
information.
To define RSTP on the device:
1. Click Switching > STP > Adva nce d > RSTP. The Rapid STP screen displays:
The Rapid STP screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the port or LAG on which Rapid STP is enabled.
•Role – Displays the port role assigned by the STP algorithm to provide to STP paths. The
possible field values are:
– Root – Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to the root switch.
– Designated – The port or LAG throug h wh ich the designated switch is attached to the
LAN.
– Alternate – Provides an alternate path to the root switch from the root interface.
Figure 4-24

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-38 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
–Backup – Provides a backup path to the designated port path toward the Spanning
Tree leaves. Backup ports occur only when two ports are connected in a loop by a
point-to-point link, or when a LAN has two or more connections connected to a shared
segment.
– Disabled – The port is not participating in the Spanning Tree.
•Mode – Displays the current STP mode. The STP mode is selected in the STP
Configuration screen. The possible field values are:
– STP – Classic STP is enabled on the device.
– RSTP – Rapid STP is enabled on the device.
•Fast Link Operational Status – Displays the Fast Link status for the interface. If Fast
Link is enabled for a port, the port is automatically placed in the forwarding state. The
possible field values are:
– Enabled – Fast Link is enabled on the interface.
– Disabled – Fast Link is disabled on the interface.
•Status – Displays the RSTP status for the interface. The possible field values are:
– Enabled – RSTP is enabled on the interface.
– Disable – RSTP is disabled on the interface. This is the default value.
•Point-to-Point Admin Status – Select whether a point-to-point link is established, or if
the device is permitted to establish a point-to-point link. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable a point-to-point link, or configure to automatically establish a point-
to-point link. To establish communications over a point-to-point link, the originating
PPP first sends Link Control Protocol (LCP) packets to configure and test the data
link. After a link is established and optional facilities are negotiated as needed by the
LCP, the originating PPP sends Network Control Protocol (NCP) packets to select and
configure one or more network layer protocols. When each of the chosen network
layer protocols has been configured, packets from each network layer protocol can be
sent over the link. The link remains configured for communications until explicit LCP
or NCP packets close the link, or until some external event occurs. This is the actual
switch port link type. It may differ from the administrative state.
– Disable – Disable point-to-point link.
–Auto – Enable the device to automatically establish a point-to-point link.
•Point-to-Point Operational Status – Displays the point-to-point operating state.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-39
v1.0, April 2008
•Activate Pro t ocol Migratio n – Activate sending Link Control Protocol (LCP) packets to
configure and test that the data link is enabled.
2. Select the interface.
3. Select the Point-to-Point Admin Status from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. To configure and test the data link, check Activate Protocol Migration in the provided field
in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Multicast
Multicast forwarding allows a single packet to be forwarded to multiple destinations. L2 Multicast
service is based on L2 switch receiving a single packet addressed to a specific Multicast address.
Multicast forwarding creates copies of the packet, and transmits the packets to the relevant ports.
•Registered Multicast traffic – If traffic addressed to a registered Multicast group is seen it is
handled by an entry in the Multicast Filtering Database and forwarded only to the registered
ports.
•Unregistered Multicast traffic – If traffic addressed to an unregistered Multicast group is
seen it is handled by a special entry in the Multicast Filtering Database. The default setting of
this is to flood all such traffic (traffic in unregistered Multicast groups).
Layer 2 switching forwards Multicast packets to all relevant VLAN ports by default, treating the
packet as a Multicast transmission. Multicast traffic forwarding is functional. However, irrelevant
ports also receive the Multicast, causing increased network traffic. Multicast forwarding filters
enable forwarding of Layer 2 packets to port subsets, defined in the Multicast filter database.
The device supports forwarding L2 Multicast Packets. Multicast forwarding is enabled by default,
and not configurable by user.
The Multicast menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The Multicast Basic menu contains the following options:
•“IGMP Snooping Configuration”
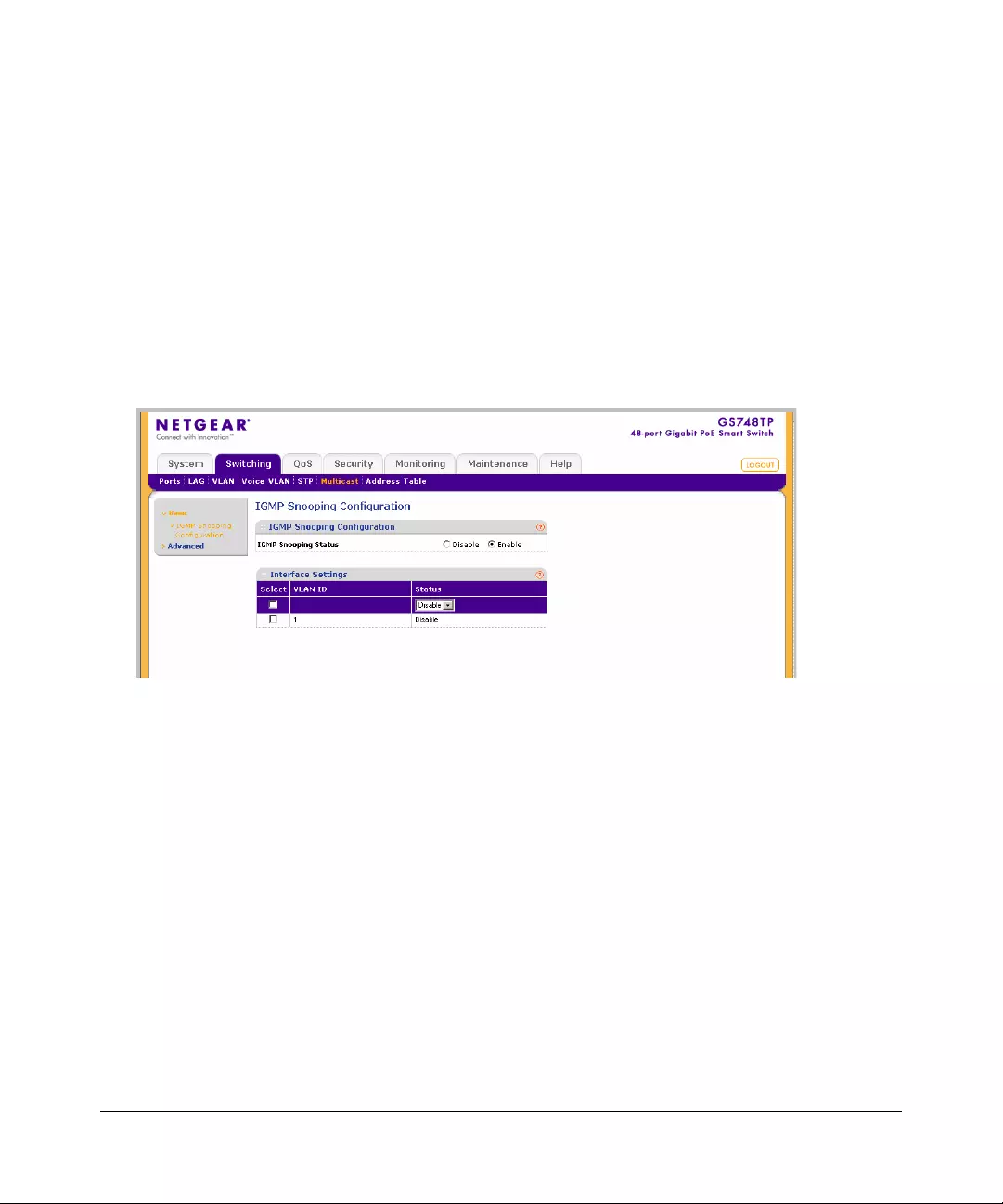
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-40 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
IGMP Snooping Configuration
When IGMP snooping is enabled, all IGMP packets are forwarded to the CPU. The CPU analyzes
the incoming packets and determines which ports want to join which Multicast groups, which
ports have Multicast routers generating IGMP queries, and what routing protocols are forwarding
packets and Multicast traffic. A port requesting to join a specific Multicast group issues an IGMP
report specifying that Multicast group. This results in the creation of the Multicast filtering
database.
To configure Basic IGMP Snooping:
1. Click Switching > Multicast > Basic > IGMP Snooping Configuration. The Basic IGMP
Snooping Configuration screen displays:
The Basic IGMP Snooping Configuration screen contains the following fields:
IGMP Snooping Configuration
•IGMP Snooping Status – Select the IGMP Snooping status on the device. The possible
field values are:
– Enable – Enable IGMP Snooping on the device.
– Disable – Disable IGMP Snooping on the device.
Interface Settings
•VLAN ID – Displays the VLAN ID.
•Status – Select the IGMP Snooping status on the VLAN. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable IGMP Snooping on the VLAN.
Figure 4-25

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-41
v1.0, April 2008
– Disable – Disable IGMP Snooping on the VLAN.
2. Select the IGMP Snooping Status in the provided field.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
To configure IGMP Snooping on a VLAN:
1. Click Switching > Multicast > Basic > IGMP Snooping Configuration. The Basic IGMP
Snooping Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the VLAN ID entry in the Interface Settings table.
3. Select the Status from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Advanced
The Multicast Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“IGMP Snooping Configuration”
•“Multicast Group Configuration”
•“Multicast Group Membership”
•“Multicast Forward All”
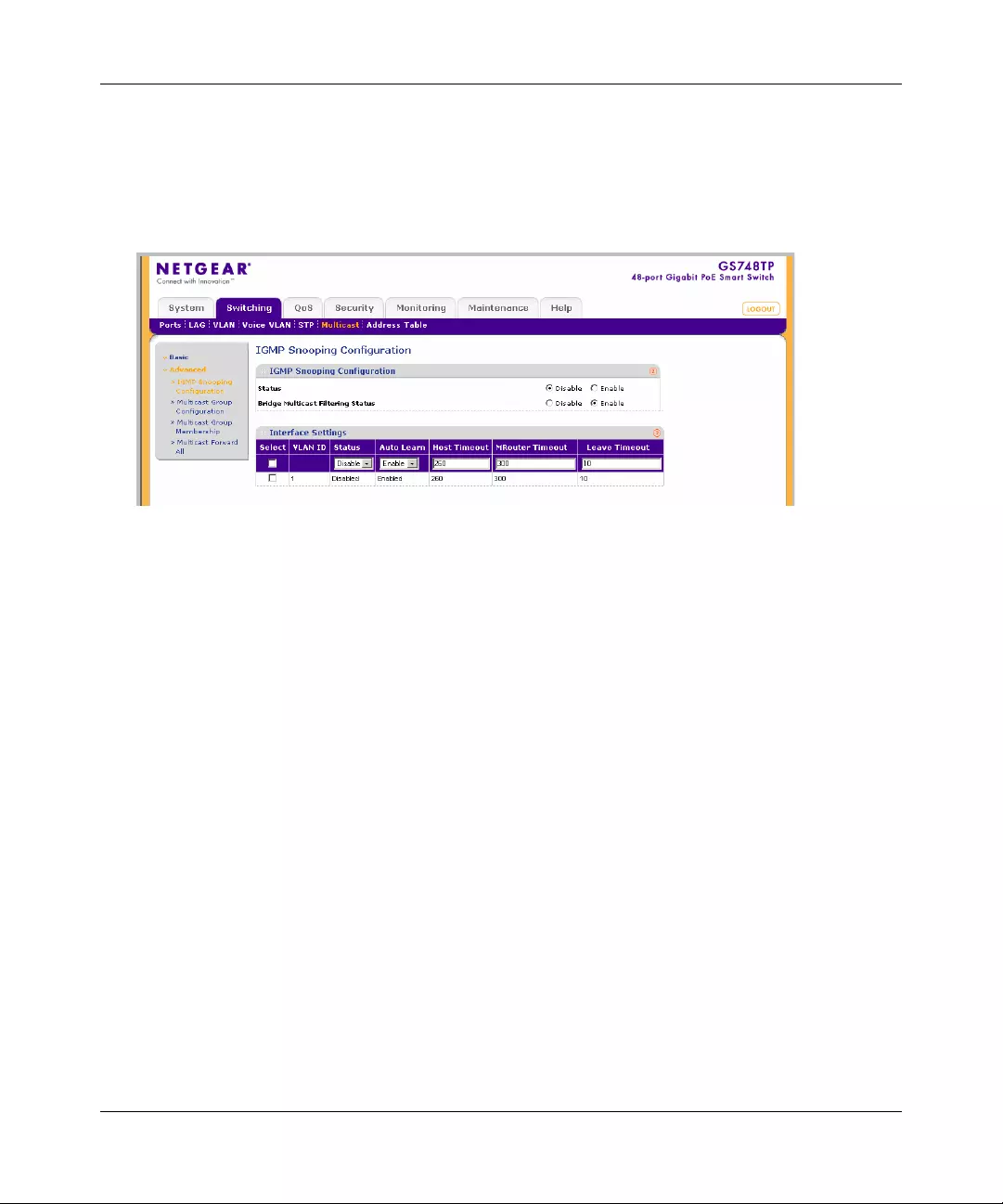
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-42 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
IGMP Snooping Configuration
To configure Advanced IGMP Snooping:
1. Click Switching > Multicast > Advanced > IGMP Snooping Configuration. The Advanced
IGMP Snooping Configuration screen displays:
The Advanced IGMP Snooping Configuration screen contains the following fields:
IGMP Snooping Configuration
•Status – Select the IGMP Snooping status on the device. IGMP Snooping is operational if
both the Status and Bridge Mu lticast Filtering fields are enabled. The possible field values
are:
– Enable – Enable IGMP Snooping on the device.
– Disable – Disable IGMP Snooping on the device.
•Bridge Multicast Filtering Status – Select the bridge Multicast filtering status on the
device. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable Multicast filtering on the device.
– Disable – Disable Multicast filtering on the device. If Multicast filtering is disabled,
Multicast frames are flooded to all ports in the relevant VLAN. Disabled is the default
value.
Interface Settings
•VLAN ID – Displays the VLAN ID.
•Status – Select the IGMP Snooping status on the VLAN. The possible field values are:
Figure 4-26

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-43
v1.0, April 2008
– Enable – Enable IGMP Snooping on the VLAN.
– Disable – Disable IGMP Snooping on the VLAN.
•Auto Learn – Select the Auto Learn status on the device. If Auto Learn is enabled, the
devices automatically learns where other Multicast groups ar e located. The possible field
values are:
– Enable – Enable auto learn.
– Disable – Disable auto learn.
•Host Timeout – Enter the amount of time in seconds the host waits to receive a message
before timing out. The default value is 260 seconds.
•MRouter Timeout – Enter the amount of the time in seconds the Multicast router waits to
receive a message before it times out. The default value is 300 seconds.
•Leave T imeou t – Enter the amount of time in seconds the host waits, after requesting to
leave the IGMP group and not receiving a Join message from another station, before
timing out. If a Leave Timeout occurs, the switch notifies the Multicast device to stop
sending traffic The field range is 0 - 2147483647. The default value is 10 seconds.
2. Select the IGMP Snooping Status and Bridge Multicast Filtering Status in the provided
fields.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
To configure IGMP Snooping on a VLAN:
1. Click Switching > Multicast > Advanced > IGMP Snooping Configuration. The Advanced
IGMP Snooping Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the VLAN ID entry in the Interface Settings table.
3. Select the Status and Auto Learn status from the lists in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Enter the Host, MRouter and Leave Timeouts in the provided fields in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Multicast Group Configuration
The Multicast Group Configuration screen allows you to create, delete and modify Multicast
service groups. The Multicast Group Configuration table can contain up to 32 Multicas t service
groups.
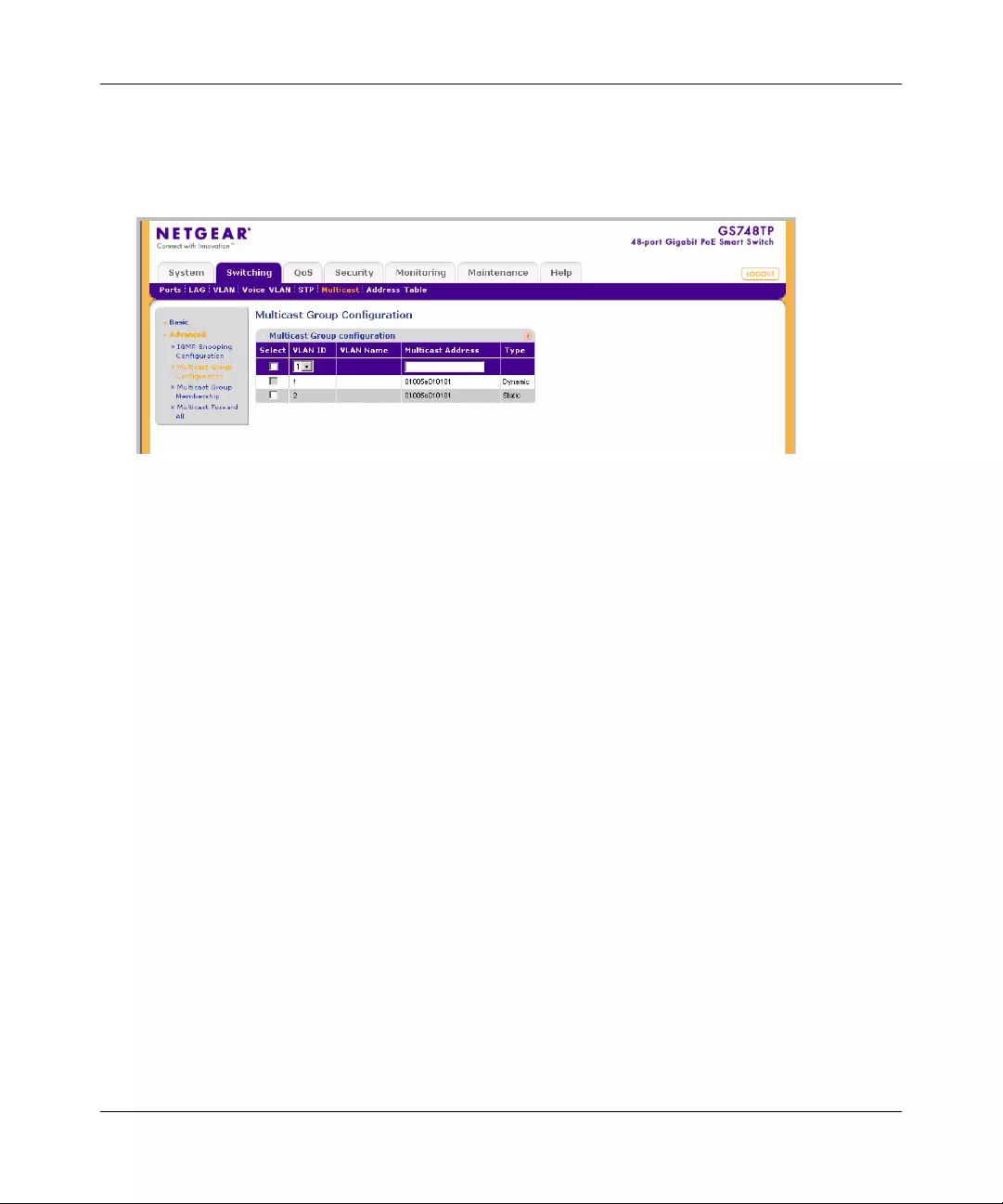
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-44 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
To configure Multicast groups:
1. Click Switching > Multicast > Advanced > Mu lticast Group Configuration . The Multicast
Group Configuration screen displays:
The Multicast Group Configuration screen contains the following information:
•VLAN ID – Displays the VLAN ID.
•VLAN Name – Displays the user-defined VLAN name.
•Multicast Addr ess – Enter the Multicast group MAC Address associated with the VLAN.
•Type – Indicates the VLAN ID status in relation to the Multicast group.
– Static – Attaches the VLAN ID to the Multicast group as static member.
– Dynamic – Dynamically joins the VLAN ID to the Multicast group.
2. Select the group entry.
3. Enter the Multicast Address in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Multicast Group Membership
The Multicast Group Membership screen displays the ports and LAGs attached to the selected
VLAN and the Multicast service group. The Port and LAG tables also reflect the manner in which
the port or LAGs joined the Multicast group.
Figure 4-27
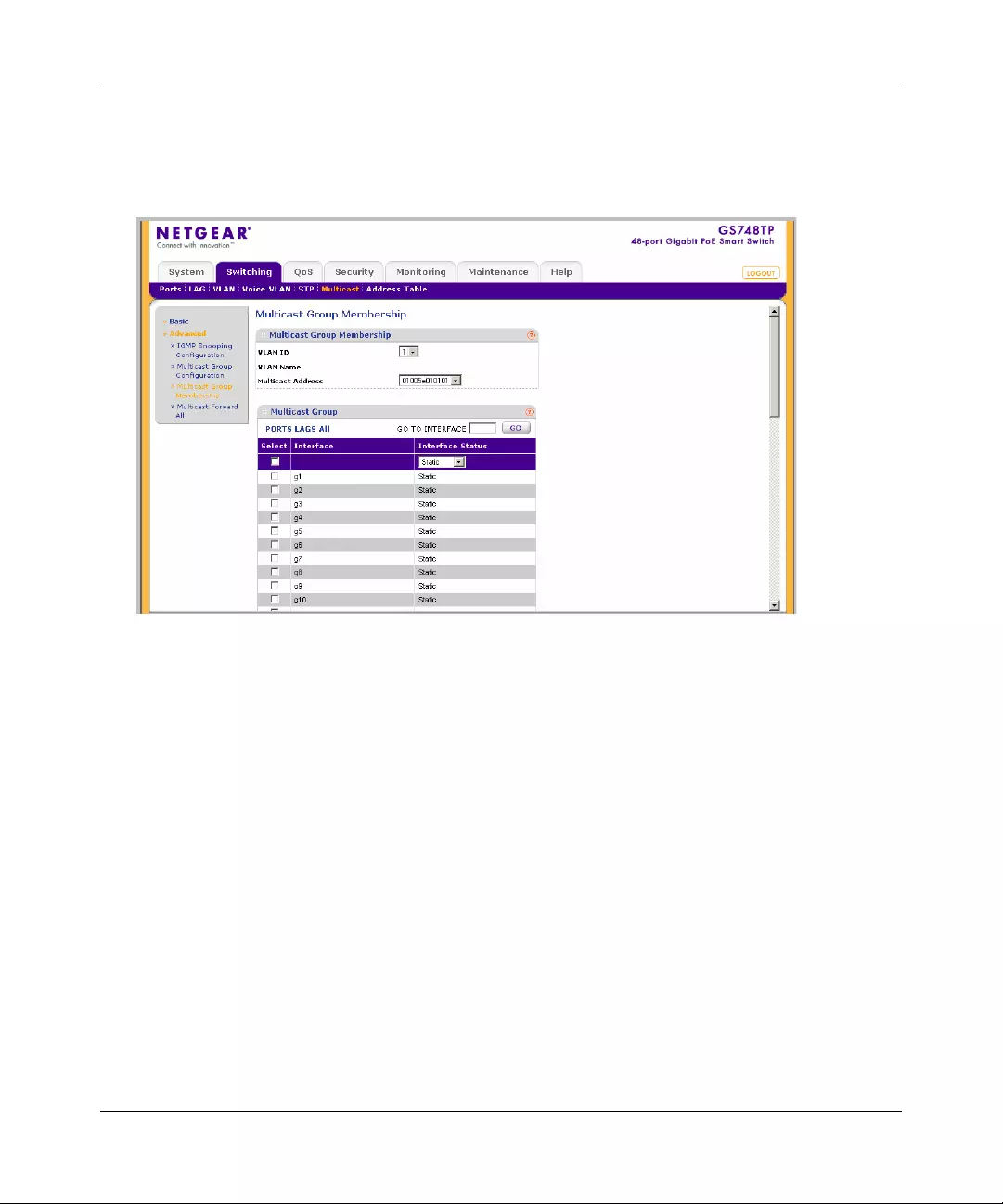
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-45
v1.0, April 2008
To configure Multicast group membership:
1. Click Switching > Multicast > Advanced > Multicast Group Membership. The Multicast
Group Membership screen displays:
The Multicast Group Membership screen contains the following information:
Multicast Group Membership
•VLAN ID – Enter the VLAN ID.
•VLAN Name – Displays the user defined VLAN name.
•Multicast Address – Enter the Multicast group MAC address.
Multicast Group
•Interface – Displays the ports and LAGs for which the Multicast settings are displayed.
•Interface Status – Select the interface status. The possible field values are:
– S tat ic – The interface is joined to the Multicast group statically.
– Forbidden – The interface is forbidden to join the Multicast group.
– Excluded – The interface is not included in the Multicast group.
2. Select the VLAN ID from the list in the provided field.
Figure 4-28
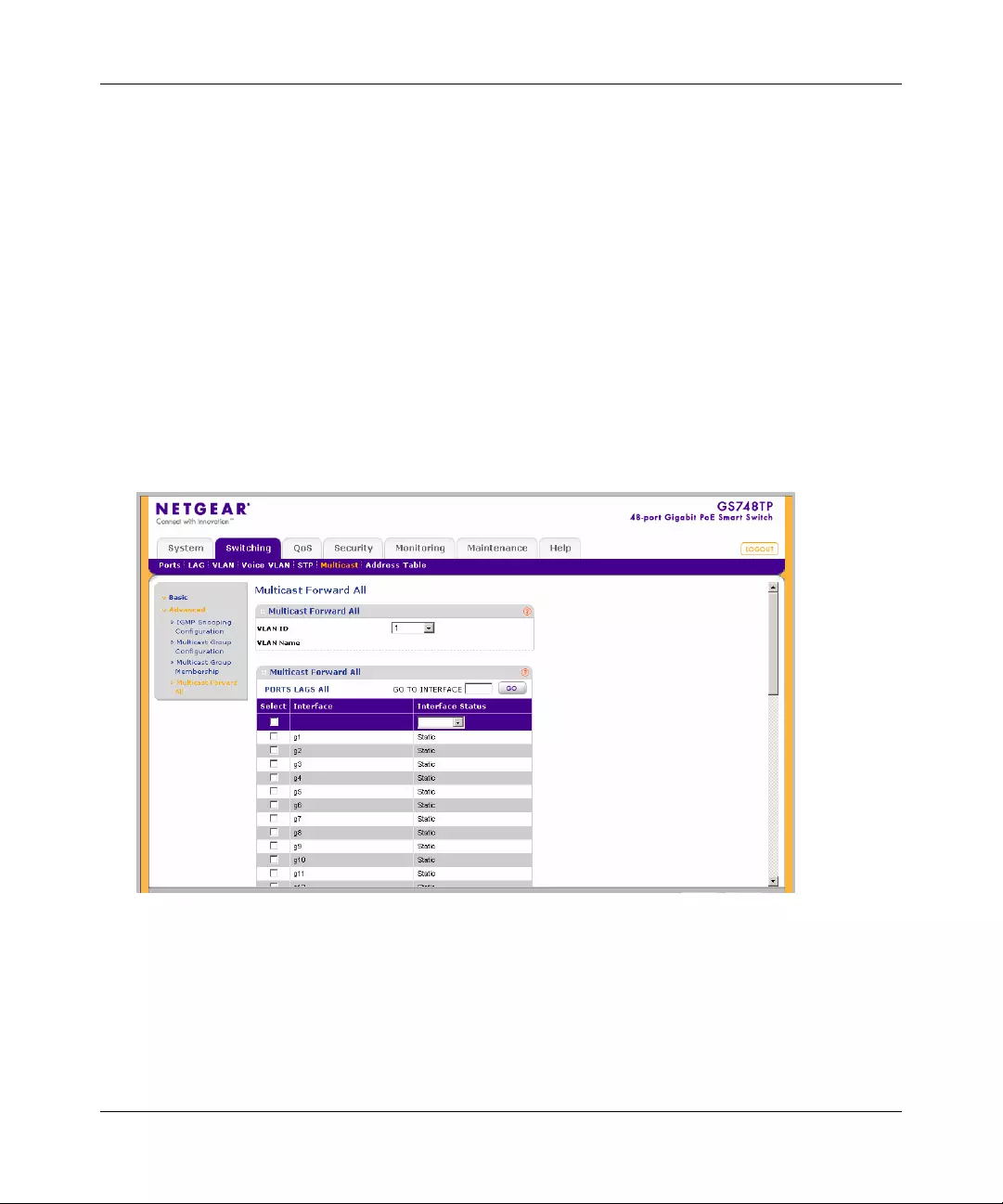
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-46 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
3. Select the Multicast Address from the list in the provided field.
4. Select the interface entry in the Multicast Group table.
5. Select the Interface Status from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. Click APPLY to update the device.
Multicast Forward All
The Multicast Forward All screen contains fields for attachin g por ts or LAGs to a device that is
attached to a neighboring Multicast router/switch. Once IGMP Snooping is enabled, Multicast
packets are forwarded only to the appropriate port or VLAN.
To define Multicast forward all settings:
1. Click Switching > Multicast > Advanced > Multicast Forward All. The Multicast Forward
All screen displays:
The Multicast Forward All screen contains the following information:
Multicast Forward All
•VLAN ID – Enter the VLAN ID.
•VLAN Name – Displays the user defined VLAN name.
Figure 4-29

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-47
v1.0, April 2008
Multicast Forward All
•Interface – Displays the interface for which the Multicast settings are displayed.
•Interface Status – Select the interface status. The possible field values are:
– S tat ic – The interface is added to the Multicast forward group statically.
– Forbidden – The interface is forbidden to join the mulitcast group.
– Excluded – The interface is not included in the Multicast group.
2. Select the VLAN ID from the list in the provided fields.
3. Select the port or LAG interface entry in the Multicast Group table.
4. Select the Interface Status from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Address Table
Packets addressed to destinations stored in either the Static or Dynamic databases are immediately
forwarded to the port. The Dynamic MAC Address Table can be sorted by interface, VLAN, or
MAC Address. Dynamic MAC addresses are learned from packets from sources that arrive at the
device, while Static addresses are configured manually.
An address becomes associated with a port by learning the port from the frame’s source address
but if a frame that is addressed to a destination MAC address is not associated with a port, that
frame is flooded to all relevant VLAN ports. To prevent the bridging table from overflowing, a
dynamic MAC address, from which no traffic arrives for a set period, is erased.
The Address Ta ble menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The Address Table Basic menu contains the following options:
•“Address Table”
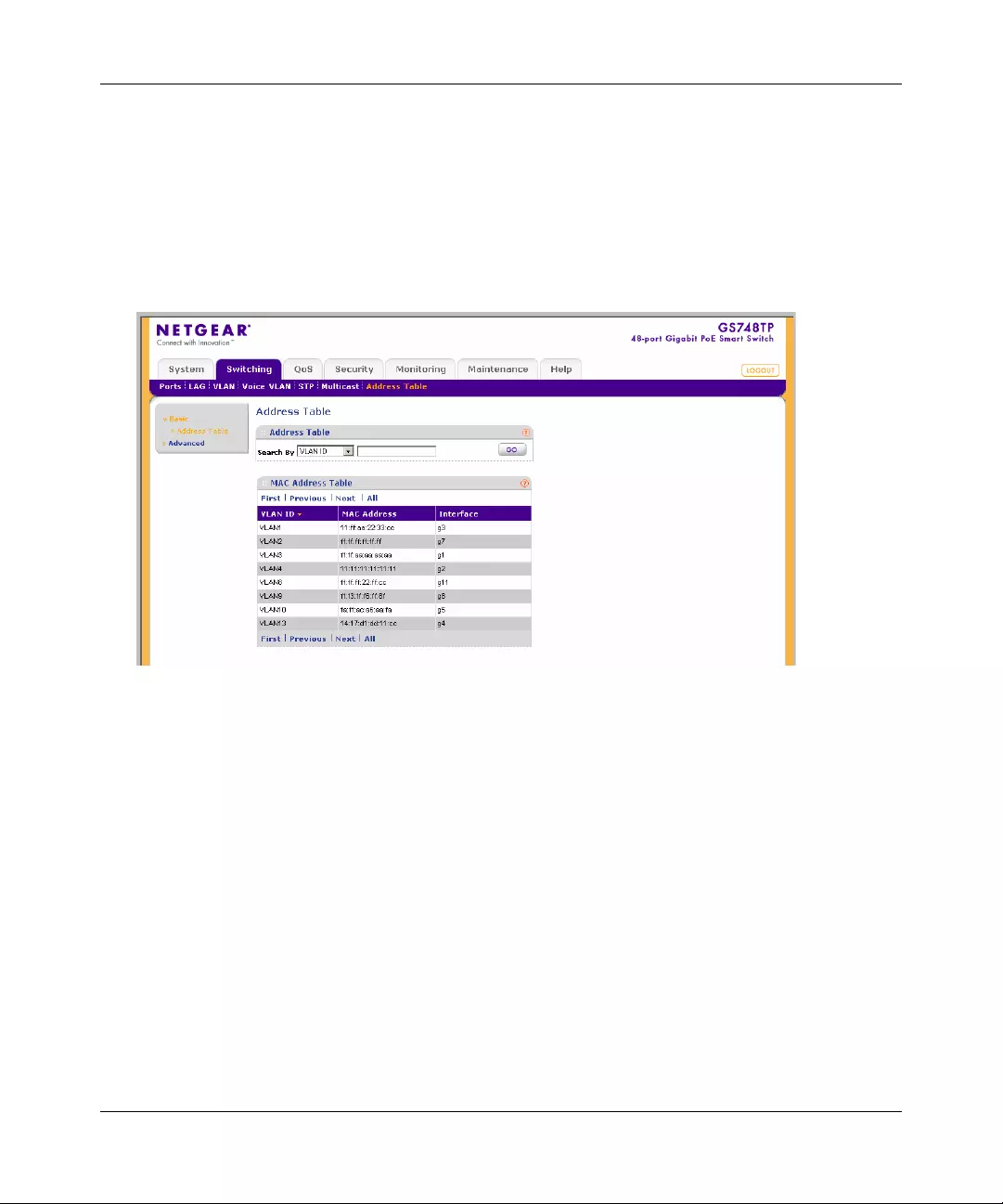
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-48 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
Address Table
The Basic Address Table screen displays the MAC Address table according to the defined
categories.
To query the Basic Address Table:
1. Click Switching > Address Table > Basic > Address Table. The Basic Address Table screen
displays:
The Basic Address Table screen contains the following fields:
•Search By – Display the MAC Address list according to selected category and query field.
The possible field values are:
– VLAN ID – Display the MAC Address table entries that relate to the specific VLAN
ID.
– MAC Address – Display the MAC Address table entries that relate to MAC Address.
– Interface – Display the MAC Address table entries that relate to the specific interface.
•VLAN ID – Displays the VLAN ID number to whic h the entry refers.
•MAC Address – Displays the MAC address to which the entry refers.
•Interface – Displays the interface to which the entry refers.
2. Select the Search By key from the list in the provided field.
Figure 4-30
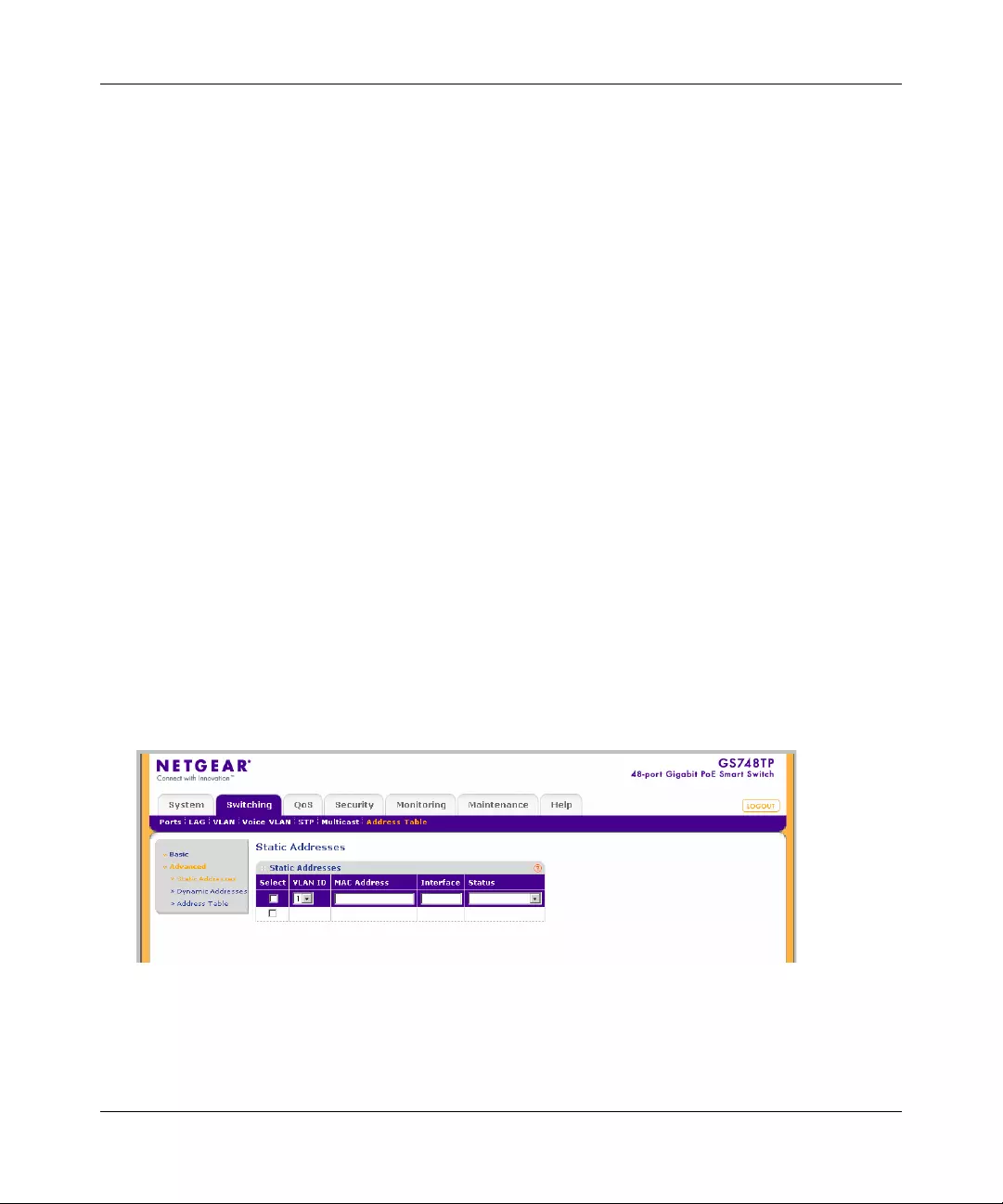
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-49
v1.0, April 2008
3. Enter the value to be searched for in the provided box.
4. Click GO to execute the query.
To delete all addresses from the Basic Address Table:
1. Click Switching > Address Table > Basic > Address Table. The Basic Address Table screen
displays.
2. Click CLEAR ALL to delete all entries in the address table.
Advanced
The Address Table Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“Static Addresses”
•“Dynamic Addresses”
•“Address Table”
Static Addresses
The Static Addresses screen contains a list of static MAC addresses. Static Addresses are added
and removed from the Static Addresses screen. To prevent static MAC addresses from being
deleted when the device is reset, ensure the port attached to the MAC address is locked.
To configure the Static MAC Address table:
1. Click Switching > Address Table > Advanced > Static Addresses. The Static Addresses
screen displays:
The Static Addresses screen contains the following fields:
•VLAN ID – Select the VLAN ID number to which the entry refers.
Figure 4-31
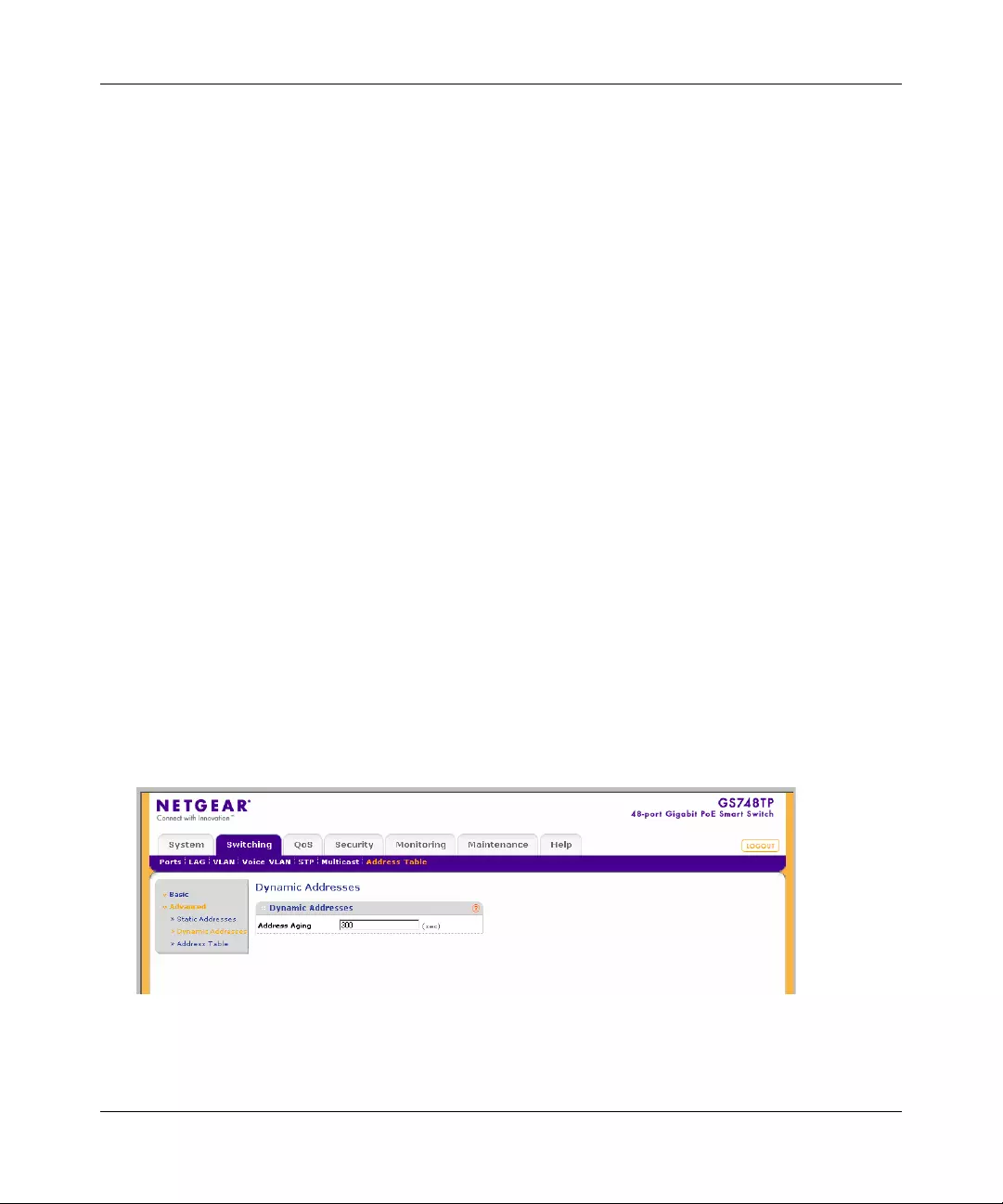
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-50 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
•MAC Address – Enter the MAC address to which the entry refers.
•Interface – Enter the interface to which the entry refers.
•Status – Select the MAC Address duration period within the table. The possible field
values are:
– Permanent – The MAC address is permanent.
– Delete on Reset – The MAC address is deleted when the device is reset.
– Delete on Timeout – The MAC address is deleted when the Address Aging Interval
expires.
– Secure – The MAC Address is defined for locked interfaces.
2. Select the address table entry.
3. Enter the MAC Address and Interface in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Select the MAC Address duration period Status from the list in the provided field in the first
row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Dynamic Addresses
The Dynamic Addresses screen contains information about the aging time before a dynamic MAC
address is erased.
To configure the Dynamic MAC Address table:
1. Click Switching > Address Table > Advanced > Dynamic Addresses. The Dynamic
Addresses screen displays:
The Dynamic Addresses screen contains the following field:
Figure 4-32
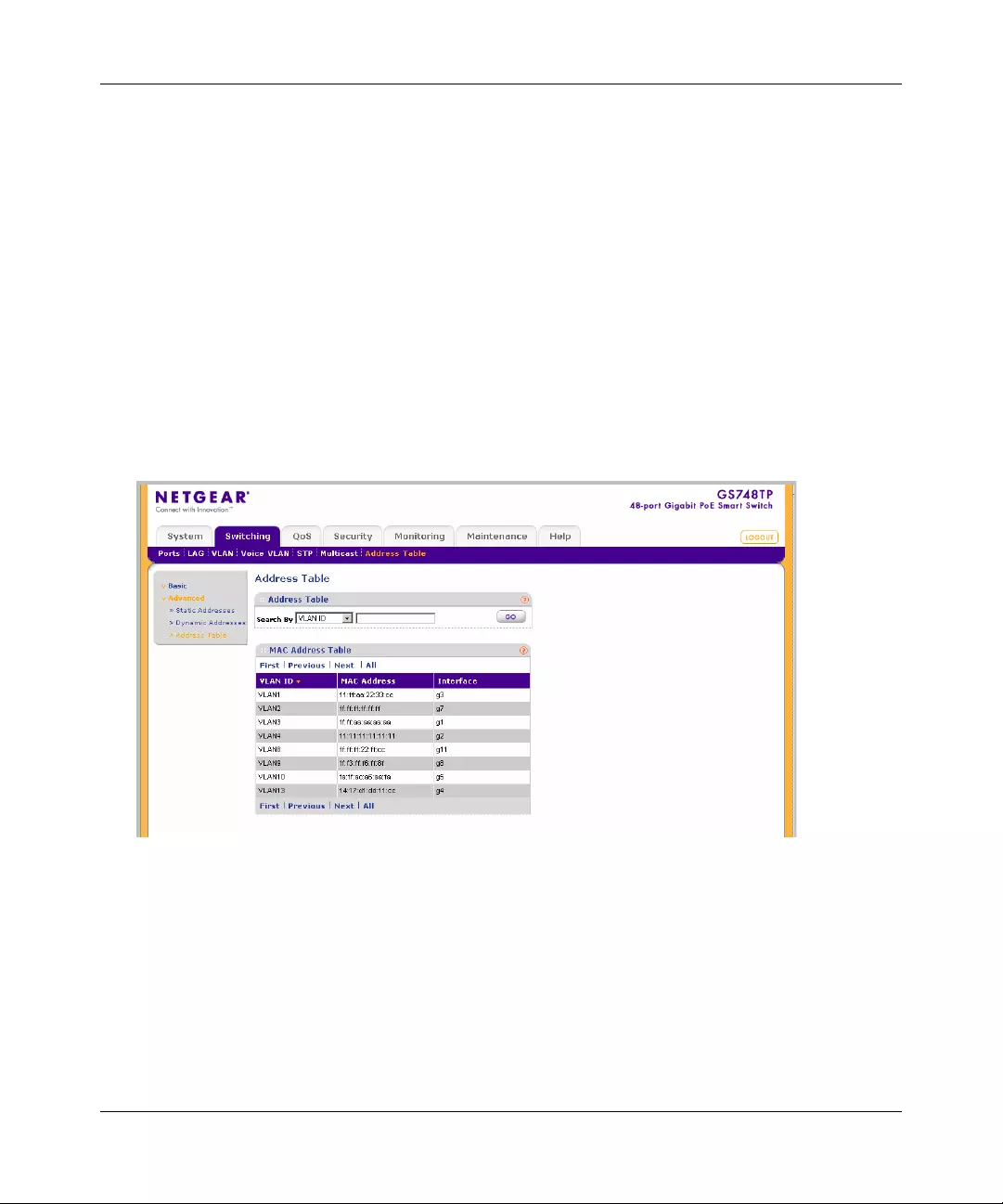
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring Switching Settings 4-51
v1.0, April 2008
•Address Aging – Enter the amount of time the MAC address remains in the Dynamic
MAC Address table before it is timed out if no traffic from the source is detected. The
range is 10 - 630 seconds. The default value is 300 seconds.
2. Enter the Address Aging in the provided field in the first row.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
Address Table
The Advanced Address Table screen displays the MAC Address table according to the defined
categories.
To query the Advanced MAC Address Table:
1. Click Switching > Address Table > Advanced > Address Table. The Advanced Address
Table screen displays:
The Advanced Address Table screen contains the following fields:
•Search By – Display the MAC Address which can be sorted according to VLAN ID,
MAC Address or Interface. The possible fie l d values are:
– VLAN ID – Display the MAC Address table entries that relate to the specific VLAN
ID.
– MAC Address – Display the MAC Address table entries that relate to MAC Address.
Figure 4-33

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
4-52 Configuring Switching Settings
v1.0, April 2008
– Interface – Display the MAC Address table entries that relate to the specific interface.
•VLAN ID – Displays the VLAN ID number to whic h the entry refers.
•MAC Address – Displays the MAC address to which the entry refers.
•Interface – Displays the interface to which the entry refers.
2. Select the Search By key from the list in the provided field.
3. Enter the value to be searched for in the provided box.
4. Click GO to execute the query.
To delete all addresses from the Advanced Address Table:
1. Click Switching > Address Table > Advanced > Address Table. The Advanced Address
Table screen displays.
2. Click CLEAR ALL to delete all entries in the address table.

5-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 5
Configuring QoS
Configuring the Basic and Advanced QoS Settings
The navigation pane at th e top of the web browser interface contains a QoS tab that enables you to
manage your GS700TP Smart Switch with features under the following main heading:
•“CoS”
The description that follows in this chapter describes configuring and managing QoS settings in
the GS700TP Smart Switch.
CoS
Quality of Service (QoS) provides the ability to implement QoS and priority queuing within a
network. For example, certain types of traffic that require minimal delay, such as Voice, Video,
and real-time traffic can be assigned to a high priority queue, while other traf fic can be assigned to
a lower priority queue. The result is an improved traffic flow for traffic with high demand. QoS is
defined by:
•Classification – Specifies which packet fields are matched to specific values. All packets
matching the user-defined specifications are classified together.
•Action – Defines traffic management where packet forwarding is based on packet information
and packet field values such as VLAN Priority Tag (VPT) and DiffServ Code Point (DSCP).
After packets are assigned to a specific egress queue, CoS services can be assigned to the queue.
Egress queues are configured with a scheduling scheme by one of the following methods:
•Strict Priority – Ensures that time-sensitive applications are always forwarded. S trict Priority
(SP) allows the prioritization of mission-critical, time-sensitive traf fi c over less time-sensitive
applications. For example, under SP, voice over IP (VoIP) traffic can be prioritized so that it is
forwarded before FTP or email (SMTP) traffic.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
5-2 Configuring QoS
v1.0, April 2008
•Weighted Round Robin – Ensures that a single application does not dominate the device
forwarding capacity. Weighted Round Robin (WRR) forwards entire queues in a round robin
order. All queues can participate in WRR, except SP queues. If the traffic flow is minimal, and
SP queues do not occupy the whole bandwidth allocated to a port, the WRR queues can share
the bandwidth with the SP queues. This ensures that the remaining bandwidth is distributed
according to the weight ratio. If WRR is selected, the following weights are assigned to the
queues: 1, 2, 4, 8.
The CoS menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The CoS Basic menu contains the following options:
•“CoS Global Configuration”
•“CoS Interface Configuration”
•“Queue”
•“Bandwidth”
CoS Global Configuration
The CoS Global Configuration screen contains information for enabling QoS globally.
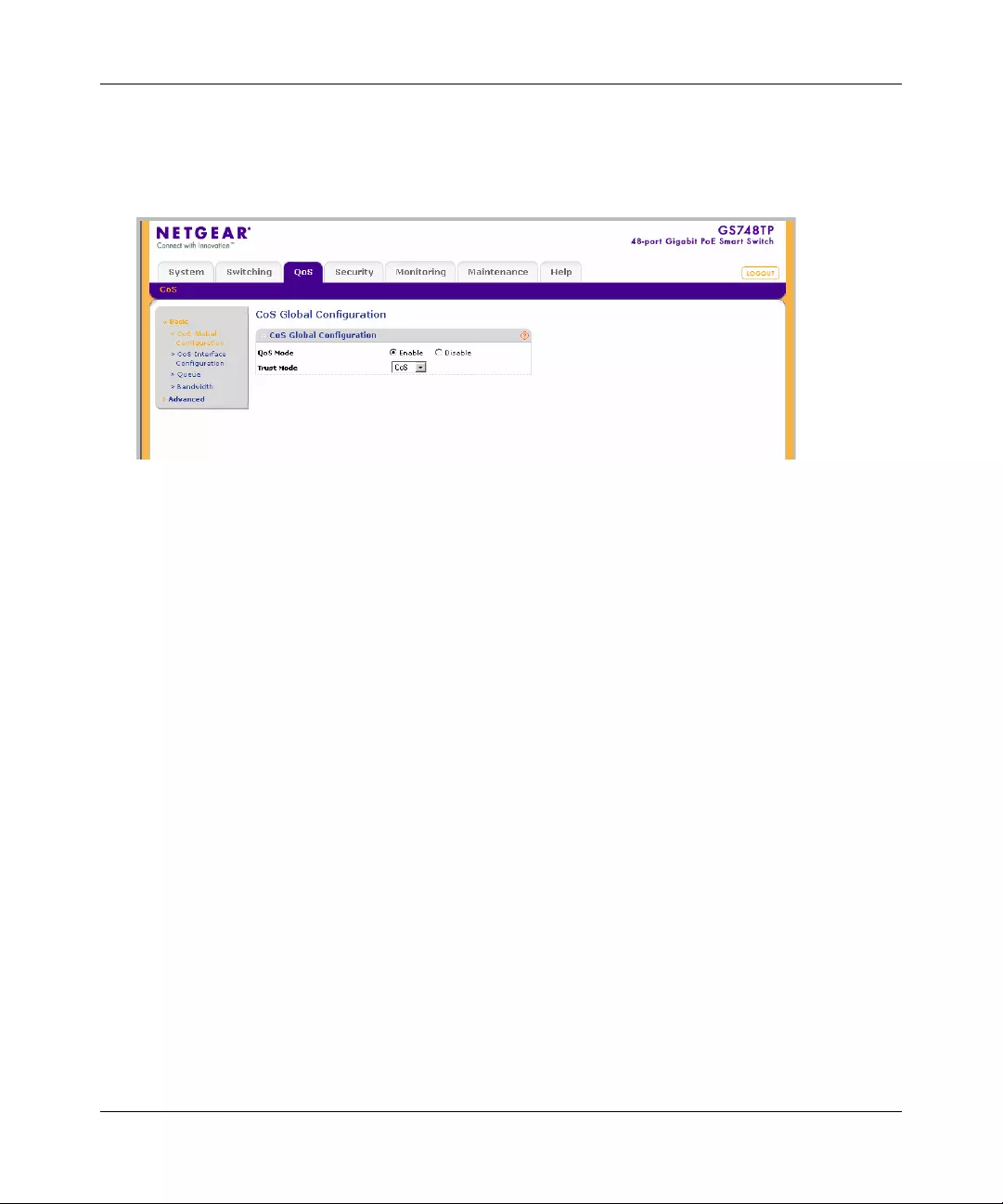
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring QoS 5-3
v1.0, April 2008
To configure CoS global parameters:
1. Click QoS > CoS > Basic > CoS Global Configuration. The CoS Global Configuration
screen displays:
The CoS Global Configuration screen contains the following:
•QoS Mode – Select whether QoS is enabled or disabled on the device. The possible values
are:
– Enable – Enable QoS globally.
– Disable – Disable QoS globally.
•Trust Mode – Select which packet fields to use for classifying packets entering the
device. The possible Trust Mode field values are:
– CoS – Classify traffic based on the CoS (VPT) tag value.
– DSCP – Classify traffic based on the DSCP tag value.
2. Select the QoS Mode and Trust Mode in the provided fields.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
CoS Interface Configuration
The CoS Interface Configuration screen contains information for configuring the default CoS
value on a selected interface. After CoS has been configured, the device original CoS default
settings can be reassigned to the interface in the CoS Interface Configuration screen.
Figure 5-1
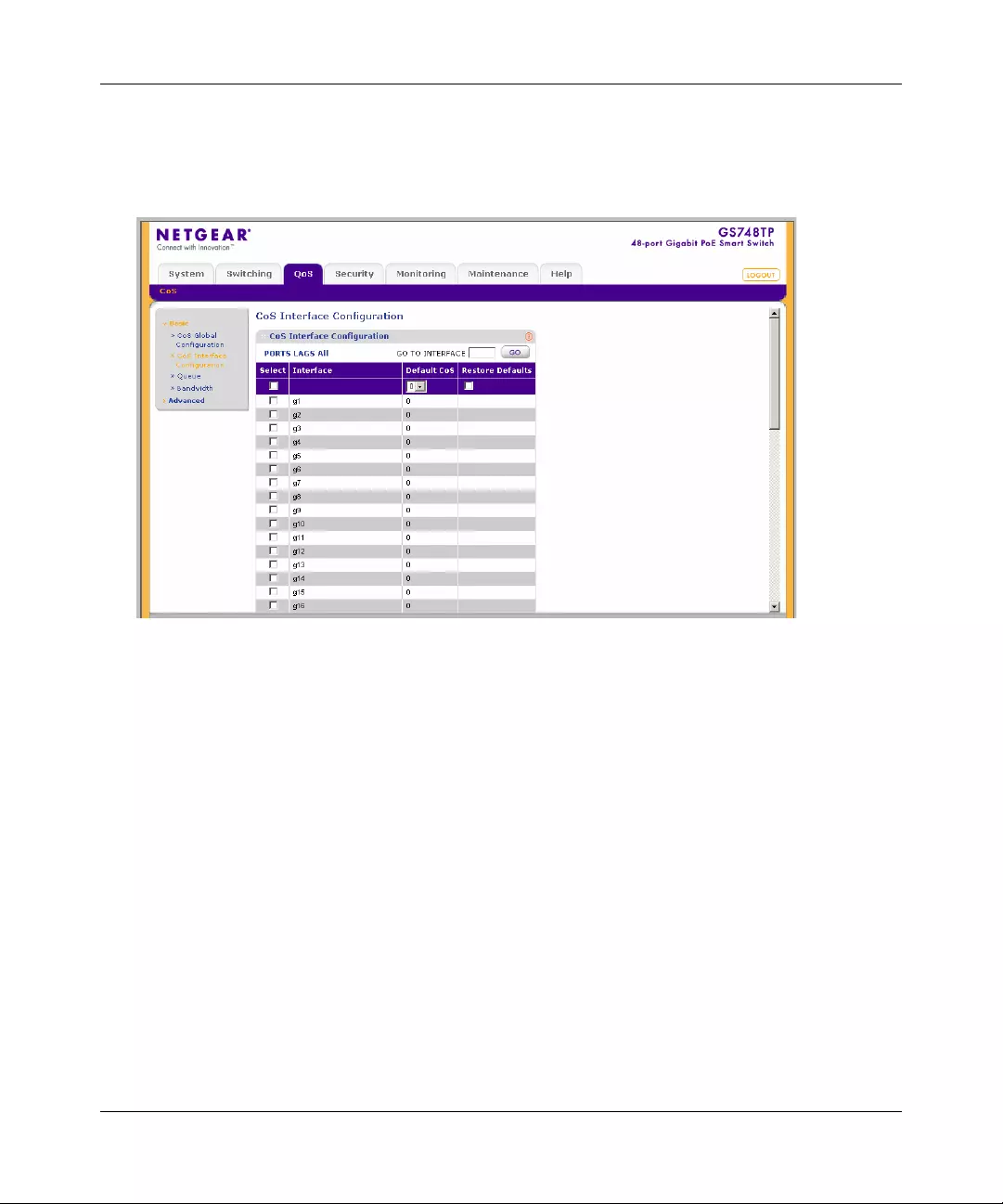
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
5-4 Configuring QoS
v1.0, April 2008
To configure CoS interface parameters:
1. Click QoS > CoS > Basic > CoS Interface Configuration. The CoS Interface Configuration
screen displays:
The CoS Interface Configuration screen contains the following:
•Interface – Displays the interface for which the default CoS parameters are defined.
•Default CoS – Select the default CoS value for incoming packets to the selected interface
for which a VLAN priority (VPT) is not defined.
•Restore Defaults – Restore the factory CoS default settings to the selected interface. The
possible field values are:
– Checked – Restore the factory CoS default settings to the ports.
– Unchecked – Maintain the current CoS settings.
2. Select the interface.
3. Select the Default CoS value from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. Check or uncheck the Restore Defaults box in the interface entry row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 5-2
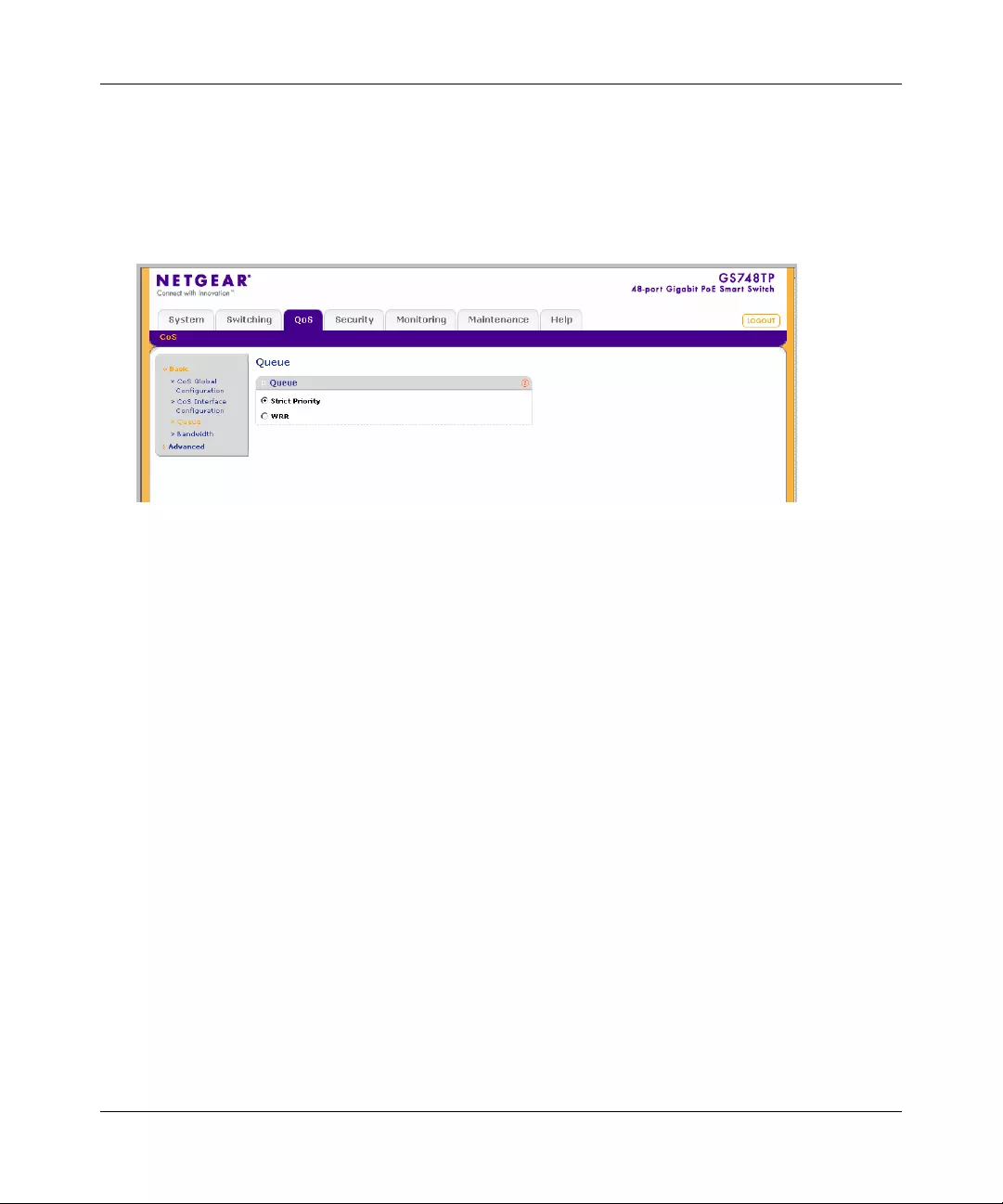
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring QoS 5-5
v1.0, April 2008
Queue
The Queue screen contains fields for defining the QoS queue forwarding types.
To set the queue settings:
1. Click QoS > CoS > Basic > Queue. The Queue screen displays:
The Queue screen contains the following fields:
•Strict Priority – Se lect to specify traffic scheduling based strictly on the queue priority.
•WRR – Select to assign WRR weights to queues. The queue weights are preconfigured
and are set to 1, 2, 4 and 8.
2. Select either Strict Priority or WRR to specify the traffic scheduling method.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
Bandwidth
After packets are assigned to a queue, a scheduling scheme can be assigned to a n inte rface, using
either:
•Committed Burs t Si ze – Indicates the maximum number of data bits transmitted within a
specific time interval.
•Committed Information Rate – Indicates the rate that data is transmitted. The rate is
averaged over a minimum time increment.
The Bandwidth screen allows the user to define Ingress Rate Limit and Egress Shaping Rate s.
Figure 5-3

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
5-6 Configuring QoS
v1.0, April 2008
To define bandwidth settings:
1. Click QoS > CoS > Basic > Bandwidth. The Bandwidth screen displays:
The Bandwidth screen cont ains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the ports for which the bandwidth settings are displayed.
•Ingress Rate Limit Status – Select whether rate limiting is defined on the interface. The
possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable ingress rate limiting on the interface.
– Disable – Disable ingress rate limiting on the interface.
•Ingress Rate Limit – Enter the rate limit in kilobits per second. The possible field range is
3500 to the maximum port speed. GE (Gigabit Ethernet) ports have a maximum speed of
1000000 kilobits per second. The field default value is 3500.
•Egress Shaping Rates Status – Select whether egress shaping is defined on the interface.
The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable egress shaping rate on the interface.
– Disable – Disable egress shaping rate on the interface. This is the default value.
Figure 5-4

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring QoS 5-7
v1.0, April 2008
•Egress Shaping Rates CIR – Enter the Egress Shaping Committed Information Rate
(CIR) in kilobits per second. The possible field range is 64 to 1000000 for GE ports.
•Egress Shaping Rates CbS – Enter the Egress Shaping Committed Burst Size (CbS) in
bits per second. The possible field range is 4096 to 16769020.
2. Select the interface.
3. Choose either Enable or Disable in the Ingress Rate Limit Status provided field in the first
row.
4. If you selected Enable in the Ingr ess Rate Limit Status field, enter the Ingress Rate Limit in
the provided field in the first row.
5. Choose either Enable or Disable in the Egress Shaping Ra te Status provided field in the first
row.
6. If you selected Enable in the Egress Shaping Rate Status field, enter the Egress Shaping
Rates CIR and CbS in the provided fields in the first row.
7. Click APPLY to update the device.
Advanced
The CoS Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“CoS to Queue Mapping”
•“DSCP to Queue Mapping”
CoS to Queue Mapping
The CoS to Queue Mapping screen contains fields for mapping CoS value s to traffic queues.
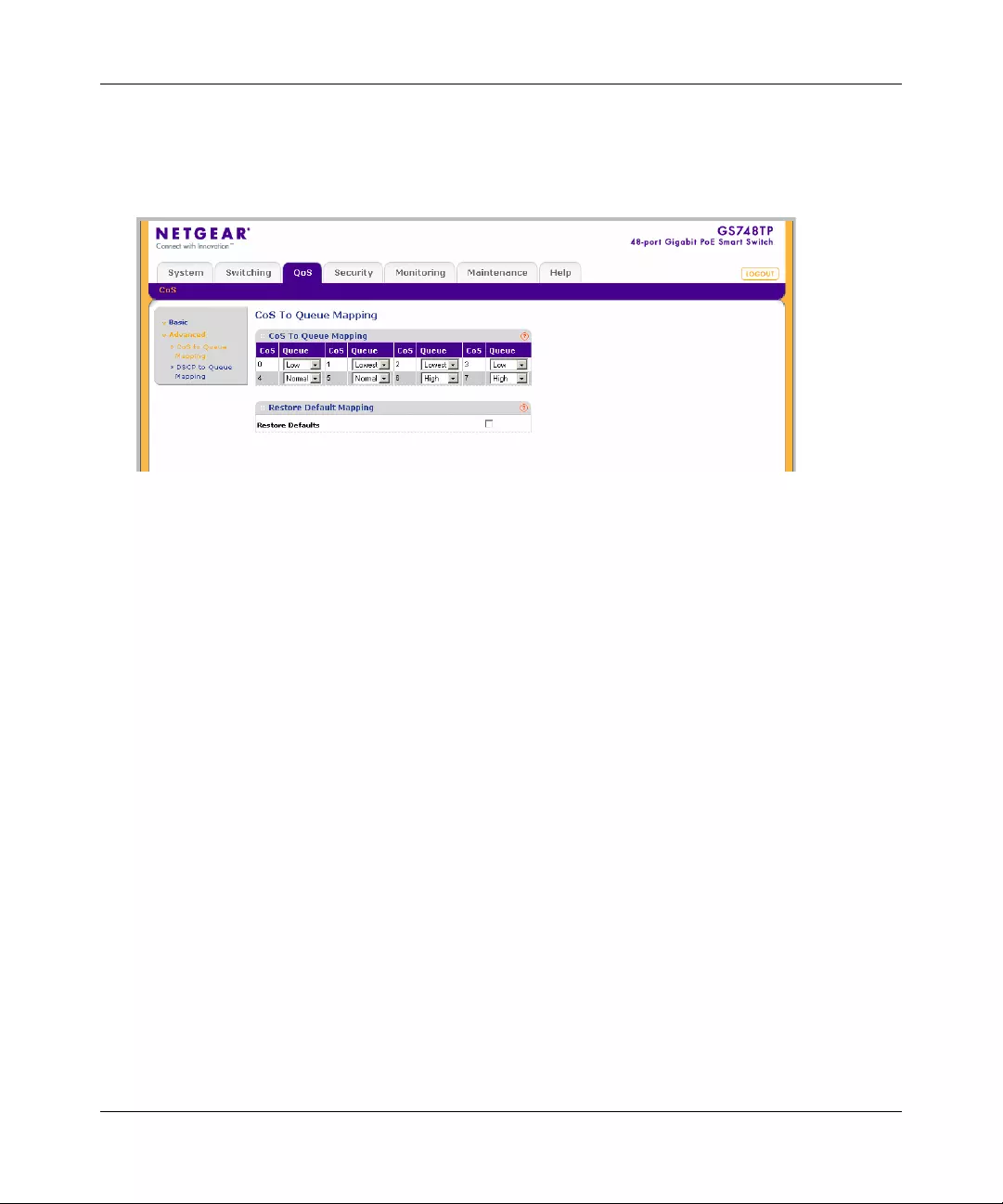
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
5-8 Configuring QoS
v1.0, April 2008
To map CoS values to queues:
1. Click QoS > CoS> Advanced > CoS to Queue Mapping. The CoS to Queue Mapping screen
displays:
The CoS to Queue Mapping screen contains the following fields:
CoS to Queue Mapping
•CoS – Displays the CoS priority tag values, where 0 is the lowest and 7 is the highest.
•Queue – Select the traffic forwarding queue to which the CoS priority is mapped. Four
traffic priority queues are supported (Lowest, Low, Normal and High). The High Queue is
reserved for special traffic and is not recommended for use.
Restore Default Mapping
•Restore Defaults – Restore the device factory defau lts for mapping CoS values to a
forwarding queue. The possible fiel d values are:
– Checked – Restore the factory default settings for mapping CoS values to a
forwarding queue.
– Unchecked – Maintain the current CoS queue mapping settings.
2. Select the Queue values for each CoS value in the provided fields.
3. Check or uncheck the Restore Defaults box in the provided field.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 5-5

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Configuring QoS 5-9
v1.0, April 2008
DSCP to Queue Mapping
The DSCP To Queue Mapping screen contains fields for mapping DSCP values to traffic queues
for various PHBs (Per-Hop Behaviors). These include the CS (Class Selector), AF (Assured
Forwarding) and EF (Expedited Forwarding). For example, a packet with a DSCP tag value of 1
can be assigned to the High queue.
To map DSCP values to queues:
1. Click QoS > CoS> Advanced > DSCP To Queue Mapping. The DSCP To Queue Mapping
screen displays:
The DSCP To Queue Mapping screen contains the following fields:
DSCP to Queue Mapping
•DSCP In – Displays the incoming packet’s DS CP value. The following DSCP In values
are predefined: 3, 11, 19, 27, 35, 43, 51, 59.
•Queue – Select the traffic-forwarding queue to which the DSCP is mapped. Four traffic
priority queues are supported (Lowest, Low, Normal and High). The High Queue is
reserved for special traffic and is not recommended for use.
Figure 5-6

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
5-10 Configuring QoS
v1.0, April 2008
Restore Default Mapping
•Restore Defaults– Restore the DSCP Mapping device factory default values. The possible
field values are:
– Checked – Restore the factory default settings for DSCP mapping values.
– Unchecked – Maintain the current DSCP mapping settings.
2. Select the Queue values for each DSCP In value in the provided fields.
3. Check or uncheck the Restore Defaults box in the provided field.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.

6-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 6
Managing Security
Setting Security Configuration Options
The navigation pane at the top of the web browser interface contains a Security tab that enables
you to manage your GS700TP Smart Switch with features under the following main menu options:
•“Management Security”
•“Port Authentication”
•“Traf fic Control”
•“ACL”
The description that follows in this chapter describes configuring and managing security settings
in the GS700TP Smart Switch.
Management Security
The Management Security menu contains the following options:
•“User Configuration”
•“RADIUS”
•“TACACS+”
•“Authentication List”
User Configuration
The User Configuration menu contains the following options:
•“Change Password”
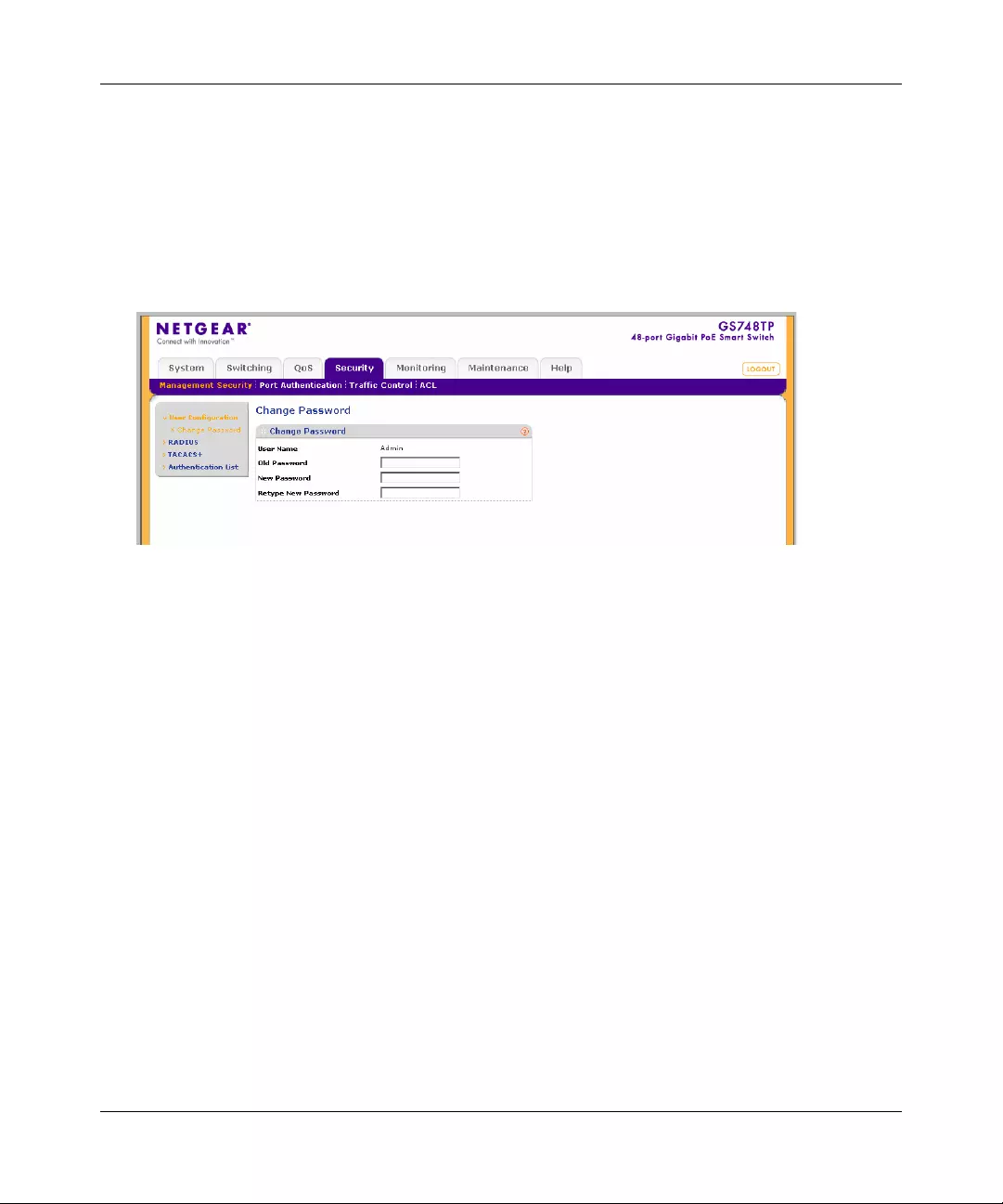
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-2 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
Change Password
The Change Password screen contains parameters for configuring device passwords.
Authentication on this device uses only a password, not a username.
To change the device password:
1. Click Security > Management Security > User Configuration > Change Password. The
Change Password screen displays:
The Change Password screen contains the following fields:
•User Name – Displays the User Name.
•Old Password – Enter the current password for accessing the system.
•New Password – Enter a new password for accessing the system.
•Retype New Password – Repeat the new pa ssword used to access the system.
2. Enter the Old Password, New Password and Retype New Password in the provided fields.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
RADIUS
Remote Authorization Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) servers provide additional security for
networks. RADIUS servers provide a centralized authentication method for web access. The user-
assigned RADIUS parameters are applie d to newly defined RADIUS servers. If values are not
defined, the system defaults are applied to the new RADIUS servers.
The RADIUS menu contains the following options:
•“Authentication Server Configurat ion”
Figure 6-1
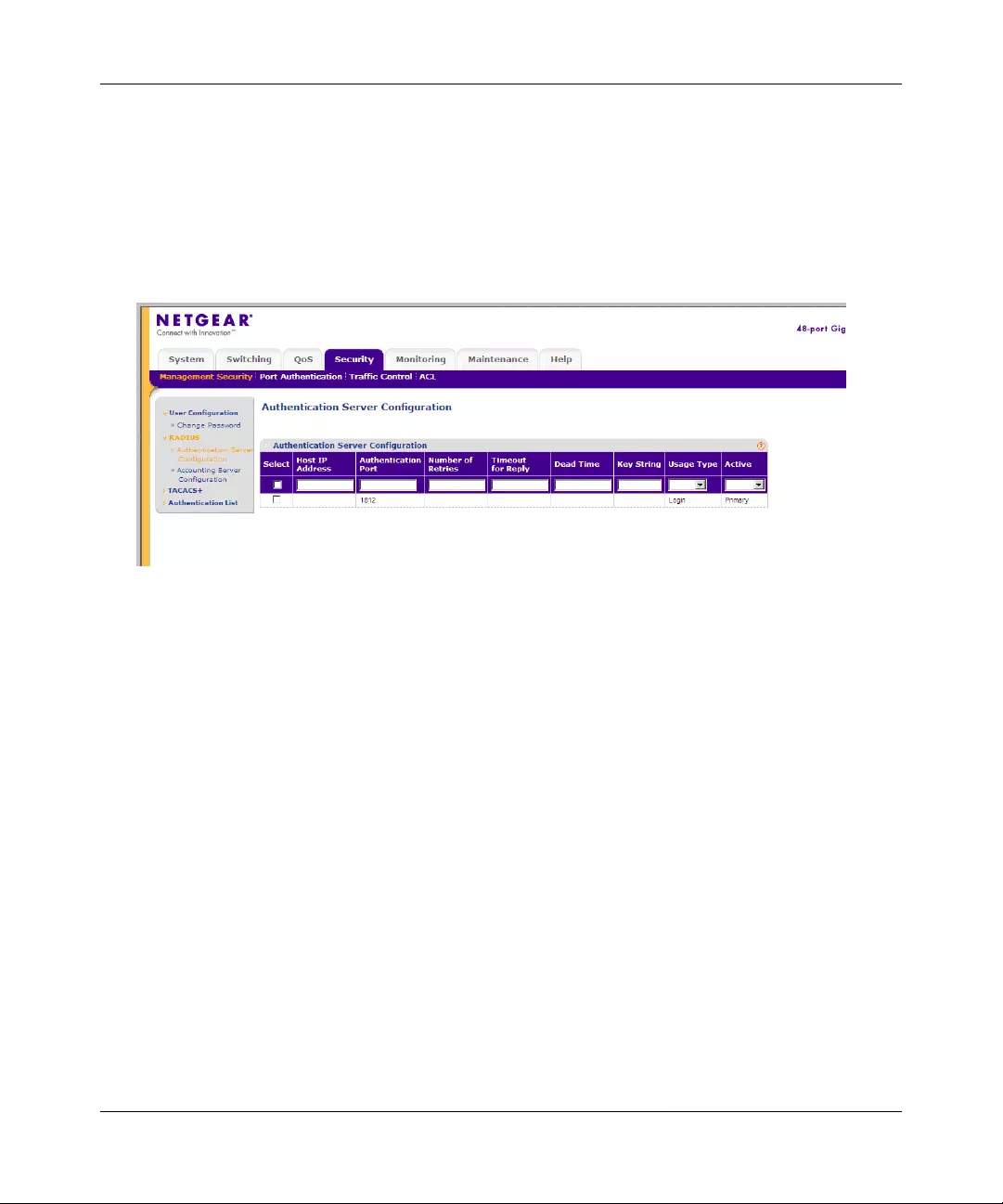
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-3
v1.0, April 2008
•“Accounting Server Configuration”
Authentication Server Con figuration
To configure RADIUS servers:
1. Click Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Authentication Server
Configuration. The RADIUS Authentication Server Configuration screen displays:
The RADIUS Authentication Server Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Host IP Address – Enter the RADIUS Authentication Server IP address.
•Authentication Port – Enter the authentication port number. The authentication port is
used to verify the RADIUS Server authentication. The field default is 1812.
•Number of Retries – Enter the number of transmitted requests sent to the RADIUS
Authentication Server before a failure occurs. Possible field values are 1-10. The default
value is 3.
•Timeout for Reply – Enter the amount of time (in seconds) the device waits for an answer
from the RADIUS Authentication Server before retrying the query, or switching to the
next server. Possible field values are 1-30. The default value is 3.
•Dead Time – Enter the default amount of time (in minutes) that a RADIUS
Authentication Server is bypassed for service requests. The range is 0-200. The default
value is 0.
•Key String – Enter the default key string used for authenticating and encrypting all
RADIUS-communications between the device and the RADIUS Authentication Server.
This key must match the RADIUS encryption.
Figure 6-2

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-4 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
•Usage Type – Select the RADIUS Authentication Server usage type. The default value is
Login. The possible fiel d values are:
– Login – The RADIUS Authentication Server is used for authenticating user names
and passwords.
– 802.1X – The RADIUS Authentication Server is used for 802.1X authentication.
– All – The RADIUS Authentication Server is used for authenticating user names and
passwords, and 802.1X port authenticatio n.
•Active – Select the priority in which the system performs authentication with a RADIUS
Authentication Server. The system performs authentication initially with the RADIUS
Primary Authentication Server , and if it fails, it performs authentication with the RADIUS
Backup Authentication Server. The possible values are:
– Primary – Defines the RADIUS Primary Authentication Server.
– Backup – Define s the RADIUS Backup Authentication Server.
2. Select the RADIUS Authentication Server entry.
3. Enter the Host IP Address, Authentication Port, Number of Retries, Timeout for Reply,
Dead Time and Key String in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Select the Usage Type and Active Authentication Server from the lists in the provided fields
in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new RADIUS Authentication Server entry:
1. Click Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Authentication Server
Configuration. The RADIUS Authentication Server Configuration screen displays.
2. Enter the Host IP Address, Authentication Port, Number of Retries, Timeout for Reply,
Dead Time and Key String in the provided fields in the first row.
3. Select the Usage Type and Active Authentication Server from the lists in the provided fields
in the first row.
4. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a RADIUS Authentication Server entry:
1. Click Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Authentication Server
Configuration. The RADIUS Authentication Server Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the RADIUS Authentication Server entry.
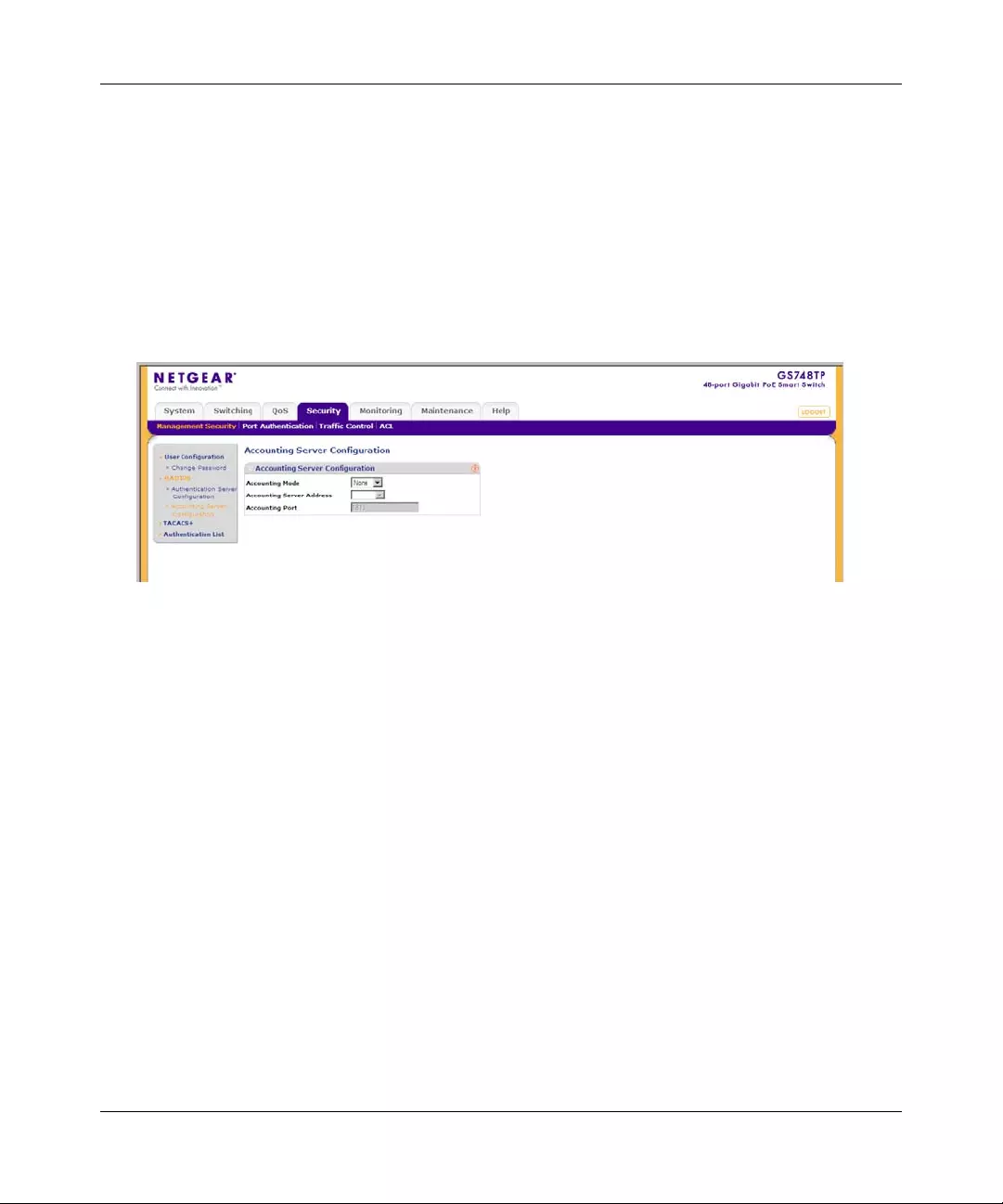
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-5
v1.0, April 2008
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
Accounting Server Configuration
RADIUS accounting enables recording of device management sessions (web login/logout but not
SNMP) as well as 802.1x authentication sessions.
To configure RADIUS Accounting Servers:
1. Click Security > Management Security > RADIUS > Accounting Server Configuration.
The RADIUS Accounting Server Configuration screen displays:
The RADIUS Accounting Server Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Accounting Mode – Select the RADIUS accounting method. The possible field values
are:
– None – RADIUS accounting is disabled. This is the default.
– 802.1x – 802.1X authentication sessions are recorded.
– Login – Device management (Web login and logout) sessions are recorded.
– Both – Both 802.1X authentication and device management sessions are recorded.
•Accouting Server Address – Select the RADIUS Accounting Server IP address.
•Accounting Port – Enter the RADIUS Accounting port number. The accounting port is
used to handle RADIUS server accounting. The field default is 1813.
2. Select the RADIUS Accounting Mode from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the RADIUS Accounting Server Address from the list in the provided field.
4. Enter the RADIUS Accounting Port in the provided field.
Figure 6-3
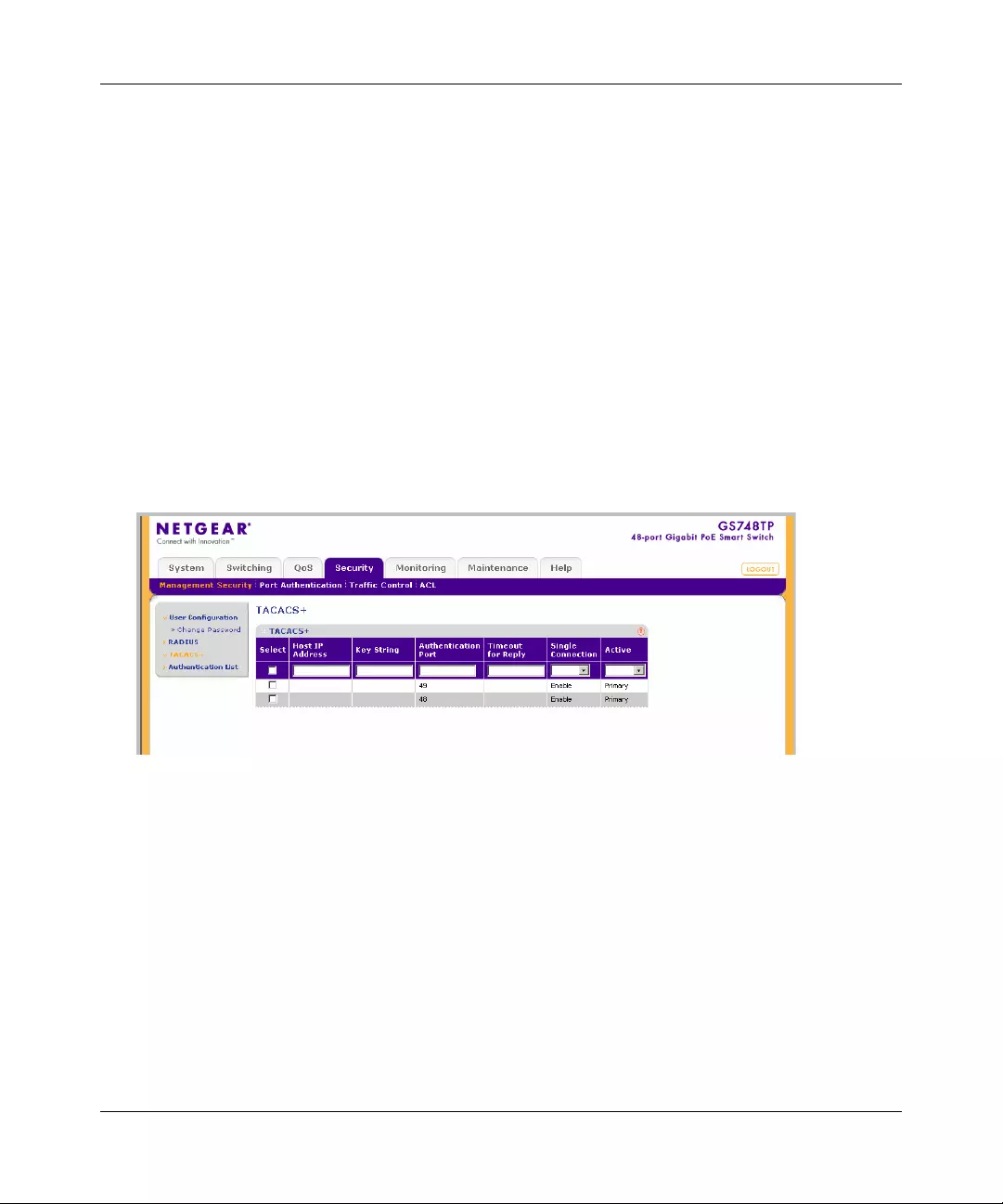
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-6 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
TACACS+
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS+) provides centralized security
user access validation. The system supports up-to 2 TACACS+ servers.
TACACS+ provides a centralized user management system, while still retaining consistency with
RADIUS and other authentication processes.
The TACACS+ protocol ensu res network integrity through en crypted protocol exchan ges between
the client and TACACS+ server. The user-assigned TACACS+ parameters are applied to newly
defined TACACS+ servers. If values are not defined, the system defaults are applied to the new
TACACS+ servers.
To configure TACACS+ Settings:
1. Click Security > Management Security > TACACS+. The TACACS+ screen displays:
The TACACS+ screen contains the following fields:
•Host IP Address – Enter the TACACS+ Server IP address.
•Key String – Enter the default authentication and encryption key for TACACS+
communication between the device and the TACACS+ server.
•Authentication Port – Enter the port number via which the TACACS+ session occurs.
The default port is port 49.
•Timeout for Reply – Enter the amount of time (in seconds) the device waits for an answer
from the TACACS+ server before retrying the query, or switching to the next server.
Possible field values are 1-30. The default value is 5.
Figure 6-4

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-7
v1.0, April 2008
•Single Connection – Select whether a single open connection between the host
Authentication Port and the TACACS+ server is enabled or disabled. The possible field
values are:
– Enable – Enable a single connection.
– Disable – Disable a single connection.
•Active – Select whether this server is the primary or backup TACACS+ server used for
authentication. The possible values are:
– Primary – Define the TACACS+ Primary Server.
– Backup – Define the TACACS+ Backup Server.
2. Select the TACACS+ server entry.
3. Enter the Host IP Address, Key String, Authentication Port and Timeout for Reply in the
provided fields in the first row.
4. Select the Single Connection status and Active server from the lists in the provided fields in
the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new TACACS+ server entry:
1. Click Security > Management Security > TACACS+. The TACACS+ screen displays.
2. Enter the Host IP Address, Key String, Authentication Port and Timeout for Reply in the
provided fields in the first row.
3. Select the Single Connection status and Active server from the lists in the provided fields in
the first row.
4. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a TACACS+ server entry:
1. Click Security > Management Security > TACACS+. The TACACS+ screen displays.
2. Select the TACACS+ server entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-8 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
Authentication List
The Authenticat ion List screen co ntains information for def ining an authentication method for the
selected Authentication List. For ex ample, if the user selects TACACS+ as the first entry, None as
the second, this causes authentication to first occur at the TACACS+ server. If the TACACS+
server is inaccessible or not defined, the session is permitted.
Once the Authentication List is defined as Local, it is not possible to define an alternative
authentication method as it is a built-in system authentication method.
In order to configure RADIUS/TACACS+ authentication, the user name shou ld be configured as
$enab15$ on the RADIUS/TACACS+ server.
To configure the Authentication List method:
1. Click Security > Management Security > Authentication List. The Authentication List
screen displays:
The Authentication List screen contains the following fields:
•1,2,3 – Select the order in which authentication is applied. The possible field values are:
– TACACS+ – Authenticate the user at the TACACS+ server . For more information, see
“TACACS+”.
– RADIUS – Authenticate the user at the RADIUS server. For more information, see
“RADIUS”.
– Local – Authenticate the user at the device level. The device checks the user name and
password for authentication
– None – Assign no authentication method to the authentication list.
2. Select the Authentication List entry.
Figure 6-5

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-9
v1.0, April 2008
3. Select the order of authentication (1,2,3) for each method from the list in the provided field in
the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Port Authentication
The Port Authentication menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The Port Authentication Basic menu contains the following option:
•“802.1X Configuration”
802.1X Configuration
The Basic 802.1X Configuration screen allows network managers to configure network
authentication parameters. In addition, the Guest VLAN option is enabled from the Basic 802.1X
Configuration screen.
To define the 802.1X configuration:
1. Click Security > Port Authentication > Basic > 802.1X Configuration. The Basic 802.1X
Configuration screen displays:
The Basic 802.1X Configuration screen contains the following fields:
Figure 6-6

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-10 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
•Port Based Authentication State – Select whether port-based authentication is enabled
or disabled on the device. The possible field values are:
– Disable – Disable port-based authentication on the device.
– Enable – Enable port-based authentication on the device.
•Authentication Method – Select the authentication method used for port authentication.
The possible field values are:
– RADIUS, No ne – Port authenti cation is first attempted through the RADIUS server. If
the RADIUS server is inaccessible or not defined, then no authentication method
(None) is used and the session is permitted.
– RADIUS – Port authentication is through the RADIUS server.
– None – No authentication method is used to authenticate the port.
•Guest VLAN – Select whether the Guest VLAN is enabled or disabled on the device. The
default VLAN cannot be defined as a Guest VLAN. The possible field values are:
– Disable – Disable the Guest VLAN on the device. This is the default value.
– Enable – Enable using a Guest VLAN for unauthorized ports. If a Guest VLAN is
enabled, the unauthorized port automatically joins the VLAN selected in the VLAN
List field.
•Guest VLAN ID – Select the guest VLAN ID from the list of currently defined VLANs.
•EAPOL Handling – Select the method of handling EAPOL (Extensible Authentication
Protocol Over LAN) packets when 802.1X authentication is disabled. The possible field
values are:
– Filtering – EAPOL packets are filtered.
– Flooding – EAPOL packets are flooded to all ports.
2. Select Disable or Enable for the Port Based Authentication State in the provided field.
3. If you selected Enable for the Port Based Authentication State, then select the
Authentication Method from the list in the provided field.
4. Select Disable or Enable for the Guest VLAN status in the provided field.
5. If you selected Enable for the Guest VLAN field, then select the VLAN ID from the list in the
provided field.
6. If you selected Disable for the Port Based Authentication State, select the EAPOL
Handling mode in the provided field.
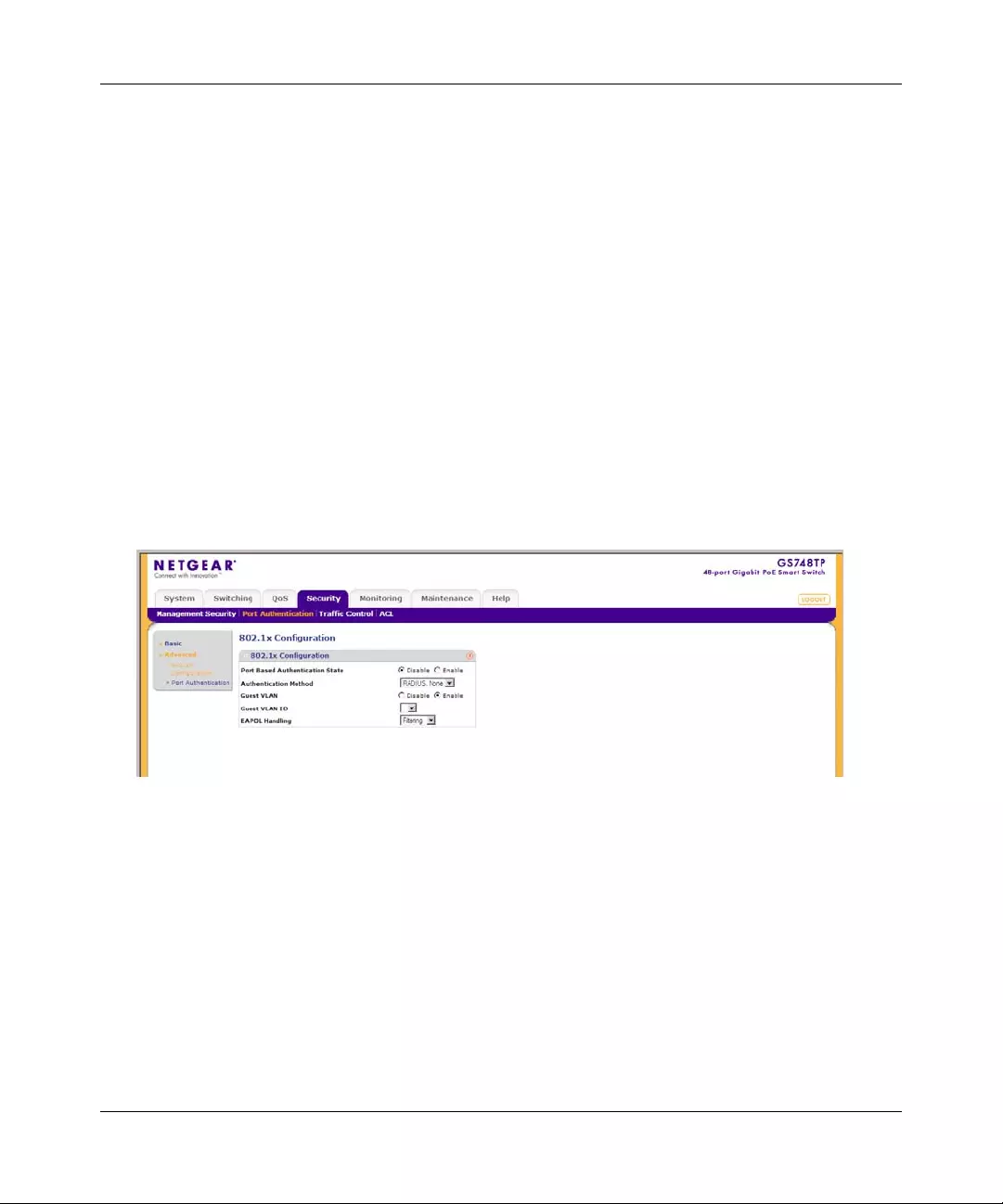
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-11
v1.0, April 2008
7. Click APPLY to update the device.
Advanced
The Port Authentication Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“802.1X Configuration”
•“Port Authentication”
802.1X Configuration
The Advanced 802.1X Co nfig uratio n screen allows network managers to configure network
authentication parameters. In addition, the Guest VLAN option is enabled from the Advanced
802.1X configuration screen.
To define the 802.1X configuration:
1. Click Security > Port Authentication > Advanced > 802.1X configuration. The Advanced
802.1X Configuration screen displays:
The Advanced 802.1X Configuration screen contains the following fields:
•Port Based Authentication State – Enable port-based authentication on the device. The
possible field values are:
– Disable – Disable port-based authentication on the device.
– Enable – Enable port-based authentication on the device.
•Authentication Method – Enter the authentication method used for port authentication.
The possible field values are:
Figure 6-7

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-12 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
– RADIUS, No ne – Port authenti cation is first attempted through the RADIUS server. If
the RADIUS server is inaccessible or not defined, then no authentication method
(None) is used and the session is permitted.
– RADIUS – Port authentication is through the RADIUS server.
– None – No authentication method is used to authenticate the port.
•Guest VLAN – Enter whether the Guest VLAN is enabled on the device. The possible
field values are:
– Disable – Disable Guest VLAN on the device. This is the default value.
– Enable – Enable using a Guest VLAN for unauthorized ports. If a Guest VLAN is
enabled, the unauthorized port automatically joins the VLAN selected in the VLAN
List field.
•Guest VLAN ID – Select the guest VLAN ID from the list of currently defined VLANs.
•EAPOL Handling – Select the method of handling EAPOL (Extensible Authentication
Protocol Over LAN) packets when 802.1X authentication is disabled. The possible field
values are:
– Filtering – EAPOL packets are filtered.
– Flooding – EAPOL packets are flooded to all ports.
2. Select Disable or Enable for the Port Based Authentication State in the provided field.
3. If you selected Enable for the Port Based Authentication State, then select the
Authentication Method from the list in the provided field.
4. Select Disable or Enable for the Guest VLAN status in the provided field.
5. If you selected Enable for the Guest VLAN field, then select the VLAN ID from the list in the
provided field.
6. If you selected Disable for the Port Based Authentication State, select the EAPOL
Handling mode in the provided field.
7. Click APPLY to update the device.
Port Authentication
The Port Authentication screen enables configuring port authentication interface parameters.
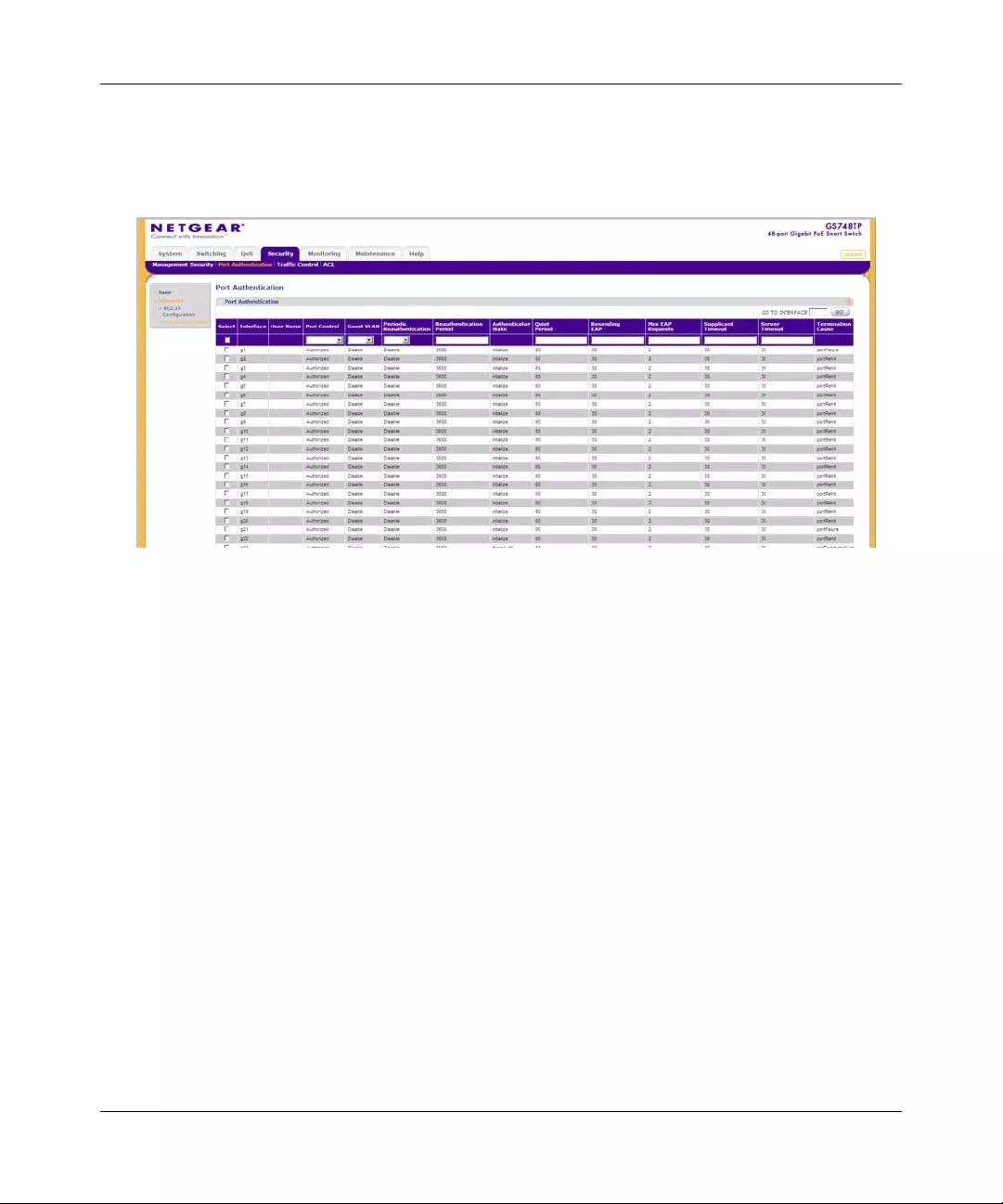
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-13
v1.0, April 2008
To configure port-based authentication global properties:
1. Click Security > Port Authentication > Advanced > Port Authentication. The Port
Authentication screen displays
The Port Authentication screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the interfaces.
•User Name – Displays the supplicant (client) user name, once the user is authenticated.
•Port Control – Select the port authorization state.
– Auto – The port control is Auto and a single client has been authenticated via the port.
– Authorized – The port control is Forced Authorized, and clients have full port access.
– Unauthorized – Either the port control is force Unauthorized, or the port control is
Auto but a client has not been authenticated via the port.
•Guest VLAN – Select whether the Guest VLAN is enabled or disabled on the port. The
default VLAN cannot be defined as a Guest VLAN. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable using a Guest VLAN for the unauthorized port. If a Guest VLAN is
enabled, the unauthorized port automatically joins the VLAN selected in the VLAN
List field.
– Disable – Disable the Guest VLAN on the port. This is the default value.
Figure 6-8

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-14 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
•Periodic Reauthentication – Select whether periodic port reauthentication i s en ab le d o r
disabled. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable perio dic port reauthentication.
– Disable – Disable port reauthentication. This is the default value.
•Reauthentication Period – Enter the time span (in seconds) in which the selected port is
reauthenticated. The field default is 3600 se conds.
•Authenticator State – Displays the port authentication status. The possible field values
are Initialize, Disconnected, Connecting, Authenticating, Authenticated, Aborting, Held,
ForceAuth and ForceUnauthNew.
•Quiet Period – Enter the number of seconds that the device remains in the quiet state
following a failed authentication exchange. The possible field range is 0-65535. The field
default is 60 seconds.
•Resending EAP – Enter the amount of time (in seconds) that lapses before EAP requests
are resent. The field default is 30 seconds.
•Max EAP Requests – Enter the total amount of EAP requests sent. If a response is not
received after the defined period, the authentication process is restarted. The field default
is 2 retries.
•Supplicant Timeout – Enter the amount of time (in seconds) that lapses before EAP
requests are resent to the supplicant. The field default is 30 seconds.
•Server Timeout – Enter the amount of time (in seconds) that lapses before the device re-
sends a request to the authentication server. The field default is 30 seconds.
•Termination Cause – Displays the reason port authentication was terminated. The
possible field values are Supplicant logoff, Port failure, Supplicant restart,
Reauthentication failed, Force unauthorized, Port reinitialize, Port admin disabled and
Undefined.
2. Select the interface.
3. Select the Port Control state, Guest VLAN mode and Periodic Reauthentication sta tus in
the provided fields in the first row.
4. If you selected Enable as the Periodic Reauthentication status, enter the Reauthentication
Period in the provided field in the first row.
5. Enter the Quiet Period, Resending EAP time, Max EAP Requests, Supplicant Timeout
and Server Timeout in the provided field in the first row.
6. Click APPLY to update the device.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-15
v1.0, April 2008
Traffic Control
The Traffic Control menu contains the following options:
•“Storm Control”
•“Port Security”
Storm Control
Storm Contr ol limits the amount of Multicast and Broadcast frames accepted and forwarded by the
device. When Layer 2 frames are forwarded, Broadcast, and Multicast frames are flooded to all
ports on the relevant VLAN. This occupies bandwidth and loads all nodes on all ports.
A Broadcast Storm is a result of an excessive amount of broadcast messages simultaneously
transmitted across a network by a single port. Forwarded message responses are heaped onto the
network, straining network resources or causing the network to time out.
Storm control can be enabled per port by defining the packet type and the rate the packets are
transmitted. The system measures the incoming Broadcast and Multicast frame rates separately on
each port, and discards the frames when the rate exceeds a user-defined rate. By default, Storm
Control is enabled on all ports for Broadcast packets with a threshold of 200 kbps.
The Storm Control screen provides fields for configuring broadcast storm control.
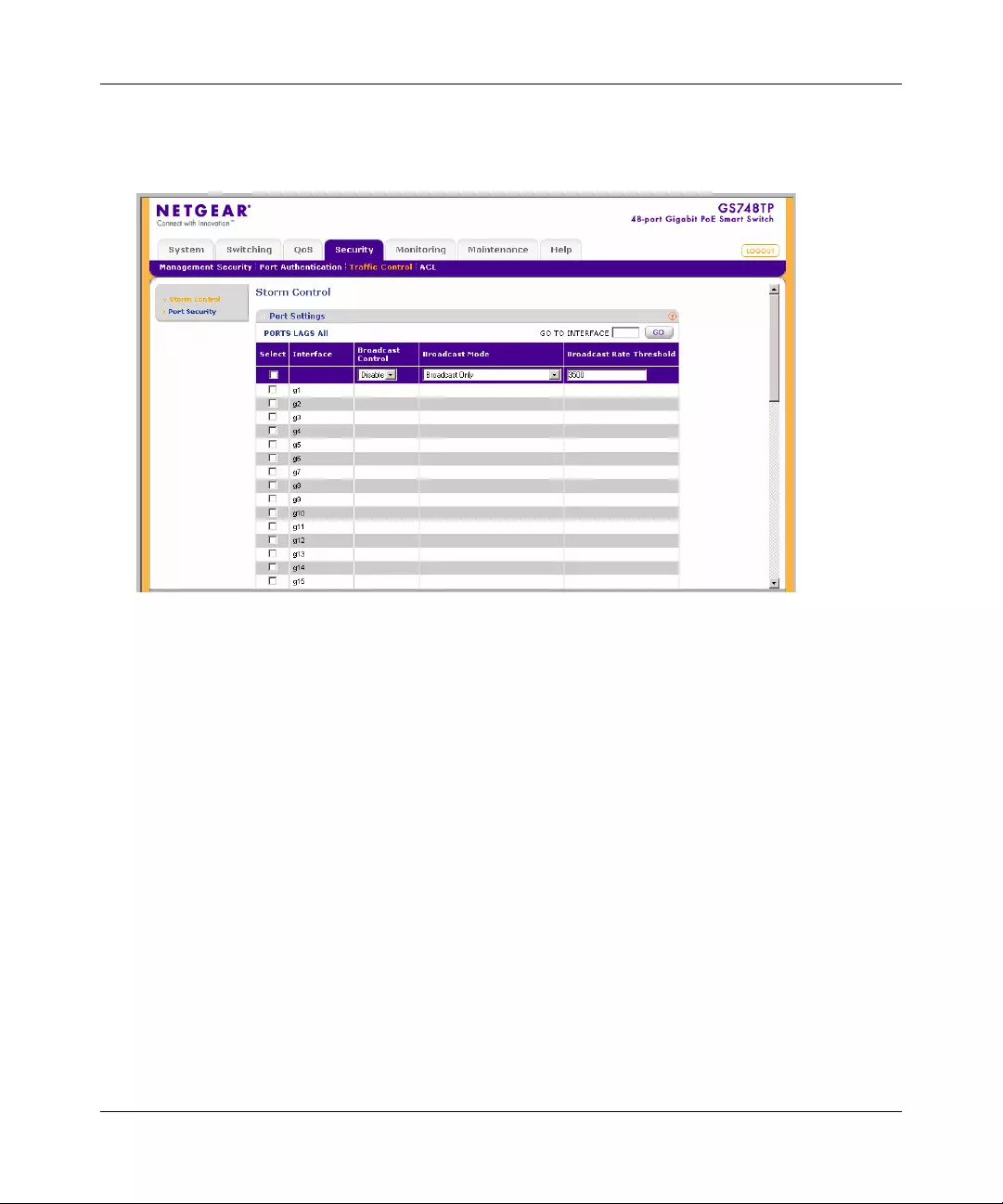
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-16 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
To configure Storm Control:
1. Click Security > Traffic Control > Storm Control. The Storm Control screen displays:
The Storm Control screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the port nu mber for which the storm control information is
displayed.
•Broa dcast Co ntrol – Select whether storm control is enabled or disabled on the interface
according to Broadcast mode. The possible field values are:
– Enable – Enable storm control on the interface.
– Disable – Disable storm control on the interface.
•Broadcast Mo de – S elect the Broadcast control mode on the interface. The possible field
values are:
– Multicast & Broadcast & Unknown Unicast – Count Broadcast, Multicast and Unicast
traffic together.
– Multicast & Broadcast – Coun t Broadcast and Multicast traffic together.
– Broadcast Only – Count Broadcast traffic only. This mode is enabled by default.
Figure 6-9

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-17
v1.0, April 2008
•Broadcast Rate Threshold – Enter the maximum rate (kilobits per second) at which
broadcast packets are forwarded. GE (Gigabit Ethernet) ports have a range of 3500 -
1000000. The default value for GE ports is 3500.
2. Select the interface.
3. Select Enable or Disable Broadcast Control in the provided field in the first row.
4. If you selected Enable Broadcast Control, select the Broadcast Mode from the list in the
provided field in the first row.
5. If you selected Enable Broadcast Control, enter the Broadcast Rate Threshold in the
provided field in the first row.
6. Click APPLY to update the device.
Port Security
Network security can be increased by limiting access on a specific port only to users with specific
MAC addresses. The MAC addresses can be dynamically learned or statically configured. Locked
port security monitors both received and learned packets that are received on specific ports.
Access to the locked port is limited to users with specific MAC addresses. These addresses are
either manually defined on the port, or learned on that port up to the point when it is locked. When
a packet is received on a locked port and the packet source MAC address is not tied to that port
(either it was learned on a dif ferent port, or it is unknown to the system), the protection mechanism
is invoked. It provides the following options for unauthorized packets arriving at a locked port:
•Forwarded
• Discarded with no trap
• Discarded with a trap
• Shuts down the port
Locked port security also enables storing a list of MAC addresses in the configuration file. The
MAC address list can be restored after the device has been reset.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-18 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
To define port security:
1. Click Security > Traffic Control > Port Security. The Port Security screen displays:
The Port Security screen con tains the following fields :
•Interface – Displays the port or LAG n ame.
•Status – Select the port security status. The possible field values are:
– Locked – The port is currently lo cked.
– Unlocked – The port is currently unlocked. This is the default value.
•Learning Mode – Select the locked port type. The possible field values are:
– Classic Lock – Locks the port, and only forwards packets that have been learned
statically or dynamically, prior to locking the port. The lock is effective immediately.
– Limited Dynamic Lock – The port is unlocked. Locks the port after a user-defined
number of MAC addresses have been dynamically learned on the port. After the port
is locked, packets are forwarded only from MAC addresses that have been learned
prior to locking the port.
Figure 6-10

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-19
v1.0, April 2008
•Max Entries – Enter the maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned on the
port. The Max Entries field is enabled only if the Limited Dynamic Lock mode is selected.
The range is 1-128 entries. The default value is 1.
•Action – Select the action to be applied to packets arriving on a locked port. The possible
field values are:
– Forward – Forward packets from an unknown source without learning the MAC
address.
– Discard – Discard packets from any unlearned source. This is the default value.
– Shutdown – Discard packets from any unlearned source and shut down the port. The
port remains shut down until reactivated or until the device is reset.
•Trap – Select whether traps are enabled or disabled when a packet from an unknown
source is received on a locked port. The possible field values are :
– Enable – Enable traps.
– Disable – Disable traps. This is the default value.
•Trap Fr equency (Sec) – Enter the frequency at which traps are sent. The field format is in
seconds. The range is 1-1,000,000. The default value is 10 seconds.
2. Select the port security Status, Learning Mode, Action and Trap status from the lists in the
provided fields in the first row.
3. Enter the Max Entries and Trap Frequency in the provided fields in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
ACL
Access Control Lists (ACL) allow network managers to define classification actions and rules for
specific ingress ports. Packets entering an ingress port, with an active ACL, are either admitted or
denied entry and the ingress port is disabled. If they are denied entry, the user can disable the port.
The ACL menu contains the following options:
•“MAC ACL”
•“MAC Rules”
•“MAC Binding Configuration”
•“IP ACL”
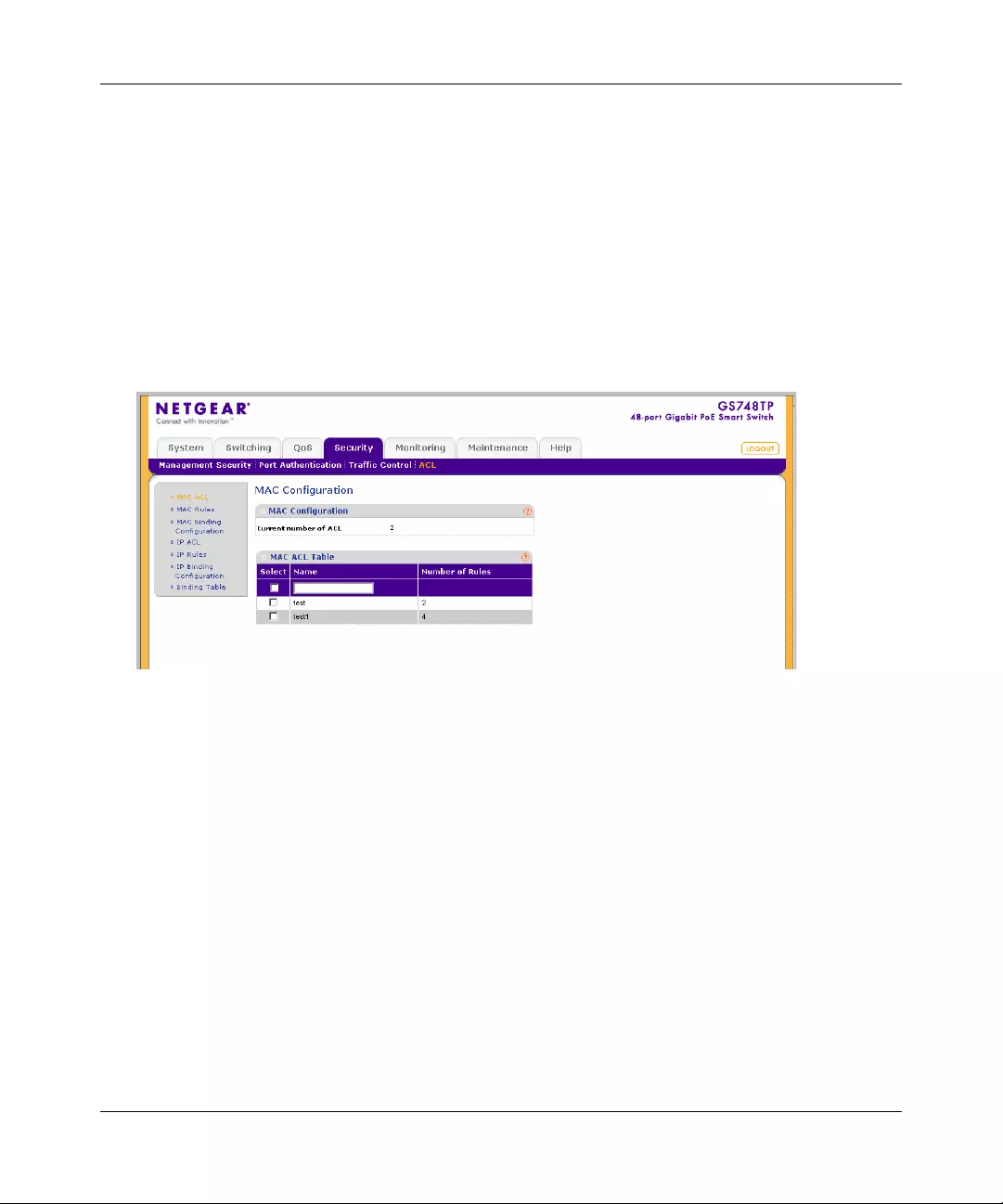
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-20 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
•“IP Rules”
•“IP Binding Configuration”
•“Binding Table”
MAC ACL
The MAC Configuration screen allows a MAC Based ACL to be defined.
To view or rename MAC Based ACLs:
1. Click Security > ACL > MAC ACL. The MAC Configuration screen displays:
The MAC Configuration screen contains the following fields:
MAC Configuration
•Current number of ACL – Displays the current number of user-defined ACLs.
MAC ACL Table
•Name – Enter the user-defined MAC based ACL name.
•Number of Rules – Displays the current number of rules in the ACL.
2. Select the ACL entry.
3. Enter the new ACL Name in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 6-11
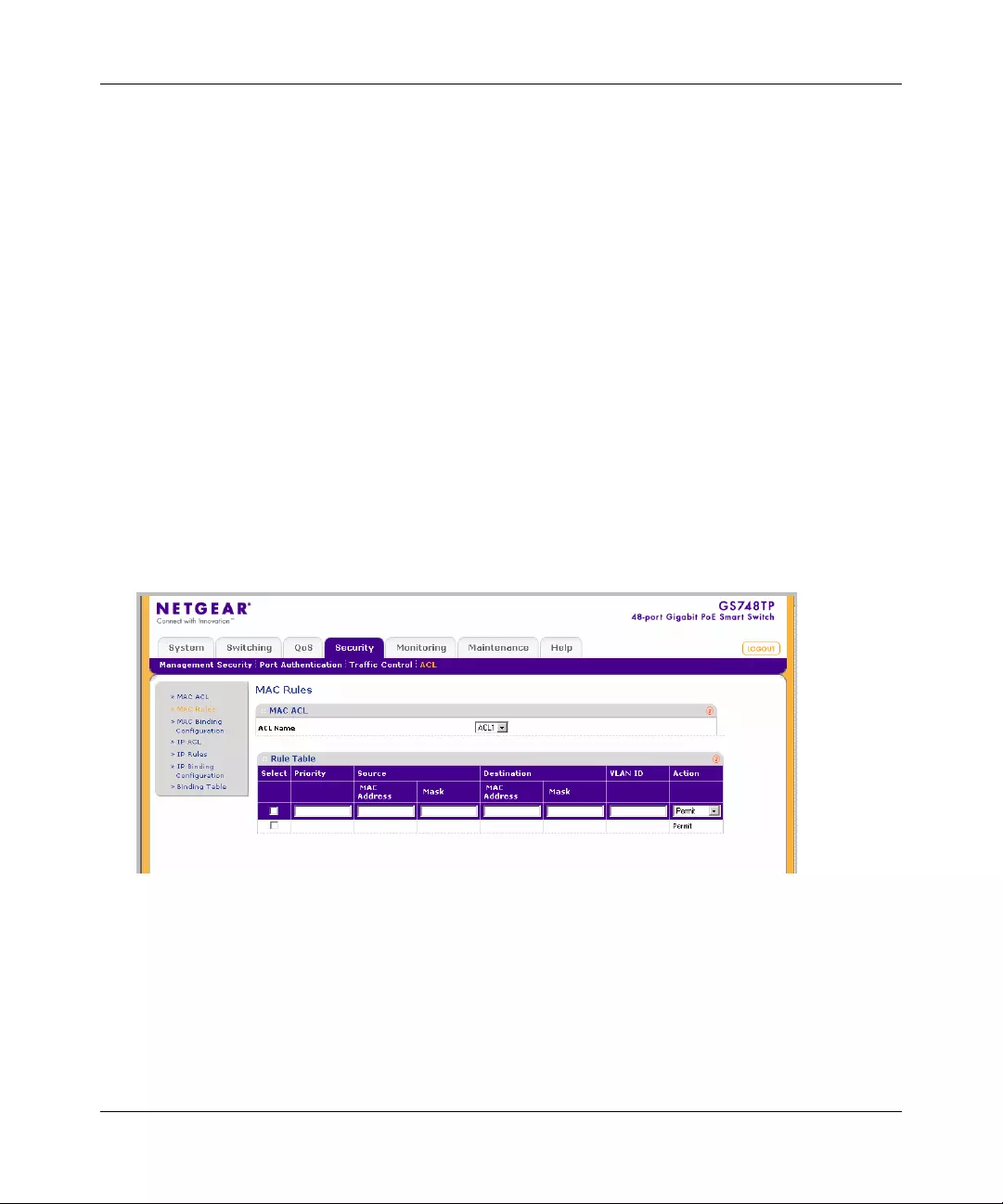
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-21
v1.0, April 2008
To add a new MAC-based ACL entry:
1. Click Security > ACL > MAC ACL. The MAC Configuration screen displays.
2. Enter the ACL Name in the provided field in the first row.
3. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a MAC-based ACL entry:
1. Click Security > ACL > MAC ACL. The MAC Configuration screen displays.
2. Select the ACL entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
MAC Rules
The MAC Rules screen allows a MAC Rule to be defined within a configured ACL. Rules can be
added only if the ACL is not bound to an interface.
To define MAC Rules:
1. Click Security > ACL > MAC Rules. The MAC Rules screen displays:
The MAC Rules screen contains the following fields:
MAC ACL
•ACL Name – Select the ACL Name from the list.
Rule Table
Figure 6-12

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-22 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
•Priority – Enter the rule priority. When the packet is matched to a rule, user groups are
either granted permission or denied device management access. The rule number is
essential to matching packets to rules, as packets are matched on a first-fit basis.
•Source MAC Ad dress – Enter the source MAC Address.
•Source Mask – Enter the mask of the new source MAC address.
•Destination MAC Address – Enter the destination MAC address.
•Destination Mask – Enter the mask of the new destination MAC address.
•VLAN ID – Enter the VLAN ID to which the MAC address is attached in the MAC Rules
database.
•Action – Select the action applied to packets with MAC addresses that have been filtered.
The possible field values are:
– Permit – Permit access to the device.
– Deny – Deny access to packets originating from the blocked MAC address.
– Shutdown – Drop packets that meet the ACL criteria, and disable the port to which the
packet was addressed.
2. Select the ACL Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the rule entry.
4. Enter the provided fields in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a MAC rule:
1. Click Security > ACL > MAC Rules. The MAC Rules screen displays.
2. Select the ACL Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Enter the provided fields in the first row.
4. Click ADD to update the device.
To delete a MAC rule:
1. Click Security > ACL > MAC Rules. The MAC Rules screen displays.
2. Select the ACL Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the rule entry.
4. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
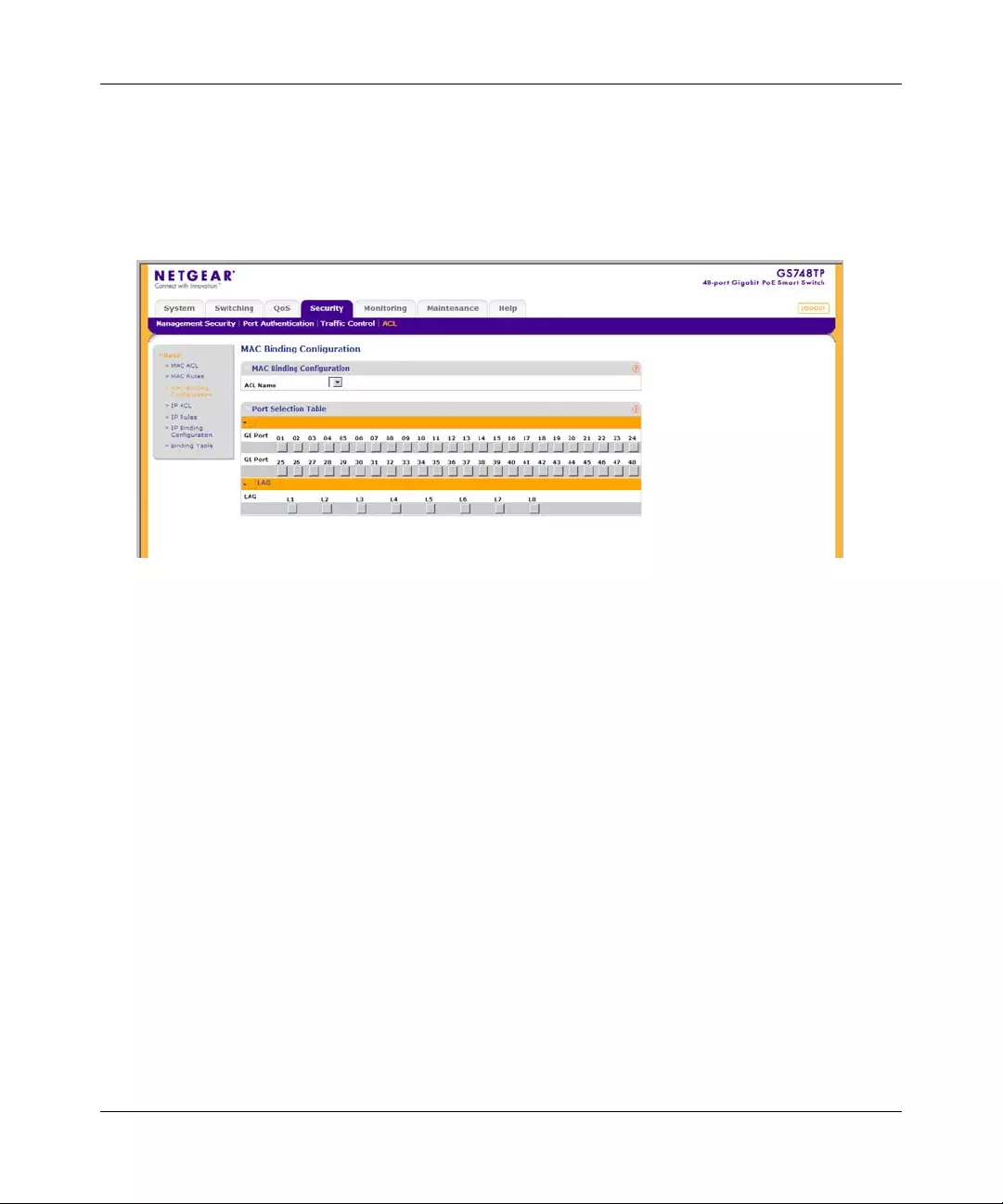
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-23
v1.0, April 2008
MAC Binding Configuration
To bind interfaces to an ACL:
1. Click Security > ACL > MAC Binding Configuration. The MAC Binding Configuration
screen displays:
The MAC Binding Configuration screen contains the following fields:
MAC Binding Configuration
•ACL Name – Select the ACL Name for viewing and modifying ACL bound interfaces.
Port Selection Table
2. Select the interfaces to which the ACLs are bound.
3. Select the ACL Name from the list in the provided field.
4. Select the interfaces to bind to the selected ACL Name by one of the following methods.
a. Click on the port’s or LAG’s gold bar to display the associated interfaces, and then select
the interfaces to bind by clicking on the boxes below the interfaces.
or
b. Click on the port’s or LAG’s quick box to select all the associated interfaces.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 6-13
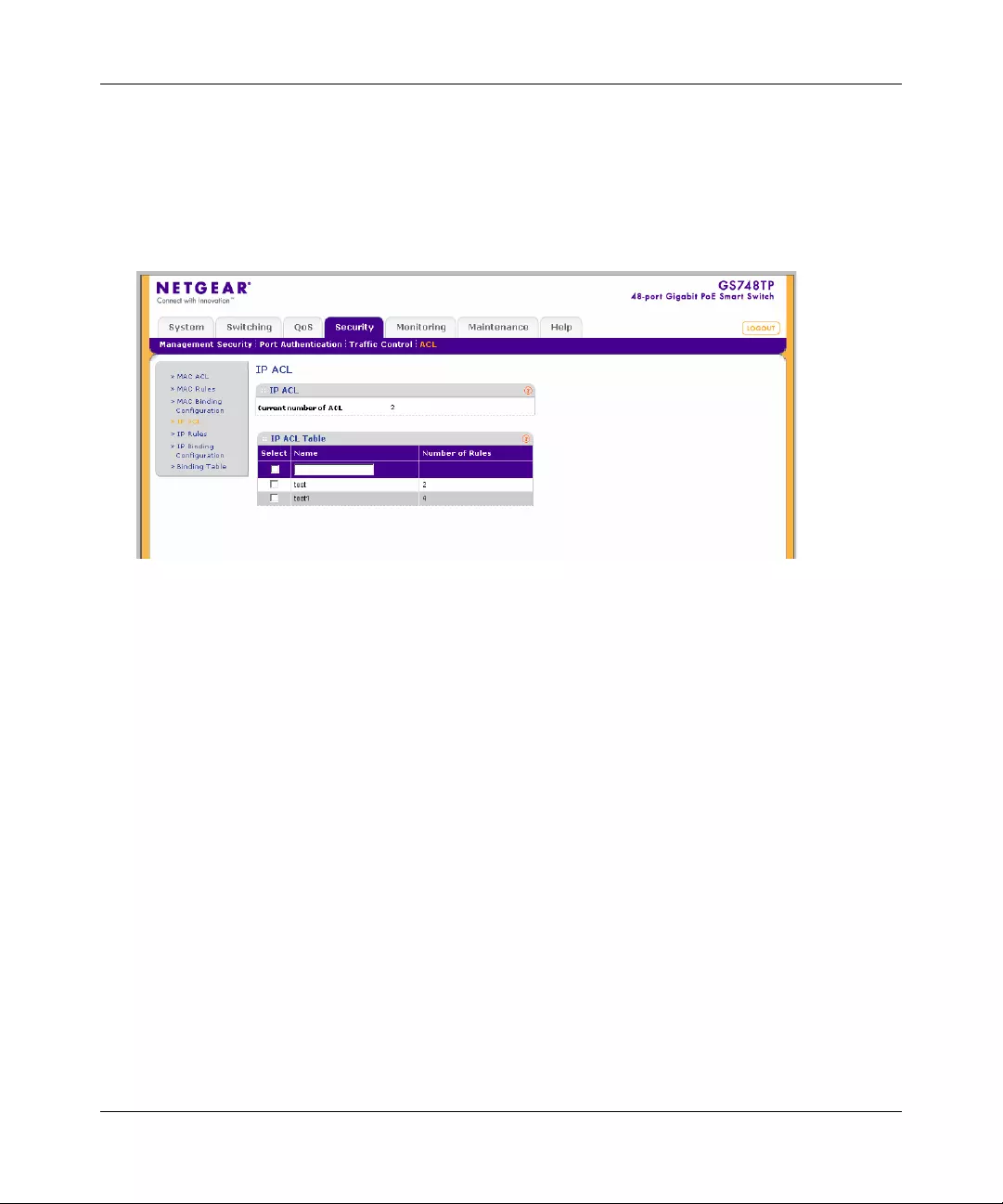
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-24 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
IP ACL
The IP ACL screen allows an IP Based ACL to be defined.
To view or rename IP Based ACLs:
1. Click Security > ACL > IP ACL. The IP ACL screen displays:
The IP ACL screen contains the following fields:
IP ACL
•Current number of ACL – Displays the current number of user-defined ACLs.
IP ACL Table
•Name – Enter the user-defined IP based ACL name.
•Number of Rules – Displays the current number of rules in the ACL.
2. Select the ACL entry.
3. Enter the new ACL Name in the provided field in the first, editable row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a new IP-based ACL entry:
1. Click Security > ACL > IP ACL. The IP ACL screen displays.
2. Click ADD to create a new entry or duplicate an existing entry.
3. Select the ACL entry.
Figure 6-14

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-25
v1.0, April 2008
4. Enter the ACL Name in the provided field in the first, editable row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To remove an IP-based ACL entry:
1. Click Security > ACL > IP ACL. The IP ACL screen displays.
2. Select the ACL entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
IP Rules
The IP Rules screen allows an IP Rule to be defined within a configured ACL. Rules can be added
only if the ACL is not bound to an interface.
To define IP Rules:
1. Click Security > ACL > IP Rules. The IP Rules screen displa ys:
The IP Rules screen contains the following fields:
IP ACL
•ACL Name – Select the ACL Name from the list.
IP Rules
•Priority – Enter the rule priority. When the packet is matched to a rule, user groups are
either granted permission or denied device management access. The rule number is
essential to matching packets to rules, as packets are matched on a first-fit basis.
Figure 6-15

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-26 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
•Pro tocol ID – Enter the protocol in the rule to which the packet is matched.
•Source IP Address – Enter the source IP Address.
•Source Mask – Enter the mask of the new source IP address.
•Destination IP Address – Enter the destination IP address.
•Destination Mask – Enter the mask of the new destination IP address.
•Source Port – Enter the source port that is matched to packets.
•Destination Port – Enter the destination port that is matched to packets.
•Action – Select the action applied to packets with IP addresses that have been filtered. The
possible field values are:
–Permit – Permit access to the device.
–Deny – Deny access to packets originating from the blocked IP address.
–Shutdown – Drop packets that meet the ACL criteria, and disable the port to which
the packet was addressed.
2. Select the ACL Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the rule entry.
4. Enter the provided fields in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add an IP rule:
1. Click Security > ACL > IP Rules. The IP Rules screen displa ys.
2. Select the ACL Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Click ADD to create a new entry or duplicate an existing entry.
4. Select the added entry.
5. Enter the provided fields in the first row.
6. Click APPLY to update the device.
To delete an IP rule:
1. Click Security > ACL > IP Rules. The IP Rules screen displa ys.
2. Select the ACL Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the rule entry.
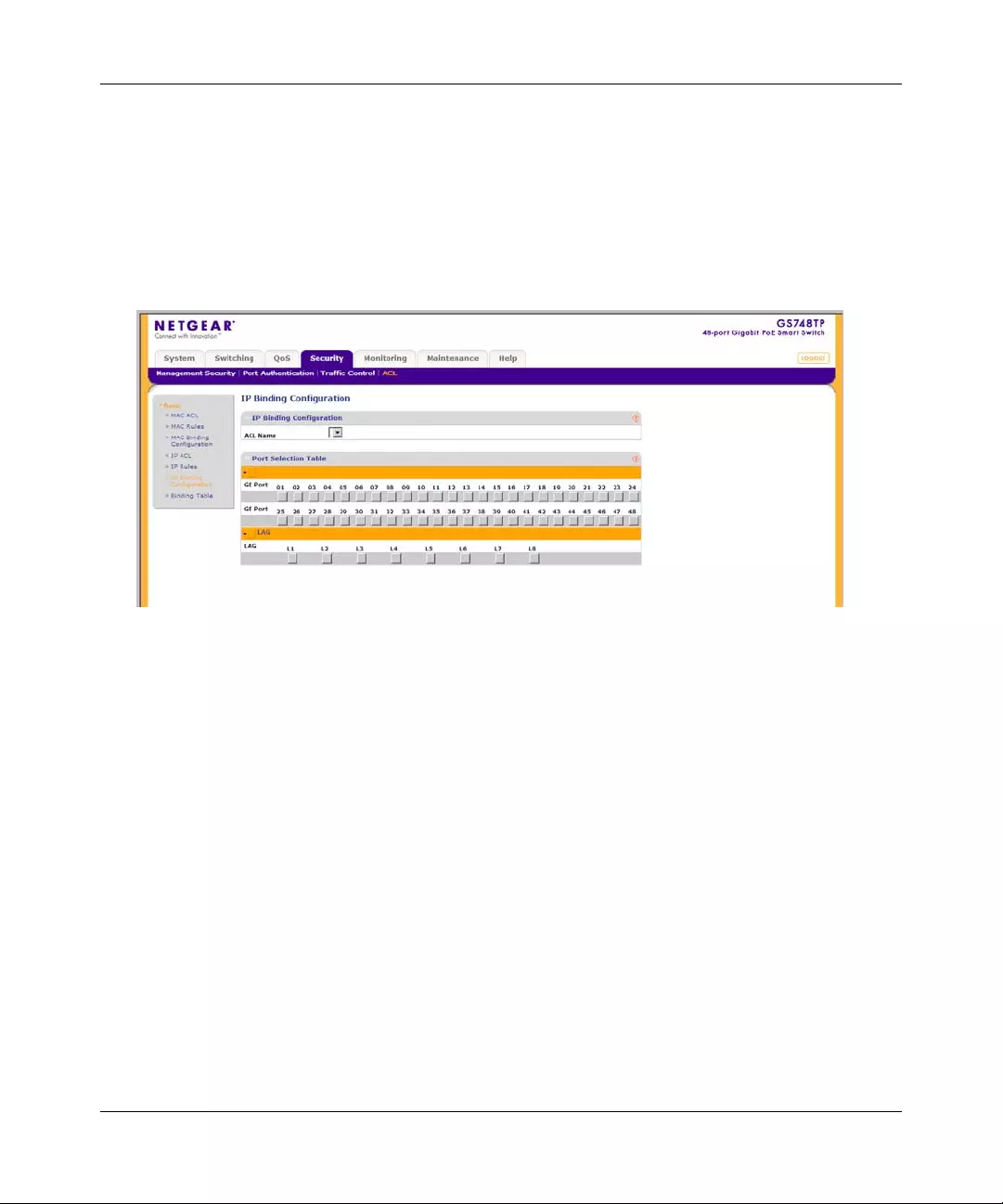
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Managing Security 6-27
v1.0, April 2008
4. Click DELETE to remove the entry.
IP Binding Configuration
To bind interfaces to an ACL:
1. Click Security > ACL > IP Binding Configuration. The IP Binding Configuration screen
displays:
The IP Binding Configuration screen contains the following fields:
IP Binding Configuration
•ACL Name – Select the ACL Name for viewing and modifying ACL bound interfaces.
Port Selection Table
• Select the interfaces for which the ACLs are bound.
2. Select the ACL Name from the list in the provided field.
3. Select the interfaces to bind to the selected ACL Name by one of the following methods.
a. Click on the port or LAG gold bar to display the associated interfaces, and then select the
interfaces to bind by clicking on the boxes below the interfaces.
or
b. Click on the port’s or LAG’s quick box to select all the associated interfaces.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 6-16
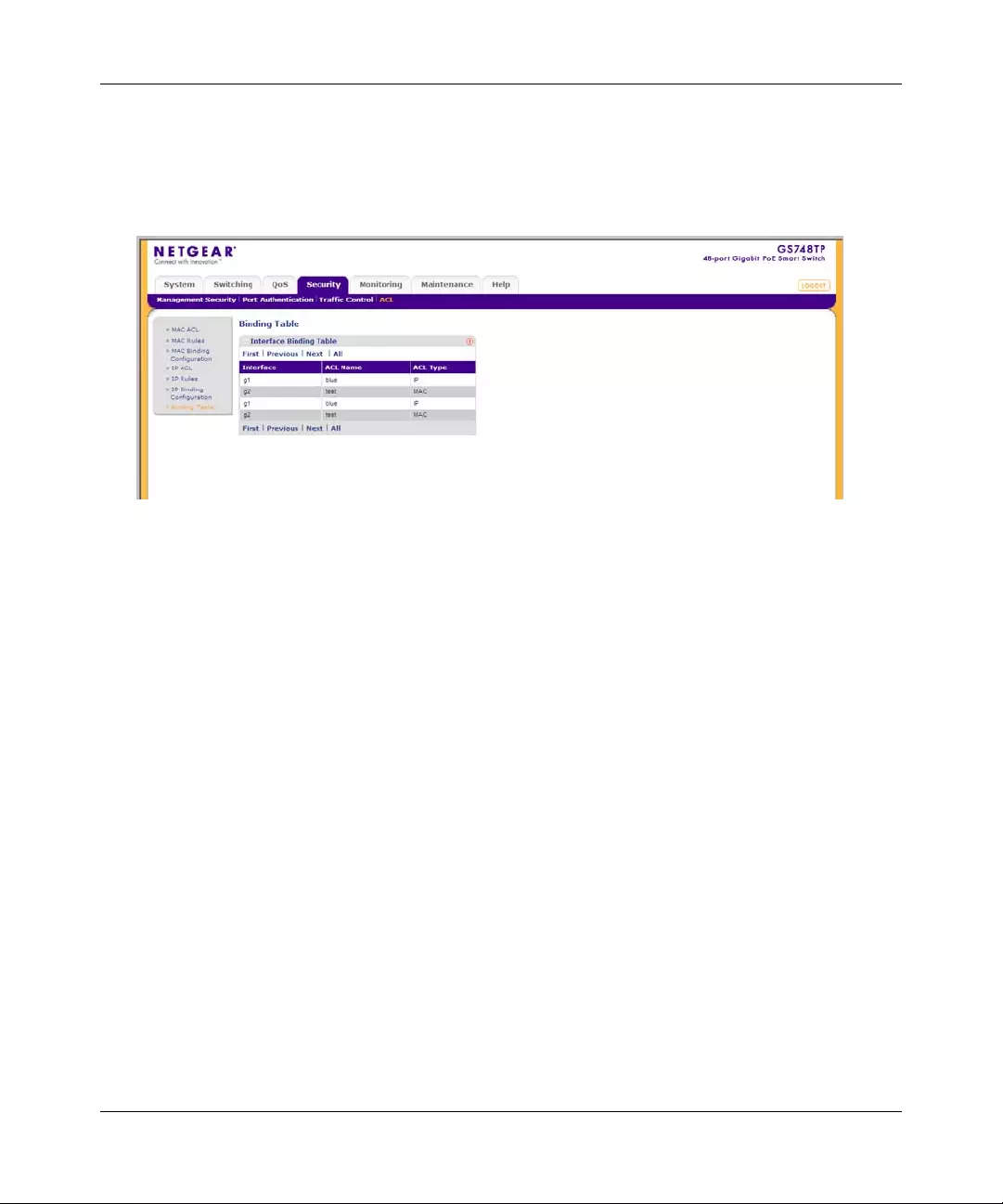
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
6-28 Managing Security
v1.0, April 2008
Binding Table
To view the ACL Binding Table:
1. Click Security > ACL > Binding Table. The Binding Table screen displays:
The Binding Table screen contains the following fields:
Interface Binding Table
•Interface – Displays the interfaces for which the ACLs are bound.
•ACL Name – Displays the ACL Name.
•ACL Type – Displays the ACL Type. The possible field values are:
– IP – The ACL is IP address based.
– MAC – The ACL is MAC address based.
Figure 6-17
7-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 7
Monitoring the Switch
Setting Monitoring Options
The navigation pane at the top of the web browser interface contains a Monitoring tab that enables
you to manage your GS700TP Smart Switch with features under the following main menu options:
•“Logs”
•“RMON”
•“Port Mirroring”
The description that follows in this chapter describes configuring and managing monitoring
settings in the GS700TP Smart Switch.
Logs
Event messages have a unique format, as per the SYSLOG RFC recommended message format for
all error reporting, for example, Syslog+ local device reporting. Messages are assigned a severity
code, and include a message mnemonic, which identifies the source application generating the
message. Messages are filtered based on their urgency or relevancy. The following table contains
the Log Severity Levels:
Table 7-1. Severity Levels
Severity Severity Level Severity Level Description
Emergency 0 The system is not functioning.
Alert 1 The system needs immediate attention.
Critical 2 The system is in a critical state.
Error 3 A system error has occurred.
Warning 4 A system warning is logged.
Notice 5 The system is functioning properly, but a system notice is logged.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-2 Monitoring the Switch
v1.0, April 2008
This section provides information for managing logs. The logs enable viewing device events in
real time, and recording the events for later usage. Logs record and manage events and report
errors and informational messages.
The Logs menu contains the following options:
•“Logs Configuration”
•“Log Filter”
•“Memory Log”
•“Flash Log”
•“Server Log”
Logs Configuration
The Logs Configuration screen contains fields for enabling and disabling logs globally.
To enable or disable event logging:
1. Click Monitoring > Logs > Logs Configuration. The Logs Configuration screen displays:
The Logs Configuration screen contains the following field:
•Logging State – Select whether to enable or disable the device global logs for Cache, File
and Server Logs. Console logs are enabled by default. The possible field values are:
Informational 6 Device information is provided.
Debug 7 Detailed log information is provided.
Figure 7-1
Table 7-1. Severity Levels (continued)
Severity Severity Level Severity Level Description
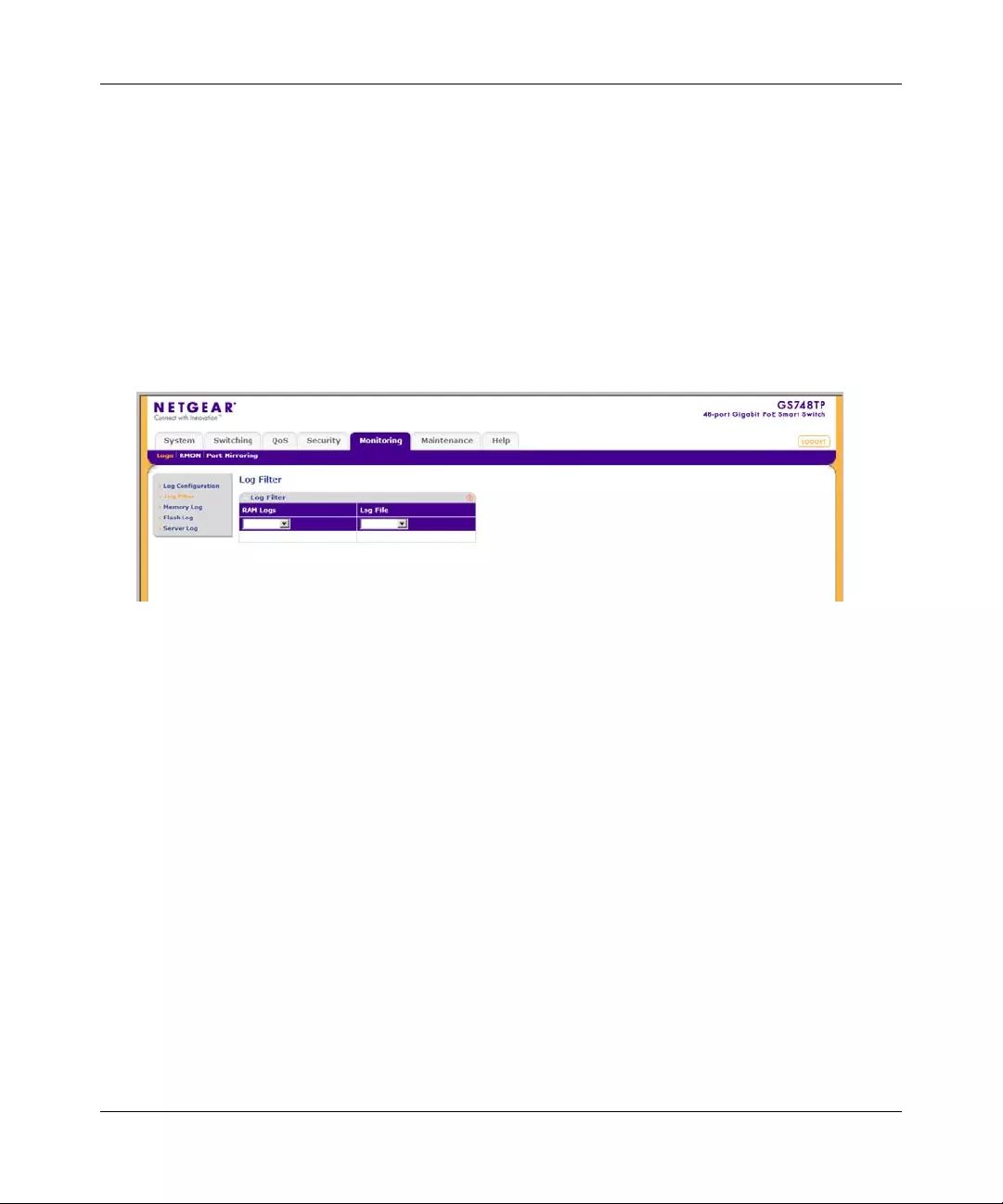
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring the Switch 7-3
v1.0, April 2008
– Disable – Disable device logs.
– Enable – Enable device logs.
2. Select either Enable or Disable as the Logging State in the provided field.
3. Click APPLY to update the device.
Log Filter
To configure log filters:
1. Click Monitoring > Logs > Log Filter. The Log Filter screen displays:
The Log Filter screen contains the following fields:
•RAM Logs – Select the minimum message severity level to appear in the RAM Log. The
following are the available message severity levels:
– Emergency – The highest warning level. If the device is down or not functioning
properly, an emergency log message is saved to the specified logging location.
– Alert – The second highest warning level. An alert log is saved, if there is a serious
device malfunction; for example, all device features are down.
– Critical – The third highest warning level. A critical log is saved if a critical device
malfunction occurs; for example, two device ports are not functioning, while the rest
of the device ports remain functional.
– Error – A device error has occurred; for example, if a single port is offline.
– Warning – The lowest level of a devi ce warning. The device is functio ning, but an
operational problem has occu rred.
– Notice – Provides device information.
Figure 7-2

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-4 Monitoring the Switch
v1.0, April 2008
– Informational – Provides device information.
– Debug – Provides debugging messages.
•Log File – Select the minimum message severity level to appear in the log file. The
following are the available message severity levels:
– Emergency – The highest warning level. If the device is down or not functioning
properly, an emergency log message is saved to the specified logging location.
– Alert – The second highest warning level. An alert log is saved, if there is a serious
device malfunction; for example, all device features are down.
– Critical – The third highest warning level. A critical log is saved if a critical device
malfunction occurs; for example, two device ports are not functioning, while the rest
of the device ports remain functional.
– Error – A device error has occurred; for example, if a single port is offline.
– Warning – The lowest level of a devi ce warning. The device is functio ning, but an
operational problem has occu rred.
– Notice – Provides device information.
– Informational – Provides device information.
– Debug – Provides debugging messages.
2. Select the minimum severity level for RAM logs.
3. Select the minimum severity level for FLASH logs.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
Memory Log
The Memory Log screen contains all system logs in a chronological order that are saved in RAM
(Cache).
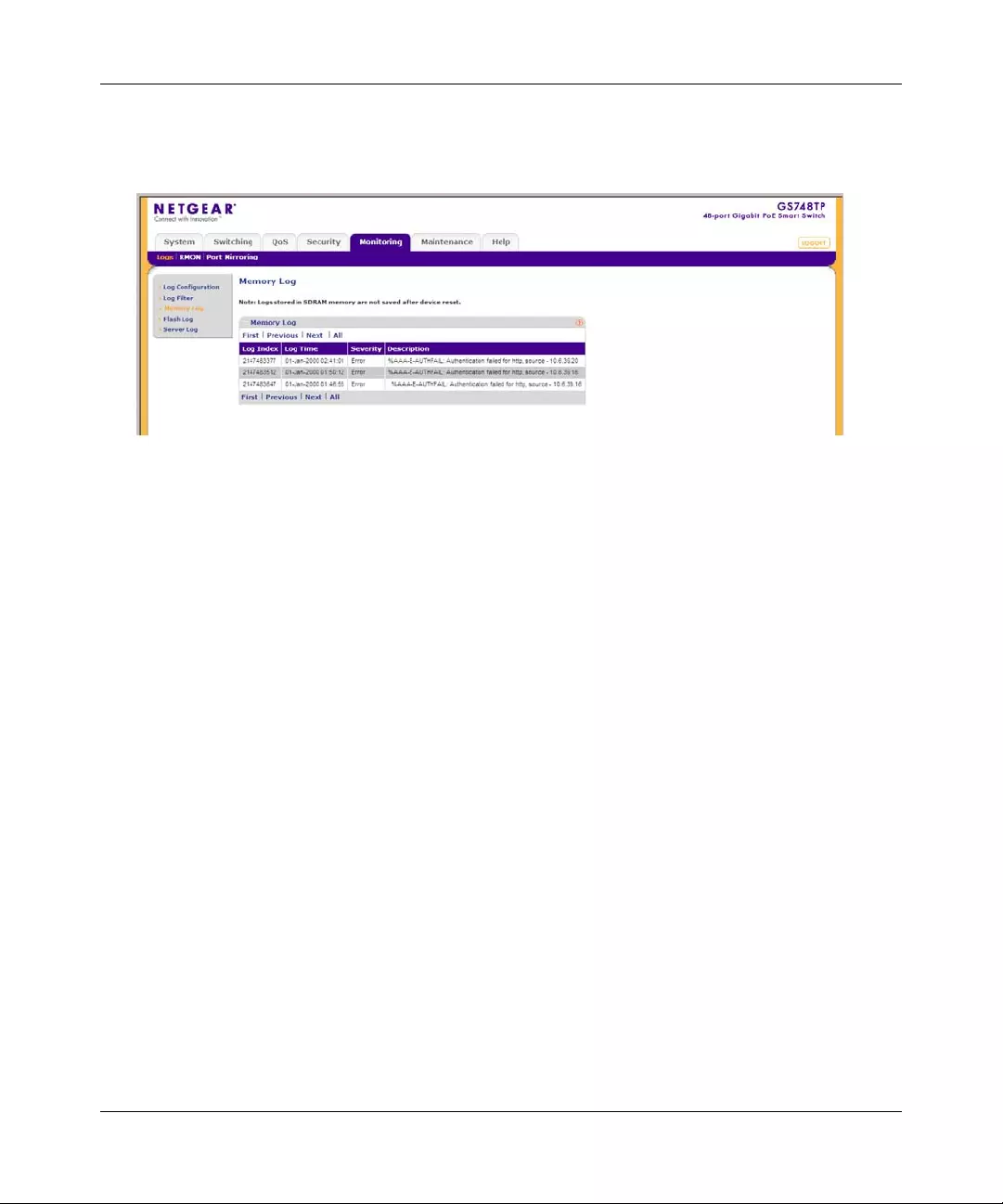
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring the Switch 7-5
v1.0, April 2008
To view the Memory Log screen:
1. Click Monitoring > Logs > Memory Log. The Memory Log screen displays:
The Memory Log screen contains the following fields:
•Log Index – Displays the log number.
•Log Time – Displays the time at which the log was generated.
•Severity – Displays the log severity and urgency level. The following are the available log
severity levels:
– Emergency – The highest warning level. If the device is down or not functioning
properly, an emergency log message is saved to the specified logging location.
– Alert – The second highest warning level. An alert log is saved, if there is a serious
device malfunction; for example, all device features are down.
– Critical – The third highest warning level. A critical log is saved if a critical device
malfunction occurs; for example, two device ports are not functioning, while the rest
of the device ports remain functional.
– Error – A device error has occurred; for example, if a single port is offline.
– Warning – The lowest level of a devi ce warning. The device is functio ning, but an
operational problem has occu rred.
– Notice – Provides device information.
– Informational – Provides device information.
– Debug – Provides debugging messages.
•Description – Displays the log message text.
Figure 7-3
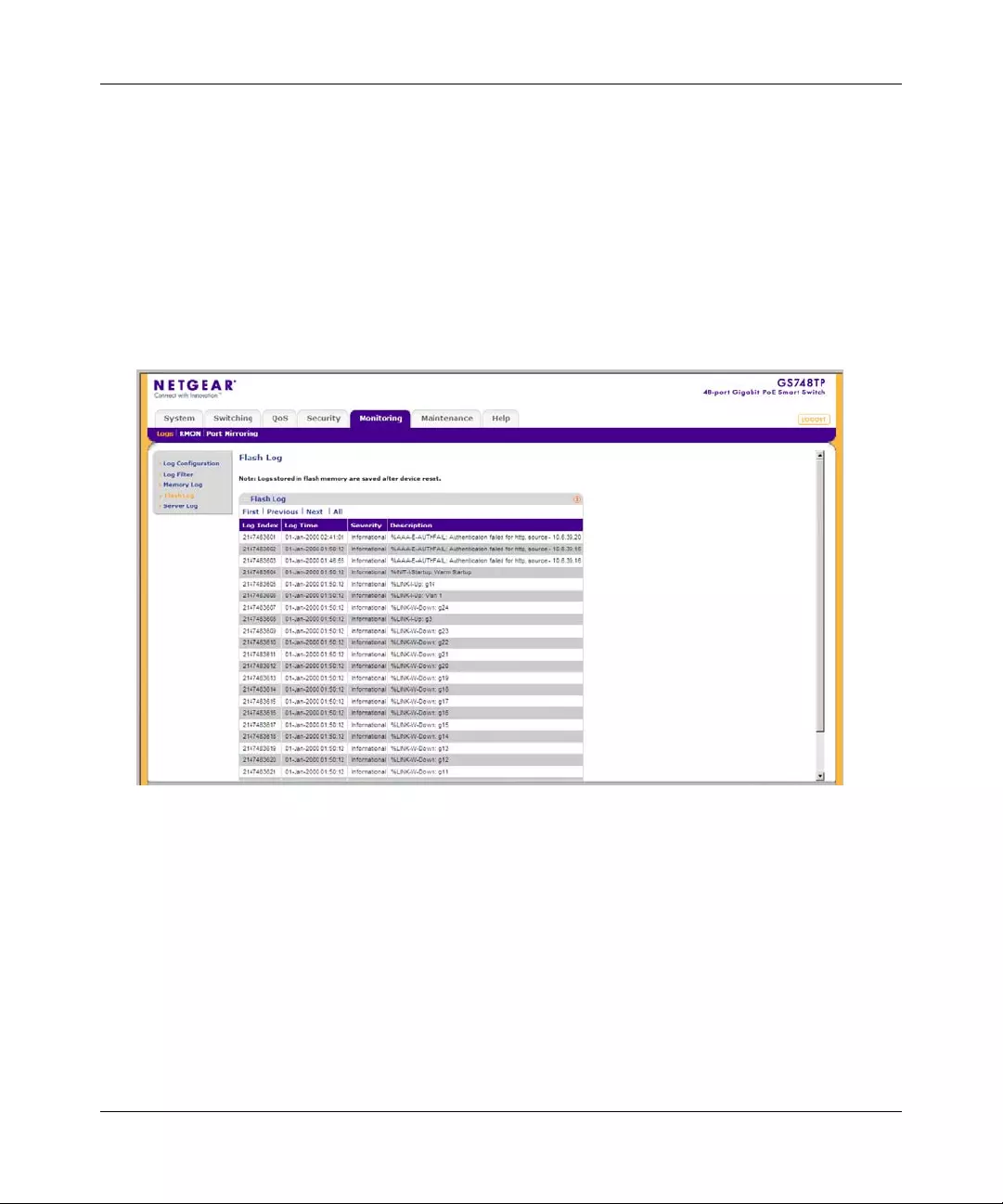
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-6 Monitoring the Switch
v1.0, April 2008
2. Click REFRESH or CLEAR LOGS to refresh or reset the Memory Logs screen.
Flash Log
The Flash Log screen contains information about log entries saved to the log file in Flash,
including the time the log was generated, the log severity, and a description of the log message.
The message log is available after reboot.
To view the message logs in Flash:
1. Click Monitoring > Logs > Flash Log. The Flash Log screen displays:
The Flash Log screen contains the following fields:
•Log Index – Displays the log number.
•Log Time – Displays the time at which the log was generated.
•Severity – Displays the log severity and urgency level. The following are the available log
severity levels:
– Emergency – The highest warning level. If the device is down or not functioning
properly, an emergency log message is saved to the specified logging location.
Figure 7-4

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring the Switch 7-7
v1.0, April 2008
– Alert – The second highest warning level. An alert log is saved, if there is a serious
device malfunction; for example, all device features are down.
– Critical – The third highest warning level. A critical log is saved if a critical device
malfunction occurs; for example, two device ports are not functioning, while the rest
of the device ports remain functional.
– Error – A device error has occurred; for example, if a single port is offline.
– Warning – The lowest level of a devi ce warning. The device is functio ning, but an
operational problem has occu rred.
– Notice – Provides device information.
– Informational – Provides device information.
– Debug – Provides debugging messages.
•Description – Displays the log message text.
2. Click REFRESH or CLEAR LOGS to refresh or reset the Flash Logs screen.
Server Log
The Server Log screen contains information for viewing and configuring the remote log servers.
New log servers can be defined and the log severity sent to each server.
To configure remote log servers:
1. Click Monitoring > Logs > Server Log. The Server Log screen displays:
The Server Log screen contains the following fields:
•Server IP – Enter the server’s IP address to which logs can be sent.
•UDP Port – Enter the UDP port to which the server logs are sent. The possible range is 1
- 65535. The default value is 514.
Figure 7-5

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-8 Monitoring the Switch
v1.0, April 2008
•Facility – Select an application from which system logs are sent to the remote server . Only
one facility can be assigned to a single server . If a second facility level is assigned, the first
facility is overridden. All applications defined for a device utilize the same facility on a
server. The field default is Loc al 0. The possible field values are Local 0 - Local 7.
•Description – Enter a user-defined server description.
•Minimum Severity – Select the minimum severity level for which logs are sent to the
server. For example, if Notice is selected, all logs with a severity level of Notice and
higher are sent to the remote server. The default value is Informational. The possible field
values are:
– Emergency – The highest warning level. If the device is down or not functioning
properly, an emergency log message is saved to the specified logging location.
– Alert – The second highest warning level. An alert log is saved, if there is a serious
device malfunction; for example, all device features are down.
– Critical – The third highest warning level. A critical log is saved if a critical device
malfunction occurs; for example, two device ports are not functioning, while the rest
of the device ports remain functional.
– Error – A device error has occurred; for example, if a single port is offline.
– Warning – The lowest level of a devi ce warning. The device is functio ning, but an
operational problem has occu rred.
– Notice – Provides device information.
– Informational – Provides device information.
– Debug – Provides debugging messages.
2. Select the server entry.
3. Enter the Server IP address in the provided field in the first row.
4. Enter the UDP Port number in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the Facility assigned to the server from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. Enter an optional server Description in the provided field in the first row.
7. Select the Minimum Severity level message sent to the server from the list in the provided
field in the first row.
8. Click APPLY to update the device.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring the Switch 7-9
v1.0, April 2008
To add a remote log server:
1. Click Monitoring > Logs > Server Log. The Server Log screen displays.
2. Enter the Server IP address in the provided field in the first row.
3. Enter the UDP Port number in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select the Facility assigned to the server from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Enter an optional server Description in the provided field in the first row.
6. Select the Minimum Severity level message sent to the server from the list in the provided
field in the first row.
7. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a remote log server:
1. Click Monitoring > Logs > Server Log. The Server Log screen displays.
2. Select the log server entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the log server entry.
RMON
This section contains information for viewing Remote Monitoring Statistics. RMON S tatistics
allow network managers to view network traffic information from a single workstation.
The RMON menu contains the following options:
•“Basic”
•“Advanced”
Basic
The RMON Basic menu contains the following options:
•“Statistics”
Statistics
The RMON Basic Stati stics screen contains fields for viewing information about device utilization
and errors that occurred on the device.
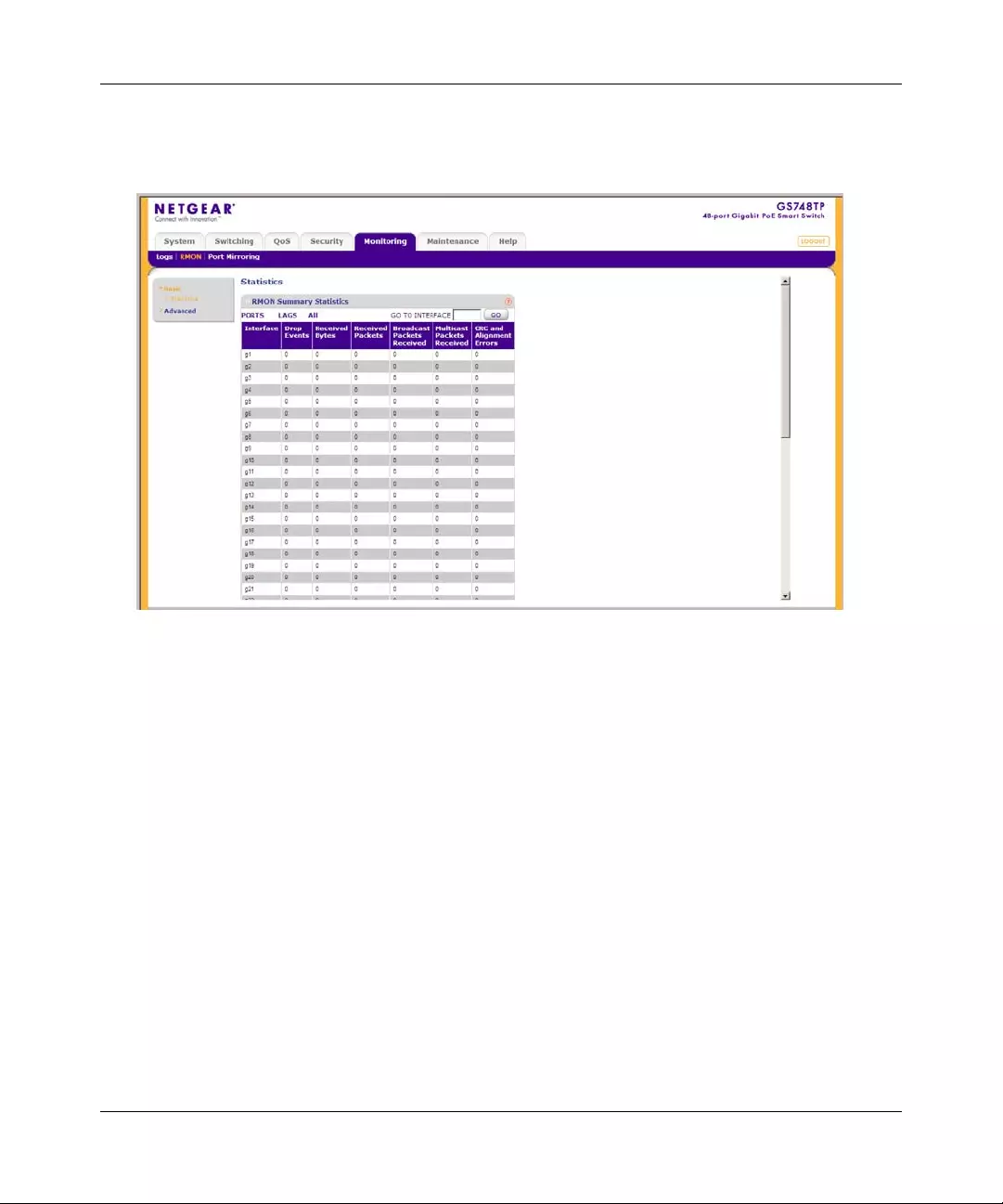
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-10 Monitoring th e Switch
v1.0, April 2008
To view RMON Basic Statistics:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Basic > Statistics. The RMON Basic S tatistics screen displays:
The RMON Basic Statistics screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Displays the port or LAG for which statistics are displayed.
•Drop Events – Displays the number of dropped events that have occurred on the interface
since the device was last refreshed.
•Received By tes – Displays the number of octets recei ved on the interface since the device
was last refreshed. This number includes bad packets and FCS octets, but excludes
framing bits.
•Received Packets – Displays the number of packets received on the interface, including
bad packets, Multicast, and Broadcast packets, since the device was last refreshed.
•Broadcast Packets Received – Displays the number of good broadcast packets received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed. This number does not include
Multicast packets.
•Multicast Packets Received – Displays the number of good Multicast packets received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
Figure 7-6

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring th e Switch 7-11
v1.0, April 2008
•CRC & Alignment Errors – Displays the number of CRC and Align errors that have
occurred on the interface since the device was last refres hed.
2. Click REFRESH or CLEAR ALL COUNTERS to refresh or reset the RMON Basic
Statistics screen.
Advanced
The RMON Advanced menu contains the following options:
•“Statistics”
•“History Control”
•“History Table”
•“Events Control”
•“Events Log”
•“Alarms”
Statistics
The RMON Advanced Statistics screen contains fields for viewing information about device
utilization and errors that occurred on the device.
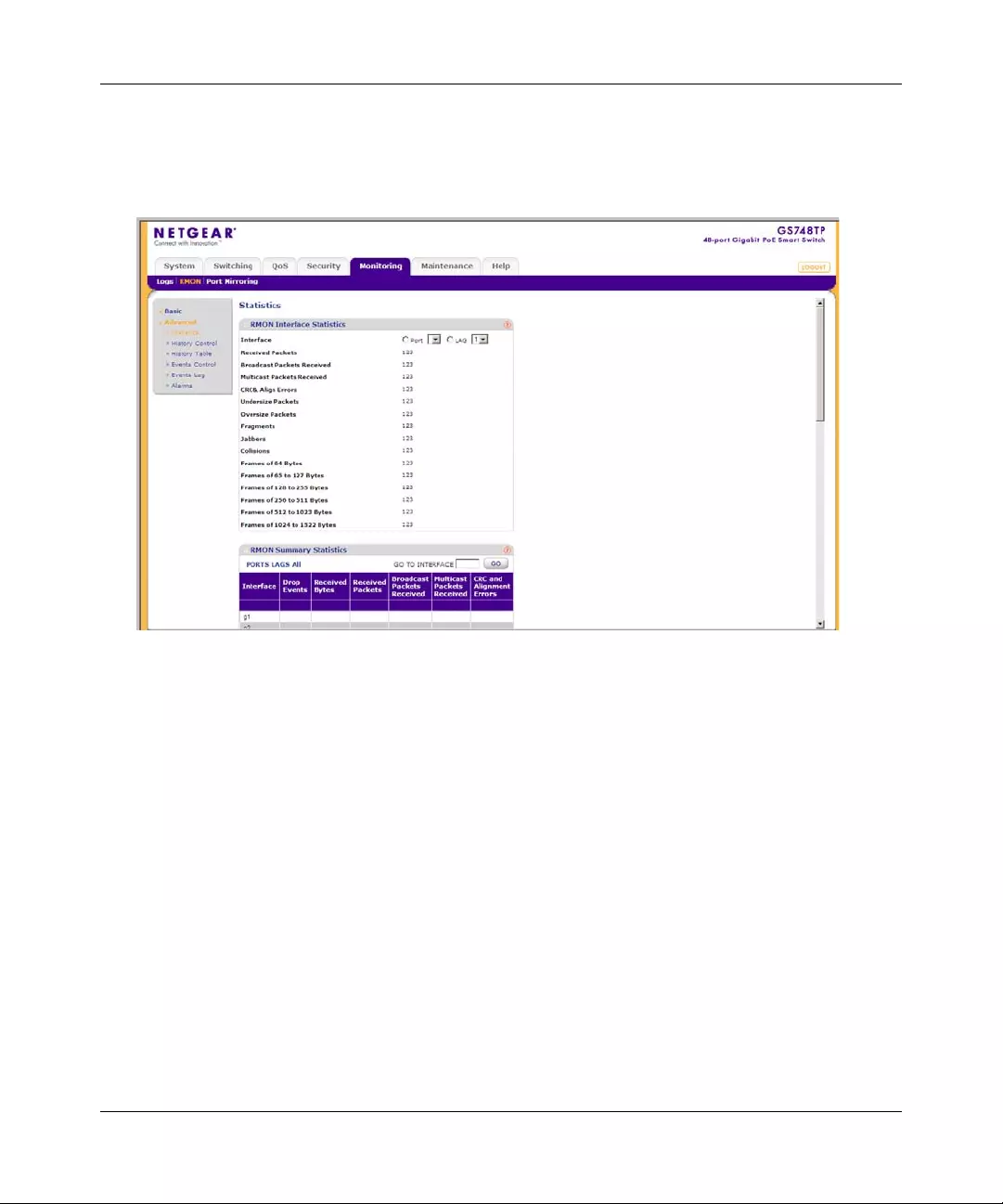
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-12 Monitoring th e Switch
v1.0, April 2008
To view RMON Advanced Statistics:
1. Click Monitoring >RMON > Advanced > Statistics. The RMON Advanced Statistics screen
displays:
The RMON Advanced Statistics screen contains the following fields:
RMON Interface Statistics
•Interface – Select the device for which statistics are displayed. The possible field values
are:
– Port – Select the specific port for which RMON statistics are displayed.
– LAG – Select the specific LAG for which RMON statistics are displayed.
•Received By tes – Displays the number of octets recei ved on the interface since the device
was last refreshed. This number includes bad packets and FCS octets, but excludes
framing bits.
•Broadcast Packets Received – Displays the number of good broadcast packets received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed. This number does not include
Multicast packets.
Figure 7-7

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring th e Switch 7-13
v1.0, April 2008
•Multicast Packets Received – Displays the number of good Multicast packets received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•CRC & Align Errors – Disp lays the number of CRC and Align errors that have occurred
on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•Undersize Packets – Displays the number of undersized packets (less than 64 octets)
received on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•Oversize Packets – Displays the number of oversized packets (over 1518 octets) received
on the interface since the device was last re freshed.
•Fragments – Displays the number of fragments (packets with less than 64 octets,
excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) received on the interface since the
device was last refreshed.
•Jabbers – Displays the total number of received packets that were longer than 1518
octets. This number excludes frame bits, but includes FCS octets that had either a bad
Frame Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS
with a non-integral octet (Alignment Error) number. The field range to detect jabbers is
between 20 ms and 150 ms.
•Collisions – Displays the number of collisions received on the interface since the device
was last refreshed.
•Frames of 64 Bytes – Displays the number of 64-byte frames received on the interface
since the device was last refreshed.
•Frames of 65 to 127 Bytes – Displays the number of 65 to 127 byte frames received on
the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•Frames of 128 to 255 Bytes – Displays the number of 128 to 2 55 byte frames received on
the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•Frames of 256 to 511 Bytes – Display s the number of 25 6 to 511 byte frames received on
the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•Frames of 512 to 1023 Bytes – Displays the numb er of 512 to 1023 byte frames received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•Frames of 1024 to 1522 Bytes – Displays the number of 1024 to 1522 byte frames
received on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
RMON Summary Statistics
•Interface – Displays the port or LAG for which statistics are displayed.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-14 Monitoring th e Switch
v1.0, April 2008
•Drop Events – Displays the number of dropped events that have occurred on the interface
since the device was last refreshed.
•Received By tes – Displays the number of octets recei ved on the interface since the device
was last refreshed. This number includes bad packets and FCS octets, but excludes
framing bits.
•Received Packets – Displays the number of packets received on the interface, including
bad packets, Multicast, and Broadcast packets, since the device was last refreshed.
•Broadcast Packets Received – Displays the number of good broadcast packets received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed. This number does not include
Multicast packets.
•Multicast Packets Received – Displays the number of good Multicast packets received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•CRC & Alignment Errors – Displays the number of CRC and Align errors that have
occurred on the interface since the device was last refres hed.
2. To view RMON Interface Statistics, select Port or LAG as the type of Interface and select the
interface from the list in the provided field. The RMON Interface Statistics for the selected
interface are displayed.
3. To view RMON Summary Statistics, select the interface and click GO.
To refresh or clear the RMON Advanced Statistics screen:
1. Open the RMON Advanced Statistics screen.
2. Click REFRESH or CLEAR ALL COUNTERS to clear or reset the RMON Advanced
Statistics screen.
History Control
The RMON History Control screen contains information abou t samples of data taken from ports.
For example, the samples may include interface definitions or polling periods.
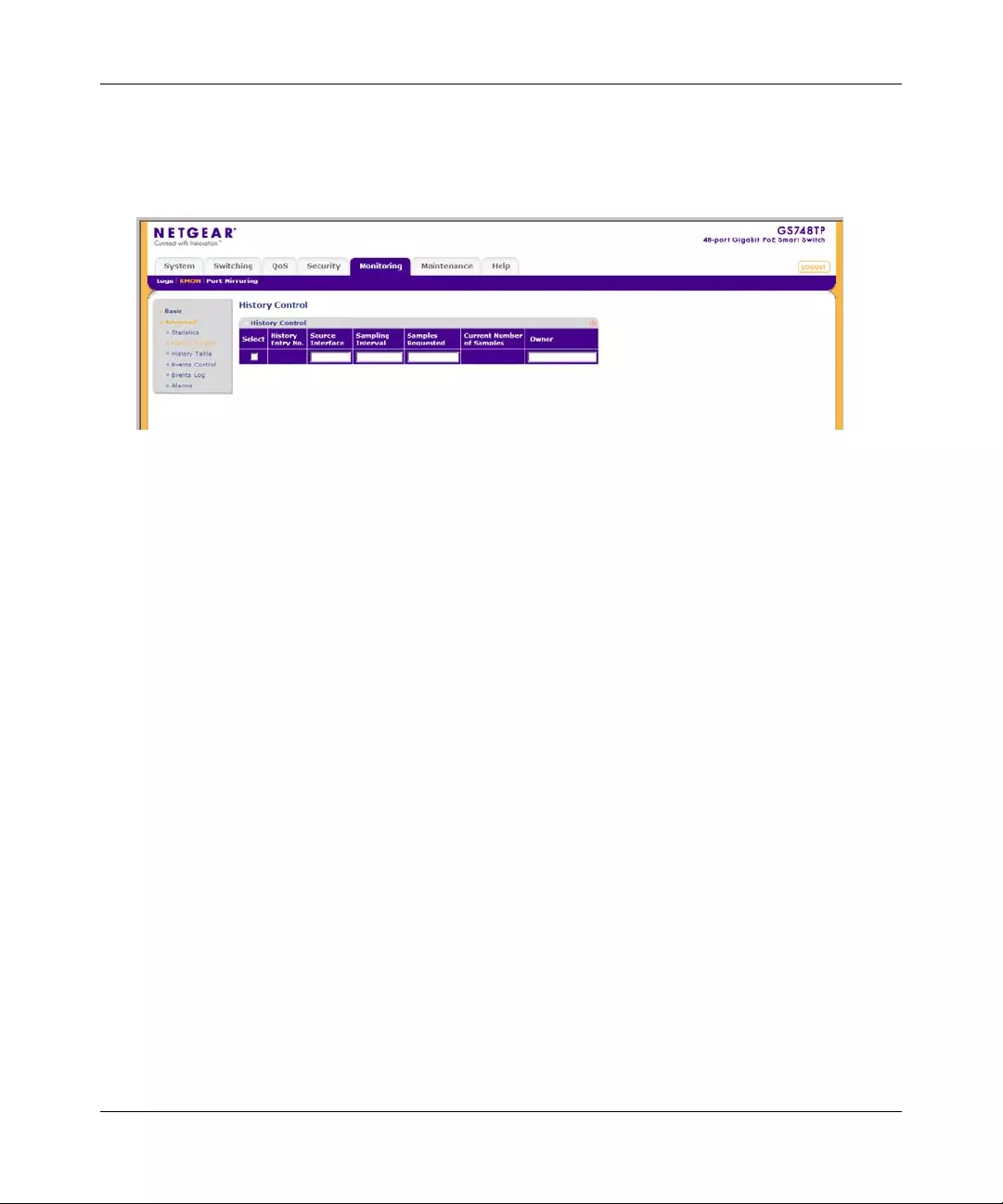
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring th e Switch 7-15
v1.0, April 2008
To configure RMON history information:
1. Click Monitoring >RMON > Advan ced > History Control. The RMON History Control
screen displays:
The RMON History Control screen contains the following fields:
•History Entry No. – Displays the entry number for the History Control Table screen.
•Source Interface – Enter the interface from which the history samples were taken.
•Sampling Interval – Enter in seconds the time that samples are taken from the ports. The
field range is 1-3600. The default is 1800 seconds (equal to 30 minutes).
•Samples Requested – Enter the number of samples to be saved. The field range is
1-65535. The default value is 50.
•Current Number of Samples – Displays the current number of samples taken.
•Owner – Enter the RMON station or user that requested the RMON information.
2. Select the history control entry.
3. Enter the Source In terface , Sampling Interval , Samples Requested and Owner in the
provided field in the first row.
4. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a history control entry:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > History Control. The RM ON His to r y Contro l
screen displays.
2. Enter the Source In terface , Sampling Interval , Samples Requested and Owner in the
provided field in the first row.
3. Click ADD to update the device.
Figure 7-8
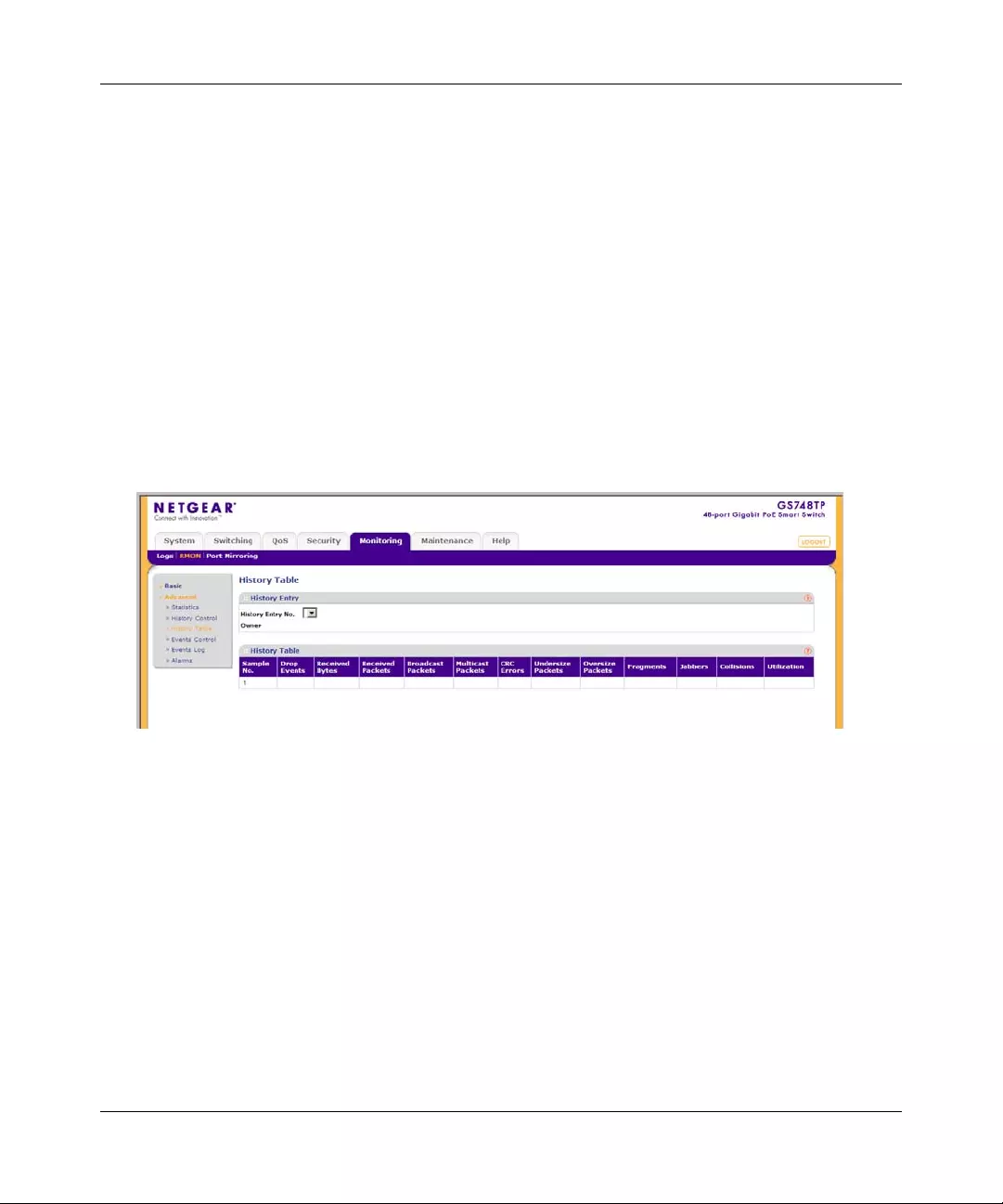
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-16 Monitoring th e Switch
v1.0, April 2008
To remove a history control entry:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > History Control. The RM ON His to r y Contro l
screen displays.
2. Select the history control entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the history control entry.
History Table
The RMON History Table screen contains interface specific statistical network samples. Each
table entry represents all counter values compiled during a single sample.
To view the RMON History Table:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > History Table. The RMON History Table screen
displays:
The RMON History Table screen contains the following fields:
History Entry
•History Entry No. – Select the entry number for the History Control Table screen.
•Owner – Displays the RMON station or user that requested the RMON information. The
field range is 0-20 characters.
History Table
•Sample No. – Displays the sample number from which the statistics were taken.
•Drop Events – Displays the number of drop ped events that have occurred on the interface
since the device was last refreshed.
Figure 7-9

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring th e Switch 7-17
v1.0, April 2008
•Received By tes – Displays the number of octets recei ved on the interface since the device
was last refreshed. This number includes bad packets and FCS octets, but excludes
framing bits.
•Received Packets – Displays the number of packets received on the interface since the
device was last refreshed, including bad packets, Multicast, and Broadcast packets.
•Broadcast Packets – Displays the number of good Broadcast packets received on the
interface since the device was last refreshe d. This number does not include Multicast
packets.
•Multicast Packets – Displays the number of good Multicast packets received on the
interface since the device was last refreshe d.
•CRC Errors – Displays the number of CRC and Align errors that have occurred on the
interface since the device was last refreshe d.
•Undersize Packets – Displays the number of undersized packets (less than 64 octets)
received on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•Oversize Packets – Displays the number of oversized packets (over 1518 octets) received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
•Fragments – Displays the number of fragments (packets with less than 64 octets,
excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) received on the interface since the
device was last refreshed.
•Jabbers – Displays the total number of received packets that were longer than 1518
octets. This number excludes frame bits, but includes FCS octets that had either a bad
Frame Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS
with a non-integral octet (Alignment Error) number. The field range to detect jabbers is
between 20 ms and 150 ms.
•Collisions – Displays the number of collisions received on the interface since the device
was last refreshed.
•Utilization – Displays the percentage of the interface utilized.
2. Select the History Entry No. from the list in the provided field. The statistics are displayed.
3. To refresh the RMON History Table screen, click REFRESH.
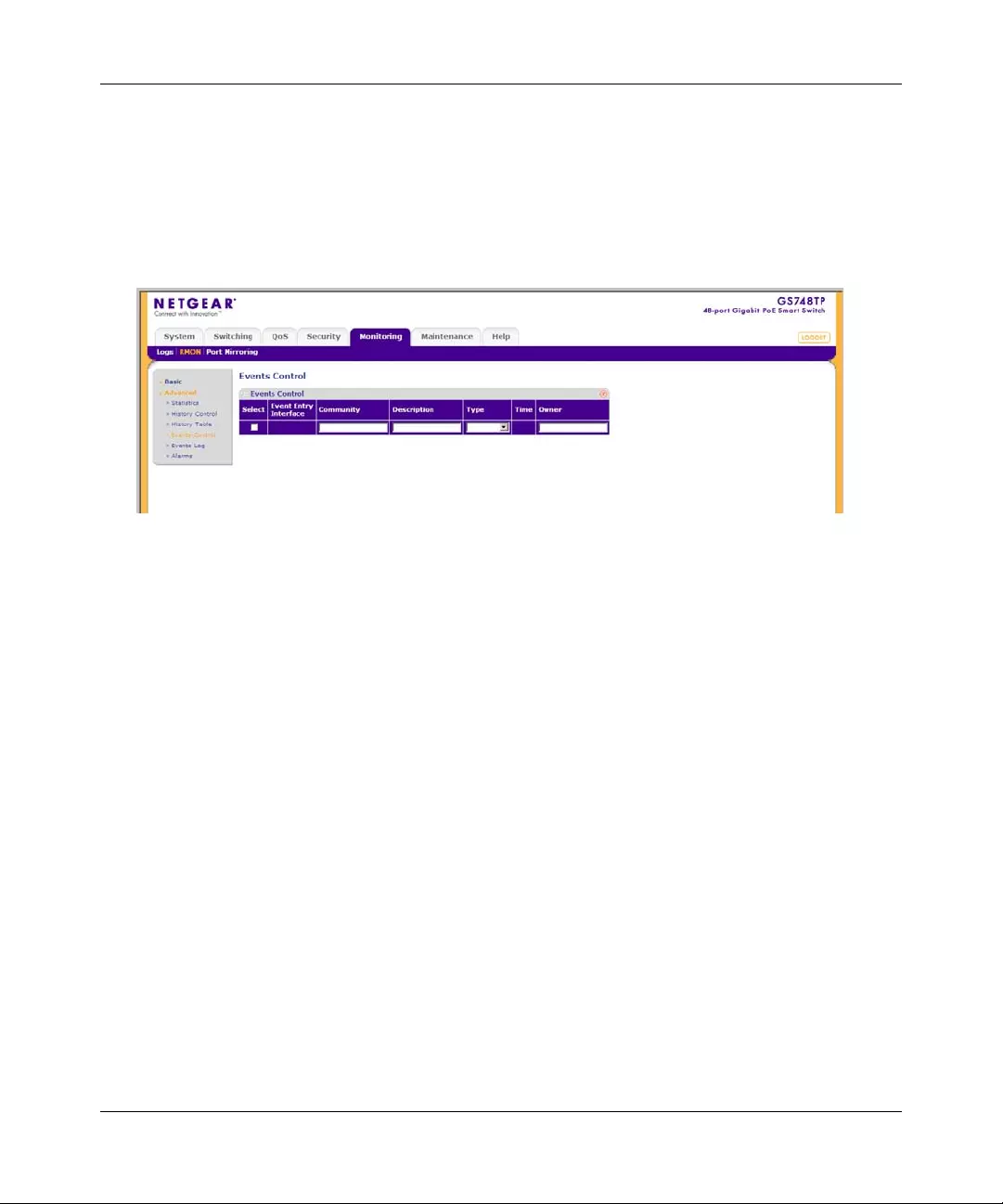
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-18 Monitoring th e Switch
v1.0, April 2008
Events Control
The RMON Events Control screen contains fields for defining RMON events.
To configure RMON events control:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > Events Control. The RMON Events Control
screen displays:
The RMON Events Control screen contains the following fields:
•Event Entry Interface – Displays the event.
•Community – Enter the community to which the event belongs.
•Description – Enter the user-defined event description.
•Type – Select the event type. Possible values are:
– None – No event has occurred.
– Log – The event is a log entry.
– Trap – The event is a trap.
– Log & Trap – The event is both a log entry an d a trap.
•Time – Displays the time that the event occurred.
•Owner – Enter the device or user that defined the event.
2. Select the events control entry.
3. Enter the Community, Description and Owner in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select the event Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
Figure 7-10

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring th e Switch 7-19
v1.0, April 2008
To add an events control entry:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > Events Control. The RMON Events Control
screen displays.
2. Enter the Community, Description and Owner in the provided field in the first row.
3. Select the event Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove an events control entry:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > Events Control. The RMON Events Control
screen displays.
2. Select the events control entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the events control entry.
Events Log
The RMON Events Log screen contains a list of RMON events.
To view RMON events logs:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > Events Log. The RMON Events Log screen
displays
The RMON Events Log screen contains the following fields:
•Event – Displays the RMON Events.
•Log Number– Displays the log number.
•Log Time – Displays the time when the log entry was entered.
Figure 7-11
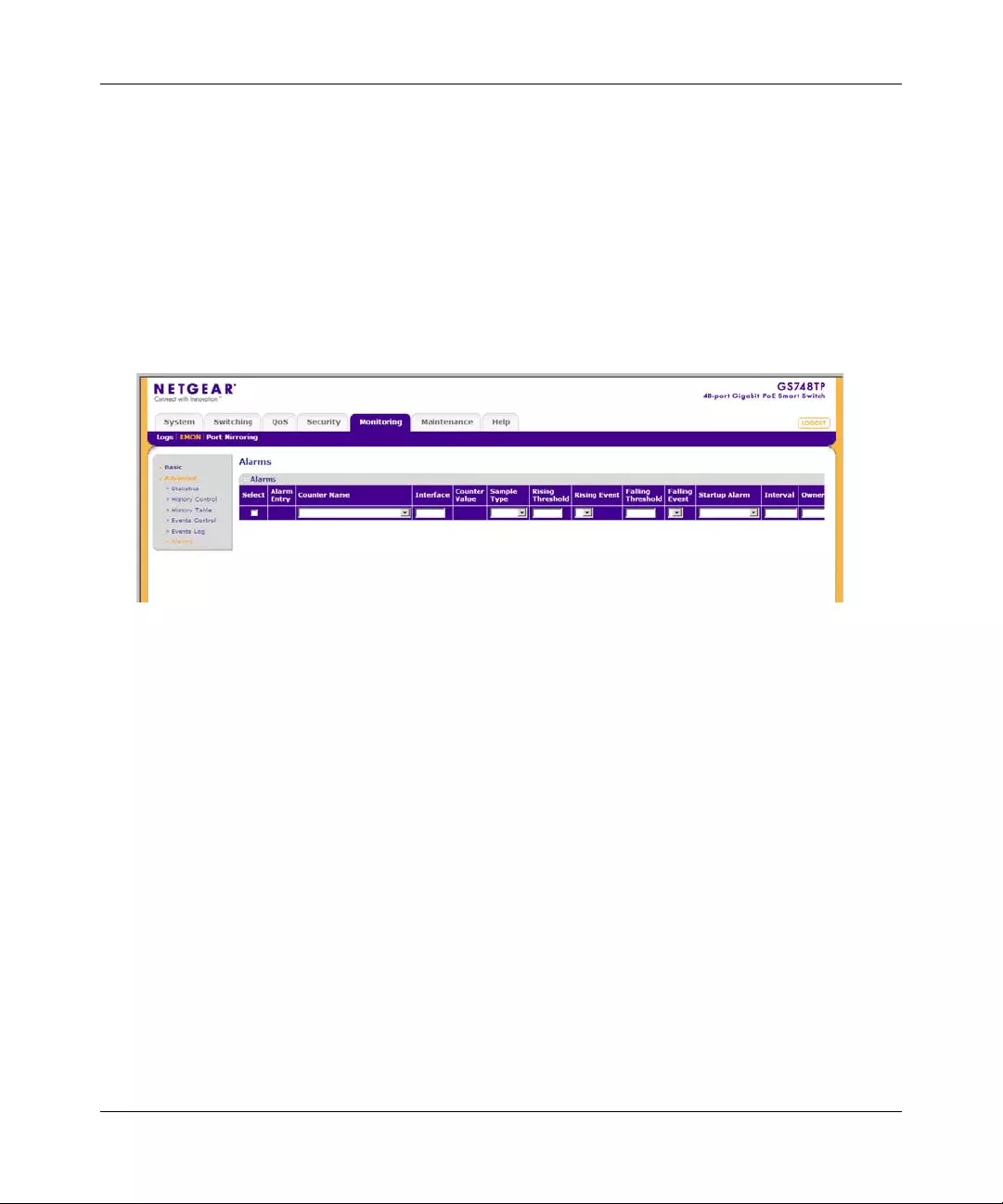
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-20 Monitoring th e Switch
v1.0, April 2008
•Description – Displays the log entry description.
2. To refresh the RMON Events Log screen, click REFRESH.
Alarms
The RMON Alarms screen contains fields for setting network alarms. Network alarms occur when
a network problem or event, is detected. Rising and falling thresholds generate events.
To set RMON alarms:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > Alarms. The RMON Alarms screen displays:
The RMON Alarms screen contains the following fields:
•Alarm Entry – Displays the alarm entry.
•Counter Name – Select the MIB variable.
•Interface – Enter the port or LAG interface.
•Counter Value – Displa ys the selected MIB variable value.
•Sample Type – Select the sampling method for the selected variable and comparing the
value against the thresholds. The possible field values are:
– Absolute – Compares the values directly with the thresholds at the end of the sampling
interval.
– Delta – Subtracts the last sampled value from the current value. The difference in the
values is compared to the threshold.
•Rising Threshold – Enter the rising counter value that triggers the rising threshold alar m.
The rising threshold is presented on top of the graph bars. Each monitored variable is
designated a color.
Figure 7-12

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring th e Switch 7-21
v1.0, April 2008
•Rising Event – Enter the event number by which rising alarms are reported.
•Falling Threshold – Enter the falling counter value that triggers the falling threshold
alarm. The falling threshold is graphically presented on top of the graph bars. Each
monitored variable is designated a color.
•Falling Event – Enter the event number by which falling alarms are reported.
•Startup Alarm – Select the trigger that activates the alarm generation. Rising is defined
by crossing the threshold from a low-value threshold to a higher-value threshold. The
possible field values are:
– Rising Alarm – The alarm is triggered by the rising counter crossing the rising
threshold value.
– Falling Alarm – The alarm is triggered by the falling counter crossing the falling
threshold value.
– Rising and Falling – The alarm is triggered by either the rising counter crossing the
rising threshold value or the falling counter crossing the falling threshold value.
•Interval – Enter the alarm interval time in seconds.
•Owner – Enter the device or user that defined the alarm.
2. Select the alarm entry.
3. Select the Counter Name from the list of MIB variable values in the provided field in the first
row.
4. Enter the Interface in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the Sample Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. Select the Startup Alarm from the list in the provided field in the first row.
7. If you selected Rising Alarm or Rising and Falling as the Startup Alarm, enter th e Rising
Threshold and select the Rising Event number in the provided fields in the first row.
8. If you selected Falling Alarm or Rising and Falling as the Startup Alarm, enter the Falling
Threshold and select the Falling Event number in the provided fields in the first row.
9. Enter the Interval and Owner in the provided fields in the first row.
10. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add an alarm entry:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > Alarms. The RMON Alarms screen displays.

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-22 Monitoring th e Switch
v1.0, April 2008
2. Select the Counter Name from the list of MIB variable values in the provided field in the first
row.
3. Enter the Interface in the provided field in the first row.
4. Select the Sample Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Select the Startup Alarm from the list in the provided field in the first row.
6. If you selected Rising Alarm or Rising and Falling as the Startup Alarm, enter th e Rising
Threshold and select the Rising Event number in the provided fields in the first row.
7. If you selected Falling Alarm or Rising and Falling as the Startup Alarm, enter the Falling
Threshold and select the Falling Event number in the provided fields in the first row.
8. Enter the Interval and Owner in the provided fields in the first row.
9. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove an events control entry:
1. Click Monitoring > RMON > Advanced > Alarms. The RMON Alarms screen displays.
2. Select the alarm entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the alarm entry.
Port Mirroring
Port mirroring monitors and mirrors network traffic by forwarding copies of incoming and
outgoing packe ts from one port to a monitoring po rt. Port mirroring can be used as a diagnos t ic
tool as well as a debugging feature. Port mirroring also enables switch performance monitoring.
Network administrators can configure port mirroring by selecting a specific port from which to
copy all packets, and other ports to which the packets are copied. The device supports one
destination port and up to eight source ports.
The Port Mirroring menu contains the following option:
•“Port Mirroring”
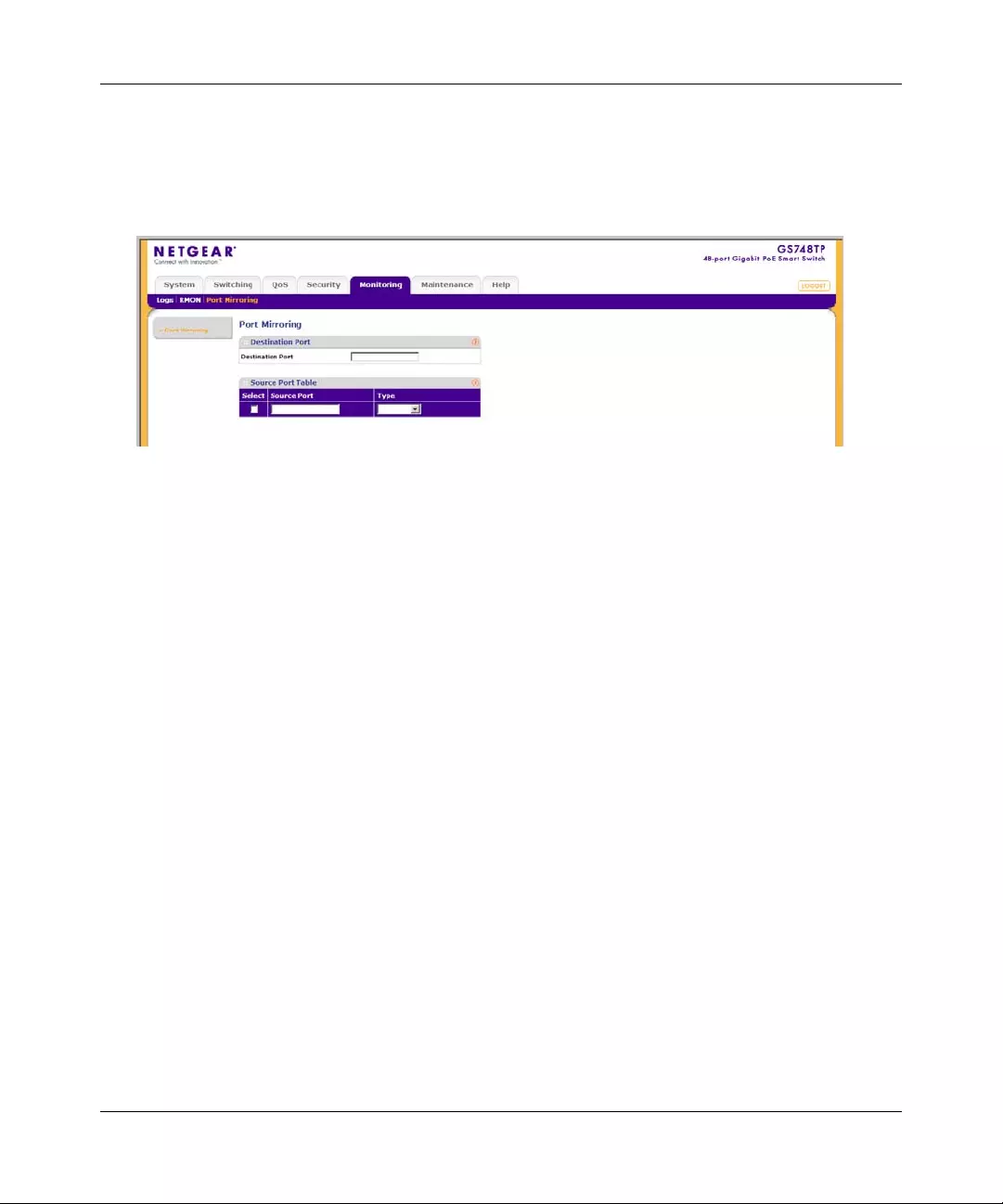
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Monitoring th e Switch 7-23
v1.0, April 2008
Port Mirroring
To define port mirroring:
1. Click Monitoring > Port Mirroring > Port Mirroring. The Port Mirroring screen displays:
The Port Mirroring screen contains the following fields:
Destination Port
•Destination Port – Enter the port to which port traffic is copied.
Source Port Table
•Source Port – Enter the port from which the packets are mirrored.
•Type – Select the port mode configuration for port mirroring. The possible field values
are:
– TX Only – Port mirroring is configured on transmitting ports only.
– RX Only – Port mirroring is configured on receiving ports only.
– TX and RX – Port mirroring is configured on both receiving and transmitting ports.
This is the default value.
2. Enter the Destination Port in the provided field.
3. Select the source port entry.
4. Select the port mirroring Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
5. Click APPLY to update the device.
To add a source port entry:
1. Click Monitoring > Port Mirroring > Port Mirroring. The Port Mirroring screen displays.
Figure 7-13

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
7-24 Monitoring th e Switch
v1.0, April 2008
2. Enter the Source Port in the provided field in the first row.
3. Select the port mirroring Type from the list in the provided field in the first row.
4. Click ADD to update the device.
To remove a source port entry:
1. Click Monitoring > Port Mirroring > Port Mirroring. The Port Mirroring screen displays.
2. Select the source port entry.
3. Click DELETE to remove the source port entry.

8-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 8
Maintenance
Using the Maintenance Options
The navigation pane at the top of the web browser interface contains a Maintenance tab that
enables you to manage your GS70 0TP Smart Switch with features un der the following main menu
options:
•“Reset”
•“Upload”
•“Download”
•“File Management”
•“Troubleshooting”
The description that follows in this chapter describes configuring and managing maintenance
options in the GS700TP Smart Switch.
Reset
The Reset menu contains the following options:
•“Device Re b oot”
•“Factory Default”
Device Reboot
The Device Rebo ot screen resets the device.
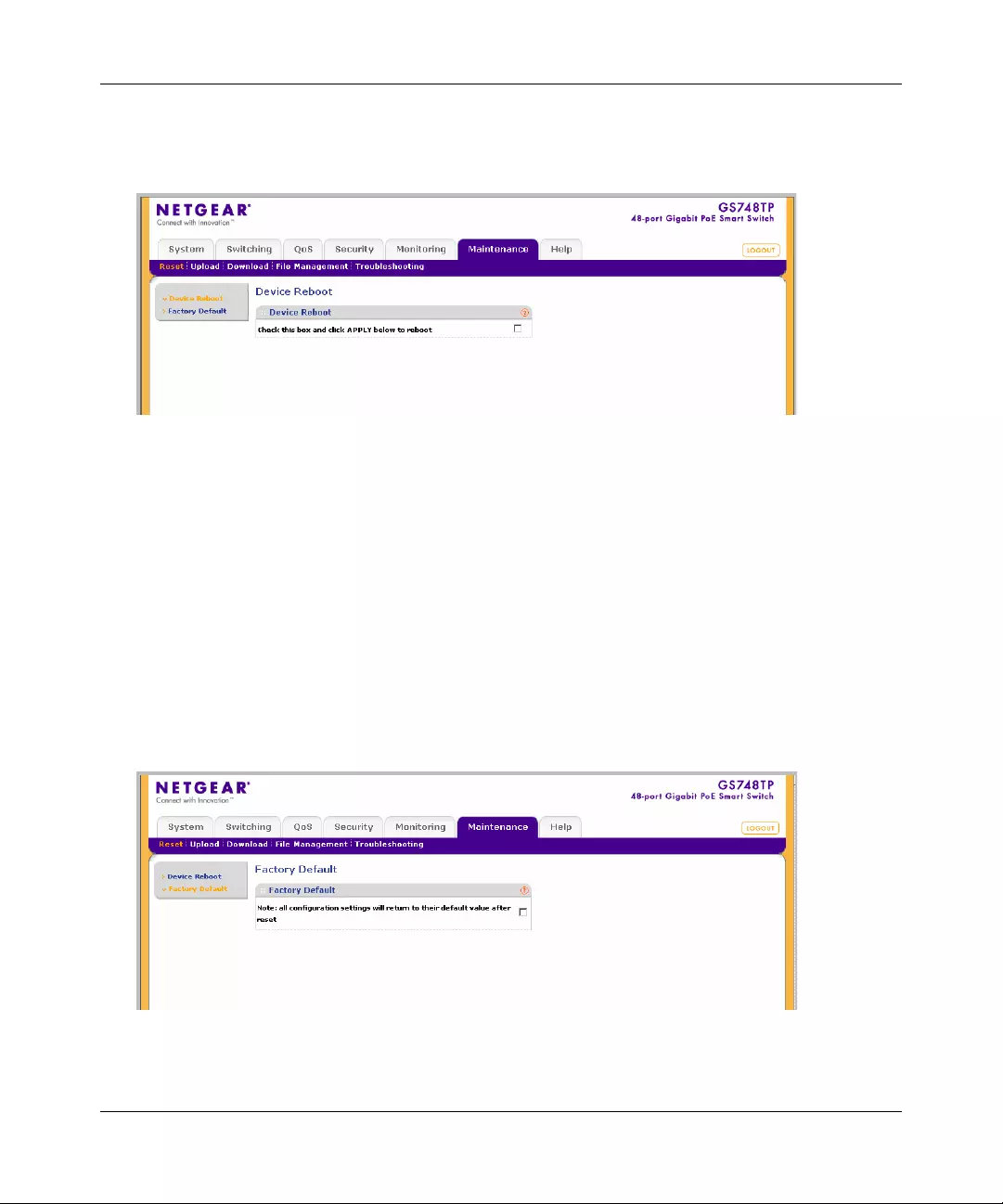
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
8-2 Maintenance
v1.0, April 2008
To reset the device:
1. Click Maintenance > Reset > Device Reboot. The Device Reboot screen displays:
2. Check the confirmation box.
3. Click APPLY to reboot the device.
Factory Default
The Factory Default sc re en allows network managers to reset the device to the factory defaults
shipped with the switch. Restoring factory defaults results in erasing the configuration file.
Note: Selecting this option automatically reboots the device.
To reset the device to the factory defaults:
1. Click Maintenance > Reset > Factory Default. The Factory Default screen displays:
Figure 8-1
Figure 8-2
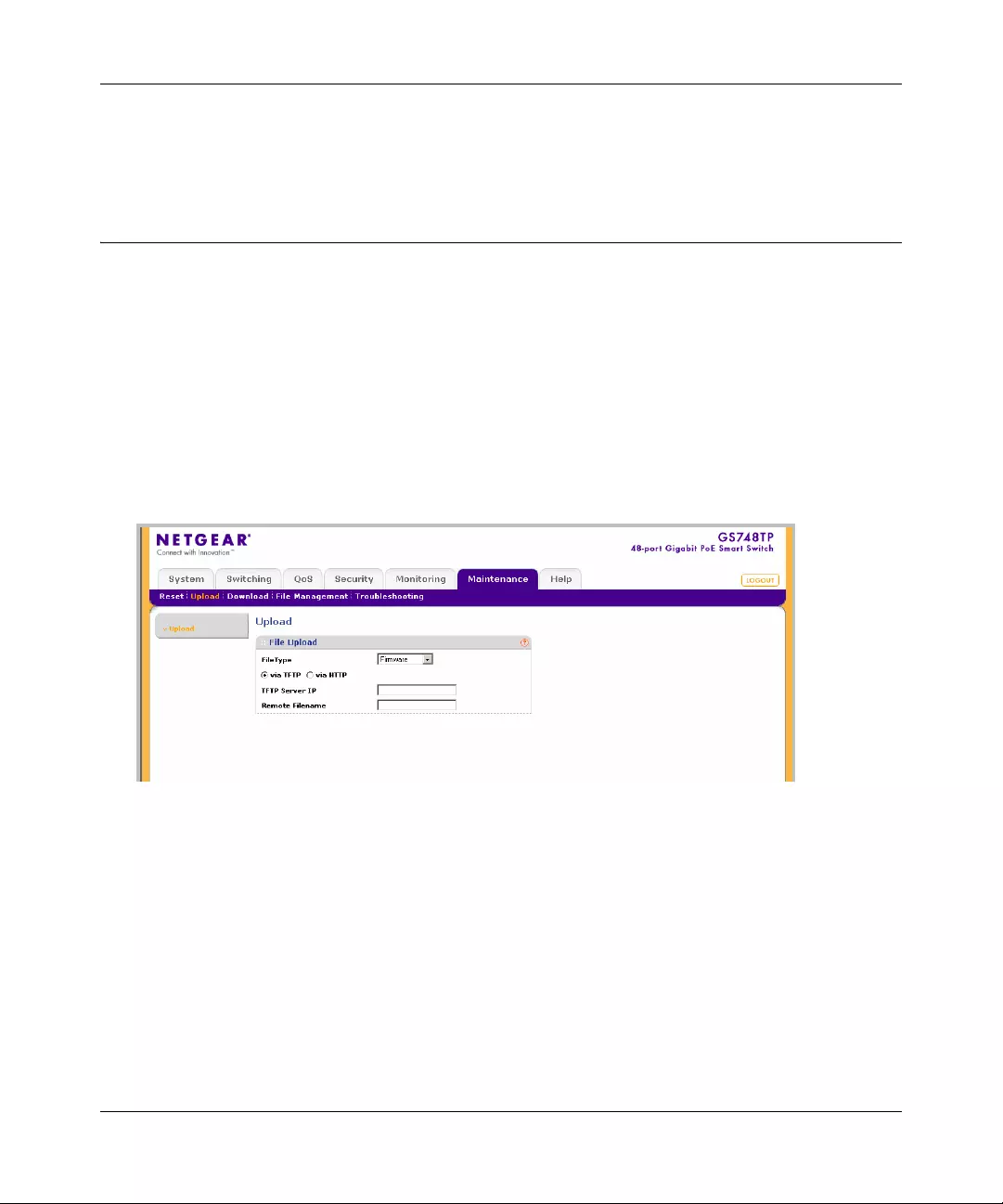
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Maintenance 8-3
v1.0, April 2008
2. Check the confirmation box.
3. Click APPLY to reset the device to the factory defaults.
Upload
The Upload menu contains the following option:
•“Upload”
Upload
System Files can be backed up using the Upload screen.
To back up files:
1. Click Maintenance > Upload. The Upload screen displays:
The Upload screen contains the following fields:
•File Type – Enter the type of file to be uploaded. The poss ib le field values are:
– Firmware – Upload the Firmware File.
– Configuration – Upload the Configuration File.
•via TFTP – Select to upload the Firmware or Configuration File to the TFTP Server.
•via HTTP – Select to upload the Configuration File via the web browser interface
(HTTP).
Figure 8-3
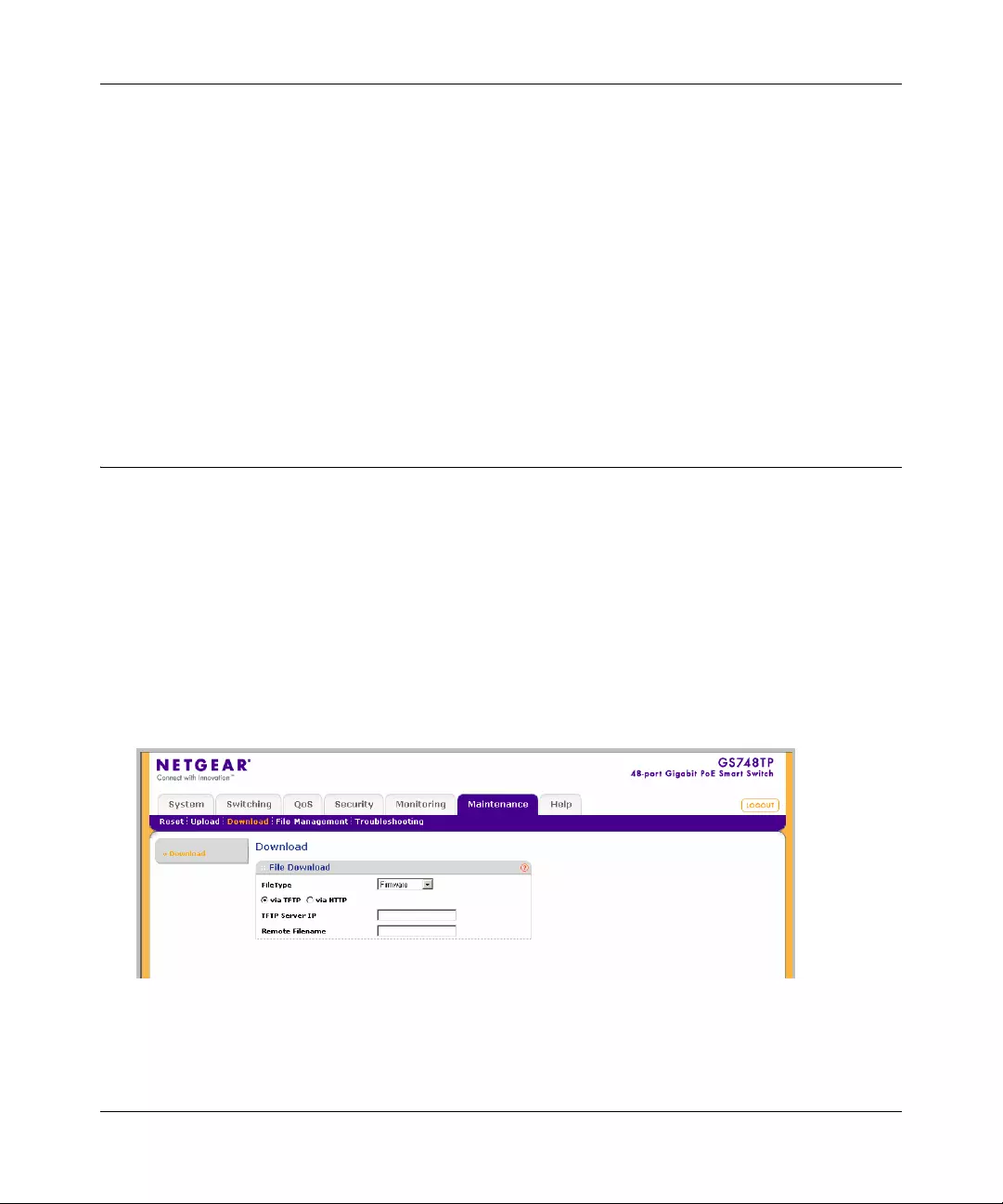
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
8-4 Maintenance
v1.0, April 2008
•TFTP Server IP – Enter the TFTP Server IP Address to which the Firmware or
Configuration file is uploaded.
•Remote Filename – Enter the name of the destination file on the TFTP server.
2. Select Firmware or Configuration as the upload File Type from the provided field.
3. Select whether to upload via TFTP or via HTTP. If you selected the Firmware File to upload,
you must select via TFTP.
4. If you selected via TFTP, enter the TFTP Server IP address in the provided field.
5. If you selected via TFTP, enter the Remote Filename in the provided field.
6. Click APPLY to upload the file.
Download
The Download menu contains the following option:
•“Download”
Download
System files can be downloaded using the Download screen.
To download system files:
1. Click Maintenance > Download. The Download screen displays:
The Download screen contains the following fields:
Figure 8-4

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Maintenance 8-5
v1.0, April 2008
•File Type – Enter the file type to be downloaded. The possible field values are:
– Firmware – Download the Firmware file.
– Boot File – Download the Boot file.
– Configuration – Download the Configuration file.
•via TFTP – Select to download the file from the TFTP Server.
•via HTTP – Select to download the file via the web browser interface (HTTP) and enter
the file name in the provided box.
•TFTP Server IP – Enter the TFTP Server IP Address from which the Firmware, Boot or
Configuration file is downloaded.
•Remote Filename – Enter the destination file name to be downloaded.
2. Select Firmware, Boot File or Configuration as the download File Type from the provided
field.
3. Select whether to download via TFTP or via HTTP.
4. If you selected via HTTP, enter the file name in the provided box.
5. If you selected via TFTP, enter the TFTP Server IP address in the provided field.
6. If you selected via TFTP, enter the Remote Filename in the provided field.
7. Click APPLY to download the file. You must reboot the device for the downloaded file
settings to take effect. See “Device Reboot” for detailed instructions on rebooting the device.
File Management
The File Management menu contains the following option:
•“Active Image”
Active Image
The Active Image screen enables the user to select which image will be set as active after the next
reset.
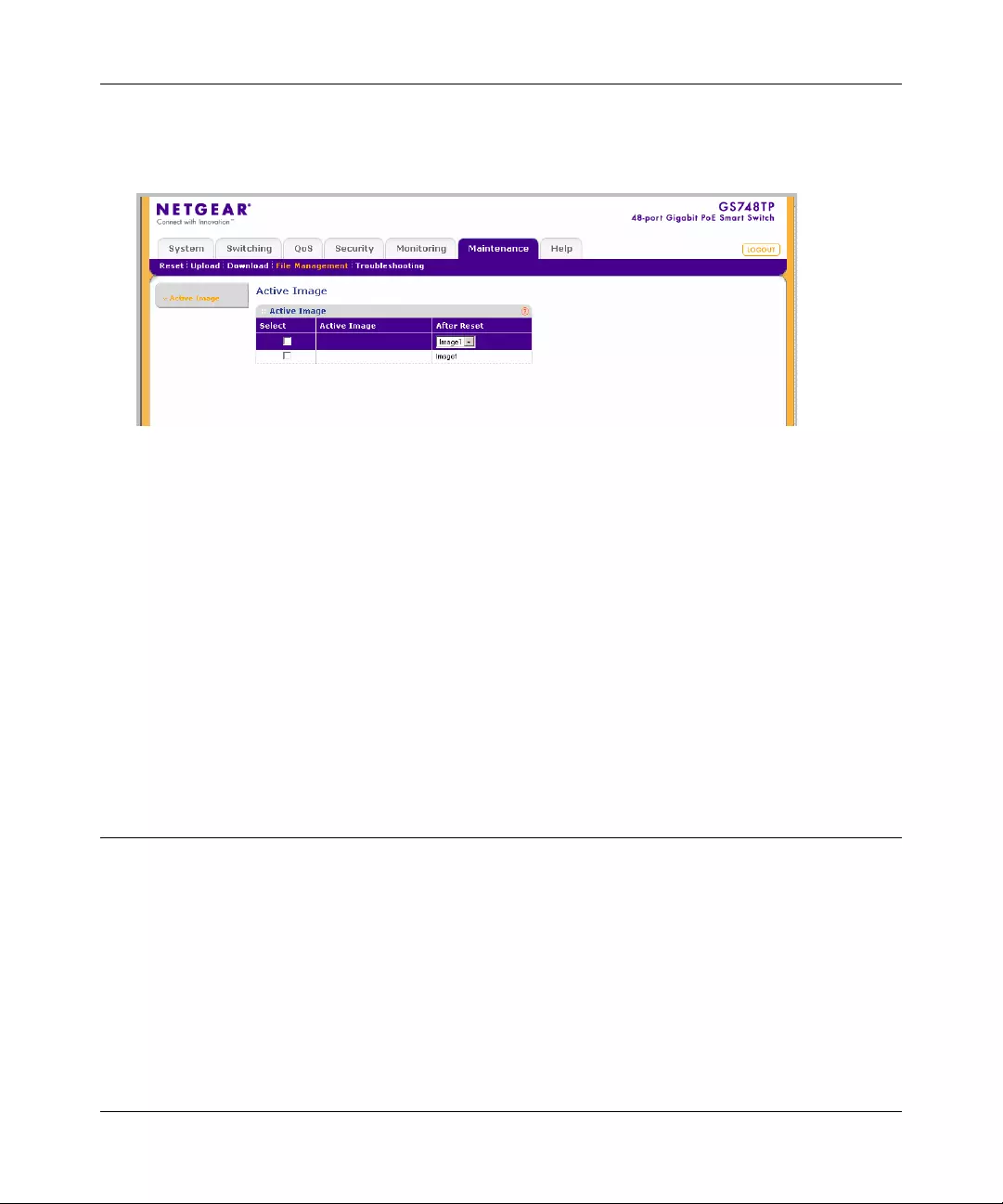
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
8-6 Maintenance
v1.0, April 2008
To define the active image:
1. Click Maintenance > File Mana gement > Activ e Image. The Active Image screen displays:
The Active Image screen contains the following fields:
•Active Image – Displays the image file which is currently active on the unit.
•After Reset – Select the image file that is active after the specific unit is reset. The
possible field values are:
– Image 1 – Activate Image file 1 after the device is reset.
– Image 2 – Activate Image file 2 after the device is reset.
2. Select the image file to be active in the After Reset provided field in the first row.
3. Click APPLY to update the device. You must reset the device for the active image setting to
take effect. See “Reset” for detailed instructions on resetting the device.
Troubleshooting
The Troubleshooting menu contains the following option:
•“Diagnostics”
Diagnostics
The Diagnostics menu contains the following option:
•“Cable Test”
Figure 8-5
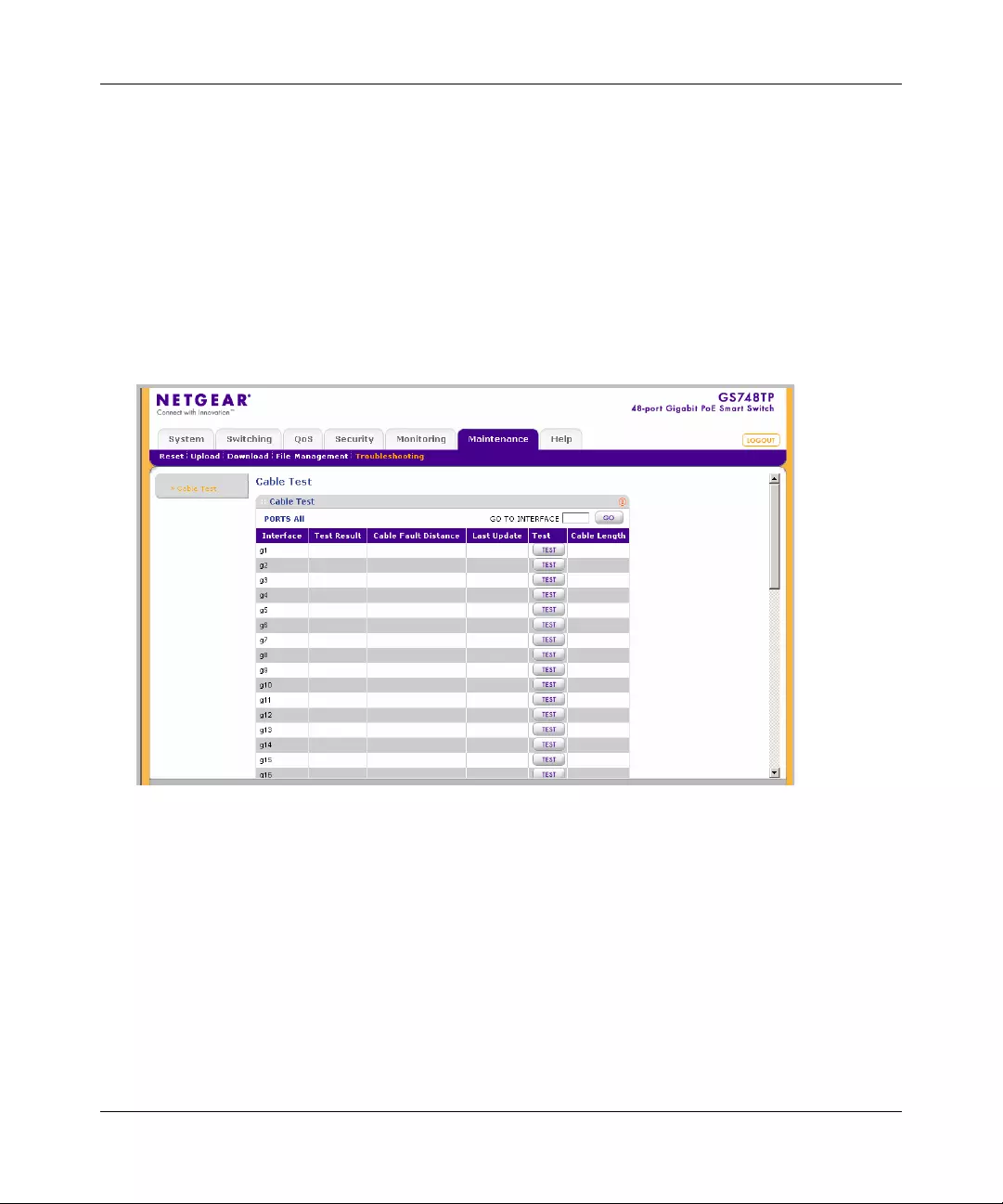
GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Maintenance 8-7
v1.0, April 2008
Cable Test
The Cable Test screen contains fields for performing tests on copper cables. Cable testing provides
information about where errors occurred in the cable, the last time a cable test was performed, and
the type of cable error that occurred. The tests use Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) technology
to test the quality and characteristics of a copper cable attached to a port. Cables up to 120 meters
long can be tested. Cables are tested when the ports are in the down state, with the exception of the
Approximated Cable Length test.
To test cables:
1. Click Maintenance > Troubleshooti ng > Cable Test. The Cable Test screen displays:
The Cable Test screen contains the following fields:
•Interface – Enter the port to which the cable is connected.
•Test Result – Displays the cable test results. Possible values are:
– No Cable – A cable is not connected to the port.
– Open Cable – A cable is connected on only one side.
– Short Cable – A short has occurred in the cable.
– OK – The cable passed the test.
Figure 8-6

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
8-8 Maintenance
v1.0, April 2008
•Cable Fault Distance – Displays the distance from the port where the cable error
occurred.
•Last Update – Displays the last time the port was tested.
•Test – Click TEST to perform the cable tests for the selected port.
•Cable Length – Displays the approximate cable length. This test can only be performed
when the port is up and operating at 100Mbps or 1 Gbps.
2. On the row containing the interface to be tested, click TEST to test the cable connected to the
interface.

9-1
v1.0, April 2008
Chapter 9
Online Help
Online Help
The navigation pane at the top of the web browser interface contains a Help tab that provides
access to informational services including support and an online user guide in PDF format. The
Help menu contains the following options:
•“Support”
•“User Guide”
The description that follows in this chapter covers these features.
c
Support
The Support screen provides access to the NETGEAR online support site at www.netgear.com.
To access the Support screen:
1. Click Help > Online Help > Support. The Online Help menu opens and the Support screen
displays:
2. Click APPLY to go to the NETGEAR Online Support site at www.netgear.com.
Figure 9-1

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
9-2 Online Help
v1.0, April 2008
User Guide
The User Guide screen provides access to the online User Guide.
To view the User Guide screen:
1. Click Help > Online Help > User Guide. The User Guide screen displays:
2. Click APPLY to open a window and display the User Guide in PDF format.
Figure 9-2
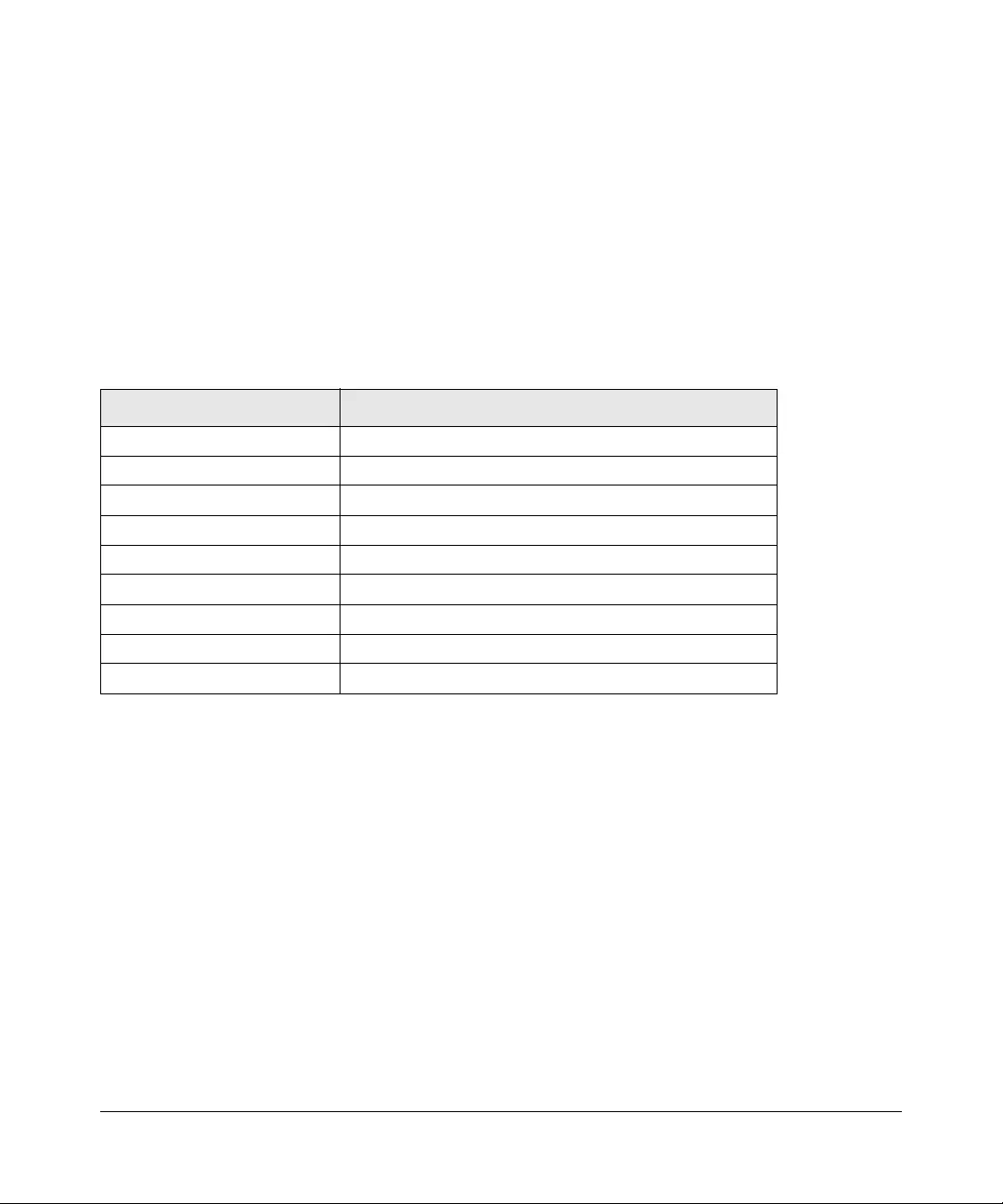
A-1
v1.0, April 2008
Appendix A
Default Settings
This appendix provides default settings for the NETGEAR Model GS700TP Smart Switch. You
can always configure the switch to default settings by using the Factory Reset function from a Web
browser.
Table A-1. Default Settings
Feature GS700TP Default Setting
Port Speed Auto-negotiation
Port Duplex Auto-negotiation
Flow Control (half duplex) Disabled
Flow Control (full duplex) Disabled
IP Configuration DHCP enabled
Password password
VLAN 802.1q based VLAN
Link Aggregation (Trunk) Disabled
Traffic Prioritization (QoS) Op ti mi z ed for flow control, all ports set normal priority

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
A-2 Default Settings
v1.0, April 2008

Index-1
v1.0, April 2008
Index
A
ACL 6-19
B
Bandwidth Settings 5-5
Boot File Download 8-5
C
changing the password 1-9
configuration
monitoring 7-1
network parameters 1-6
QoS 5-1
security 6-1
switch 4-1
system settings 3-1
Configuration Download 8-5
Configuration Upload 8-3
CoS 5-3
CPU 4-40
D
defaults
IP address 1-8
subnet mask 1-8
DHCP 3-3
DHCP server 1-3
DSCP 5-1
Dynamic MAC Address Table 4-47
F
Firmware Download 8-5
Firmware Upload 8-3
Flash Logs 7-6
G
getting started 1-1
H
History Table Page 7-16
I
IGMP Snooping 4-40
installing 1-3, 1-5
interfaces
switch management 1-2
Web browser 2-1
IP address
default 1-8
L
L2 4-39
LACP 4-12
LAG 4-4
Layer 2 4-39
Link Aggregated Groups 4-4
Link Aggregation Control Protocol 4-12
list of RMON events 7-19
logging into the switch 2-1
Logs Configuration 7-2
M
map CoS 5-7

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Index-2 v1.0, April 2008
Memory Logs 7-4
menus 2-2
Multicast Forward All Page 4-46
Multicast Groups 4-43, 4-44
N
navigation menu 2-2
network alarms 7-20
network parameters 1-5
NIC settings 1-7
P
password
changing 1-9
PoE 3-7
Port mirroring 7-22
Port VLAN ID (PVID) 4-20
PVID 4-20
Q
QoS 5-1
QoS configuration 5-1
Queue shaping 5-5
R
RADIUS 6-2
Remote Monitoring Statistics 7-9
Restoring factory defaults 8-2
S
scheduling scheme 5-5
security configuration 6-1
Server Logs 7-7
SNMP 3-13
SNMP groups 3-23, 3-25
SNMP v3 3-13
STP 4-29
subnet mask 1-8
switch
device 3-7
switch configuration 4-1
switch monitoring 7-1
System Logs 7-1
system requirements 1-1
T
TACACS+ 6-6
TDR 8-7
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
(TACACS+) 6-6
traffic queues 5-9
Trap Filter 3-30, 3-31
U
upgrading the firmware 1-9
utilities
Smartwizard Discovery 1-2
switch maintenance 8-1
system settings 3-1
V
view 3-7
VLAN 4-14, 4-16, 4-22
VLAN Membership 4-17
VLANs 4-14
VPT 5-1
W
Web access 1-8, 2-1

GS700TP Smart Switch Software Administration Manual
Index-3
v1.0, April 2008